Khalji Dynasty
Khalji Dynasty
This article is about the specific polity Khalji Dynasty and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Turco-Afghan dynasty which ruled the Delhi sultanate, covering large parts of the Indian subcontinent for nearly three decades between 1290 and 1320.
Establishment
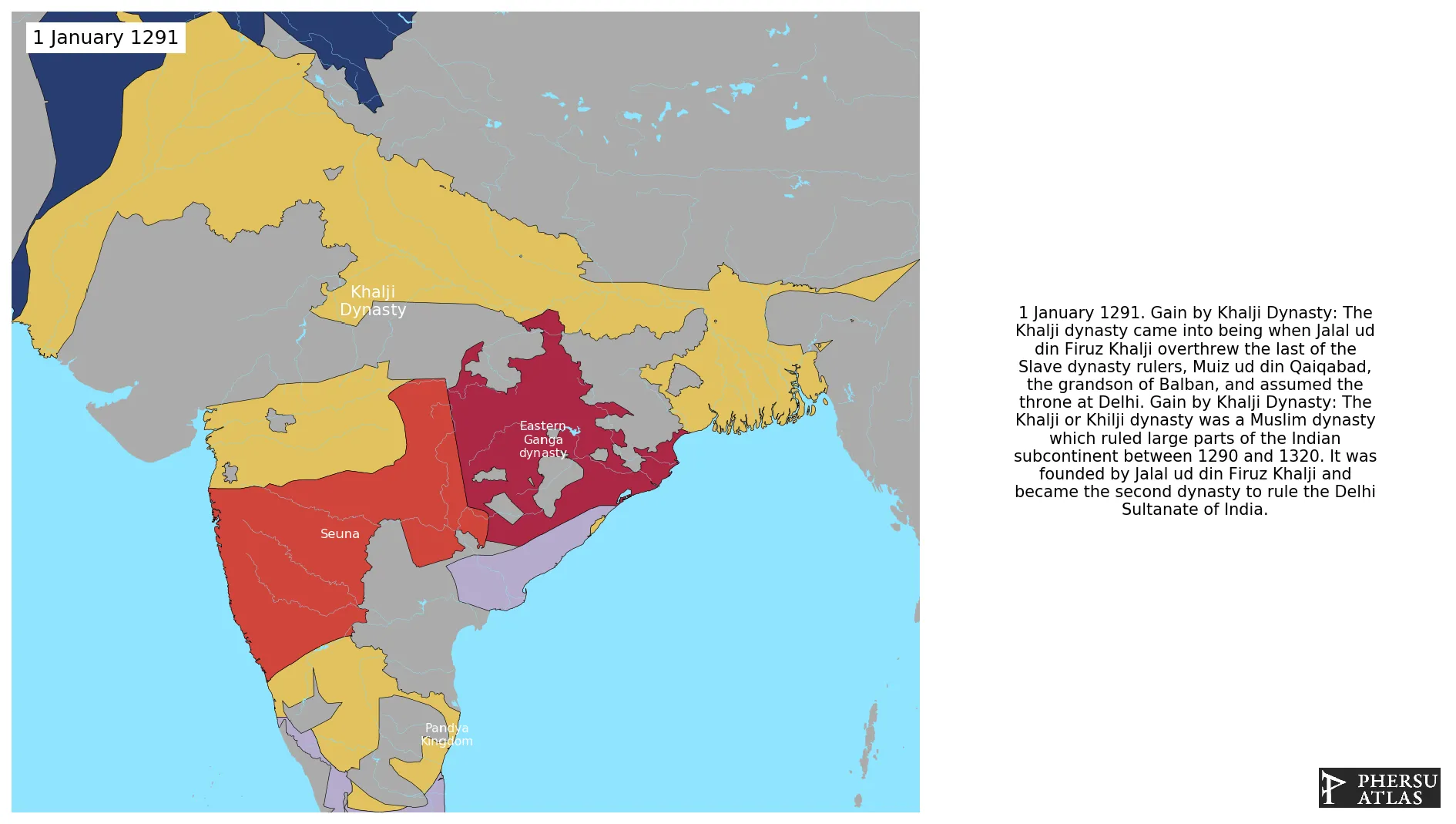
January 1291: The Khalji or Khilji dynasty was a Muslim dynasty which ruled large parts of the Indian subcontinent between 1290 and 1320. It was founded by Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji and became the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate of India.
January 1291: The Khalji dynasty came into being when Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji overthrew the last of the Slave dynasty rulers, Muiz ud din Qaiqabad, the grandson of Balban, and assumed the throne at Delhi.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
1.1.Invasions of India
The Mongol Empire launched several invasions into the Indian subcontinent from 1221 to 1327.
