If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Were the overseas territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia and Oceania. The bulk of these territories was the archipleago of the Philippines.
Establishment
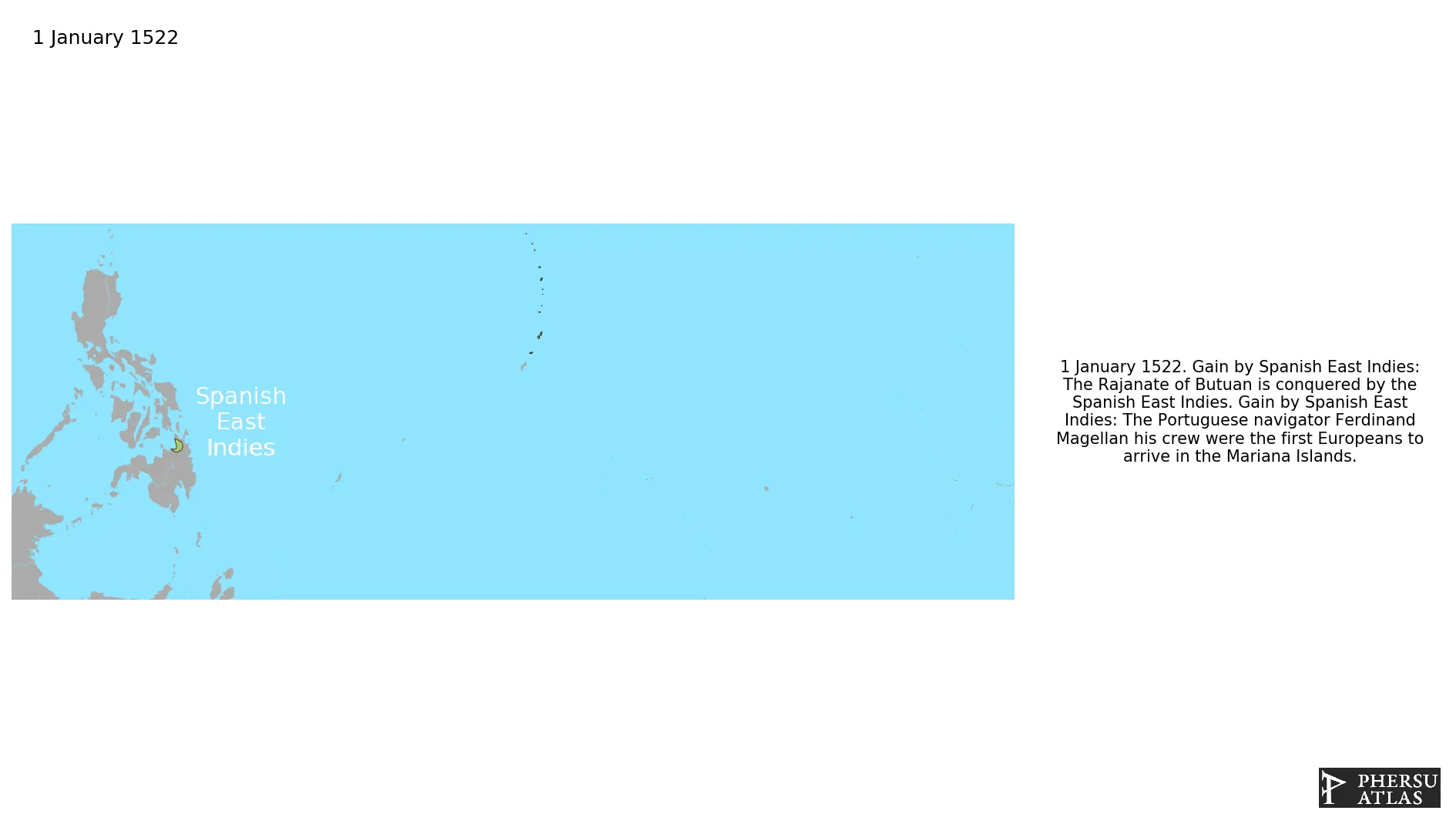
January 1522: The Rajanate of Butuan is conquered by the Spanish East Indies.
