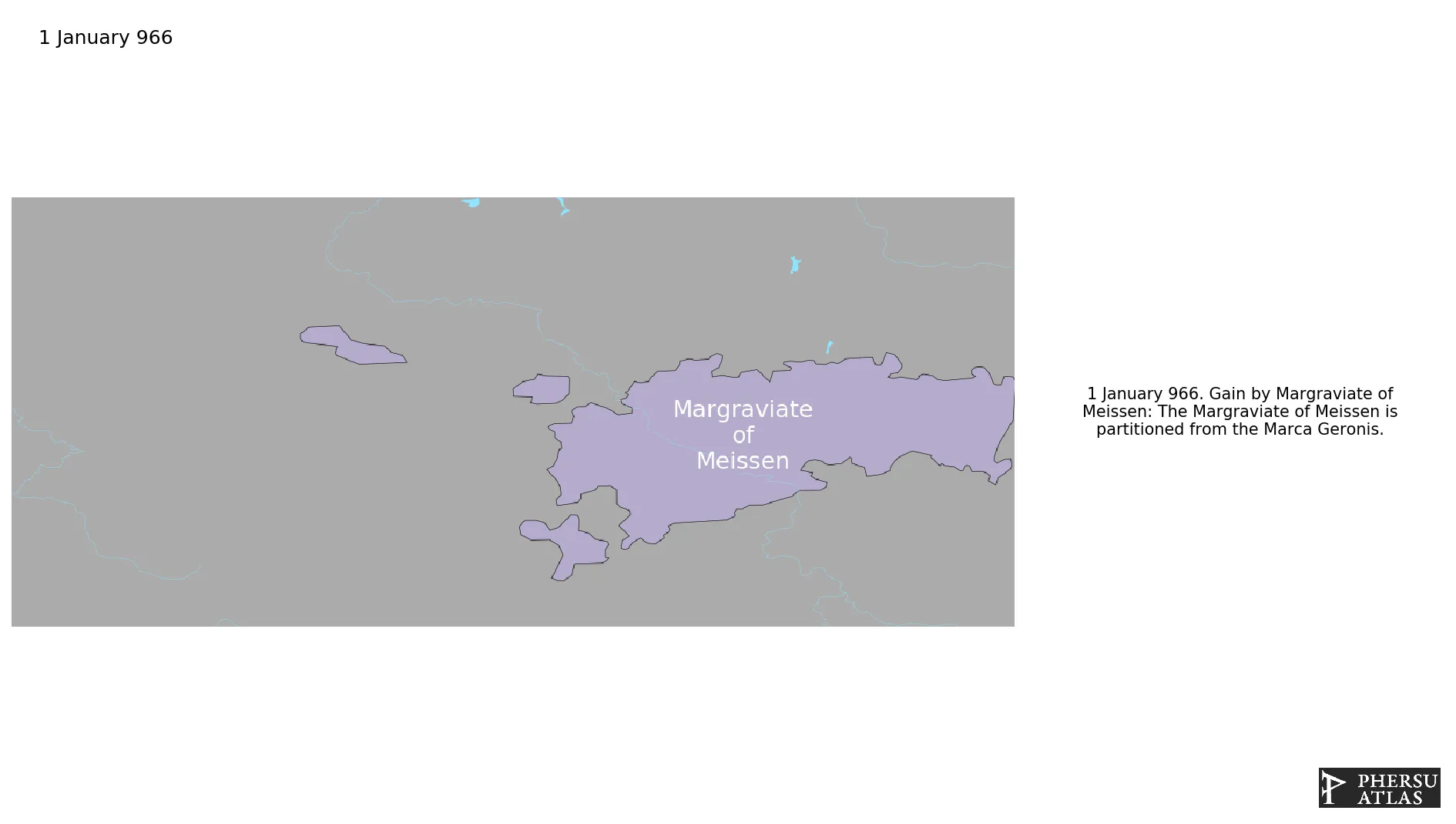
Margraviate of Meissen
Margraviate of Meissen
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a polity of the Holy Roman Empire located in modern-day eastern Germany. It was one of the several polities that originated from the division of the Marca Geronis.
Establishment
January 966: The Margraviate of Meissen is partitioned from the Marca Geronis.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
1.1.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
1.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Germany
Was a Mongol raid in the Holy Roman Empire.
May 1241: The Mongols invaded the Holy Roman Empire without major clash of arms.The army invaded eastern Germany, and crossed the March of Moravia in April-May 1241.
June 1241: The Mongols left eastern Germany and Moravia.
January 983: The Margraviate of Meissen acquired the territories of Merseburg and Zeitz.
January 984: In 983, Zeitz was overrun by the Sorbs and the marcher territory fell into the hands of the Slavs.
January 1005: Establishment of the Merseburg Prince-Bishopric.
January 1007: Meissen Burgraviate is mentioned for the first time in 1006.
