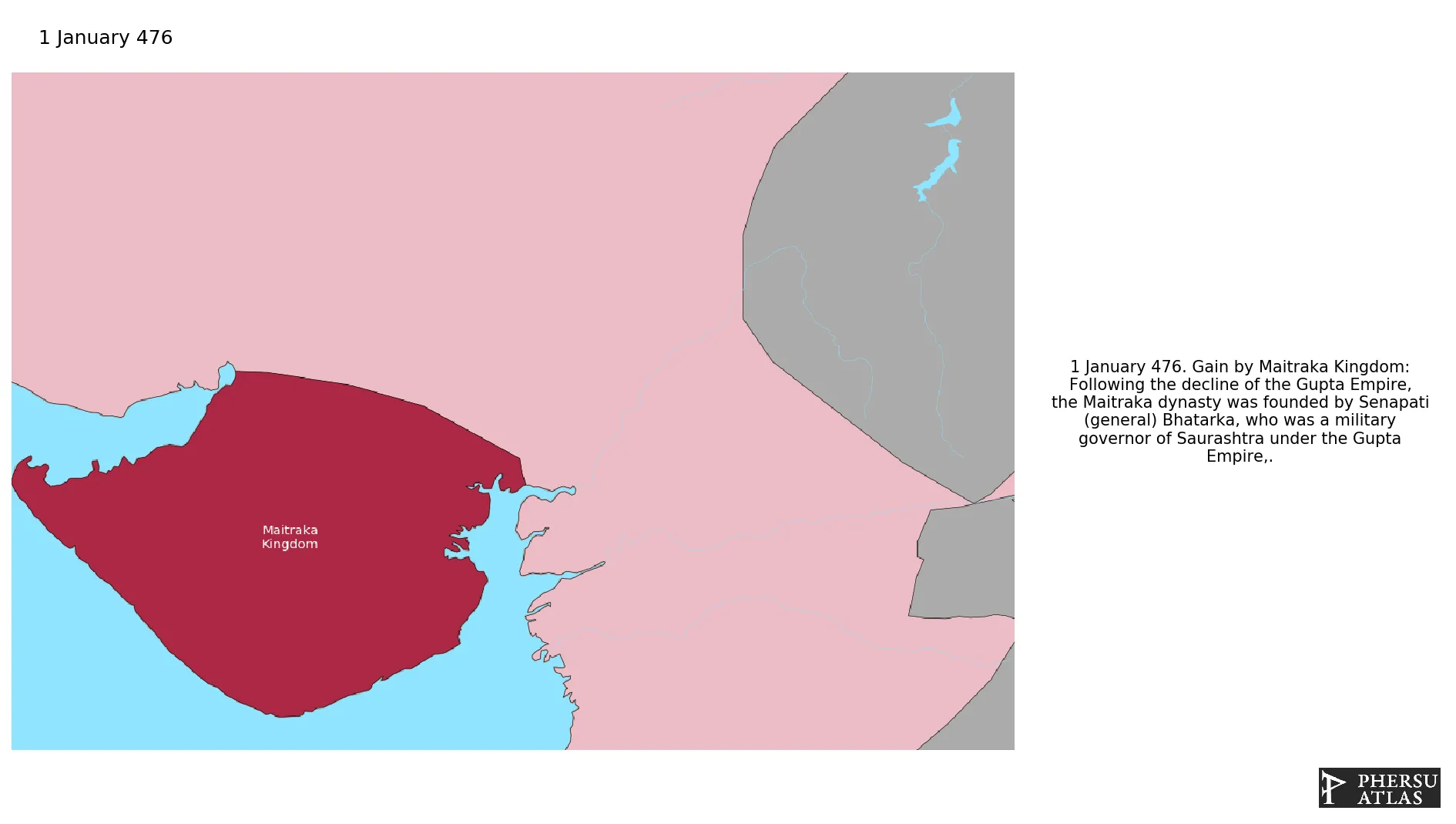
Maitraka Kingdom
Maitraka Kingdom
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was country that emerged from the military government of Saurashtra (located in Gujarat, India) in the Gupta Empire.
Establishment
January 476: Following the decline of the Gupta Empire, the Maitraka dynasty was founded by Senapati (general) Bhatarka, who was a military governor of Saurashtra under the Gupta Empire,.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military campaigns by Yashodharman, ruler of the Second Aulikara dynasty, that resulted in the conquest (albeit short-lived) of most of the Indian Subcontinent.
