This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Yugoslavia and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
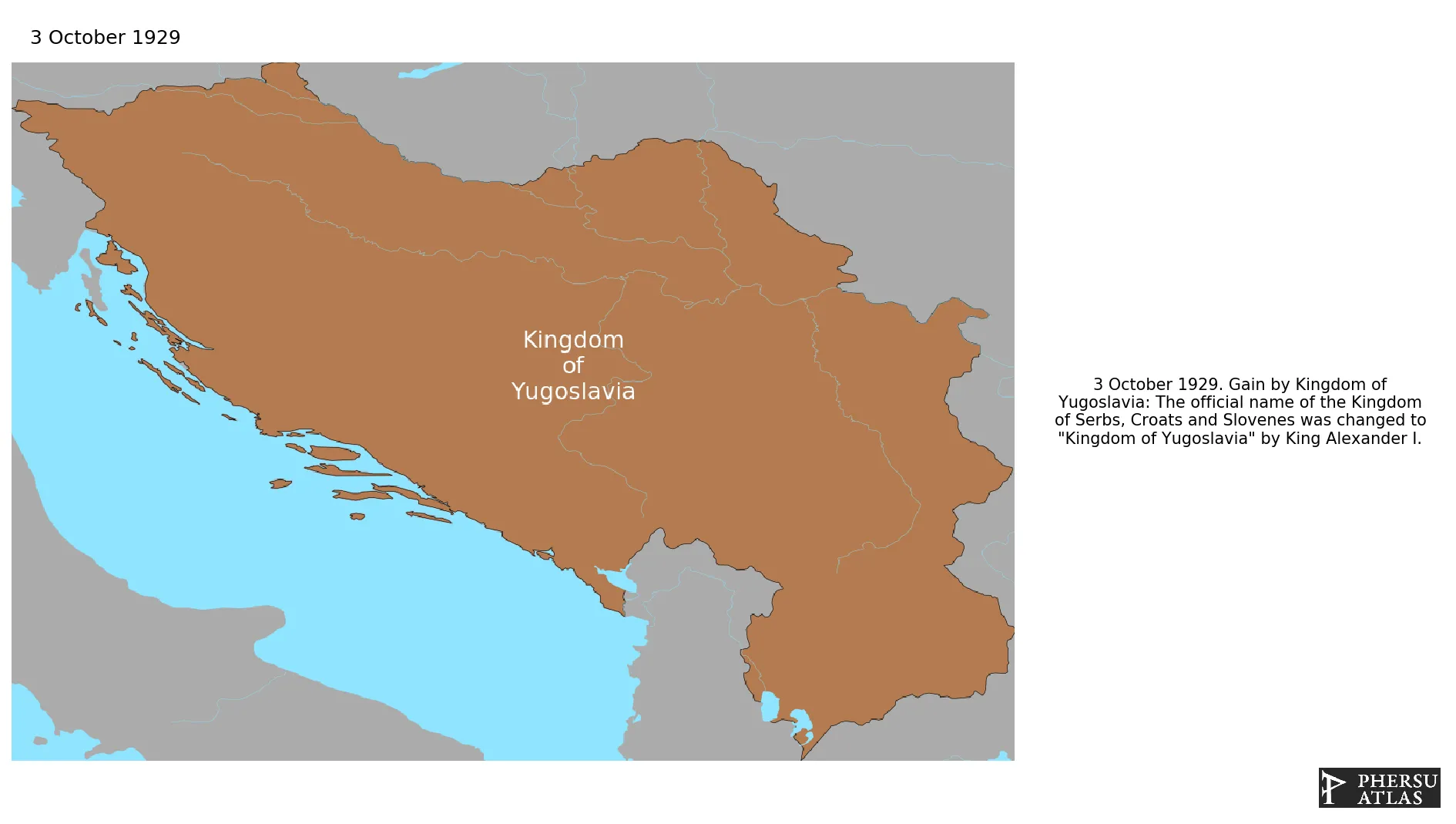
Was a state in southeast and central Europe that was established under the name of Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes when Serbia united with the newly created State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs. The official name of the state was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I on 3 October 1929. During World War II the country was occupied and partitioned between the Axis powers. After the liberation of the country, Yugoslavia was re-established as the Democratic Federal Yugoslavia.
