If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the countries established by the Gepids during Antiquity and the Middle Ages.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
Kingdom of the Gepids (First Kingdom)
Kingdom of the Gepids (Second Kingdom)
Establishment
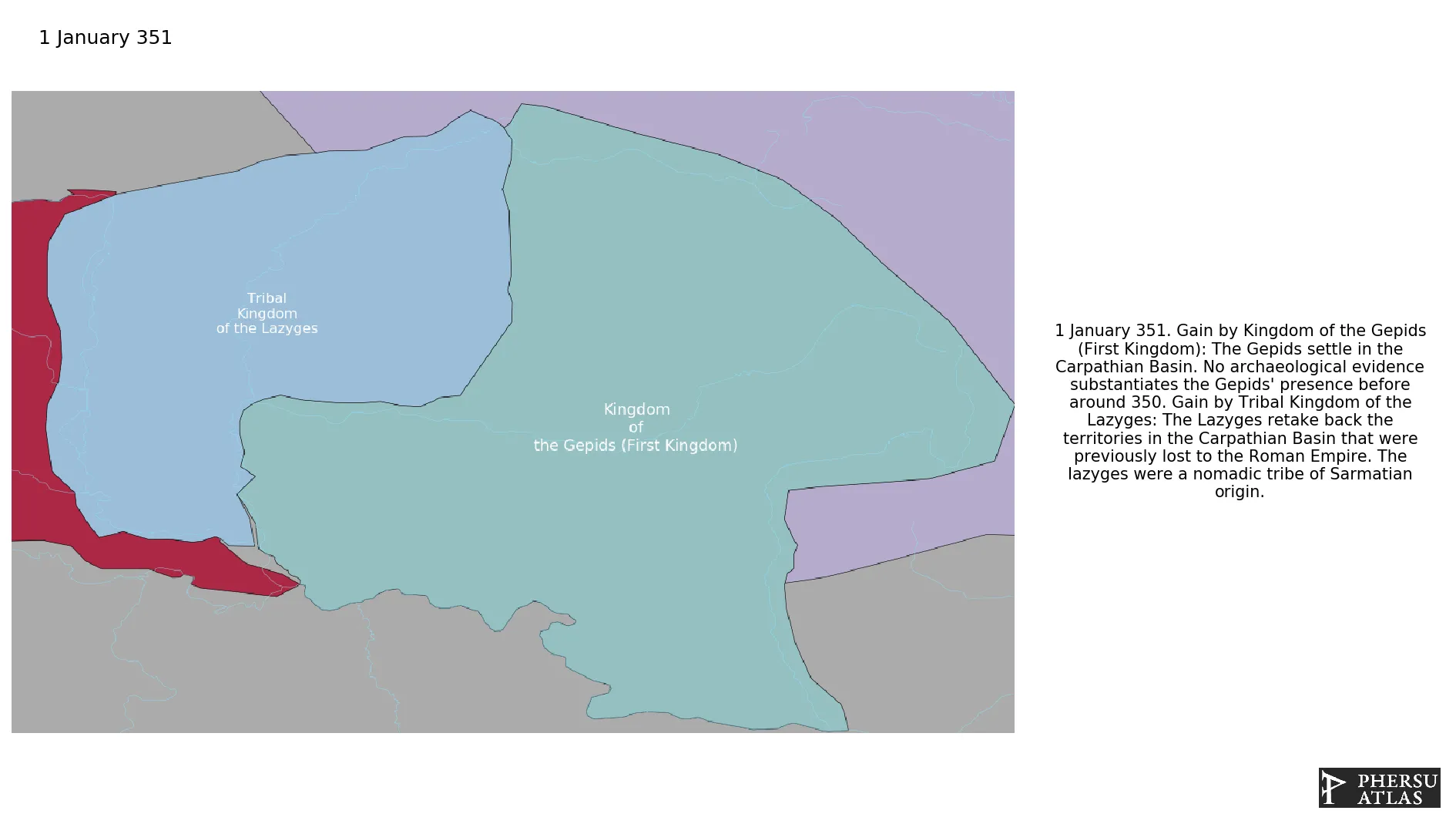
January 351: The Gepids settle in the Carpathian Basin. No archaeological evidence substantiates the Gepids' presence before around 350.
January 351: The Lazyges retake back the territories in the Carpathian Basin that were previously lost to the Roman Empire. The Iazyges were a nomadic tribe of Sarmatian origin.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Gepids invaded Dacia and created their own kingdom in the area.
