If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
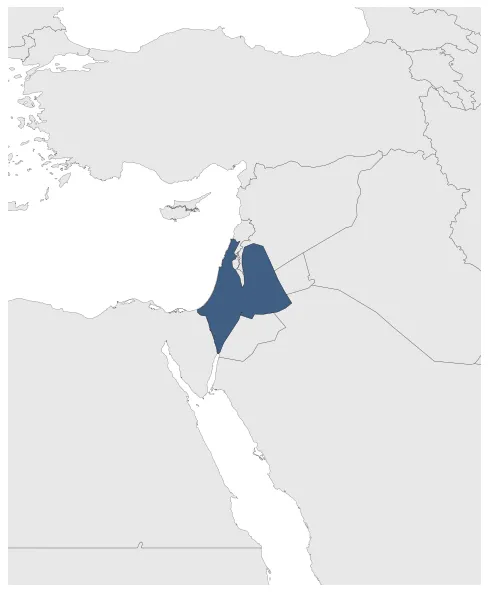
Kingdom of Jerusalem
Kingdom of Jerusalem (Personal Union with HRE)
Establishment
July 1099: Godfrey is elected as the ruler of Jerusalem.
August 1099: Battle of Ascalon.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the Medieval period. The best known of these military expeditions are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291.
June 1291: The Mamluks capture Sidon.
July 1291: Beirut surrenders to the Mameluk troops.
1.1.First Crusade
Was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Medieval period. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Islamic rule.
1.2.Battle of Ramla (1101)
The second Battle of Ramla (or Ramleh) took place on 17 May 1102 between the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Fatimids of Egypt.
May 1102: The second Battle of Ramla took place on 17 May 1102 between the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Fatimids of Egypt.
1.3.Siege of Tripoli
Tripoli was captured by the Crusaders, becoming the capital of the County of Tripoli.
July 1109: Tripoli is captured by the Crusaders and becomes the capital of the County of Tripoli.
July 1109: When the Frankish Crusaders - mostly southern French forces - captured Tripoli in 1109, Bertrand of Toulouse became the first Count of Tripoli as a vassal of King Baldwin I of Jerusalem.
1.4.Norwegian Crusade
Led by Norwegian King Sigurd I, was a crusade that lasted from 1107 to 1111, in the aftermath of the First Crusade.
October 1110: Sidon is besieged by the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
1.5.Venetian Crusade
Was an expedition to the Holy Land launched by the Republic of Venice that succeeded in capturing Tyre.
February 1124: On 15 February 1124, the Venetians and the Franks began the siege of Tyre.
June 1124: Tyre surrendered on 29 June 1124.
1.6.Second Crusade
Was the second of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi.
July 1148: Siege of Damascus.
July 1148: The siege of Damascus resulted in the defeat of the Crusaders and the territory of Damascus remained under Burid control.
1.7.Crusader invasions of Egypt
Were a series of campaigns undertaken by the Kingdom of Jerusalem to strengthen its position in the Levant by taking advantage of the weakness of Fatimid Egypt.
1.7.1.Siege of Ascalon
Capture of that Egyptian fortress by the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem.
January 1154: Capture of Ascalon, an Egyptian fortress, by the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem.
1.8.Battle of Marj Ayyun
Was a battle between the Christian crusaders of the Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Ayyubids.
June 1179: Marjayoun is conquered by Ayyubid troops led by Saladin against the Christians.
1.9.Siege of Jacob's Ford
A victory of the Muslim Sultan Saladin over the Christian King of Jerusalem, Baldwin IV.
August 1179: A victory of the Muslim sultan Saladin over the Christian King of Jerusalem, Baldwin IV, resulted in the conquest of Jacob's Ford.
1.10.Battle of Cresson
Was a small battle between Frankish and Ayyubid forces on 1 May 1187.
May 1187: Battle of Cresson: Muzzafar al-Din annihilates an army of Hospitallers and Templars.
1.11.Battle of Hattin
Was a battle between the Christian Crusader states and the Ayyubid Sultan Saladin.
September 1187: After the Battle of Hattin, 52 towns and fortifications were captured by Saladin's forces. By mid-September, Saladin had taken Acre, Nablus, Jaffa, Toron, Sidon, Beirut, and Ascalon.
September 1187: The Siege of Jerusalem was a siege on the city of Jerusalem that lasted from September 20 to October 2, 1187, when Balian of Ibelin surrendered the city to Saladin.
October 1187: The Siege of Jerusalem was a siege on the city of Jerusalem that lasted from September 20 to October 2, 1187, when Balian of Ibelin surrendered the city to Saladin.
November 1187: Tyre was saved by the arrival of Conrad of Montferrat, resulting in Saladin's siege of Tyre.
January 1188: The Siege of Tyre ended on January 1, 1188.
1.12.Siege of Safed (1188)
Was part of Saladin's invasion of the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
January 1189: Siege of Safed (1188).
1.13.Third Crusade
Was an attempt led by three European monarchs of Western Christianity to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by the Ayyubid sultan Saladin in 1187.
August 1189: Siege of Acre (1189-1191).
July 1191: Siege of Acre (1189-1191).