January 1298: In the winter of 1297, the Chagatai noyan Kadar led an army that ravaged the Punjab region, and advanced as far as Kasur.
February 1298: After being defeated by the Delhi Sultanate in the Battle of Jaran-Manjur, the Chagatai army left Punjab.
November 1299: In late 1299, Chagatai Khan Duwa sent his son Qutlugh Khwaja to conquer Delhi.
December 1299: The Mongols retreated from India afteri being defeated at Kili. Their leader Qutlugh Khwaja was seriously wounded, and died during the return journey.
September 1303: The Mongols launched another invasion of India around August 1303. Alauddin managed to reach Delhi before the invaders, but did not have enough time to prepare for a strong defence. He took shelter in a heavily-guarded camp at the under-construction Siri Fort.
October 1303: The Mongols ransacked Delhi and its neighbourhoods, but ultimately retreated after being unable to breach Siri.
January 1306: In December 1305, Chagatai khan Duwa invaded India and proceeded south-east to the Gangetic plains along the Himalayan foothills.
February 1306: Chagatai forces leave recently conquered territories in India.
January 1307: A Mongol army sent by Duwa advanced up to the Ravi River, ransacking the territories along the way.
February 1307: In 1306, a Mongol army sent by Duwa, a Chagatai Khan, advanced up to the Ravi River, ransacking the territories along the way. The region up to the Ravi River was under the control of the Khalji Dynasty at that time.
The Hoysala capital Halebidu was sacked by the Delhi Sultanate in 1311.
January 1312: The Hoysala capital Halebidu is sacked by Delhi Sultanate forces.
February 1312: End of the sack of Halebidu by the forces of the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1295: The Deva Dynasty is conquered by the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1295: The founder of the Kampili Kingdom was a Hoysala commander, Singeya Nayaka-III (1280-1300 AD), who declared independence after the Muslim forces of the Delhi Sultanate defeated and captured the territories of the Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri in 1294 CE.
January 1297: Alauddin Khalji raided Devagiri.
February 1297: In 1297, after the raid on Devagiri by Alauddin Khalji, the territory was retaken by the Seuna dynasty.
January 1299: The last known ruler of the Yajvapala Dynasty was Ganapatideva. It is known that the Yajvapalas ruled Narwar until 1298 CE, but the end of the dynasty is not certain. Historians generally assume that the Yajvapalas fell to an invasion by the Delhi Sultan Alauddin Khalji.
January 1301: During the 14th century, the Sambuvarayas, a dynasty in the Tondaimandalam region, gained power as the Telugu Cholas, Hoysala, and Pandya kingdoms declined. They ruled independently in this period.
January 1301: By the 13th century, the Dimasa kingdom extended along the southern banks of Brahmaputra River, from Dikhow river to Kallang River and included the valley of Dhansiri and present-day Dima Hasao district.
January 1302: The Chahamanas of Ranastambhapura ended with a defeat against the Delhi Sultan Alauddin Khalji at the Siege of Ranthambore in 1301.
September 1303: Guhila Chitrakuta ended with Ratnasimha's defeat against the Delhi Sultanate at the 1303 Siege of Chittorgarh.
January 1305: Vaghela ruler Karna was defeated by Alauddin Khalji of Delhi Sultanate in 1304 CE.
January 1306: Duwa was a ruler of the Chagatai Khanate. His younger son, Kebek, succeeded him as khan. Kebek invaded the Delhi Sultanate in 1305, specifically targeting the Multan region, which was known for its wealth and strategic importance.
January 1306: The last known Paramara king, was defeated and killed by the forces of Alauddin Khalji of Delhi in 1305 CE.
January 1312: The Hoysala capital Halebidu is sacked by Delhi Sultanate forces.
January 1312: Sirohi State was founded in c. 1311 by Lumbha, who conquered the area which later formed the state. In 1311, then-ruler Shivabhan established the capital of the state at Shivpuri, 3 kilometers east of the present-day town of Sirohi.
January 1313: Goa came under the governance of the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1316: The Chandelas of Jejakabhukti were disestablished in 1315 CE.
January 1318: Seuna annexed by the Khalji Sultanate.
Disestablishment
January 1321: Ghazi Malik's forces marched on Delhi, captured the Khalji ruler Khusraw Khan and beheaded him. Upon becoming sultan, Ghazi Malik renamed himself Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq. He was the first ruler of the Tughluq dynasty of the Sultanate of Delhi.
.png.webp)
 Khalji Dynasty
Khalji Dynasty