If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Polity that includes all territories militarly occupied by Bulgaria that are not part of a specific military territory.
Establishment
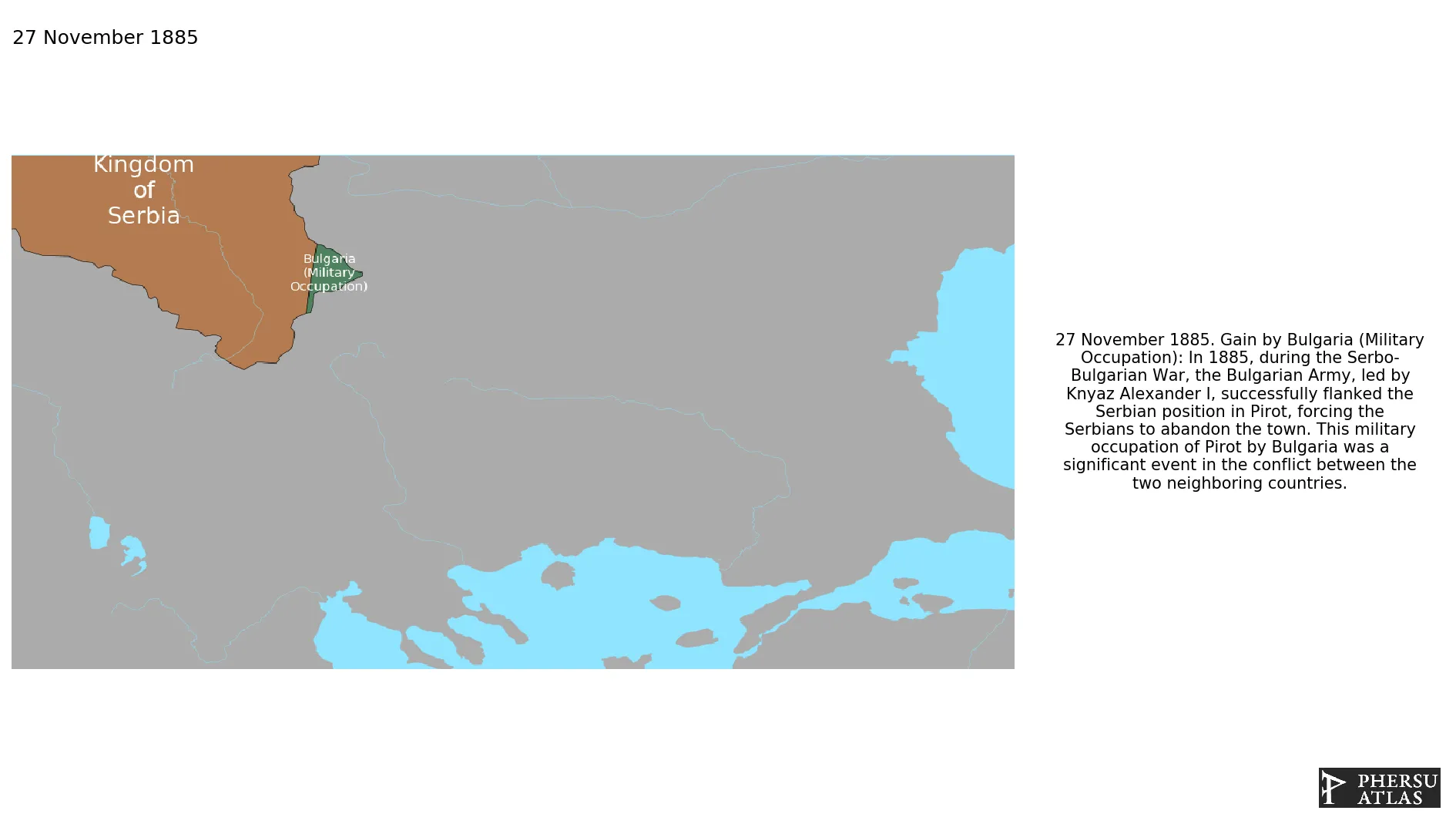
November 1885: In 1885, during the Serbo-Bulgarian War, the Bulgarian Army, led by Knyaz Alexander I, successfully flanked the Serbian position in Pirot, forcing the Serbians to abandon the town. This military occupation of Pirot by Bulgaria was a significant event in the conflict between the two neighboring countries.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a war between the Kingdom of Serbia and the Principality of Bulgaria.
March 1886: According to the terms of a peace treaty signed in Bucharest, no changes were made to the Bulgarian-Serbian border (status quo ante bellum).
Were two wars fought in southeastern Europe in 1912-1913 during which the states of the Balkan League (Bulgaria, Greece, Montenegro and Serbia) first conquered Macedonia and much of Thrace from the Ottomans and then clashed with each other over the division of the conquered lands.
