If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a medieval Republic that controlled southern Tuscany and was centred on Siena.
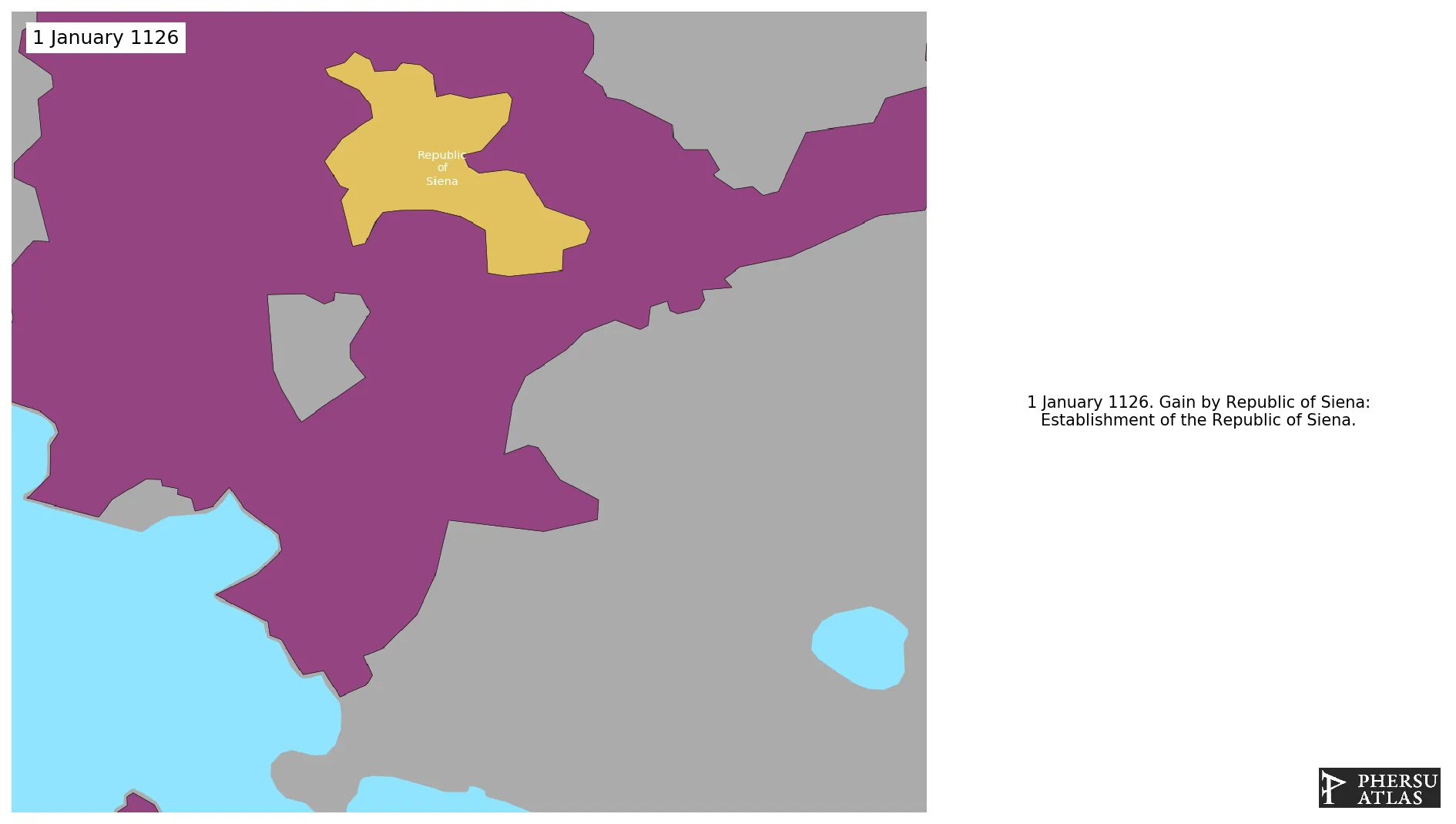
Establishment
January 1126: Establishment of the Republic of Siena.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a battle fought on 4 September 1260 between Florence and Siena in Tuscany as part of the conflict between the Guelphs and Ghibellines. The Florentines were routed. It was the bloodiest battle fought in Medieval Italy, with more than 10,000 fatalities.
