If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Polity that includes all territories militarly occupied by Morocco that are not part of a specific military territory.
Establishment
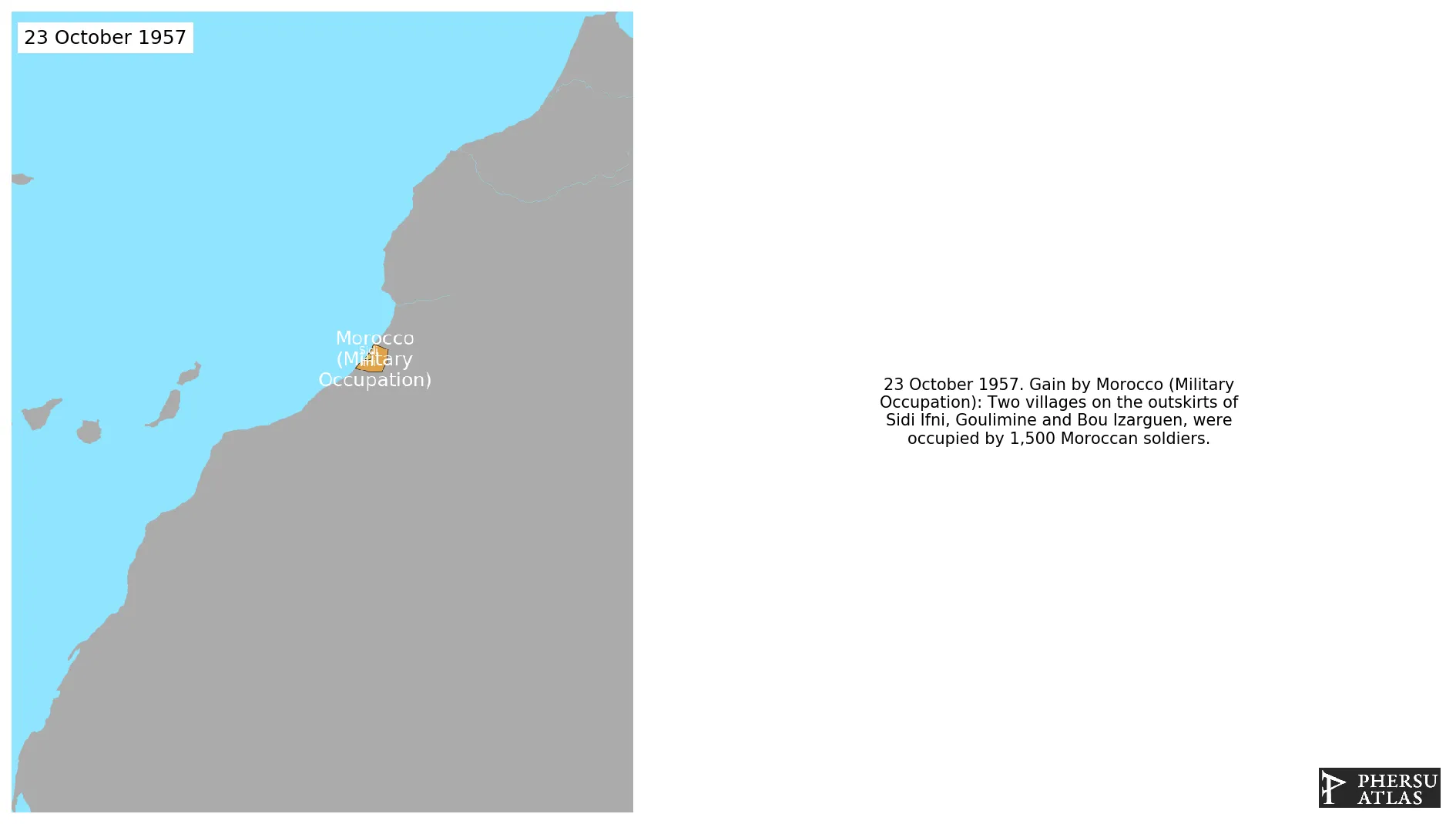
October 1957: Two villages on the outskirts of Sidi Ifni, Goulimine and Bou Izarguen, were occupied by 1,500 Moroccan soldiers.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a series of armed incursions into Spanish West Africa by Moroccan insurgents.
February 1958: Morrocco invaded the north of Western Sahara up to Edchera.
February 1958: In 1958, Morocco invaded the northern region of Western Sahara up to Edchera. This military occupation was part of King Mohammed V's efforts to expand Moroccan territory and assert control over the region. The invasion sparked tensions with neighboring countries and led to ongoing conflicts over the sovereignty of Western Sahara.
February 1958: The 4th, 9th, and 13th Spanish Legion battalions, organised into a motorised group, drove the Moroccans from Edchera and advanced to Tafurdat and Smara.
February 1958: The Spanish army at El Aaiún, in conjunction with French forces from Fort Gouraud, struck the Moroccans on February 21, destroying Saharan Liberation Army concentrations between Bir Nazaran and Ausert.
March 1958: First to fall were the Moroccan mountain strongholds at Tan-Tan.
