This article is about the specific polity Mughal Empire and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
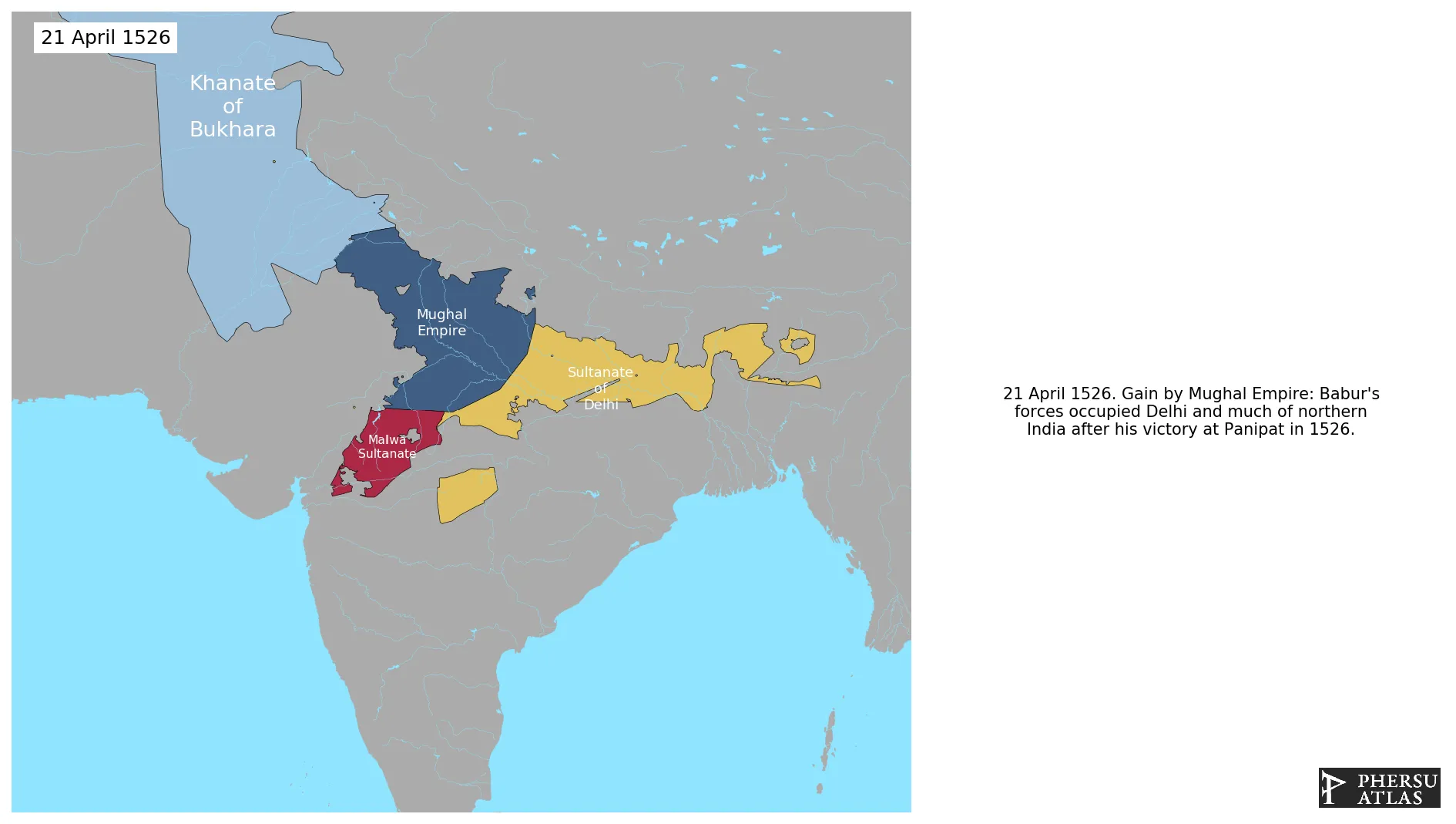
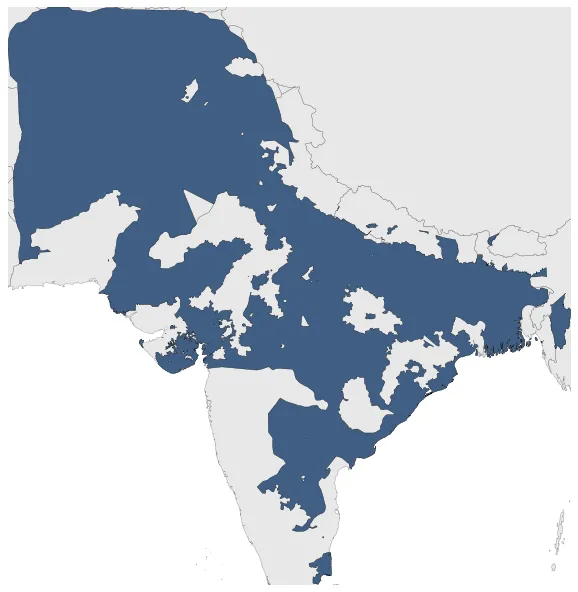
Was an empire that at its heigth controlled most of the Indian Subcontinent and nearby regions. It was founded by Babur in 1526.
