This article is about the specific polity Sultanate of Delhi and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
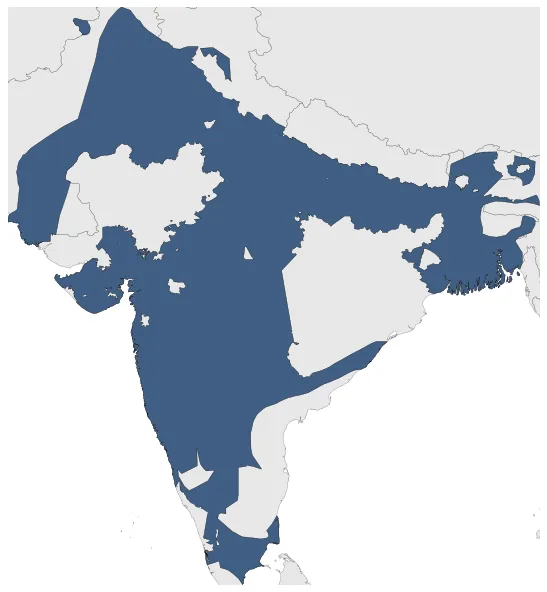
Was a Muslim empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent during the period of Medieval India, for 320 years. In 1526, the Sultanate was conquered and succeeded by the Mughal Empire.
Establishment
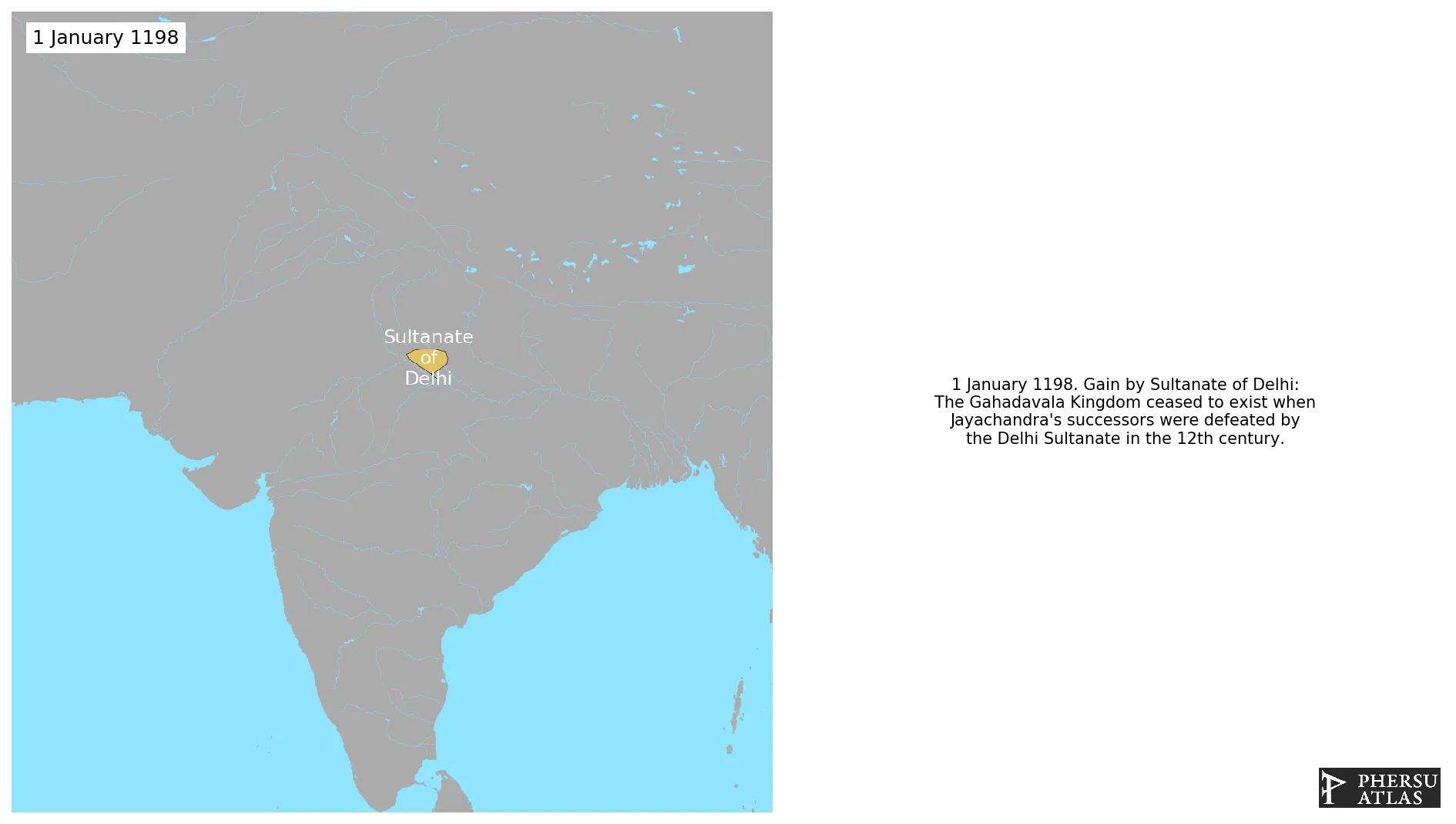
January 1198: The Gahadavala Kingdom ceased to exist when Jayachandra's successors were defeated by the Delhi Sultanate in the 12th century.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was an era of disunity in Tibetan history lasting from the death of the Tibetan Empire's last emperor, Langdarma, in 842 until Drogön Chögyal Phagpa became the Imperial Preceptor of the three provinces of Tibet in 1253, under the Yuan dynasty.
January 1221: The Khasa Kingdom expands into the territory of Garhwal and Kumaon.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
January 1246: The city of Multan was captured by the Mongols under Sali Noyan in 1245-6.
The Hoysala capital Halebidu was sacked by the Delhi Sultanate in 1327.
January 1328: The Hoysala capital Halebidu is sacked by Delhi Sultanate forces.
February 1328: End of the sack of Halebidu by the forces of the Delhi Sultanate.
Was a long-lasting conflict between the Bengal Sultanate and the Delhi Sultanate.
4.1.First Phase of the Bengal Sultanate-Delhi Sultanate War
Was the first phase of the Bengal Sultanate-Delhi Sultanate War and consisted in an invasion of Bengal by the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1371: Territorial change based on available maps.
Military campaigns of Timur (or Tamerlane), a Turco-Mongol conqueror who founded the Timurid Empire in and around modern-day Afghanistan, Iran, and Central Asia.
5.1.Timurid invasion of India
Were the military campaigns of Timur in India.