January 1522: The Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan his crew were the first Europeans to arrive in the Mariana Islands.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
1.1.Anglo-Spanish War (1762-63)
Was a military conflict fought between Britain and Spain as part of the Seven Years' War.
October 1762: The British forces, led by Admiral Samuel Cornish and Brigadier General William Draper, successfully captured Manila from the Spanish in 1762 during the Seven Years' War. The Battle of Manila resulted in significant plunder being taken from the city.
1.2.Treaty of Paris (1763)
Was a treaty signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the Seven Years' War.
February 1763: Treaty of Paris (1763): Britain restored Manila and Havana to Spain.
Was a war of independence of the Philippines, at the time part of the Spanish East Indies, against the Spanish Empire. However, the Philippine efforts proved useless as the outbreak of Spanish-American War resulted in the U.S. army invading and occupying the Philippines.
2.1.First Phase (Philippine Revolution)
Was the first phase of the Philippine Revolution, a revolt against Spanish rule.
January 1897: By December, there were three major centers of rebellion: Cavite (under Mariano Alvarez, Baldomero Aguinaldo and others), Bulacan (under Mariano Llanera) and Morong (now part of Rizal, under Bonifacio).
March 1897: In 1897, government troops led by General Camilo Polavieja, with the support of new recruits from Spain, recaptured several towns in Cavite, including Imus, during the Philippine Revolution against Spanish colonial rule.
June 1897: In May 1897, the Spanish captured Maragondon.
July 1897: By June, the Spanish had taken Mendez Nunez, Amadeo, Alfonso, Bailen and Magallanes with little resistance.
November 1897: Aguinaldo and his men retreated northward, from one town to the next, until they finally settled in Biak-na-Bato, in the town of San Miguel de Mayumo in Bulacan. Here they established what became known as the Republic of Biak-na-Bato.
December 1897: The Pact of Biak-na-Bato, signed on December 15, 1897, created a truce between Spanish colonial Governor-General Fernando Primo de Rivera and the revolutionary leader Emilio Aguinaldo to end the Philippine Revolution.
2.2.Second Phase (Philippine Revolution)
Was the second phase of the Philippine Revolution, a revolt against Spanish rule. The First Philippine Republic was proclaimed.
May 1898: In the Battle of Alapan, Aguinaldo raided the last remaining stronghold of the Spanish Empire in Cavite.
June 1898: The Philippine rebels captured Imus and Bacoor in Cavite, Parañaque and Las Piñas in Morong, Macabebe, and San Fernando in Pampanga, as well as Laguna, Batangas, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Bataan, Tayabas, and the Camarines provinces, were liberated by the Filipinos. They were also able to capture the port of Dalahican in Cavite.
Was a war between Spain and the United States of America. The immediate cause of the war was the American support to Cuban independence.
3.1.Pacific theatre (Spanish-American War)
Was the Pacific theatre of the Spanish-American War.
May 1898: The first battle between American and Spanish forces was at Manila Bay where, on May 1, Commodore George Dewey, commanding the U.S. Navy's Asiatic Squadron aboard USS Olympia, in a matter of hours defeated a Spanish squadron under Admiral Patricio Montojo.
June 1898: A small U.S. task force under Captain Henry Glass captures Guam.
January 1556: Charles V, who was King of Spain and Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire, left the Spanish Empire to his son Philip and the Austrian Lands to his brother Ferdinand I.
January 1565: Guam was not officially claimed by Spain until January 26, 1565, by General Miguel López de Legazpi.
June 1565: Rajanate of Cebu conquered by spain.
January 1570: Confederation of Madya-as conquered by spain.
May 1571: The Spaniards take power over Manila, Tondo and Sapa.
June 1571: Annexation of the Rjanate of Manila by Spanish conquistador Miguel López de Legazpi.
January 1572: Cainta conquered by spain.
January 1572: Kingdom of Namayan conquered by spain.