Establishment
April 1526: Babur's forces occupied Delhi and much of northern India after his victory at Panipat in 1526.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Expansion during the rule of Akbar the Great in the Mughal Empire.
January 1557: Suri Empire disestablished.
January 1563: Constitution of the Malwa Sultanate.
January 1566: Laur lost its independence and became a mahal/mahallah of the Sylhet Sarkar in the Bengal Subah of the Mughal Empire.
January 1568: The Mughal emperor Akbar conquered Guhila Sisioda in 1567.
January 1570: Emperor Akbar conferred the title of Rao Raja upon Rao Surjan Singh of Bundi after the surrender of Ranthambore Fort and his submission.
January 1573: Mughal emperor Akbar annexed Gujarat in 1572.
January 1581: Orcha state ruler Madhukar's position had become so precarious in the 1570s that he agreed to Orchha becoming a tributary state and to enlistment of himself and his family in the service of the Mughal empire.
January 1582: Jodhpur annexed by the Mughal Empire.
January 1586: In 1585, there was mughal invasion of the Nagvanshis of Chotanagpur during reign of Raja Madhu Singh. He became a tributary to the Mughals.
January 1587: The Mughal padishah (emperor) Akbar conquered Kashmir from 1585 to 1586, taking advantage of Kashmir's internal Sunni-Shia divisions.
January 1591: In 1590, Mughal ruler Man Singh attacked the Cheros of Palamu. Cheros offered strong resistance to invading army but they were outnumbered. A large number of them were killed and many taken as prisoners. Raja Man Singh captured valuable booty including fifty four elephants. The Chero dynasty was brought under Mughal administration.
January 1592: In 1591 Akbar sent an army to conquer lower Sindh. Tarkhan ruler Jani Beg put up a resistance but was defeated by the Mughal forces and his principality was annexed.
August 1600: After the death of Chand Bibi in July 1600, Ahmadnagar was conquered by the Mughals, and Bahadur Shah was imprisoned.
January 1601: Through warfare and diplomacy, Akbar (1556-1605) was able to extend the empire in all directions and controlled almost the entire Indian subcontinent north of the Godavari River.
January 1601: On April 8, 1599 Akbar reached Burhanpur.
1.1.Mughal invasion of Bengal
Was an invasion of the Sultanate of Bengal, then ruled by the Afghan Karrani dynasty, by the Mughal Empire in 1572-1576. After a series of intense battles, the Mughals eventually defeated the Sultanate of Bengal in the Battle of Raj Mahal in 1576, and annexed the region into their empire as the province of Bengal.
July 1576: After a series of intense battles, the Mughals eventually defeated the Sultanate of Bengal in the Battle of Raj Mahal in 1576, and annexed the region into their empire as the province of Bengal.
A series of conflicts between the Mughal Empire and the Ahom Kingdom in Assam.
November 1615: In 1615, the Mughal Empire, led by Emperor Jahangir, reached the confluence of the Brahmaputra and the Bharali rivers facing Samdhara.
November 1615: In 1615, the Mughal Empire, led by Emperor Jahangir, reached the confluence of the Brahmaputra and the Bharali rivers facing Samdhara.
December 1615: In November 1615, Abu Bakr, a Mughal general, attacked Kajali, an Ahom frontier post. The Ahoms, led by their ruler Swargadeo Pratap Singha, were defeated in a short skirmish and fled, leaving behind their war boats and the fort.
April 1616: The Ahoms reoccupied Samdhara at the mouth of Bharali.