September 1191: The Crusaders, now under the unified command of Richard I of England, defeated Saladin at the Battle of Arsuf, allowing for the Crusader conquest of Jaffa and much of coastal Palestine.
September 1191: Battle of Arsuf: Richard I of England overcomes Saladin.
January 1192: The crusaders seized the abandoned Ascalon.
June 1192: The crusaders march as far as Bayt Nuba near Jerusalem.
July 1192: In July 1192 Saladin, at the head of thousands of men, took Jaffa.
July 1192: The city of Jaffa was reconquered by Richard I of England.
1.13.1.Treaty of Jaffa (1192)
A treaty between the Muslim ruler Saladin and Richard the Lionheart, King of England, restoring the Kingdom of Jerusalem to a coastal strip between Jaffa and Beirut.
September 1192: Richard I of England signed a treaty with Saladin in 1192, restoring the Kingdom of Jerusalem to a coastal strip between Jaffa and Beirut.
1.14.Crusade of 1197
Was a crusade launched by the Hohenstaufen emperor Henry VI.
October 1197: A substantial German army under the command of Archchancellor Conrad of Mainz and Marshal Henry of Kalden landed at Acre. They captured the wealthy and important city of Sidon.
October 1197: Archchancellor Conrad of Mainz and Marshal Henry of Kalden entered Beirut.
1.15.Frankish conquest of Sidon, Lydda and Ramla
Frankish conquest of Sidon, Lydda and Ramla, in the Holy Land.
October 1204: Aimery and Al-Adil conclude a six-year truce. The Franks take full control of Sidon, Lydda and Ramla.
1.16.Fifth Crusade
Was a Crusade initiated by Pope Honorius III. The military actions took place in Palestine and Egypt.
December 1217: The crusaders capture Beisan.
1.17.Sixth Crusade
Was a military expedition to recapture Jerusalem and the rest of the Holy Land. The diplomatic maneuvering of the Holy Roman Emperor and King of Sicily, Frederick II, resulted in the Kingdom of Jerusalem regaining some control over Jerusalem.
February 1229: Even with the military orders on board, Frederick of Sicily's force was a mere shadow of the army that had amassed when the crusade had originally been called. He realised that his only hope of success in the Holy Land was to negotiate for the surrender of Jerusalem as he lacked the manpower to engage the Ayyubid sultanate in battle. He hoped that a token show of force, a threatening march down the coast, would be enough to convince al-Kamil, the sultan of Egypt, to honor a proposed agreement that had been negotiated some years earlier, prior to the death of al-Muazzam, the governor of Damascus. The Egyptian sultan, occupied with the suppression of rebellious forces in Syria, agreed to cede Jerusalem to the Franks, along with a narrow corridor to the coast. In addition, Frederick received Nazareth, Sidon, Jaffa, and Bethlehem.
1.18.Barons' Crusade
Was a crusade to the Holy Land that, in territorial terms, was the most successful crusade since the First Crusade.
December 1239: An-Nasir Dawud of Transjordan, whose caravan had been seized by Peter, marched on Jerusalem, which was largely undefended. After a month of being holed up in the Tower of David, the garrison of the citadel surrendered to Dawud on 7 December.
March 1241: The Ayyubid signed a treaty with the crusaders. Galilee and the hinterland of Jaffa were restored to the Kingdom of Jerusalem which reaches its greatest territorial extent after 1187.
1.19.Siege of Jerusalem (1244)
The 1244 Siege of Jerusalem took place after the Sixth Crusade, when roaming Khwarazmians clans conquered the city on July 15, 1244.
July 1244: The 1244 Siege of Jerusalem took place after the Sixth Crusade, when roaming Khwarazmians clans conquered the city on July 15, 1244.
1.20.Ayyubid campaign against the crusaders (1247)
Was a military campaign of the Ayyubids that led to the conquest of important cities controlled by the Crusader states, like Ascalon.
June 1247: Ayyubids occupies Tiberias.
June 1247: Mount Tabor and Belvoir surrendered to Ayyub's troops.
October 1247: In 1247, the Ayyubid Dynasty, led by the Egyptian sultan As-Salih Ayyub, captured the city of Ascalon from the Crusaders.
1.21.Fall of Arsuf
Arsuf was conquered by the Mamluk Sultanate.
March 1265: Mamluk sultane Baibars captures and destroys Caesarea.
March 1265: Baibars could not take Chastel Pelerin, but he destroyed Haifa.
March 1265: In late March 1265 Sultan Baibars, Muslim ruler of the Mamluks, laid siege to Arsuf. It was defended by 270 Knights Hospitallers.
April 1265: At the end of April, after 40 days of siege, the town of Arsuf surrendered to the Mamluks.
1.22.Siege of Safed (1266)
The Siege of Safed (13 June - 23 July 1266) was part of the campaign of the Mamlūk sultan Baybars I to reduce the Kingdom of Jerusalem. .
June 1266: The Siege of Safed in 1266 was led by Mamluk sultan Baybars I as part of his campaign to conquer the Kingdom of Jerusalem. Safed fell to the Mamluks, further weakening the Kingdom's defenses.
