Garhwal Kingdom
Garhwal Kingdom
This article is about the specific polity Garhwal Kingdom and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
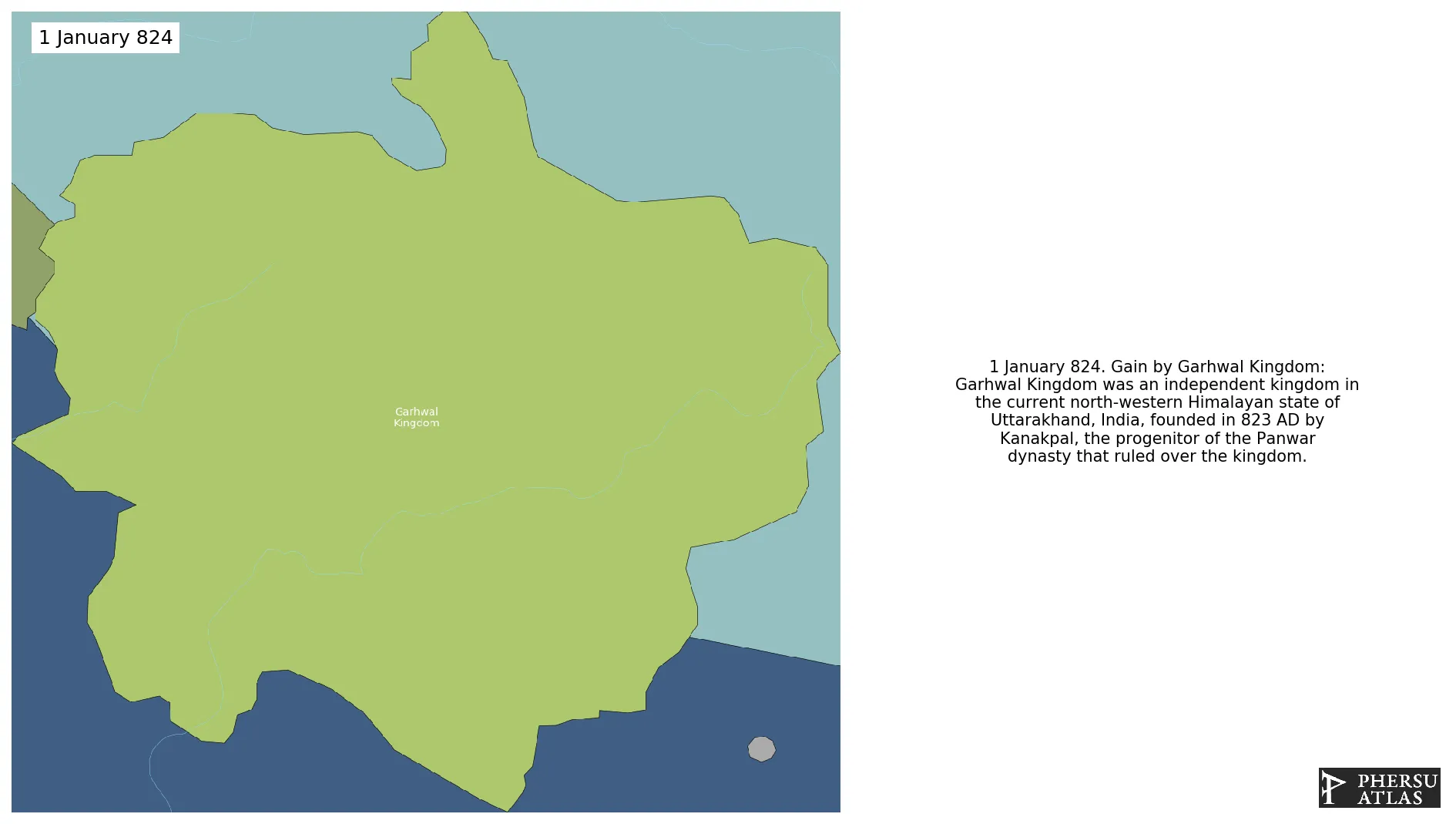
Was an independent Himalayan kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 688 CE by Kanak Pal, the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled over the kingdom uninterrupted until 1803 CE.
Establishment
January 824: Garhwal Kingdom was an independent kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 823 AD by Kanakpal, the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled over the kingdom.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was an era of disunity in Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three provinces of Tibet in 1253, under the Yuan dynasty.
January 1221: The Khasa Kingdom expands into the territory of Garhwal and Kumaon.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
2.1.Invasions of India
The Mongol Empire launched several invasions into the Indian subcontinent from 1221 to 1327.
November 1299: In late 1299, Chagatai Khan Duwa sent his son Qutlugh Khwaja to conquer Delhi.
December 1299: The Mongols retreated from India afteri being defeated at Kili. Their leader Qutlugh Khwaja was seriously wounded, and died during the return journey.
January 1096: Nahan, the predecessor state of Sirmur, was founded by Soba Rawal in 1095 AD who assumed the name Raja Subans Prakash. The new capital was founded in 1621 by Raja Karam Prakash, and the state was renamed to Sirmur.
January 1205: After 1204 once the Islamic invaders defeated the Sena dynasty in Gaur (Bengal), the royal family members fled to the hills and raja Bir Sen established the state of Suket.
January 1413: Bushahr, also spelt as 'Bashahr' and 'Bussahir' or 'Bushair' was a princely state in India during the British Raj. It was located in the hilly western Himalaya promontory bordering Tibet in the northern part of colonial Punjab region.
January 1551: The Baise and Chaubisi Rajya (Nepali petty kingdom) existed since the early XVI Century.
January 1617: Foundation of the Sirmur Kingdom.
January 1702: In 1701, Fateh Shah entered in Chaukot (now Syalde region with 3 part, Talla Chaukot (lower), Malla Chaukot (Upper) and Bichla Chaukot (middle)) and Gewar Valley (region of Chaukhutia, Masi, and Dwarahat) as reply.
February 1702: In 1701, Fateh Shah, the ruler of the Kingdom of Kumaon, entered Chaukot and Gewar Valley in response to a previous event. Chaukot is now known as the Syalde region with three parts, while Gewar Valley includes Chaukhutia, Masi, and Dwarahat.
January 1708: The Kingdom of Kumaon razed the old fort at Chandpur Garhi, the capital of Garhwal Kingdom.
January 1708: Kingdom of Kumaon razed the old fort at Chandpur Garhi, the capital of Garhwal Kingdom.
February 1708: In 1708, the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb's forces, led by his son Prince Muazzam, razed the old fort at Chandpur Garhi, the capital of the Garhwal Kingdom. This marked a significant event in the conflict between the Mughal Empire and the Garhwal Kingdom.
January 1718: Najib-ud-daula Governor of Saharanpur, who invaded in 1757 along with his Rohilla Army and captured Dehradun.
January 1771: The Garhwali forces, led by King Pradyuman Shah, defeated the Rohillas, a Pashtun tribe, in 1770. This victory allowed the Garhwal Kingdom to regain control of the Dun region, a strategic territory in present-day Uttarakhand, India.
Disestablishment
January 1804: Nepalese invasion of Garhwal.
Selected Sources
European Bulletin of Himalayan Research, p. 78. retrieved 26 March 2024 on http://himalaya.socanth.cam.ac.uk/collections/journals/ebhr/pdf/EBHR_50-51.pdf
Unification of Nepal and pre-unification kingdoms. Historum. 31 July 2019. https://historum.com/t/unification-of-nepal-and-pre-unification-kingdoms.179881/

 Garhwal Kingdom
Garhwal Kingdom