January 1398: In 1397, Multan, a city in present-day Pakistan, was besieged by Pir Muhammad, the grandson of the famous conqueror Tamerlane. The territory of Multan ultimately fell under the control of the Timurid Empire as a result of this siege.
September 1398: In 1398, the famous conqueror Timur, also known as Tamerlane, invaded the north Indian subcontinent by crossing the Indus River. This marked the beginning of the Timurid Empire's expansion into the region, which included present-day Pakistan and North India.
November 1398: Timurid forces firstly sacked Tulamba and then Multan by October of 1398.
December 1398: Sultan Nasir-ud-Din Tughlaq was the ruler of the Tughlaq dynasty in Delhi, Mallu Iqbal was a nobleman allied with him, and Timur was the founder of the Timurid Empire. Timur invaded Delhi in 1398, defeating Sultan Nasir-ud-Din Tughlaq and leaving the city in ruins after sacking it.
5.1.1.Sack of Delhi
Sack of the capital of the Delhi Sultanate by the Timurid Empire.
January 1399: Timur conquered Delhi.
February 1399: Timur left Delhi.
January 1204: Around 1202-1203 CE the Ghurid governor of Delhi invaded the Chandela kingdom.
January 1207: In 1193 the Ghurid Sultan Muhammad conquered Delhi and left a slave lieutenant Qutab-ud-din Aybak, in charge when he returned to Afghanistan. When Muhammad was assassinated in 1206, Aybak declared independency and established the Mamluk Dynasty of the Sultanate of Delhi.
January 1207: Ghurid Sultan Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori was assassinated in 1206, by Ismāʿīlī Shia Muslims. After the assassination, one of Ghori's slaves (or Mamluks), the Turkic Qutb al-Din Aibak, assumed power, becoming the first Sultan of Delhi.
January 1211: Following the death of the first Mumluk Sultan, Qutb al-Din Aibak in 1210, Multan came under the rule of Nasiruddin Qabacha.
