If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a confederation of tribal communities and cities in ancient Greece centered in Aetolia, in central Greece.
Establishment
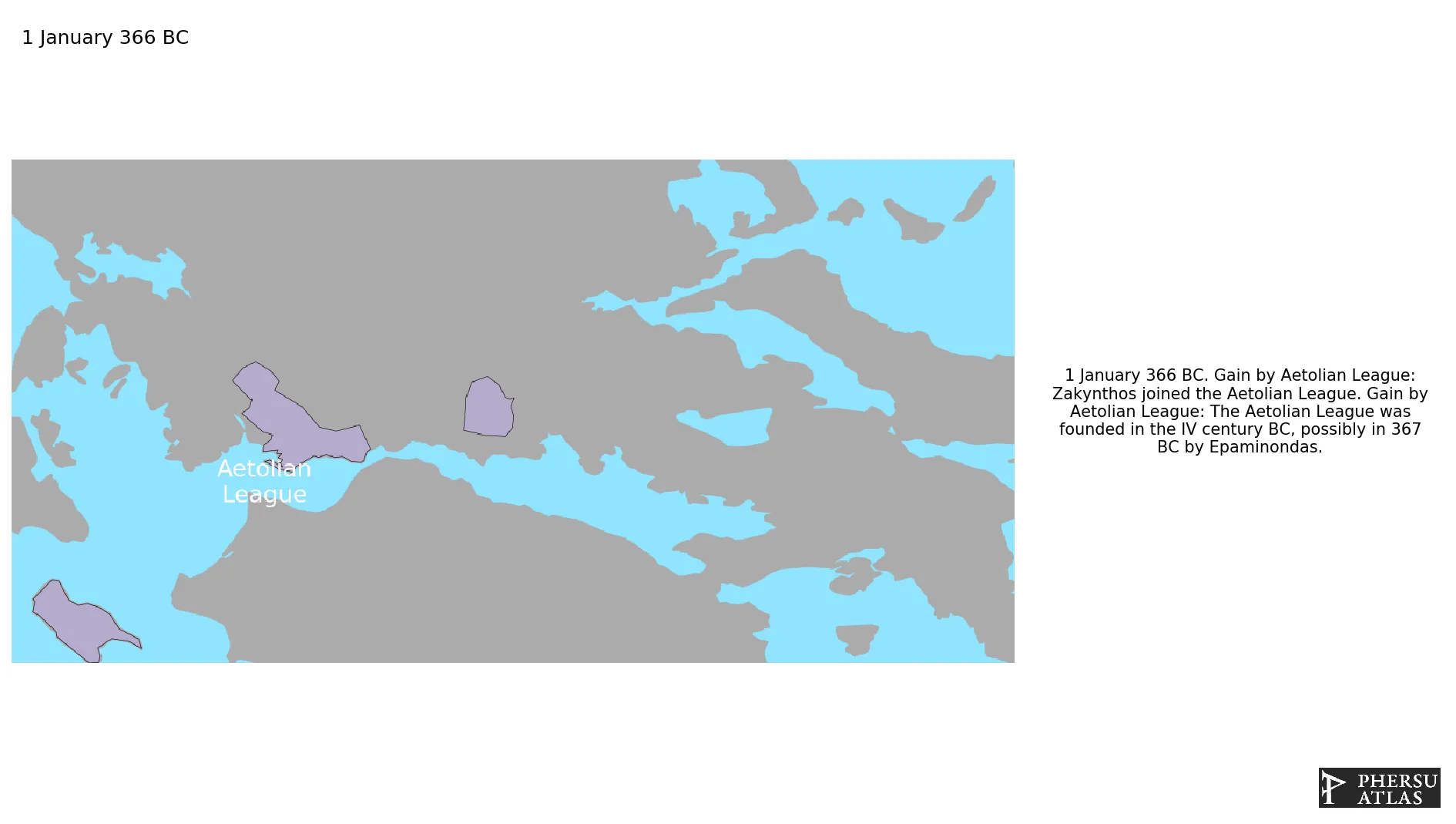
January 366 BC: The Aetolian League was founded in the IV century BC, possibly in 367 BC by Epaminondas.
January 366 BC: Zakynthos joined the Aetolian League.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Creation of the Aetolian League (a league of ancient Greece).
Were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule his empire following his death.
2.1.Third War of the Diadochi
Was a war between Macedonian Generals that saw Ptolemy, Lysimachus and Cassander fight against Antigonus.
September 312 BC: Ptolemaic march in Chalkis, Oropos, Attica, Boeotia and Locris.
October 312 BC: Ptolemy (the nephew of general of Antigonus I Monophthalmus) marches through Chalkis and Oropos, as well as Attica, Boeotia and Locris freeing these regions from the occupation of the Ptolemaic Kingdom.
2.2.Consolidation of the borders after the Third War of the Diadochi
Were a series of events and military operations after the Third war of the Diadochi that led to the consolidation of the borders between the successor states of the Macedonian Empire.
January 299 BC: Philip V of Macedon seized Zakynthos in the early 3rd century BC.
2.3.Fourth War of the Diadochi
Was a war between Macedonian generals that saw Ptolemy, Lysimachus and Cassander fight against Antigonus and Demetrios.
April 304 BC: Military offensive of Cassander in Aetolia and in Athens.
September 304 BC: Demetrios (Antigonid Dynasty) liberates Chalkidiki, Boeotia, and Aetolia.
Were a seris of conflicts between the Roman Republic and Antigonid Macedonia over control of Greece and the eastern Mediterranean Basin. .
