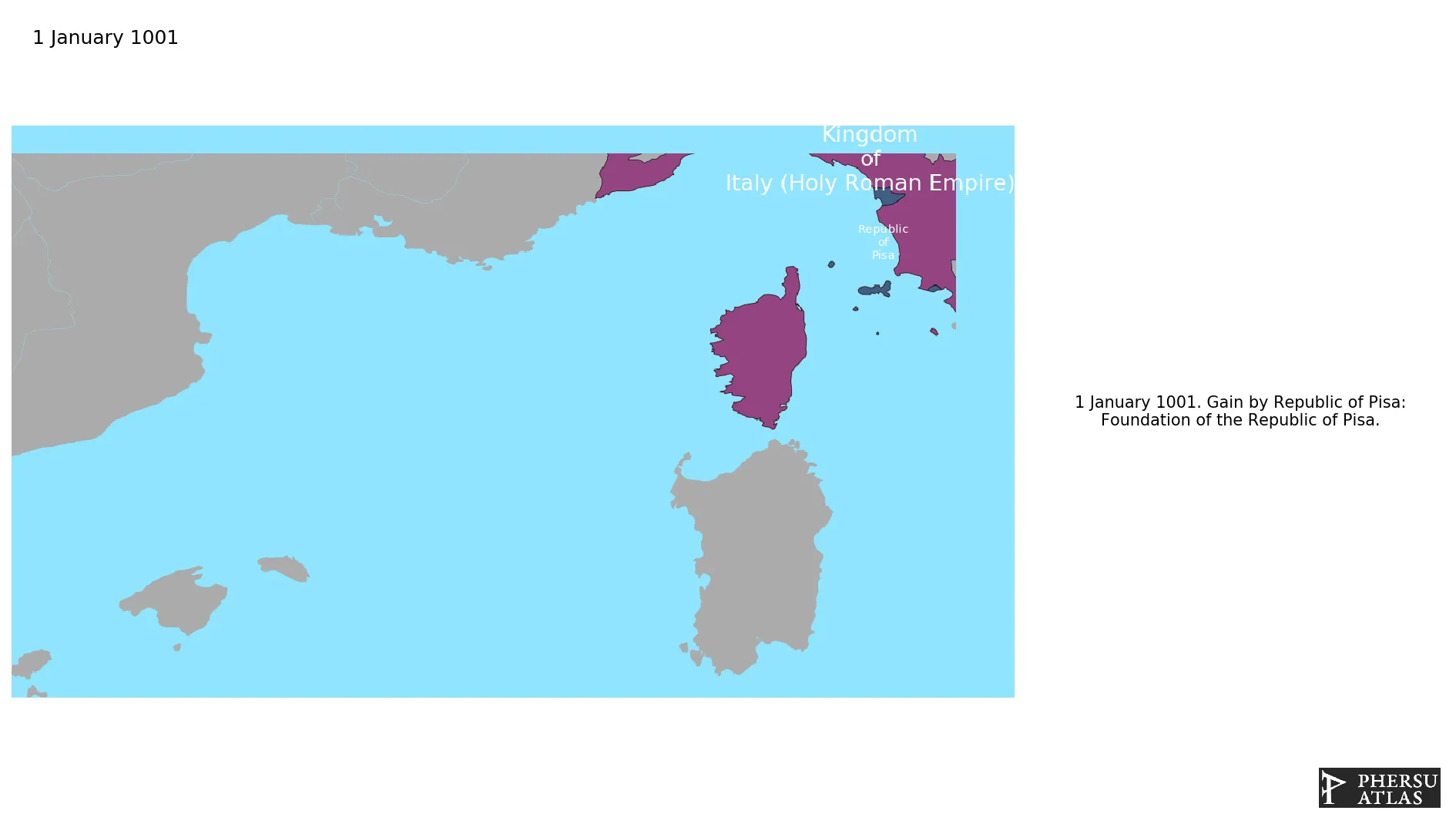
Republic of Pisa
Republic of Pisa
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a maritime Republic in Tuscany, centred on the city of Pisa.
Establishment
January 1001: Foundation of the Republic of Pisa.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the Medieval period. The best known of these military expeditions are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291.
1.1.1113-15 Balearic Islands expedition
An expedition to the Balearic Islands, then a Muslim Taifa (principality), was launched in the form of a Crusade.
September 1114: Pisan troops made their way into the city of Ibiza and the Muslim commander surrendered unconditionally.
May 1115: With the capitulation of the Fort of Majorca, the Pisans completed their conquest of the Balearic Islands in April 1115.
January 1117: The Almoravids coming from the Iberian peninsula reconquered the Balearic Islands in 1116.