December 1637: The Mughals entered Kamrup proper. The decisive defeat inflicted by the imperialists on Balinarayan and the Ahoms in November 1637 turned the tide of fortune in favour of imperialists. The whole of Kamrup was then re-annexed to the Pan-Mughalia.
March 1662: Siege of Simalugarh.
March 1662: Mir Jumla entered the Ahom capital Garhgaon.
April 1662: Mir Jumla entered Assam in the beginning of 1662.
October 1662: With the progress of monsoon, the Ahoms easily recovered all the country east of Lakhau. Only Garhgaon and Mathurapur remained in the possession of Mughals.
February 1663: A treaty was concluded at Ghilajharighat in January 1663, according to which the Ahoms ceded western Assam to the Mughals.
November 1667: Itakhuli and the contiguous garrison of Guwahati fell into the hands of the Ahoms.
January 1680: Laluksola Borphukan was an influential military commander in the Ahom Kingdom of Assam. In 1679, he conspired with the Mughal Empire and betrayed Guwahati, leading to its capture by the Mughals. This event marked a significant shift in power dynamics in the region.
September 1682: Battle of Itakhuli: With this win, the Ahoms recovered Sarkar Kamrup from the Mughals.
Was a war between the Mughal and Safavid empires in the territory of modern Afghanistan.
September 1648: In 1648, Shah Abbas II of the Safavid dynasty marched from Isfahan with 40,000 troops and captured Bost.
February 1649: Siege of Kandahar.
Expansion during the rule of Aurangzeb in the Mughal Empire.
January 1663: On one occasion in 1662, the Mughals under Mir Jumla occupied the capital, Garhgaon.
February 1663: In 1662, the Mughal Empire, led by Mir Jumla, captured the capital city of Garhgaon.
January 1667: Arakan suffered a major defeat to the forces of Mughal Bengal during the Battle of Chittagong in 1666.
January 1667: Mughal annexation of Chittagong.
October 1687: The Portuguese outpost of Nagulavancha was destroyed on 13 October 1687 by locals.
January 1688: In 1687, the Dutch factory in Malda was taken over by the Mughal Empire.
January 1701: Mughal emperor Aurangzeb (1658-1707) expanded the empire to include almost the whole of South Asia.
January 1701: The plains areas fell away from Tripura state due to the actions of a renegade Tripuri prince who was backed by Mughal governors of Eastern Bengal plains. After this, plains Twipra became a separate Mughal client kingdom, with the Mughal rulers exerting influence on the appointment of its kings.
January 1701: Shahuji I was the eldest son of Venkoji and he ascended the throne at the age of twelve. During his reign, the Mughals occupied the Coromandel coast and Tiruchirapalli and forced him to pay tribute.
January 1702: Kalhora dynasty were assigned to hold authority in Sindh by the Mughal Grand Vizier Mirza Ghazi Beg and later formed their own independent dynasty. Their domain included lower and higher Sindh including the key cities of Hyderabad, Khairpur, Mirpur Khas, and Tando Muhammad Khan.
April 1705: In March 1705, Mazulipatam was taken over by the Mughal Empire.
Were a series of wars fought between the Mughal Empire and the Maratha Empire.
October 1686: In April 1685, Aurangzeb changed his strategy. He planned to consolidate his power in the south by undertaking expeditions to the Muslim kingdoms of Golkonda and Bijapur. Both of them were allies of Marathas and Aurangzeb was not fond of them. He broke his treaties with both kingdoms, attacked them and captured them by September 1686.
January 1691: Aurangzeb himself had to come and Panhala was surrendered.
January 1698: Jinji Fort in modern day Tamil Nadu is besieged by the Mughal Empire.
April 1700: Prayagji Prabhu defended Satara for a good six months but surrendered in April 1700.
January 1701: The Marathas expanded eastwards into Mughal lands, capturing Hyderabad in 1700.
January 1705: By 1704 Aurangzeb conquered Torana, Rajgad and some other handful forts mostly by bribing maratha commanders.
January 1706: A Marata army under the leadership of Nemaji Shinde, hit as far north as Bhopal. The second Maratha army, headed by Khanderao Dabhade, struck Bharoch and the west.
January 1706: By 1705 end, Marathas had penetrated Mughal possession of Central India and Gujarat. Nemaji Shinde defeated Mughals on the Malwa plateau.
January 1707: In 1706, Mughals started retreating from Maratha dominions.