January 531: Yashodharman conquered much of the Indian subcontinent between c. 530-540 CE according to Mandsaur pillar inscription.
January 541: Yashodharman's short-lived empire disintegrated between 530 and 540 CE.
Were the military campaigns by the first three Islamic Caliphates (the Caliphate of Muhammad, the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate) that led to the Islamic conquest of most of the Middle East as well as the Iberian Peninsula.
2.1.Islamic conquest of Deccan
Was the invasion of Deccan (India) initiated by the Umayyad Caliphate.
January 734: Arab invaders who had established themselves in the Sindh made a push into the Deccan.
January 551: Krishnaraja (r. c. 550-575) was the earliest known ruler of the Kalachuris of Mahishmati dynasty.
January 570: Gahasena was succeeded by his son Dharasena II, who used the title of Samanta in his early grants and later readopts the title of Maharaja and later again as Mahasamanta. He reigned from 569 to 589-90 CE. It is considered that he had become subordinate to Maukhari ruler Ishanavarman for sometime between which reflect in the changes in titles.
January 591: Gahasena was succeeded by his son Dharasena II, who used the title of Samanta in his early grants and later readopts the title of Maharaja and later again as Mahasamanta. He reigned from 569 to 589-90 CE. It is considered that he had become subordinate to Maukhari ruler Ishanavarman for sometime between which reflect in the changes in titles.
January 617: Siladitya I was succeeded by his younger brother Kharagraha I, also known as Ishwaragraha. Virdi copperplate grant (616 CE) of Kharagraha I proves that his territories included Ujjain which is mentioned as "victorious camp".
January 637: During the reign of Pulakeshin II (r. c. 610-642 CE), the Chalukya kingdom expanded to cover most of the Deccan region in peninsular India.
January 641: Dhruvasena II was a ruler of the Maitraka Kingdom in India during the 7th century. His rule extended to Ratlam, a town west of Ujjain, which led to the entire modern central and north Gujarat coming under the control of the Maitrakas in 640.
January 661: Dhruvasena III was a son of Derabhatta. He reigned from c. 650 to 654-655 CE. He had dropped the title of Chakravartin and was Shaiva. He may have lost his sway on Lata region to Chalukyas.
January 691: The Chavda was a dynasty that ruled the region of modern-day Gujarat in India, from c. 690.
January 701: Siladitya III was the son and successor of Siladitya II, ruling from c. 690 - 710 CE. Panchasar, held by Jayasekhara of Chavda dynasty, was attacked during his reign in 700, leading to territorial changes in the Maitraka Kingdom.
January 701: Siladitya II probably recovered the Lata region from the Sendraka governor under the Chalukyas.
January 701: The Chalukyas recovered the Lata region under Vikramaditya I and placed his son Dharashraya Jayasimha as its governor.
February 701: Siladitya was a ruler of the Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty in India. His father, Siladitya II, was also a prominent ruler. Jayasekhara was a ruler of the Chavda dynasty, a powerful dynasty in Gujarat. The attack on Panchasar in 701 was likely a result of territorial disputes or power struggles between these two dynasties.
January 729: Mewar was founded by Bappa Rawal, formerly a chieftain of the Mori king of Chittor, who acquired control of Chittor in c.728.
January 741: Gurjara-Pratihara ruler Nagabhata I (730-756) extended his control east and south from Mandor, conquering Malwa as far as Gwalior and the port of Bharuch in Gujarat.
January 761: Siladitya V probably had tried to recover Malwa as one of his grant (760 CE) is made from military camp at Godraka (Godhra). He must have failed to recover Malwa but nonetheless recovered the Khetaka (Kheda) region.
January 777: Saurashtra was again invaded by the Tajjikas (Arabs) in 776 CE (AH 159). They captured the township of Barada but the epidemic broke out.
February 777: The Arabs had to return and the Caliph had decided to stop further attempt to enter India.
Disestablishment
January 784: Agguka I of the Saindhava dynasty had claimed in his inscription a victory thus they had to withdraw. The Maitraka dynasty ended by c. 783 CE. Apart from legendary accounts which connects fall of Vallabi with the Tajjika (Arab) invasions, no historical source mention how the dynasty ended.
Selected Sources
Sagar, K.C. (1992): Foreign Influence on Ancient India, Northern Book Centre, p.216
 Maitraka Kingdom
Maitraka Kingdom