January 1261: Conquests of Siena after the Battle of Montaperti (September 4, 1260)
Were the military campaigns of Ladislaus I of Hungary during his reign.
January 1409: Ladislaus of Naples expanded the northern border of the Kingdom of Naples up to the Talamone fortress on the Tyrrhenian Sea, where the State of Presidi would later develop.
January 1411: The weak Neapolitan garrisons left to defend Rome were unable to repel the attack of the allied forces of Florence and Siena and the city was handed over to them in early 1410, followed by other castles in the area including Tivoli.
Were a series of conflicts covering the period between 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The primary belligerents were the Valois kings of France, and their Habsburg opponents in the Holy Roman Empire and Spain.
3.1.War of the League of Cognac
Was one of the so-called Italian Wars. It was fought between the Habsburg dominions of Charles V —primarily the Holy Roman Empire and Spain— and the League of Cognac, an alliance including the Kingdom of France, Pope Clement VII, the Republic of Venice, the Kingdom of England, the Duchy of Milan, and the Republic of Florence.
January 1528: The Republic of Siena looses control of Porto Ercole, which is conquered by Papal troops.
3.2.Italian War of 1551-1559
Was one of the so-called Italian Wars.
3.2.1.Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis
Was the treaty that ended the Italian War of 1551-1559, the last of the Italian Wars (1494-1559).
April 1559: The Duchy of Florence absorbed the Republic of Siena (allied with France).
3.3.Siena War
Was a war of the Duchy of Florence (which controlled northern Tuscany), supported by Spanish and Imperial forces, against the Republic of Siena (which controlled southern Tuscany). The Republic of Siena was invaded and annexed by Florence.
March 1553: Spanish general García de Toledo invaded the Republic of Siena, conquering Lucignano, Montefollonico and Pienza for Florence.
July 1553: The imperial troops that were aiding the Republic of Florence, left part of the territories conquered from Siena because they had to go fighting with the Ottomans that had started an invasion of southern Italy.
January 1554: At the end of January 1554, Siena was placed under siege.
April 1554: The Val di Chiana was put to fire and sword. Sinalunga and Torrita were taken by Florence.
April 1555: The enemies who entered Siena victorious on April 17, 1555, the date of the stipulation of the capitulation after the surrender of the city due to hunger.
June 1555: The Take of Porto Ercole took place between May 25 and June 18 1555.
Expansion during the rule of Cosimo I in the Duchy of Florence .
January 1555: The Florentines occupied the northern part of the Republic of Siena.
April 1555: The city of Siena surrenders to the Florentine army. The nobility of Siena flees to Montalcino.
January 1152: Submission of Grosseto and San Giovanni d'Asso to the Republic of Siena.
January 1156: Siena annexes the County of Berardinghi.
January 1168: The Republic od Siena conquers Civitella Marittima.
January 1176: Rapolano is acquired by the Republic of Siena.
January 1181: The imperial archchancellor trasnfers San Quirico d'Orcia to the Republic of Siena.
January 1194: Paganico's submission to Siena.
January 1198: Sinalunga conquered by Siena.
September 1204: Grosseto declares itself Free Commune. The city controlled a large district (about 300 square kilometres) which extended as far as the coast and the mouth of the Bruna River.
January 1211: The Republic of Siena conquers Turrita di Siena.
January 1213: Submission of Montalcino to Siena.
January 1231: Conquest of Chianciano, Riadicondoli and Chiusdino by the Republic of Siena.
January 1232: The Chiusi Commune is acquired by the Republic of Siena.
January 1233: The Montepulciano Commune is acquired by the Republic of Siena.
January 1236: Siena looses Montepulciano.