2.1.First Balkan War
Was a war fought in southeastern Europe where the states of the Balkan League (Kingdom of Bulgaria, Kingdom of Greece, Kingdom of Montenegro and Kingdom of Serbia) conquered Macedonia and much of Thrace (virtually all remaining territories of the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans) from the Ottomans.
.
2.1.1.Bulgarian offensive (First Balkan War)
Was the Bulgarian military invasion of Ottoman territories during the First Balkan War.
October 1912: On the night of October 18, 1912, the Bulgarian vanguards began to penetrate enemy territory, easily pushing back the few Ottoman forces stationed to guard the border.
October 1912: The important center of Kardzhali was occupied by Bulgarian forces.
October 1912: The Bulgarians arrived in front of the main body of the Ottoman Eastern Army, deployed between the cities of Adrianople and Kirk Kilisse.
October 1912: On October 24, the Bulgarians took Kirk Kilisse.
October 1912: Between 26 and 27 October the Bulgarian forces secured the town of Smoljan and the Mesta valley.
October 1912: The Bulgarians did not immediately press the Ottomans, who were thus able to entrench themselves on a 40 km long second defensive line between the towns of Lüleburgaz, Karaağaç and Bunarhisar, 150 km west of Istanbul: on 29 October the Bulgarian First and Third Armies attacked the Ottoman line, but met stiff resistance.
November 1912: Bulgarian victory at the battle of Lüleburgaz.
November 1912: On November 5, Bulgarian forces forced the Ottoman positions on the Rhodope mountain chain and occupied the important railway center of Drama.
November 1912: Adrianople (modern-day Edirne) was completely surrounded by the Bulgarians.
November 1912: After massing the First and Third Armies in front of Çatalca, the Bulgarian forces launched their offensive on 17 November.
November 1912: Bulgarian forces occupied İskeçe on November 26.
November 1912: Bulgarian forces reached the Aegean coast at Dedeağaç (now Alexandroupoli).
November 1912: Bulgarian troops from Lüleburgaz reached the coast of the Marmara Sea near Şarköy, isolating the Ottoman forces barricaded in the Gallipoli peninsula, which were however able to hold their position.
November 1912: Ottoman forces were forced to surrender at Feres.
March 1913: The Ottoman commander Şükrü Pasha surrendered Adrianople (modern-day Edirne) to the Bulgarians, ending a siege that lasted 155 days.
2.1.2.Macedonian Front (Balkan War)
Was the Macedonian front of the First Balkan War.
November 1912: Encountering negligible resistance, the Bulgarians took Petriç, Demirhisar and Serez.
2.2.Second Balkan War
Was a war fought by Bulgary against a coalition of Balkan states. During the First Balkan War the Balkan League had conquered most of the Ottoman Balkan territories. Bulgaria was dissatisfied by the territorial partition and invaded its former allies.
2.2.1.Bulgarian Offensive in Greece
Was a Bulgarian military offensive in Greece during the Second Balkan War.
June 1913: Bulgarian troops moved up to positions between Kilkis and the Struma River.
June 1913: The Bulgarian forces were forced to withdraw from their positions north of Thessaloniki (except the isolated battalion stationed in the city itself which was quickly overrun) to defensive positions between Kilkis and Struma river.
June 1913: On the Bulgarian right, Greek Evzones (light infantry) captured Gevgelija and the heights of Matsikovo.
July 1913: The Greeks captured Dojran on 5 July.
July 1913: The Greek forces with the support of their navy landed in Kavala.
July 1913: On 19 July the Greeks captured Nevrokop.
July 1913: Greek entered Alexandroupoli, cutting off the Bulgarians completely from the Aegean sea.
2.2.2.Ottoman intervention (Second Balkan War)
Was an Ottoman military offensive against Bulgaria during the Second Balkan War.
July 1913: Ottoman troops garrisoning Çatalca and Gelibolu reached the Enos-Midia line.
July 1913: Edirne is occupied by the Ottomans on 23 July.
August 1913: The Ottoman armies crossed into Bulgarian territory. A cavalry unit advanced on Yambol.
2.2.3.Serb Offensive (Second Balkan War)
Was a Serb military offensive against Bulgaria during the Second Balkan War.
July 1913: Bulgarians stopped the Serbian offensive in Macedonia at Kalimanci.
2.2.4.Greek offensive (Second Balkan War)
Was a Greek military offensive against Bulgaria during the Second Balkan War.
July 1913: After bitter fighting the Greek side managed to break through the Kresna pass and captured Simitli.
July 1913: The Greek forces continued their march inland into western Thrace and they entered Xanthi.
July 1913: Greek conquest of Komotini.
2.2.5.Treaty of Bucarest
Was the treaty that ended the Second Balkan War.
August 1913: The Sofia government obtained the Blagoevgrad district and a part of Western Thrace.