Were a series of wars fought by the British East India Company in the Indian Subcontinent that resulted in the British conquest and colonial rule of the region.
6.1.Child's War
Was a conflict between the English East India Company and the Mughal Empire. It was the first Anglo-Indian War on the Indian subcontinent.
January 1689: Emperor Aurangzeb issued orders for the occupation of the British possessions all over the subcontinent, and the confiscation of their property. As a result, possessions of East India Company were reduced to the fortified towns of Madras and Bombay.
January 1691: Set up of a new english base in Calcutta.
January 1691: In 1690 the company sent envoys to Aurangzeb's court to plea for a pardon and to renew the trade firman. The company's envoys had to prostrate themselves before the emperor, pay a large imperial fine of 1,50,000 rupees, and promise better behavior in the future. Emperor Aurangzeb then ordered Sidi Yaqub to lift the Siege of Bombay and the company subsequently re-established itself in Bombay and set up a new base in Calcutta.
Expansion during the rule of Shahu I in the Maratha Empire.
January 1720: In 1719, an army of Marathas marched to Delhi after defeating Sayyid Hussain Ali, the Mughal governor of Deccan, and deposed the Mughal emperor. The Mughal Emperors became puppets in the hands of their Maratha overlords from this point on.
Expansion during the rule of Ranjit Singh in the Sikh Empire.
January 1840: Expansion of the Sikh Empire by 1839.
January 1527: The city of Multan submitted to the Mughal Empire, which had been founded by Babur after his capture of Delhi in 1526.
January 1527: Babur defeated and killed Ibrahim Lodi, the Sultan of Delhi, in the Battle of Panipat in 1526. The death of Ibrahim Lodi ended the Delhi Sultanate, and the Mughal Empire replaced it.
January 1527: Demise of the Oiniwar Dynasty.
January 1529: Multan, which was ruled by the Langah, fell in 1528 when it was attacked, probably at Babur's insistence.
January 1531: Gondwana Kingdom independent.
January 1531: The second Mughal ruler Humayun occupied the Bengali capital of Gaur during the invasion of Sher Shah Suri against both the Mughals and Bengal Sultans.
January 1532: Orchha State was founded in 1531 by the Rudra Pratap Singh, who became its first king.
January 1533: In 1532, Gujarat came under attack of the Mughal Emperor Humayun and fell.
January 1536: Mughal padshah (emperor) Humayun, son of Babur, captured the Malwa Sultanate in 1535 for a short period of time before it was eventually incorporated into the expanding Mughal Empire.
January 1536: In 1535 Bahadur Shah, the Sultan of Gujarat, concluded a defensive alliance with the Portuguese against the Mughal emperor Humayun and allowed the Portuguese to construct the Diu Fort and maintain a garrison on the island.
January 1536: Khandesh sultan Miran Muhammad occupied Mandu, the capital of Malwa. Here, on hearing the death of Bahadur Shah, he declared himself the sultan of Gujarat.
January 1537: Mughal padshah (emperor) Humayun, son of Babur, captured the Malwa Sultanate in 1535-36. The Malwa Sultanate was ruled by Baz Bahadur at the time, who was defeated by Humayun during his campaign to expand the Mughal Empire in India.
May 1540: The Sur Empire (1540-1555), founded by Sher Shah Suri (reigned 1540-1545), briefly interrupted Mughal rule.
January 1556: Humayun's triumphant return from Persia in 1555 restored Mughal rule over the Sur Empire.
January 1575: In 1574 CE, Murtaza Nizam Shah of Ahmadnagar annexed Berar.
January 1580: The Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama established the town of Hooghly-Chuchura in 1579 as a trading post in the Bengal region of India. The town became an important center for Portuguese trade and influence in the area.
January 1585: The state of Jhabua was founded by Kesho Das or Kishan Das, in 1584. He was granted the title of Raja by Mughal Emperor Akbar as a reward for a successful campaign in Bengal.
January 1587: Cooch Behar State was formed in 1586 when the Kamata Kingdom split after the death of Nara Narayan, a ruler from the Koch dynasty. The territory went to Cooch Behar State, which was ruled by the Koch dynasty.
January 1587: The kingdom of the Koch Dynasty split in two: Koch Bihar and Koch Hajo.
January 1596: Dhrol State was founded in 1595 by Jam Hardholji, a brother of Jam Rawal, the founder of Nawanagar State.