July 1266: The Siege of Safed in 1266 was led by Mamluk sultan Baybars I as part of his campaign to conquer the Kingdom of Jerusalem. Safed fell to the Mamluks, further weakening the Kingdom's defenses.
1.23.Siege of Antioch (1268)
The Siege of Antioch occurred in 1268 when the Mamelukes under Baibars finally succeeded in capturing the city of Antioch.
March 1268: Mamluk sultane Baibar captures and destroys Jaffa.
1.24.Siege of Acre (1291)
The Siege of Acre took place in 1291 and resulted in the Crusaders losing control of Acre to the Mamluks.
April 1291: The Siege of Acre in 1291 led to the fall of the Crusader-controlled city to the Mamluks, marking the end of the Crusader presence in the Holy Land. The Mamluks were a powerful military caste in Egypt, known for their role in the overthrow of the Ayyubid dynasty.
May 1291: The Mamluks capture Acre.
May 1291: The Siege of Acre in 1291 led to the fall of the Crusader-controlled city to the Mamluks, marking the end of the Crusader presence in the Holy Land. The Mamluks were a powerful military caste in Egypt, known for their role in the overthrow of the Ayyubid dynasty.
1.25.Fall of Ruad
When the garrison on the tiny Isle of Ruad fell to the Mamluks, it marked the loss of the last Crusader outpost on the coast of the Levant.
September 1302: Fall of Ruad: the Crusaders surrendered on September 26, 1302, following a promise of safe conduct.
August 1100: Tancred's crusader troops and the Venetians capture Haifa.
January 1101: The castle of Gibelet was built by the Crusaders in the 12th century from indigenous limestone and the remains of Roman structures. The finished structure was surrounded by a moat. It belonged to the Genoese Embriaco family, whose members were the Lords of Gibelet from 1100.
January 1103: In 1102, Raymond IV, Count of Tripoli, occupied Tortosa (now Tartus) in present-day Syria.
May 1105: Baldwin I of Jerusalem captures Acre with the assistance of Genoese and Pisan fleets.
May 1110: Baldwin I of Jerusalem and a Genoese fleet capture Beirut.
December 1110: Baldwin I, Sigurd I of Norway and a Venetian fleet capture Sidon.
August 1111: Tyre was never conquered during all the military passages in the region.
August 1111: The population of Ascalon revolted against the Crusaders. Taken over by the Fatimids, Ascalon was their last stronghold in Palestine.
December 1129: The Franks seized Banias.
January 1130: The Franks seized Banias.
January 1136: Expansion of the Kingdom of Jerusalem by ca. 1140 AD:
June 1140: Jerusalemite and Damascene troops capture Banias.
June 1147: Baldwin III of Jerusalem makes a raid against the fertile Hauran region near Damascus.
July 1147: The forces of Baldwin III of Jerusalem leave the Hauran region after a raid.
December 1157: The united crusader forces capture Shaizar.
January 1158: The crusaders abandoned Shaizar.
October 1164: Zengid Nur ad-Din went on to besiege and capture Banias.
January 1171: Saladin destroyed the Frank colonists' unfortified quarters at Darum and Gaza.
July 1187: The Crusader stronghold of Acre was captured by Saladin.
July 1187: Ayyubid brigades took Haifa, Caesarea, Sebastia and Nablus.
July 1187: In 1187, the Ayyubid Dynasty, led by Al-Adil, conquered the cities of Mirabel and Jaffa.
September 1187: In August, the Ayyubids conquered Ramla, Darum, Gaza, Bayt Jibrin, and Latrun.
September 1187: Ascalon conquered by Ayyubid Dynasty.
September 1187: Saladin captures Jaffa, Arsuf, Caesarea, Haifa, Sidon and Ascalon.
November 1187: Karak and Mont Real in Transjordan soon fell, followed by Safad in the northeastern Galilee. By the end of 1187 the Ayyubids were in control of virtually the entire Crusader kingdom in the Levant with the exception of Tyre.
December 1188: Saladin's troops capture Kerak.
January 1189: Belvoir surrenders to Saladin's troops.
June 1189: Saladin's troops capture Montreal. Only Tyre and Belfort remain under Frankish rule in the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
January 1195: Personal union of the Kingdom of Jerusalem with the Holy Roman Empire.
September 1197: Al-Adil captures Jaffa.
November 1197: German and Frank troops seized Sidon and Beirut.
June 1198: A new truce with Ayyubid Al-Adil, allowed the Kingdom of Jerusalem to retain Jaffa.
January 1226: End of the personal union of the Holy Roman Empire with the Kingdom of Jerusalem: 1225-1228.
July 1266: Baibars captures Safed, Toron and Chastel Neuf and takes control of whole Galilee.
January 1267: Ramla conquered by Mamluk Sultanate of Egypt.
June 1271: Baibars captures the Teutonic Knights' fortress at Montfort.
Disestablishment
September 1302: Fall of Ruad: the Crusaders surrendered on September 26, 1302, following a promise of safe conduct.
Selected Sources
Shephard, W. R. (1923): Historical Atlas, New York, Henry Holt and Company, p. 68
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.115

 kingdom of jerusalem
kingdom of jerusalem




