Were a series of military campaign by the Crown of Aragon to conquer the island of Sardinia.
January 1324: In December 1323, the King of Aragon, Alfonso IV, led a military campaign from Goceano into the Baronie region, capturing 33 villages including Orosei and Dorgali. This marked the expansion of Aragon's territory in Sardinia.
February 1324: On the 7 February 1324, the city of Villa di Chiesa (now known as Iglesias) in Sardegna surrendered to the Kingdom of Aragon, led by King Alfonso IV of Aragon. This marked the incorporation of Iglesias into the Aragonese territories in Italy.
February 1324: On the 29 February the Aragonese and the Pisan armies engaged in a pitched battle near the present day centre of Elmas […] After the defeat in Lucocisterna the Pisans were forced to accept the surrender and give to the Aragonese their territorial possessions in Sardinia.
January 1051: Pisa conquers Piombino.
January 1078: Towards the end of the 11th century, the Papacy raised the question of its sovereignty over Corsica. This claim found wide acceptance within the island itself, starting with its clergy, and in 1077 the Corsicans declared themselves subject to Rome. Pope Gregory VII (1073-1085), in the midst of the investiture controversy with the emperor Henry IV, did not directly take control of the island, but entrusted its administration to the bishop of Pisa.
January 1201: Castiglione della Pescaia became a free commune in the XIII century.
January 1217: Pisa conquers Massa.
January 1226: Massa Marittima experienced the peak of its splendor in the years in which it became a free municipality (1225-1337).
January 1259: William III was deposed and the Judicate of Cagliari was divided into three parts and divided between the Judicate of Gallura, which included the north-eastern part (Ogliastra, Sarrabus), the Judicate of Arborea, which annexed the central-northern area, and the della Gherardesca family, which was responsible for the western region of Sulcis-Iglesiente.
January 1265: Giglio Island was added to the possessions of Pisa in 1264.
January 1275: In 1274 the Pisans resumed control of Castiglione della Pescaia.
August 1284: The Island of Corsica and the Island of Capraia definitively passed under the control of Genoa after the defeat of the Republic of Pisa in the battle of Meloria.
January 1288: One third of the Judicate of Gallura was incorporated into the Pisan territories in 1287.
January 1297: Death of Nino Visconti, last judge of Gallura. His Judicate is conquered by the Republic of Pisa.
January 1334: The castle of Galtellì did not recognize the authority of the king of Aragon and the castle withstood a siege. The castle passed under the dominion of the Aragonese only in 1333.
January 1346: Pisa conquers Sarzana.
February 1399: On February 19, 1399, Gherardo Appiano ceded Pisa, which his family had owned since 1392, to the Visconti of Milan for 200,000 florins, reserving Piombino for himself and his successors, becoming lord; moreover he also took possession of Populonia, Suvereto, Scarlino, Buriano, Badia al Fango and the islands of Pianosa, Montecristo, and Elba.
February 1399: Milan conquers Pisa and Siena.
January 1401: Castiglion della Pescaia came under the influence of Florence during the 14th century (in 1404, the citizens spontaneously surrendered to the Republic of Florence).
January 1403: Gabriele Maria Visconti (1385 - December 15, 1408) was the illegitimate son of the Duke of Milan Gian Galeazzo Visconti. He was Lord of Pisa from 1402 to 1405.
Disestablishment
January 1407: In 1406, the Florentines became lords of Pisa after a costly war. Florentine dominion thus extended over most of Tuscany, except for the Sienese region.
Selected Sources
Cambridge Scholars Publishing (2020): Conflict and Collaboration in Medieval Iberia, Cambridge Scholars Publishing, p. 113
Capo, L. / Ciaralli, A. (2016): Per Enzo. Studi in memoria di Vincenzo Matera, Firenze University Press, p.39
Kim Bergqvist, Kurt Villads Jensen, Anthony John Lappin
Moroni Romano, G. (1856): Dizionario di erudizione storico-ecclesiastica da san Pietro sino ai nostri giorni, Vol. LXXVIII, Venice (Italy), p. 134
Repetti, E. (1833), Dizionario geografico, fisico, storico della Toscana: contenente la descrizione di tutti i luoghi del granducato, ducato di Lucca, Garfagnana e Lunigiana, Volume 1, Florence (Italy), p. 602
Repetti, E. (1845), Supplemento al Dizionario geografico, fisico, storico della Toscana, Florence (Italy), p. 9
Rogers, R. (1997): Latin Siege Warfare in the Twelfth Century, Clarendon Press, p.167

 Republic of Pisa
Republic of Pisa