January 1212: Following Qabacha's death that same year, the Turkic king Iltutmish, the third Sultan of the Mamluk dynasty, captured and then annexed Multan in an expedition.
January 1216: The Ghurids were succeeded in Khorasan and Persia by the Khwarazmian dynasty.
January 1221: Iltutmish of Delhi conquered Multan and Bengal from contesting Muslim rulers, as well as Ranthambore and Siwalik from Hindu rulers.
January 1227: Foundation of the Jodhpur Kingdom, also known as Kingdom of Marwar.
January 1229: Prithu was the ruler of the Kamarupa Kingdom, while Ghiyasuddin Iwaj Shah was the ruler of Gauda. Nasiruddin Mahmud was the ruler of the Sultanate of Delhi. In 1228, after invading Kamarupa, Ghiyasuddin was defeated, captured, and killed by Nasiruddin Mahmud.
January 1230: Delhi sultan Nasir-ud-din installed a tributary king but after his death in 1229 the control of Kamarupa lapsed back to local rulers.
January 1235: Paramara ruler Devapala defeated the Delhi Sultanate's governor and regained control of the city of Bhilsa (modern-day Vidisha).
January 1243: Later the region was governed by Rao Deva, who took over Bundi from Jaita Meena in 1242, renaming the surrounding area as Haravati or Haroti. For the next two centuries, the Hadas of Bundi were the vassals of the Sisodias of Mewar and ruled by the title of Rao.
January 1247: The city of Multan was captured by the Mongols under Sali Noyan in 1245-6. However, it was later recaptured by Sultan Ghiyas ud din Balban of the Sultanate of Delhi in 1246.
January 1250: Multan then fell to the Qarlughids in 1249.
January 1255: Multan was then conquered by Izz al-Din Balban Kashlu Khan in 1254.
January 1258: The Kamata Kingdom emerged in western Kamarupa probably when Sandhya, a ruler of Kamarupanagara, moved his capital west to Kamatapur sometime after 1257 CE.
January 1263: Dharampur State was founded in 1262.
January 1267: Qarlugh Kingdom disestablished.
January 1281: Seuna ruler Ramachandra subjugated the rulers of Vajrakara (probably modern Vairagarh) and Bhandagara.
January 1282: In 1281, Nasiruddin Bughra Khan, the Governor of Lakhnauti, declared independence from the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1291: The Khalji dynasty came into being when Jalal ud din Firuz Khalji overthrew the last of the Slave dynasty rulers, Muiz ud din Qaiqabad, the grandson of Balban, and assumed the throne at Delhi.
January 1321: Expansion of the Sultanate of Delhi by 1320.
January 1321: Ghazi Malik's forces marched on Delhi, captured the Khalji ruler Khusraw Khan and beheaded him. Upon becoming sultan, Ghazi Malik renamed himself Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq. He was the first ruler of the Tughluq dynasty of the Sultanate of Delhi.
January 1322: Delhi prince Ulugh Khan plundered Arangal and Tilang.
February 1322: Delhi forces leave Arangal and Tilang.
January 1324: Another attack by Delhi Sultan Ulugh Khan in 1323 saw stiff resistance by the Kakatiyan army, but they were finally defeated. The Kakatiya dynasty was annexed.
January 1325: The Karnatas of Mithila conquered by the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1325: Bastar State was founded in the early 14th century, supposedly by a brother of the last ruler of the Kakatiya dynasty proper, Prataparudra II.
January 1325: In 1324 CE, Ghiyasuddin Tughlaq attacked the fort of Simroungarh and demolished it.
January 1325: Ghiyasuddin Bahadur Shah lost independence to the Delhi Sultanate once again.
January 1326: The Reddi Kingdom was established in southern India by Prolaya Vema Reddi who was part of the confederation that started a movement against the invading Turkic armies of the Delhi Sultanate in 1323 and succeeded in repulsing them from Warangal.
January 1329: The Kampili kingdom finally fell to the invasion in 1327/28 CE from the north by the forces of Muhammad bin Tughluq, the Sultan of Delhi.
January 1331: Expansion of the Sultanate of Delhi up to 1330.
January 1331: The Pandyas were a dynasty in South India, known for their rule in the region. In 1330, they shifted their capital to Tenkasi, where they continued to govern a small territory until the late 16th century. During this time, they were known as the Tenkasi Pandyas.