January 1018: In 1017, Castle Düben was owned by Count Albi, who was shortly followed by Count Friedrich von Eilenburg.
January 1018: In the Treaty of Bautzen, which was concluded between the two rulers of Poland and Meissen on January 30, 1018 after several changeable and bitter campaigns of war, Milzenerland and Mark Lusatia (today's Lower Lusatia) remained with the Duchy of Poland.
January 1032: After King Konrad II had defeated the Polish King Mieszko II Lambert, the Kingdom of Poland came under the rule of the Meissen Margraves again.
January 1077: In 1076, King Henry IV of Germany transferred the Bautzener Land to Duke Vratislav II of Bohemia as an imperial fiefdom after there had been disputes with the Saxon-Thuringian regional nobility, including the Margrave of Meissen, over his imperial property policy.
January 1128: Since Gero's sons, Dietrich, Wilhelm, and Günther, had no children, the County of Brehna fell to Konrad I von Wettin in 1106. Konrad I was Margrave of Meissen from 1127 and Lower Lusatia from 1136, Count of Brehna, Camburg and lord of the Eilenburg dominion.
January 1145: Towards the middle of the 12th century, probably as early as 1143 or 1144 under King Conrad III, the burgraveship of Dohna came as an imperial fief to the noble Heinricus de Rodewa.
January 1159: Colditz Castle in Saxony was elevated to imperial property by Emperor Barbarossa in 1158 as part of the Pleissenland.
January 1159: Around 1158, Emperor Friedrich Barbarossa gave the Mildenstein Castle in Leisnig, first mentioned in 1046, along with its accessories, as imperial property to a family that now called itself the Burgraves of Leisnig.
January 1181: Meissen Prince-Bishopric gains Imperial immediacy.
January 1201: In the 12th century, the Wettin margraves of Meissen began to expand into Lusatia.
January 1213: The County of Anhalt finally arose upon the death of Duke Bernhard in 1212, when his sons divided their heritage. The younger Albert I became Duke of Saxony, while the elder Henry I went on to rule the Ascanian lands, now definitely separated from Saxony, as Count of Anhalt.
January 1266: As a result of the War of the Thuringian Succession, Henry of Meissen gained the bulk of Thuringia in 1264, while the Hessian possessions of the landgraves was separated as the Landgraviate of Hesse.
January 1289: Wettin, the ancestral seat of the House of Wettin, the former ruling dynasty of Saxony, passed to the Archdiocese of Magdeburg.
January 1292: Through an inheritance contract, the Dewin castle came into the possession of the Thuringian landgraves.
January 1304: Margrave Dietrich IV sold Lausitz in 1303 to the Brandenburg line of the Ascanians.
January 1330: With the death of burgrave Albrecht IV in 1329, an imperial diploma confirmed the transfer of the Altenburg burgrave office to the House of Wettin.
January 1332: Saalburg fell to the Margraviate of Meissen.
January 1343: In 1342 the town of Sömmerda came into the possession of the County of Schwarzburg.
January 1343: In 1342, the counts of Tonna became vassals of the Wettin Margraves of Meissen. The Wettin dynasty was a powerful German noble family that ruled over various territories in the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. The Margraviate of Meissen was one of their important domains.
January 1351: Dresden (Altendresden), today's Inner Neustadt, on the right bank of the Elbe, was first mentioned in 1350 as an independent settlement called "Antiqua Dressdin". It was part of the Margraviate of Meissen.
January 1358: As a result of the Vogtland War, the town and Voigtsberg Castle came from the possession of the Plauen bailiffs to the Wettin family.
January 1366: Sale of the Leisnig and Mutzschen estates to the House of Wettin in 1365.
January 1379: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XIV century.
January 1390: In 1389, Saalfeld was transferred from the Schwarzburg family to the Wettin family, specifically to the Margraviate of Meissen. The Wettins ruled over Saalfeld until the monarchy was abolished in 1918.
January 1403: In 1402 the castle of Dohna was completely destroyed by miners from Dippoldiswalde and Freiberg. The Burggraviate of Dohna was taken over by the Meißner Margrave.
January 1405: In 1404, the territory of the Colditz family was acquired by the House of Wettin, who incorporated it as the margravial office of Colditz into the margraviate of Meissen.
January 1424: The Margrave of Meissen purchased Saxony, becoming Elector of Saxony.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
Disestablishment
January 1483: After the death of the Landgrave of Thuringia and Margrave of Meissen, in 1482 Saxon Elector Ernest inherited the landgraviate, uniting the Wettin lands under his rule.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 30-31
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Strakosh-Grassmann, G. (1893): Der Einfall der Mongolen in Mitteleuropa in den Jahren 1241 und 1242, Innsbruck (Austria), pp. 53-67
.png.webp)
 Margraviate of Meissen
Margraviate of Meissen