Data
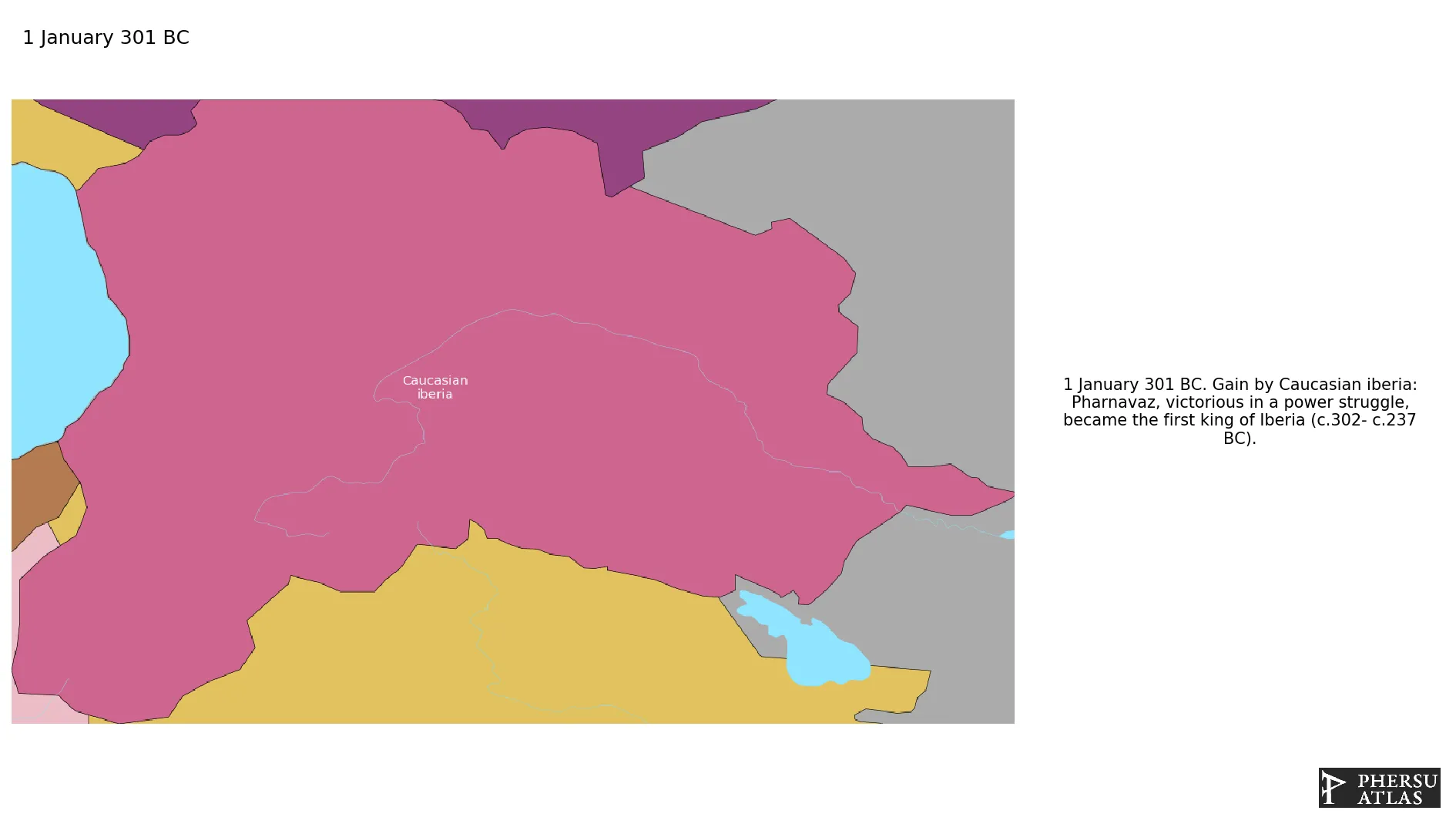
Name: Caucasian iberia
Type: Polity
Start: 301 BC
End: 260 AD
Nation: caucasian iberia
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Caucasian iberia
Caucasian iberia
This article is about the specific polity Caucasian iberia and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the Georgian kingdom of Kartli which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages was a significant monarchy in the Caucasus, either as an independent state or as a dependent state of larger empires, notably the Sassanid and Roman empires.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Mithridatic Wars
Were three conflicts fought by Rome against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 BC and 63 BC. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus during the course of the wars.
Was the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. The conflict ended in defeat for Mithridates, ending the Pontic Kingdom, ending the Seleucid Empire (by then a rump state), and also resulting in the Kingdom of Armenia becoming an allied client state of Rome.
1.1.1.Caucasian campaign of Pompey
Was a succesful Roman military campaign led by Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in the Caucasus during the Third Mithridatic War.
2. Roman-Persian Wars
Were a series of Wars between Rome (first the Roman Republic then the Roman Empire and finally the Eastern Roman Empire) and Persia (the Parthian Empire, and then its successor, the Sasanian Empire). The wars were ended by the early Muslim conquests, which led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire and huge territorial losses for the Byzantine Empire.
2.1.Military Campaigns of Shapur I in Syria and Mesopotamia
Was a military campaign by Sassanid King Shapur I against the Roman Empire.