January 1331: The Tughluqs under Ulugh Khan annexed the former Pandya dominions to the sultanate as the province of Ma'bar. Most of south India came under the sultanate rule and was divided into five provinces - Devagiri, Tiling, Kampili, Dorasamudra and Ma'ba.
January 1335: In c. 1334, Jalal ud-Din Hasan Khan declared his independence and created Madurai sultanate.
January 1336: The Vijayanagara Empire liberated southern India from the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1337: After the fall of the Kakatiyas, their empire was annexed by the Delhi Sultanate. Ulugh Khan, the general that conquered Warangal, renamed it "Sultanpur" and remained as the governor of the region for a short period. In 1324, he was recalled to Delhi to succeed the Khaljis as Muhammad bin Tughluq. A former Kakatiya commander, Nagaya Ganna Vibhudu, now renamed Malik Maqbul, was appointed as the governor of the region. However, the Tughluq hold over the erstwhile Kakatiya empire was tenuous and a number of local chieftains seized effective power. Kapaya Nayaka took control of Warangal from Malik Maqbul in 1336 and thus also of a wider swathe of eastern Telangana that was governed from there.
January 1339: When Bahram Khan was transferred to Sonargaon, Izzuddin Yahya was made the next governor of Saptagram in 1328. After his death in 1338, his deputy Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah took control and declared independence from Delhi.
January 1339: The Sultanate of Sonargaon became a short-lived independent state with control over central, northeastern and southeastern Bengal. When Bahram Khan died in 1338, his armour-bearer, Fakhruddin Mubarak Shah, declared himself the independent Sultan of Sonargaon.
January 1341: Samarsinhji acceded to the gadi (throne) of Rajpipla around 1340, assuming the name Arjunsinhji. From then, Rajpipla was ruled by the Gohil Rajput dynasty.
January 1343: The Sultanate of Satgaon annexed Lakhnauti (actual Gauḍa) in 1342.
May 1343: On 6 June 1306, Jayabha Mukne, a Poligar, took possession of the fort at Jawhar. His elder son, Dulbarrao, expanded his patrimony and conquered a large territory, controlling 22 forts, comprising most of the Nasik and Thana districts, and yielding annual revenues valued at £90,000. He received recognition as ruler by Sultan Muhammad bin Tughlaq, receiving the new name of Nimshah and the hereditary title of Raja on 5 June 1343.
January 1345: In 1344, the city of Uchchakalpa, present-day Unchahara, was founded by Raja Veerraj Judeo when he seized the fort of Naro.
January 1348: The empire was established by an Ismaili military general from Badakhshan, Ala-ud-Din Bahman Shah, after revolting against the Turkic Delhi Sultanate of Muhammad bin Tughlaq.
January 1349: Karauli State was a princely state in India from 1348 to 1949.
January 1353: Unification of Bengal by Ilyas Shah. He controlled an area stretching from Assam in the east to Varanasi in the west.
January 1353: Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah was the ruler of Satgaon who defeated Sonargaon in 1352, establishing the Bengal Sultanate. This marked the consolidation of power in the region under the rule of the Ilyas Shahi dynasty.
January 1354: The Oiniwar dynasty was a Maithil ruling dynasty of territories that form part of the Mithila region of the Indian subcontinent. They governed the area between 1353 and 1526, being preceded by the Karnat dynasty.
January 1371: According to tradition Palanpur state was founded in 1370 and was ruled by the pashtun tribe of Lohani (Hetani, Bihari Pathan) of Jhalori dynasty.
January 1383: The founder of the Khandesh dynasty, Malik Ahmad (also known as Malik Raja) participated in a rebellion against the Bahmani ruler Muhmmad Shah I in his early years. When he was compelled to flee from Deccan, he established himself in Thalner on the Tapti River (in present-day Dhule district in Maharashtra). After receiving the grant of the fiefdoms of Thalner and Karanda (the present day Karwand, 19 km north of Thalner) from Firuz Shah Tughluq in 1370, he conquered the region around Thalner, which later became known as Khandesh (the land of the Khans). By 1382, he started ruling independently.
January 1395: Establishment of the Jaunpur Sultanate. To the east, the kingdom extended to Bihar, and to the west, to Kanauj.