January 1236: Submission of the city of Pienza to Siena.
January 1251: The region of Maremma fell under the influence of the Republic of Siena in the 13th century.
January 1253: Independence of Montalcino from Siena.
January 1256: The city of Trequanda is annexed by the Republic of Siena.
January 1260: The Republic of Siena occupies Grosseto.
January 1261: Conquests of Siena after the Battle of Montaperti (September 4, 1260)
January 1268: Rebellion of Montepulciano.
January 1270: The Republic of Siena conquers Monticiano.
January 1276: The Cacciaconti-Scialenga family of Siena buys the city of Asciano.
January 1283: The Republic of Siena purchased Campagnatico from the Viscounts of Campiglia.
January 1294: The Republic of Siena acquired corralbegna from the Ranieri counts.
January 1295: Submission of Montepulciano to Siena.
January 1302: The Republic of Siena acquired Roccastrada from the Aldobrandeschi family.
September 1303: In May 1303, the abbot of the monastery of San Salvatore, Fra Ranieri, arrived in Siena proposing to the government of the Nine the purchase of the land owned by the monastery (even though at the time they were however militarily occupied by the Counts of Santa Fiora) including Talamone and Castiglion di Val d'Orcia.
January 1311: Grosseto revolted against Siena.
January 1327: The city of Montieri is conquered by Republic of Siena.
January 1332: Arcidosso and Castel del Piano are conquered by the Republic of Siena.
January 1336: In 1335, the Republic of Siena annexed the territories of Massa Marittima, Monterotondo, and Gavorrano.
March 1338: At the beginning of 1334 the government of the Nine undertook the decisive effort to strengthen the Sienese policy in the border areas with the Pisan countryside, in a phase of open conflict with the maritime city, subduing Grosseto and Massa Marittima. The first was fully included in the state structure of Siena in February 1338.
January 1376: Talamone was occupied by Papal militias.
January 1379: The Republic of Siena reconquers Talamone.
January 1388: Recognition of Sienese sovereignty over Murlo.
January 1391: Siena looses Montepulciano, which allies with Florence.
January 1391: The counts of Battifolle sell Cinigiano to the Republic of Siena.
February 1399: The Visconti Dynasty if Milan extended its control to the Republic of Siena.
February 1404: Visconti ruled in Siena lasted just five years (1399-1404).
January 1433: Castiglion della Pescaia temporarily rebels against Florence and falls under the domain of Siena (around 1431 or 1432 until around 1433).
January 1434: Castiglion della Pescaia, temporarily occupied by Siena following a revolt, returns under the control of Florence.
January 1450: Sovana was conquered by the Sienese.
January 1472: Santa Flora fell under Siena.
January 1479: Siena conquers Colle Val d'Elsa and Castellina in Chianti from Florence.
January 1484: Colle Val d'Elsa returns to Florence's control thanks to the mediation of Lorenzo the Magnificent.
January 1531: Siena reconquers Porto Ercole.
Disestablishment
April 1559: The Duchy of Florence absorbed the Republic of Siena (allied with France).
Selected Sources
Barsacchi, M. (2007): Cacciate Lorenzo! La guerra dei Pazzi e l'assedio di Colle Val d'Elsa (1478-1479), Siena (Italy), p.148
Barsacchi, M. (2007): Cacciate Lorenzo! La guerra dei Pazzi e l'assedio di Colle Val d'Elsa (1478-1479), Siena (Italy), p.57
Moroni Romano, G. (1856): Dizionario di erudizione storico-ecclesiastica da san Pietro sino ai nostri giorni, Vol. LXXVIII, Venice (Italy), pp. 34-39
Naldi, A. (2001), Mille e una Toscana, Empoli (Italy), p. 153
Repetti, E. (1833), Dizionario geografico, fisico, storico della Toscana: contenente la descrizione di tutti i luoghi del granducato, ducato di Lucca, Garfagnana e Lunigiana, Volume 1, Florence (Italy), pp. 602-605

 Republic of Siena
Republic of Siena