June 1958: The Moroccan Army of Liberation (which was not a part of the regular Moroccan army) declared a ceasefire, bringing to an end the Ifni War. The enclave of Sidi Ifni, which was surrounded by Moroccan territory, was not ceded. It was, however, greatly reduced in size, since its outlying regions, occupied by the Ait Ba Amran tribe were abandoned.
Was a border conflict between Algeria and Morocco.
September 1963: In 1963, during the Sand War between Morocco and Algeria, the Royal Moroccan Army, led by King Hassan II, crossed into Algeria and captured the border posts of Hassi-Beida and Tindjoub. This military occupation escalated tensions between the two countries.
October 1963: The Algerian forces began to retaliate against the Moroccan advances, taking back the ports of Hassi-Beida and Tindjoub.
Was a conflict of Marocco and Mauritania (until 1979) against the Sahrawi Indigenous Polisario Front that followed the Spanish withdrawal from Spanish Sahara. The Sahrawi indigenous Polisario Front established the Sahrawi Republic and engaged in a guerrilla warfare with Moroccan forces. Morocco did also build several walls in the region to consolidate its control. The conflict ended with a ceasefire in 1991 with most of former Spanish Sahara under Moroccan control.
3.1.Moroccan-Mauretanian Invasion
Was the occupation and partition of Spanish Sahara by Morocco and Mauritania after the withdrawal of the Spanish forces.
November 1975: Moroccan troops capture Smara.
December 1975: Laayoune conquered by morocco.
January 1976: The last Spanish troops leave Laâyoune while the Moroccan troops arrive in Dakhla.
January 1976: Mauritanian troops occupy Dakhla.
January 1976: At the beginning of 1976, Mauritania, under President Moktar Ould Daddah, controlled the southern third of Western Sahara, while Morocco, under King Hassan II, controlled the northern two thirds through military occupation. This division was a result of the Madrid Accords of 1975, which divided the territory between the two countries.
3.2.Algerian Intervention
Was the military invasion of Moroccan-held territories in Western Sahara by Algeria to support the Sahrawi indigenous Polisario Front.
January 1976: In January 1976, Algeria decided to participate in the conflict and advanced to Amgala, more than 300 km west of its border with Western Sahara.
January 1976: The First Battle of Amgala took place in 1976 when the Polisario Front, a Sahrawi rebel national liberation movement, clashed with Moroccan forces in Amgala, Western Sahara. The territory was under Spanish control until 1976 when it was divided between Morocco and Mauritania, leading to ongoing conflict with the Sahrawi people seeking independence.
February 1976: Second Battle of Amgala.
3.3.Creation of the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic
Was the establishment of the Sahrawi Republic in West Sahara by the Sahrawi indigenous Polisario Front.
September 1976: Haouza was a strategic location in Western Sahara, where the Polisario Front, a Sahrawi rebel national liberation movement, clashed with Moroccan forces in 1976. The Polisario Front eventually gained control of Haouza, contributing to the territory's transfer to the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic.
3.4.Mauretania leaves Western Sahara
Mauritania declared a unilateral ceasefire with the Sahrawi Republic and withdraw its troops form Western Sahara.
August 1979: In 1979, Mauritania declared a unilateral ceasefire against the Polisario Front because of the military putsch that overthrew former President Moktar Ould Daddah a year earlier. The Mauritanian forces handed over the occupied territories to Morocco.
August 1979: Situation in Mauretania at the end of the war.
August 1979: The Moroccans reconquered the Mauretanian occupied region in Western Sahara.
3.5.Construction of Moroccan Western Sahara Wall
Morocco built a series of walls in Western Sahara to secure its territorial occupation during the Western Sahara War.
July 1982: Moroccan authorities complete the construction of the first wall of Western Sahara.
February 1984: Moroccan authorities complete the construction of the second wall of Western Sahara.
June 1984: In 1984, the third wall of Western Sahara was completed, solidifying the de facto situation in the region.
February 1985: In 1985, the fourth wall was completed in Western Sahara, marking the de facto control of the territory by the Kingdom of Morocco.
October 1985: Completion of the fifth wall in Western Sahara by Morocco.
May 1987: Moroccan authorities complete the construction of the sixth wall of Western Sahara.
Was a conflict between Spain and Morocco that took place over the small, uninhabited Perejil Island.
July 2002: Relations between Spain and Morocco degenerated on July 11, 2002 when a group of six Moroccan soldiers landed on Perejil Island and set up an outpost.
July 2002: On July 18, at 6:21 a.m., Spain landed on the Perejil Island ("Operation Romeo-Sierra"). The attack was carried out by 28 Spanish commando units from the Grupos de operaciones especiales deployed by 6 helicopters from Alicante. The Spanish Navy and Air Force provided support. The Moroccans left the island.
Disestablishment
July 2002: Relations between Spain and Morocco degenerated on July 11, 2002 when a group of six Moroccan soldiers landed on Perejil Island and set up an outpost.
July 2002: On July 18, at 6:21 a.m., Spain landed on the Perejil Island ("Operation Romeo-Sierra"). The attack was carried out by 28 Spanish commando units from the Grupos de operaciones especiales deployed by 6 helicopters from Alicante. The Spanish Navy and Air Force provided support. The Moroccans left the island.
.png.webp)
 Morocco (Military Occupation)
Morocco (Military Occupation)