August 1913: The eastern frontier of Serbia was drawn from the top of Patarika and followed the watershed between the Vardar and Struma rivers to the Greek-Bulgarian border, except for the Strumica valley which remained in Bulgaria.
August 1913: The European borders of Turkey were set with the Treaty of Bucarest that ended the Second Balkan War.
August 1913: The border between Greece and Bulgaria was drawn from the Belasica crest at the mouth of the Mesta river on the Aegean Sea, including large parts of Epirus, Macedonia and Thessaloniki.
August 1913: Bulgarians stopped the Serbian offensive in Macedonia at Kalimanci.
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
3.1.World War I Balkan Theatre
Was the theatre of war in the Balkan Peninsula during World War I.
3.1.1.Albania during World War I
Albanian theatre of World War I.
3.1.1.1.Collapse of Albania
Invasion of Albania by the central powers during World War I.
January 1916: Bulgarian units entered Albania from the north-east across the Drin river taking Elbasan on 29 January.
May 1916: An agreement between Vienna and Sofia in April 1916 finally resulted in the cession of the districts of Prizren and Pristina in Kosovo to Bulgaria in exchange for the Bulgarian evacuation of Elbasan in northeastern Albania, where the Austro-Hungarians established a provisional government.
August 1916: As early as 18 August 1916, a Bulgarian column from Ohrid had occupied the city of Korçë in southeastern Albania, without opposition from the local Greek garrison.
November 1916: French general Sarrail detached a French cavalry column which occupied Korçë the following November 29 with little resistance.
3.1.2.Serbia during World War I
Serbian theatre of World War I.
3.1.2.1.Invasion of Serbia
Invasion of Serbia by the Central Powers during World War I.
October 1915: The Bulgarian Army attacked Serbia from the north of Bulgaria towards Niš and from the south towards Skopje.
November 1915: The Morava Offensive Operation was undertaken by the Bulgarian First Army between 14 October 1915 and 9 November 1915. As a result, the Serbian forces were compelled to retreat towards Kosovo and Metohija.
November 1915: The Ovche Pole Offensive Operation was an operation of the Bulgarian Army that occurred between 14 October 1915 and 15 November 1915. It secured the south-eastern front of Serbia to Bulgaria.
November 1915: The Serbian government and supreme command made the decision to retreat through Montenegro and Albania where they hoped to reach the Adriatic coast and be rescued by Allied ships.
January 1916: By January 1916, the Serbian Army had been defeated by an Austrian-Hungarian, German and Bulgarian invasion.
3.1.3.Liberation of the Balkan States
Was the liberation of the Balkan states from the Central Powers during World War I.
September 1918: Serbian and French forces liberated Skopje.
October 1918: Vranje was liberated on 5 October.
October 1918: The 2nd Serbian Army under Stepa Stepanovic, with French forces, advanced northwest towards Kosovo. Pristina was liberated by the 11th French Colonial Division on 10 October.
October 1918: Niš conquered by Kingdom of Serbia.
November 1918: The Serbian army reached the border with Bosnia-Hercegovina at Dobor Pole.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
4.1.World War II (Balkan Theatre)
Was the theatre of conflict of World War II that took place in the Balkans.
4.1.1.Axis Occupation of Greece
After the German invasion of Greece, the country was partitioned among the Axis powers. The territorial division changed during the war, and after the surrender of Italy to the Allies the Italian zone was occupied by Germany.
August 1943: Part of the Bulgarian occupation zone in Greece fell under German control from 1943.
4.1.1.1.Greece divided in Occupation zones by Axis powers
Division in occupation zones of Greece by the Axis.
June 1941: East Macedonia and Thrace came under Bulgarian occupation and were annexed to Bulgaria.
4.1.2.Soviet invasion of Bulgaria
Was the Soviet invasion of Bulgaria during World War II.
September 1944: The Soviets established a new communist government in Bulgaria, with Kimon Georgiev as prime minister. The Red Army remained in occupation of Bulgaria until 1947.
4.1.3.German Withdrawal from Greece (World War II)
The evacuation of Greece by German troops during World War II.
June 1945: Isolated Axis garrisons remained in Crete, the Dodecanese and various other Aegean islands until the end of the war in May 1945.
4.2.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
4.2.1.The Surrender of German forces
Surrender of German forces at the end of World War II.
May 1945: At the end of World War II Greece freed its islands from German forces.
Disestablishment
May 1945: At the end of World War II Greece freed its islands from German forces.
June 1945: Isolated Axis garrisons remained in Crete, the Dodecanese and various other Aegean islands until the end of the war in May 1945.
Selected Sources
The Times (1917): History of the War - vol. XII, London (UK), p. 35.
.png.webp)
 Bulgaria (Military Occupation)
Bulgaria (Military Occupation)