Summary
In 1929, King Alexander I dissolved the parliament, abolished the constitution, and declared a new unitary and centralized Kingdom of Yugoslavia. This followed a period of political instability, with 24 governments in just 10 years.
Alexander justified his authoritarian move as a necessary step to overcome the abuses of the previous party regimes and unite the divided country. He banned political parties based on regional or religious lines, imposed strict censorship, and centralized power under the monarchy.
In 1931, Alexander promulgated a new constitution that nominally revived parliamentary rule, but maintained his firm personal control. An upper house was created with both elected and appointed members. However, opposition parties were still not allowed to freely operate.
Alexander sought to unify the country through administrative reforms, renaming it the "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" in 1929 and replacing the former provinces with new regions (banovinas) that disregarded ethnic and historical boundaries. This was seen by the Croats as a mere ploy to preserve Serbian hegemony.
Tensions continued to simmer, with the Croats demanding greater autonomy and the government cracking down on dissent. In 1934, Alexander was assassinated by Ustasha terrorists, reportedly with the backing of Italy and Hungary. His underage son Peter II became king, with Prince Paul serving as regent.
The Regency period under Prince Paul was characterized by economic decline, the growth of extremist movements, and failed attempts at Serb-Croat reconciliation. In 1941, with Yugoslavia facing German invasion, Prince Paul aligned the country with the Axis powers, leading to a military coup that brought the young King Peter II to power. This proved futile, as Yugoslavia was swiftly conquered by the Nazis in April 1941, ending the monarchy.
Establishment
October 1929: The official name of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes was changed to "Kingdom of Yugoslavia" by King Alexander I.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
1.1.World War II (Western Front)
Was the Western European theatre of World War II.
1.1.1.Ardennes Counteroffensive
Was the last major German offensive campaign on the Western Front during World War II.
1.1.1.1.German Offensive in Yugoslavia
German offensive during the World War II Axis invasion of Yugoslavia.
April 1941: Late in the afternoon of the 10th April German Tanks entered the city of Zagreb.
April 1941: SS-Obersturmfuehrer (1st Lt.) Klingenberg of the 2d SS Motorized Infantry Division entered Belgrade with an SS patrol. The mayor of Belgrade officially handed over the city to Klingenberg
1.2.World War II (Balkan Theatre)
Was the theatre of conflict of World War II that took place in the Balkans.
1.2.1.Greco-Italian War
Was a conflict between Greece and Italy during World War II that started with the Italian invasion of Greece.
1.2.1.1.Italian offensive (Greco-Italian War)
Were the Italian operations during the Greco-Italian War.
April 1941: Knin was taken by the Axis forces.
April 1941: The Italian army conquers of Kastav, Kalce and Logatec.
April 1941: On 11 April, the Italian 2nd Army launched its offensive, capturing Ljubljana, Sušak and Kraljevica on the same day.
April 1941: The Italian 133rd Armoured Division Littorio and the 52nd Infantry Division Torino took Senj.
April 1941: On 13 April the Italian occupied Otočac and Gradac.
April 1941: Split and Sibenik were taken by Italian forces on 15 and 16 April, respectively.
April 1941: Italian Motorized Corps took Dubrovnik.
1.2.2.Invasion of Yugoslavia by the Axis
Was a military operation by the Axis forces that resulted in the occupation and partition of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
1.2.2.1.Surrender and partition of Yugoslavia
Was the partition of Yugoslavia among the invading Axis forces.
April 1941: Yugoslavia was partitioned ca. April 20-22, 1941 among the Axis countries (Italy and Germany) and their satellite states (Hungary, Bulgaria, Albania).
1.2.2.2.Hungarian Offensive (Axis invasion of Yugoslavia)
Was the offensive of the Hungarian army during the Axis invasion of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
April 1941: The Hungarian 1st Parachute Battalion captured canal bridges at Vrbas and Srbobran. Meanwhile, Sombor was captured against determined Chetnik resistance, and Subotica was also captured.
April 1941: The Hungarian 1st and 2nd Motorised Brigades occupied Novi Sad.
April 1941: The Hungarian army captured Vinkovci and Vukovar on 18 April.
April 1941: Hungarian forces occupied the Yugoslavian regions of Prekmurje and Međimurje.
April 1941: Valjevo conquered by hungary.