January 1600: The Khandpara State was initially part of Nayagarh State, founded by a former ruler of Rewa State, but became a separate kingdom in 1599 .
January 1601: Malik Ambar defied the Mughals and declared Murtaza Shah II as sultan at a new capital, Paranda.
January 1606: Soon after death of Akbar, Anant Chero drove out imperial troops out and declared his independence.
January 1608: In 1607, Jahangir ordered an expedition against Anant Chero. Mughal officials launched repeated attacks on Cheros and Chero had to shift their capital into deep jungle.
January 1614: Establishment of the Surguja State.
January 1616: In 1615, after four decades of skirmishing, Mewar and the Mughals entered into a treaty under which Mewar territory under the Mughals' possession was returned in exchange for the crown prince of Mewar attending the Mughal court and Mewar providing a force of 1,000 horsemen to the Mughals.
January 1618: The Dutch established a post at Cambay. It was a rather unsuccessful post due to the inability of ships to dock at the port at low tide.
January 1618: The Dutch East India Company office was founded in 1617.
January 1620: The British East India Company established trading posts in Surat (1619).
January 1621: Saraikela State was founded in 1620 by Raja Bikram Singh, who was a forerunner to the ruling family's current nomenclature of Singh Deo. The state was located in present-day Jharkhand, India.
January 1621: Wankaner State was founded in 1620 by Sartanji, son of Prathirajji, eldest son of Raj Chandrasinghji of Dhrangadhra (1584-1628).
January 1621: The fort of Kangra resisted Akbar's siege. Akbar's son Jahangir successfully subdued the fort in 1620 annexing the surrounding area and reducing the Katoch rajas to the status of vassals.
January 1621: Rajkot was founded by Thakur Sahib Vibhoji Ajoji Jadeja in 1620.
January 1626: Establishment of a Danish outpost in Pipli.
January 1626: Establishment of the Danish outpost in Balasore.
January 1626: Raigarh estate was founded in 1625.
January 1627: Foundation of Datia.
January 1627: Ngawang Namgyalm the founder of the Bhutanese state, consolidates control over western Bhutan.
January 1628: In 1627, the Ottomans lost control of Aden and Lahej to the Zaidi Imamate.
January 1631: Wadhwan was founded as a state around 1630.
January 1632: In 1631, Kota state seceded from Bundi State under the rule of Rao Madho Singh.
January 1633: The Mughal governor of Bengal expelled the Portuguese from Hugli-Chuchura.
January 1635: Gondal State was established in 1634 AD by Thakore Shri Kumbhoji I Meramanji, who received Ardoi and other villages from his father Meramanji.
January 1636: Sonepur state was founded in 1635.
January 1636: Foundation of the Dutch factory of Hougli.
January 1637: In 1636, Aurangzeb, the Mughal viceroy of Deccan, finally annexed the Ahmadnagar Sultanate to the Mughal empire, after defeating Shahaji.
January 1637: Foundation of the Dutch factory of Pipley (Pipli).
January 1637: Hugli-Chuchura was abandoned by the Dutch.
January 1642: Like neighboring Balkh Subah, Badakshan was shortly conquered in 1641 by Mughal padshah (emperor) Shah Jahan, who turned it also into a short-lived subah (imperial top-level province), only to be lost again in 1647.
January 1643: The Kingdom of Sikkim (Classical Tibetan and Sikkimese: འབྲས་ལྗོངས། Drenjong), earlier known as Dremoshong (Classical Tibetan and Sikkimese: འབྲས་མོ་གཤོངས།, official name until 1800s), was a hereditary monarchy from 1642 to 16 May 1975 in the Eastern Himalayas. It was ruled by Chogyals of the Namgyal dynasty.
January 1644: After problems with local merchants, Cambay closed in 1643.
January 1644: Establishment of the Danish outpost in Balasore.
January 1644: Establishment of a Danish outpost in Pipli.
January 1646: The territory of Hugli-Chuchura is re-occupied by the Dutch.
January 1648: Badakshan was shortly conquered in 1641 by Mughal padshah (emperor) Shah Jahan, who turned it also into a short-lived subah (imperial top-level province), only to be lost again in 1647.
January 1651: Kharsawan estate was founded in 1650.
January 1651: In 1818, Dungarpur State became a 15-gun salute state under a treaty with the British.
January 1651: Jafarabad State was founded around 1650.