January 1395: The Khwajah-i-Jahan Malik Sarwar, the first ruler of the dynasty was a wazir under Sultan Nasiruddin Muhammad Shah IV Tughluq (1390-1394).
January 1401: It was the ruling kingdom in Gondwana region of India. From the 14th to the 18th century the area was held by powerful Gond dynasties, which during Mughal times remained independent or served as tributary chiefs.
January 1401: The Tomaras were a dynasty who ruled the Gwalior Fort and its surrounding region in central India during 14th-16th centuries. In the 1390s, they gained control of Gwalior, and became independent in the subsequent years.
January 1401: Jambughoda State was established towards the end of the 14th century by Thakore Vachhaji, a descendant of the Malwa ruling dynasty.
January 1401: The Kingdom of Kozhikode captured Thirunavaya.
January 1402: The sultanate of Malwa was founded by Dilawar Khan Ghuri, the governor of Malwa for the Delhi Sultanate, who asserted his independence in 1392, but did not actually assume the ensigns of royalty till 1401.
January 1403: Establishment of the Jaunpur Sultanate. To the east, the kingdom extended to Bihar, and to the west, to Kanauj.
January 1408: Following Timur's invasion of Delhi, the Delhi Sultanate weakened considerably so Zafar Khan declared himself independent in 1407 and formally established Gujarat Sultanate.
January 1408: Mahmud Shah, the ruler of the Jaunpur Sultanate, was successful in conquering Chunar, but failed to capture Kalpi.
January 1413: Bushahr, also spelt as 'Bashahr' and 'Bussahir' or 'Bushair' was a princely state in India during the British Raj. It was located in the hilly western Himalaya promontory bordering Tibet in the northern part of colonial Punjab region.
January 1415: In 1414, Multan's Khizr Khan, a governor under the Tughlaq dynasty, captured Delhi from Daulat Khan Lodi, establishing the short-lived Sayyid dynasty. This marked the beginning of the fourth dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate.
January 1421: Bahlul Lodi began his reign by attacking the Muslim Jaunpur Sultanate to expand the influence of the Delhi Sultanate, and was partially successful through a treaty. Thereafter, the region from Delhi to Varanasi (then at the border of Bengal province), was back under influence of Delhi Sultanate.
January 1434: The cessation of the Ming treasure voyages, led by Chinese explorer Zheng He, had negative consequences for the Kingdom of Cochin in 1433. The Zamorin of Calicut, a powerful ruler in the region, took advantage of the weakened state of Cochin and launched an invasion against the kingdom.
January 1444: Vinayak Dev, a prince from Kashmir whose family claimed descent from the mythical Suryavanshis, established the little kingdom of Nandapur located in the Eastern Ghats in 1443.
January 1449: Rajahmundry was conquered by the Gajapatis.
January 1451: Peshawar was an important regional centre under the Lodi Empire.
January 1451: Multan then passed to the Langah, who established the Langah Sultanate in Multan under the rule of Budhan Khan, who assumed the title Mahmud Shah.
January 1466: The state of Bikaner was founded in 1465.
January 1501: Vijapur, an independent state during the later middle ages, was ruled by the Adil Shah dynasty. In 1500, the territory came under the control of Yusuf Adil Shah, who expanded the kingdom and established Vijayapur as a prominent center of art, culture, and trade in South India.
January 1501: The greatest achievement of Sikandar Lodi was the conquest and annexation of Bihar.
January 1517: Hussain Shah extended Bengali territory in the west beyond Bihar, up to Saran in Jaunpur.
January 1519: Borders of the Ahmadnagar Sultanate by 1518.
January 1519: Borders of the Berar Sultanate by 1518.
January 1526: The Tomaras were displaced from Gwalior by Ibrahim Lodi in the first quarter of the 16th century.
April 1526: Babur's forces occupied Delhi and much of northern India after his victory at Panipat in 1526.
Disestablishment
January 1527: Babur defeated and killed Ibrahim Lodi, the Sultan of Delhi, in the Battle of Panipat in 1526. The death of Ibrahim Lodi ended the Delhi Sultanate, and the Mughal Empire replaced it.
Selected Sources
Middleton, J. (2005): World Monarchies and Dynasties, Volumes 1-3, Routledge, p. 644
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.164-165

 Sultanate of Delhi
Sultanate of Delhi