Were a series of conflicts between the Roman Empire and the Goths.
2.1.Gothic War (367-369)
Was a military campaign of Roman Emperor Valens against the Visigoths under Athanaric.
June 367: Valens was the Roman Emperor at the time, while Athanaric was the king of the Visigoths. The Visigoths were a Germanic tribe that had settled north of the Danube. Valens' attack on Athanaric's Visigoths in 367 marked a significant event in the Roman Empire's efforts to control the territory north of the Danube.
July 367: In the spring of 367, Roman Emperor Valens crossed the Danube River and launched an attack on the Visigoths led by their king Athanaric. This event took place in the territory north of the Danube, which later came under the control of the Kingdom of the Gepids.
January 370: In 369, Valens crossed again, from Noviodunum, and by devastating the country forced Athanaric to attack him.
February 370: Valente sent the general Arinteo to restore Pope to the Armenian throne already the summer following the first action against the Goths (in 369?), also at the request of the Armenian nobility itself.
Were a series of conflicts that saw the Huns, an invading tribe probably from Central Asia, fighting against the Romans as well as the Germanic tribes of Europe.
3.1.Hunnic Invasion of Europe
The Huns invaded Europe starting with the Ukrainian Steppe.
3.1.1.The Kingdom of the Goths is absorbed by the Huns
The Huns invaded and annexed the Kingdom of the Goths.
January 377: The Huns expelled the Goth from eastern Europe and expanded between the Danube and the Black Sea.
3.2.Germanic-Hunnic Wars
Was the conflict between the Germanic Tribes of central and eastern Europe against the Huns.
3.2.1.Battle of Nedao
The Battle of Nedao was a battle fought in Pannonia in 454 CE between the Huns and their former Germanic vassals. It was decisive Germanic victory.
January 455: After the Battle of Nedao, the Hunnic Empire disintegrated and the Gepids became the dominant power in the eastern regions of the Carpathian Basin. According to Jordanes, the Gepids "by their own might won for themselves the territory of the Huns and ruled as victors over the extent of all Dacia, demanding of the Roman Empire nothing more than peace and an annual gift" after their victory.
After the Ostrogoths left Pannonia in 473, the Gepids captured Sirmium (now Sremska Mitrovica in Serbia), a strategically important town on the road between Italy and Constantinople.
January 474: After the Ostrogoths left Pannonia in 473, the Gepids captured Sirmium, a strategically important town on the road between Italy and Constantinople.
The Gepids invaded Sirmium, which was part of the Kingdom of the Ostrogoths at the time.
January 505: Theoderic the Great dispatched one comes Pitzia to launch a campaign against the Gepids who either tried to capture Sirmium or wanted to get rid of Theoderic's suzerainty in 504. Comes Pitzia expelled the Gepid troops from Sirmium without much resistance.
January 531: After the death of Theoderic the Great in 526, the Gepids, led by their king Vitiges, invaded Sirmium in 528 or 530. However, they were ultimately defeated by the forces of the Kingdom of the Gepids (Second Kingdom).
February 531: After the death of Theoderic the Great in 526, the Gepids invaded Sirmium in 528 or 530. However, Vitiges, who was the king of the Ostrogoths at the time, successfully defeated the Gepids in Sirmium in 531.
The Gepids reached the zenith of their power after 537, settling in the rich area around Singidunum (today's Belgrade). For a short time, the city of Sirmium (present-day Sremska Mitrovica) was the center of the Gepid State.
January 538: The Gepids reached the zenith of their power after 537, settling in the rich area around Singidunum. For a short time, the city of Sirmium was the center of the Gepid State and the king Cunimund minted golden coins in it.
Was a war between the Kingdom of the Gepids on one side and the Lombards and the Avar Khaganate on the other side.
January 568: The Gepids were destroyed by the Avars and Lombards in 567. The Avars subsequently occupied "Gepidia", forming the Avar Khaganate.
7.1.Collapse of the Gepid Kingdom
The Gepids were defeated by the Avars and Lombards in 567 and their kingdom destroyed.
January 568: Sirmium and the Dalmatian coast reverted to the Byzantines.
Disestablishment
January 568: Sirmium and the Dalmatian coast reverted to the Byzantines.
January 568: The Gepids were destroyed by the Avars and Lombards in 567. The Avars subsequently occupied "Gepidia", forming the Avar Khaganate.
 gepids
gepids