January 1651: The Sultanate of Muscat possessed a powerful naval force, which enabled the creation of a maritime empire dating from the expulsion of the Portuguese in 1650 through the 19th century, at times encompassing modern Oman, the United Arab Emirates, southern Baluchistan.
January 1651: Foundation of Ranasan State.
January 1651: Korea State was founded in the 17th century.
January 1653: Foundation of Ratlam State.
January 1653: The local trading post of Visakhapatnam was enlarged into a fort in 1758.
January 1657: Rathore's ruled Idar for 12 generations after which they were defeated by the Mughals under Murad Baksh in 1656.
January 1658: The Dutch West India Company, a trading company established by the Dutch government, established a post on Saint Thomas in 1657.
January 1661: Jaoli was centered on the valley surrounding Javli. In the 1650s, it was ruled by Chandra Rao More, a vassal of the Adil Shah of the Bijapur Sultanate.
January 1661: Conquests of the Ahom Kingdom by 1660 (based on maps).
February 1663: In 1662, the Mughal Empire, led by Mir Jumla, captured the capital city of Garhgaon.
January 1664: According to legend Makrai princely state was established in 1663 century by Gond Raja Karkat Rai who hailed from a family that owned land in Harda tehsil.
January 1667: The Khanate of Kalat was founded in 1666 by Mir Ahmad Khan.
February 1667: Arakan suffered a major defeat to the forces of Mughal Bengal during the Battle of Chittagong in 1666.
January 1672: After the Battle of Saraighat, the Ahoms not only fended off a major Mughal invasion but extended their boundaries west, up to the Manas river.
January 1674: Raghogarh State was established in 1673 by Lal Singh Khichi, a Rajput of the Chauhan Khichi clan, a branch of the clan to which Prithviraj Chauhan the founder of Delhi belonged.
January 1675: Shivaji (1627-1680) was a Maratha aristocrat of the Bhosale clan who is the founder of the Maratha empire. Shivaji led a resistance to free the people from the Sultanate of Bijapur in 1645 by winning the fort Torna, followed by many more forts, placing the area under his control and establishing Hindavi Swarajya (self-rule of Hindu people). He created an independent Maratha kingdom with Raigad as its capital and successfully fought against the Mughals to defend his kingdom. He was crowned as Chhatrapati (sovereign) of the new Maratha kingdom in 1674.
January 1677: In 1676, the Dutch established a factory at Patna in Bengal.
January 1677: In 1676, the Dutch established a factory at Bellasoor (Baleshwar) in Bengal.
January 1677: In 1676, the Dutch East India Company established a trading post in Malda, a city in Bengal, India.
January 1681: The formation of the state of Bharatpur was a result of revolts by the Jats living in the region around Delhi, Agra and Mathura against the imperial Mughals.
January 1681: In 1680, the Maratha Empire, under the leadership of King Shivaji and his successors, expanded its territory to include a vast area in present-day India. This growth solidified the Marathas as a dominant power in the region during this time period.
January 1688: In 1687, Mazulipatam was captured by the French under the leadership of Governor General François Martin.
January 1690: The Ambliara State was ruled by a Chauhan family that is categorized among the "Kshatriya Koli" Thakordas (minor lords). According to the Gujarat State Gazetteers, the rulers were "Khant Kolis" by caste, and their family claimed descent from the Chauhans of Sambhar and Ajmer.
May 1690: In 1690, Chandernagore (Chandernagor) became a French possession in India.
January 1691: The Nawabs of the Carnatic (also referred to as the Nawabs of Arcot) were the nawabs who ruled the Carnatic region of South India between about 1690 and 1855.
January 1691: Towards 1690 Udot Singh, the Maharaja of Orchha, gave to his brother, Diwan Rai Singh, the jagir of Baragaon near Jhansi.
January 1693: Tori Fatehpur was established.
January 1699: Establishment of the Danish outpost of Dannemarksnagore in Bengal.
January 1699: Morvi was founded as a princely state around 1698 by Kanyoji when the heir apparent of Cutch State fled Bhuj with his mother after his father Ravaji was murdered and the throne was seized by his uncle Pragmalji I.
January 1700: Aundh was a Jagir granted by Chhatrapati Sambhaji to Parshuram Trimbak Pant Pratinidhi, who was a general, administrator and later Pratinidhi of the Maratha Empire during the reign of Chhatrapati Sambhaji and Chhatrapati Rajaram. He played a crucial role in re-capturing Panhala Fort, Ajinkyatara (at Satara), Bhupalgad forts from Mughals during period of 1700-1705.