January 1575: The coast of Samtoy, already familiar to Chinese and Japanese traders before Magellan's time, was known to the Spanish colonizers in 1572 when Juan de Salcedo traveled along Samtoy or what is now known as the Ilocos Provinces. Sent by the "Adelantado", Miguel López de Legazpi, to explore the whole island of Luzón, Salcedo founded Ciudad Fernandina in 1574 in the heart of Yloko settlement in Bigan, in what is now Ilocos Sur.
January 1575: Spain was the first European nation to explore the Palau islands in the 16th century, and they were made part of the Spanish East Indies in 1574.
January 1575: The Spanish, once reached the Carolines in the 16th century, established their sovereignty.
January 1576: By 1575 Spain conquered Dapitan.
January 1576: By 1575 Spain conquered the territories of the Igorot people on the Philippines.
January 1577: Spanish conquest of Pangasinan.
January 1583: When the Spanish arrived in the area of Cagayan, they incorporated this territory to the Captaincy of the Philippines following the 1582 Cagayan battles.
January 1593: Spain claimed the Marshall islands in 1592.
January 1601: By 1600 Spain completed the conquest of the Philippines.
January 1624: The town of Taytay was formally founded in 1623 , during the Spanish colonization of the region.
January 1641: The Spaniards formally annexed the Sultanate of Lanao, without actually controlling it.
January 1706: The Sultanate of Sulu totally gave up its rule over Palawan to Spain in 1705 and Basilan to Spain in 1762.
January 1741: The Empire lost much of its territory due to the arrival of the western powers such as the Spanish in the Philippines.
January 1784: In 1783, the Spaniard invaders claimed Batanes as part of the Philippines under the auspices of Governor-General José Basco y Vargas. This made its own history to be vanished rapidly.
February 1845: In 1845, France, represented by Admiral Cécille, forced the Sulu Sultanate, led by Sultan Muizzuddin, to formally cede Basilan Island to France. This marked the beginning of French colonial presence in the region.
August 1845: The claims were made by French explorer Jules Dumont d'Urville, who initially declared Basilan as part of French territory. However, after negotiations, the claims were withdrawn and sovereignty of the island was officially transferred to Spain on August 5, 1845.
April 1851: In 1848 and 1851, the Spanish launched attacks on Balanguingui and Jolo respectively. A peace treaty was signed on 30 April 1851 in which the sultan could only regain its capital if Sulu and its dependencies became a part of the Philippine Islands under the sovereignty of Spain.
January 1862: From 1837, the Spanish colonial power gained control of the Sultanate of Maguindanao and by 1861 they managed to occupy the entire area of today's Cotabato.
January 1878: The concession treaty signed in 1878 by Sultan Jamal ul-Azam of Sulu appointed Baron de Overbeck as Dato Bendahara and Raja Sandakan in North Borneo. This treaty marked the transfer of territory to the State of North Borneo.
October 1885: Spain sold some of the Marshall islands to the German Empire in 1886.
August 1898: Spain ceded its claims over the islands to Germany.
Disestablishment
May 1898: The first battle between American and Spanish forces was at Manila Bay where, on May 1, Commodore George Dewey, commanding the U.S. Navy's Asiatic Squadron aboard USS Olympia, in a matter of hours defeated a Spanish squadron under Admiral Patricio Montojo.
May 1898: In the Battle of Alapan, Aguinaldo raided the last remaining stronghold of the Spanish Empire in Cavite.
June 1898: The Philippine rebels captured Imus and Bacoor in Cavite, Parañaque and Las Piñas in Morong, Macabebe, and San Fernando in Pampanga, as well as Laguna, Batangas, Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, Bataan, Tayabas, and the Camarines provinces, were liberated by the Filipinos. They were also able to capture the port of Dalahican in Cavite.
June 1898: A small U.S. task force under Captain Henry Glass captures Guam.
August 1898: Spain ceded its claims over the islands to Germany.
Selected Sources
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1492
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.1497
Kitchin, T. (1778). The Present State of the West-Indies: Containing an Accurate Description of What Parts Are Possessed by the Several Powers in Europe
.svg.png.webp)

 Spanish East Indies
Spanish East Indies