3.1.First Macedonian War
Was a war fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218-201 BC) against Carthage. There were no decisive engagements, and the war ended in a stalemate.
January 204 BC: In the First Macedonian War (214-205 BC), Oiniadai was lost again.
3.1.1.Campaign of Laevinus in Greece
Was a Roman military campaign in Greece led by Marcus Valerius Laevinus during the first Macedonian War.
January 210 BC: The region was conquered by the Aetolians.
January 209 BC: Corinth was assaulted by the Romans via sea and by the Aetolians via land. The assault from the sea was better managed as it was carried out by the Roman fleet, armed with various types of siege engines and war machines. In a few days, the city surrendered and handed itself over to the Aetolians. According to the agreement, the spoils of war went to the Romans.
January 209 BC: Conquests of Attalus of Pergamon.
January 209 BC: The Macedonian king probably took Phalara.
January 209 BC: The Romans conquered three cities of Acarania: Eniade, Nasos and Acarnanus, which he returned to the Aetolians.
January 207 BC: The Macedonians took Thronium, followed by Tithronium and Drymaea north of the Cephissus river, at that point controlling all of Locris.
January 204 BC: After another season of fighting, in 206 BC, the members of the Aetolian League surrendered and, without the consent of Rome, signed a separate peace on the terms imposed on them by Philip of Macedon. With no more allies in all of Greece, but having nonetheless achieved their objective of preventing Philip from helping Hannibal, the Romans were now willing to sign peace. A treaty was signed at Phoenix in 205 BC, the so-called Peace of Phoenix, thus ending the First Macedonian War.
Was a military conflict between two coalitions led by the Roman Republic and the Seleucid Empire. The fighting ended with a clear Roman victory. In the Treaty of Apamea, the Seleucids were forced to give up Asia Minor, which fell to Roman allies.
January 191 BC: Seleucid Invasion of Greece up to the Thermopylae.
4.1.Treaty of Apamea
Was a peace treaty conducted in 188 BC between the Roman Republic and Antiochus III, ruler of the Seleucid Empire. It ended the Roman-Seleucid War.
January 187 BC: The defeat of Antiochus in 189 BC robbed the league of its principal foreign ally and made it impossible to stand alone in continued opposition to Rome. The league was forced to sign a peace treaty with Rome that made it a subject ally of the republic.
January 187 BC: The Romans sent an army to Greece which defeated Antiochus' army at Thermopylae. This defeat proved crushing, and the Seleucids were forced to retreat from Greece.
January 322 BC: In the time of Alexander the Great, the Aetolians, who had extended their dominions on the west bank of the Achelous, succeeded in obtaining possession of Oeniadae, and expelled its inhabitants.
January 322 BC: After the time of Alexander the Great it fell into the hands of the Aetolians, together with the other towns in the west of Acarnania.
January 322 BC: Matropolis fell into the hands of the Aetolians.
January 299 BC: Myania entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Naupaktos entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Tolophon entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Oianthea entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Amphissa entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Tritea entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Hypnia entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Chaleion entered the Aetolian League.
January 299 BC: Alpa entered the Aetolian League.
January 272 BC: c. 273 BC the Aetolian League expanded to Hypata.
January 269 BC: After the death of Pyrrhus, King of Epirus, in around 270 BC, the Acarnanians and Aetolians reached a peace agreement. They established the Acheloos River as their shared border.
January 251 BC: Stratos fell to the Aetolians.
January 250 BC: In the 3rd century BC the Doric Tetrapolis joined the Aetolian League.
January 249 BC: Thebai (Achaia Phthiotis) became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Halos became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Kypaira became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Larisa (Achaia Phthiotis) became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Melitaia became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Phylake became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Thaumakoi became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Proerna became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Ekkarra became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Pyrasos became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 249 BC: Peuma became a member of the Aetolian League in the 3rd century BC.
January 244 BC: Boeotia was enrolled for a short time in the Aetolian League (245-244 BC).
January 243 BC: Boeotia leaves the Aetolian League.
January 234 BC: The Oitaians, the Ainians, and the Malians became members of Aetolian League in 235 BC.
January 216 BC: During the Social War (220-217 BC), the Acarnanians, led by their general Dorimachos, successfully regained control of Phoitia and Oiniadai from the Aetolian League.
January 204 BC: Ambracia joined the Aetolian League.
January 195 BC: Daulis was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Amphikaia was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Abai was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Charadra was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Delphoi was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Drymos was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Elateia (Phokis) was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Erochos was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Hyampolis was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Ledon was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Parapotamioi was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Pedieis (Phokis) was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Phanoteus was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Phlygonion was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Stiris was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Teithronion was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Trachis (Phokis) was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Boulis was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Medeon was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Lilaia was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Troneia was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Ambryssos was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Antikyra was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
January 195 BC: Neon/Tithorea was annexed by the Aetolian League in 196 BC.
Disestablishment
January 187 BC: The defeat of Antiochus in 189 BC robbed the league of its principal foreign ally and made it impossible to stand alone in continued opposition to Rome. The league was forced to sign a peace treaty with Rome that made it a subject ally of the republic.
January 187 BC: The Romans sent an army to Greece which defeated Antiochus' army at Thermopylae. This defeat proved crushing, and the Seleucids were forced to retreat from Greece.
Selected Sources
Piganiol, A. (1989): Le conquiste dei romani, Milan (Italy), p. 236
Piganiol, A. (1989): Le conquiste dei romani, Milan (Italy), p. 237
Polybius: The Histories, IX, 39
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita,XXVI, 24.15-16
Titus Livius: Ab Urbe Condita, XXVI, 26.1-4
 Aetolian League
Aetolian League