1.2.2.3.Yugoslav Albanian offensive
Was the offensive of the Italian forces in Albania during the Axis invasion of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia.
April 1941: Between 11-13 April 1941, with German and Italian troops advancing on its rear areas, the Zetska Division was forced to retreat back to the Pronisat River by the Italian 131st Centauro Armoured Division.
1.2.3.German invasion of Greece
Was the invasion of Greece Germany during World War II. The Invasion followed the unsuccesful invasion of Greece by Italian forces.
April 1941: German conquest of Veles.
April 1941: German conquest of Skopje.
April 1941: The Germans captured the town of Strumica.
April 1941: The German 73rd Infantry Division captured Prilep.
April 1941: The Italian armoured division along with the 18th Infantry Division Messina advanced upon the Yugoslav fleet base of Kotor in Montenegro, also occupying Cettinje and Podgorica.
Disestablishment
April 1941: German conquest of Veles.
April 1941: German conquest of Skopje.
April 1941: The Germans captured the town of Strumica.
April 1941: The German 73rd Infantry Division captured Prilep.
April 1941: Knin was taken by the Axis forces.
April 1941: The Italian army conquers of Kastav, Kalce and Logatec.
April 1941: Late in the afternoon of the 10th April German Tanks entered the city of Zagreb.
April 1941: On 11 April, the Italian 2nd Army launched its offensive, capturing Ljubljana, Sušak and Kraljevica on the same day.
April 1941: The Italian 133rd Armoured Division Littorio and the 52nd Infantry Division Torino took Senj.
April 1941: The Hungarian 1st Parachute Battalion captured canal bridges at Vrbas and Srbobran. Meanwhile, Sombor was captured against determined Chetnik resistance, and Subotica was also captured.
April 1941: SS-Obersturmfuehrer (1st Lt.) Klingenberg of the 2d SS Motorized Infantry Division entered Belgrade with an SS patrol. The mayor of Belgrade officially handed over the city to Klingenberg
April 1941: The Hungarian 1st and 2nd Motorised Brigades occupied Novi Sad.
April 1941: On 13 April the Italian occupied Otočac and Gradac.
April 1941: Between 11-13 April 1941, with German and Italian troops advancing on its rear areas, the Zetska Division was forced to retreat back to the Pronisat River by the Italian 131st Centauro Armoured Division.
April 1941: Split and Sibenik were taken by Italian forces on 15 and 16 April, respectively.
April 1941: The Italian armoured division along with the 18th Infantry Division Messina advanced upon the Yugoslav fleet base of Kotor in Montenegro, also occupying Cettinje and Podgorica.
April 1941: Italian Motorized Corps took Dubrovnik.
April 1941: The Hungarian army captured Vinkovci and Vukovar on 18 April.
April 1941: Valjevo conquered by hungary.
April 1941: Hungarian forces occupied the Yugoslavian regions of Prekmurje and Međimurje.
April 1941: Yugoslavia was partitioned ca. April 20-22, 1941 among the Axis countries (Italy and Germany) and their satellite states (Hungary, Bulgaria, Albania).
Selected Sources
Blau, G.E.(1953): PART TWO THE YUGOSLAV CAMPAIGN. U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://history.army.mil/books/wwii/balkan/20_260_2.htm
Campaign In The Balkans, Invasion Of Yugoslavia And Greece, April 1941. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope17.jpg
Carr, John (2013). The Defence and Fall of Greece 1940–41. Pen and Sword Military. p. 211.
Enrico Cernuschi, Le operazioni aeronavali contro la Jugoslavia, 6–8 aprile 1941, in Storia Militare no. 242, p. 30
Enrico Cernuschi, Le operazioni aeronavali contro la Jugoslavia, 6–8 aprile 1941, in Storia Militare no. 242, p. 31.
Enrico Cernuschi, Le operazioni aeronavali contro la Jugoslavia, 6–8 aprile 1941, in Storia Militare no. 242, p. 33
McClymont, W. G. (1959): To Greece, Historical Publications Branch, p. 159
Tomasevich, J. (1975): War and Revolution in Yugoslavia, 1941-1945, Stanford University Press, p.68
Tomasevich, J. (1975): War and Revolution in Yugoslavia, 1941-1945, Stanford University Press, pp. 89-92
.svg.png.webp)
 Kingdom of Yugoslavia
Kingdom of Yugoslavia