January 1701: Kachari conquest of Pratapgarh Kingdom.
January 1701: During the reign of Chikka Devaraja (r. 1672-1704), the Kingdom of Mysore grew to include Salem and Bangalore to the east, Hassan to the west, Chikkamagaluru and Tumkur to the north and the rest of Coimbatore to the south.
January 1701: According to tradition Ranpur State is of very ancient origin. The legendary date of its foundation is placed some time in the 18th century BC when the founder, a hunter named Basara Basuk, having defeated a giant demon named Ranasura, established his rule in the area.
January 1702: During Shahu's reign, Raghoji Bhosale expanded the empire Eastwards, reaching present-day Bengal.
January 1702: Orchha was the only Bundela state not entirely subjugated by the Marathas in the 18th century.
January 1702: Khanderao Dabhade and later his son, Triambakrao, expanded Westwards into Gujarat.
January 1702: During this time, Durgadas Rathore, a prominent leader of the Rathore dynasty in Jodhpur State, successfully fought against the Mughal Empire for 31 years to free Marwar from their control. His efforts ultimately preserved the Rathore dynasty's rule in the region.
January 1702: Sitamau State was a princely state of the British Raj before 1947. Its capital was in Sitamau town, Mandsaur district, Madhya Pradesh. The total area of the state was 350 square miles. The average revenue of the state was Rs.130,000. The ruling dynasty was historically related to the Rathores of Ratlam State.
January 1708: Patiala State was founded.
January 1709: The ruling dynasty were descendants of Ranoji Lokhande, who was adopted by Chhattrapati Shahu, grandson of Shivaji, around the year 1708. Upon his adoption, Ranoji assumed the name 'Fatehsinh Bhonsle' and received in appenage the town of Akkalkot and surrounding areas.
April 1709: Mirwais and his followers revolted against Safavid rule in Kandahar.
January 1710: The Khanate of Kokand was established in 1709 when the Shaybanid emir Shahrukh, of the Ming Tribe of Uzbeks, declared independence from the Khanate of Bukhara, establishing a state in the eastern part of the Fergana Valley.
January 1711: Kirat Parkäsh was the ruler of Sirmur Kingdom in 1710. He defeated the Räja of Garhwal and captured Naraingarh, Morni, Pinjaur, and other territories from the Sikhs.
January 1711: In 1710, Murshidabad became a Dutch trading post in Bengal, India.
January 1713: Bhurshut was conquered by Kirtichand Rai of Bardhaman in the 18th century.
January 1714: The Sandur state was founded around 1713 by a Maratha Shrimant Sidalji Ghorpade, who died in 1715 without any heir. From 1731 until the accession to India, the Sandur state was ruled by Marathi Brahmin royals.
January 1715: Establishment of the Danish outpost of Dannemarksnagore in Bengal.
January 1718: Najib-ud-daula Governor of Saharanpur, who invaded in 1757 along with his Rohilla Army and captured Dehradun.
May 1819: In 1819, the British East India Company completed its conquest of the Maratha Empire. This marked the end of Maratha rule and the consolidation of British control over much of the Indian subcontinent.
January 1821: Expansion of the Qing Dynasty by 1820 after the so-called "Ten Great Campaigns".
January 1843: The Sikhs reached an agreement with the Tibetans in 1842 under which the Sikh Confederation took possession of the territory south of the Karakoram pass and Pangong lake. The British also recognized this border, which took the name of the Johnson Line.
Disestablishment
January 1859: After a crushing defeat in the war of 1857-1858, the last Mughal, Bahadur Shah Zafar, was deposed by the British East India Company and exiled in 1858.
Selected Sources
Die Dänen in Indien, Südostasien und China (1620-1845), Wiesbaden (Germany), pp. 215-219
Imperial Gazetteer of India, v. 16, p. 2 retrieved on https://dsal.uchicago.edu/reference/gazetteer/
Larsen, K. (1940): Guvernører, Residenter, Kommadanter og Chefer samt enkele andre fremtradende personer i de tidligere Danske Tropokolonier, Copenhagen (Denmark), p. 18
Pradhan, U. K. (2007): Ports of Baleswar in the Maritime History, Orissa Review of November - 2007, p. 42
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.164-165

 Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire