This article is about the specific polity Commonwealth of the Philippines and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
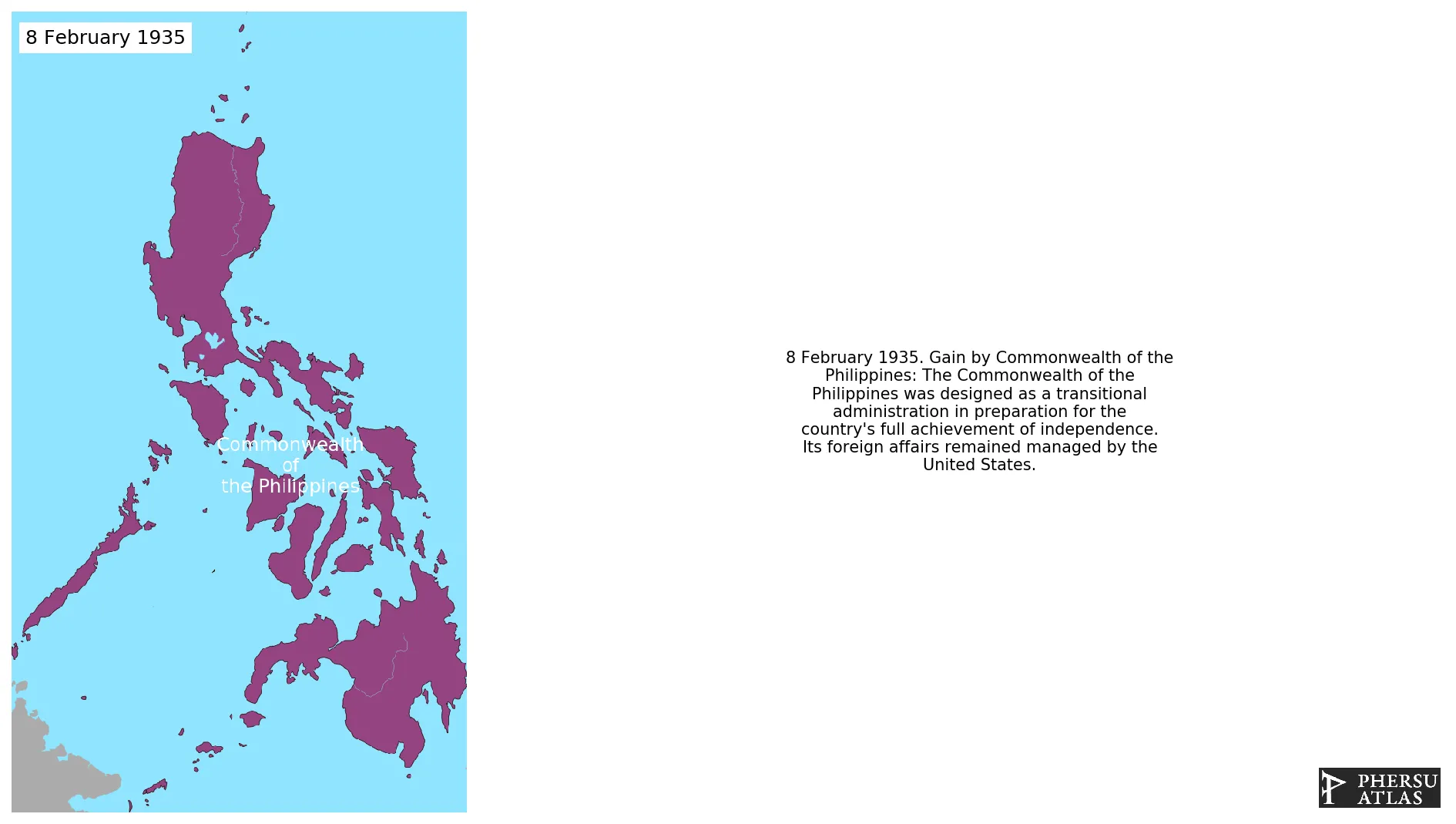
Was the administrative body that governed the Philippines from 1935 to 1946, aside from a period of exile in the Second World War from 1942 to 1945 when Japan occupied the country. The Commonwealth was designed as a transitional administration in preparation for the country's full achievement of independence. Its foreign affairs remained managed by the United States.
Establishment
February 1935: The Commonwealth of the Philippines was designed as a transitional administration in preparation for the country's full achievement of independence. Its foreign affairs remained managed by the United States.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
1.1.World War II (Asia & Pacific)
Was the East Asian, South Asian and Pacific theatre of World War II.
1.1.1.Philippines campaign (1941-1942)
Was the invasion of the Philippines by the Empire of Japan during World War II.
1.1.1.1.Japanese occupation of Luzon and surrounding islands
Were the operations of the Japanese army in Luzon and surrounding islands during the invasion of the Philippines.
December 1941: The Japanese 14th Army began its invasion with a landing on Batan Island (not to be confused with Bataan Peninsula), 190 km off the north coast of Luzon, on 8 December 1941.
December 1941: Japanese Landings at Vigan, Aparri, and Gonzaga.
December 1941: Japanese landings on Camiguin Island.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Olaoag.
December 1941: The Japanese landed 2,500 men of the 16th Division at Legazpi.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Uguegarao.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of S. Fernando.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Imugan.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Lingayen.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Baguio.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Mauban.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of St. Jose.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Cabanatuan.
December 1941: Japanese conquest of Tarlag.
January 1942: Japanese conquest of Batangas.
January 1942: Japanese conquest of Manila.
January 1942: Japanese conquest of Cavite.
April 1942: The American surrended at Bataan to the Japanese.
May 1942: Fall of Corregidor to Japanese forces (6 May 1942).
1.1.1.2.Japanese occupation of Mindanao and surrounding islands
Were the operations of the Japanese army in Mindanao and surrounding islands during the invasion of the Philippines.
December 1941: In the night between the 19th and 20th the island of Mindanao was also occupied, after resistance by the garrison.
December 1941: The Japanese landed at Jolo, in the Sulu Archipelago, finding light resistence.
1.1.2.Philippines campaign
Was the American, Mexican, Australian and Filipino campaign to defeat and expel the Imperial Japanese forces occupying the Philippines during World War II.
1.1.2.1.Battle of Leyte
Was the amphibious invasion of the island of Leyte in the Philippines, occupied by Japan at the time, by American forces.
October 1944: The U.S. Sixth Army, supported by naval and air bombardment, landed on the favorable eastern shore of Leyte.
December 1944: U.S. liberation of Irpil.
December 1944: American avances during the Battle of Ormoc Bay.
December 1944: U.S. liberation of Ormoc.
December 1944: U.S. liberation of Valencia.
December 1944: U.S. liberation of Paolompon.
December 1944: U.S. conquest of the barrio of Tibur.
December 1944: U.S. liberation of San isidoro.
December 1944: U.S. liberation of Tabango.
December 1944: U.S. liberation of Villaba.
December 1944: The Japanese evacuated Leyte island.
1.1.2.2.Battle of Mindoro
Was a battle in World War II between forces of the United States and Japan, in Mindoro Island in the central Philippines.
December 1944: American forces invade Mindoro.
1.1.2.3.Battle of Luzon
Was a land battle of the Pacific Theater of Operations of World War II by the Allied forces of the U.S., its colony the Philippines, and allies against forces of the Empire of Japan.
January 1945: American landings at the Lingayen Gulf on 9 January .
January 1945: American advance up to Clark Field and Fort Stotsenburg by January 31th.
February 1945: American forces conclude operations on the Bataan Peninsula, which is fully occupied.
March 1945: American forces conclude operations in Manila, clearing the area.
June 1945: The Bessang Pass fall at the hands of the United States Army Forces in the Philippines - Northern Luzon (USAFP-NL) on June 14, 1945.
1.1.2.4.Battle of the Mindanao
Was a battle fought by the Americans and allied Filipino guerrillas against the Japanese forces on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines. It was part of the campaign to liberate the Philippines during World War II.
March 1945: The American 41st Division troops quickly captured Zamboanga.
March 1945: After an heavy fight, the center of the Japanese line in the Zamboanga peninsula broke.
April 1945: American amphibious operation to secure Malabang-Parang-Cotabato area of Mindanao.
April 1945: By 22 April, the Allies took the position in Jolo after hard fighting and the rest of the Japanese troops fled and held out in the west for another two months.
April 1945: Upon reaching Digos, the Americans quickly overwhelmed the defending Japanese.
May 1945: On 3 May, the U.S. 31st Division reached Kibawe.
May 1945: U.S. Eight Army clears Malaybalay-Kalasungay region.
June 1945: Battle of Davao.
July 1945: Allied units seized Sarangani and Balut islands.
1.1.2.5.Battle of the Visayas
Was a battle fought by the Americans and allied Filipino guerrillas against the Japanese forces in the
Visayas region in the Philippines. It was part of the campaign to liberate the Philippines during World War II.
March 1945: Within two weeks of aerial bombardment on Japanese positions, the 40th Infantry Division, spearheaded by the 185th Infantry Regiment landed unopposed at Tigbauan district, in southern Panay.
March 1945: Guimaras and Inampulagan islands, between Panay and Negros, were freed on the same day Iloilo fell, 20 March and the next day, respectively with no opposition.
March 1945: On Talisay Beach, 6.5 km west of Cebu City, the 182nd Infantry and 132nd Infantry landed on 26 March 1945.
March 1945: The U.S. Eighth Army seizes Cebu City.
March 1945: U.S. Eighth Army captured Bacolod City.
April 1945: The coastal plain of Negros was in Allied hands.
April 1945: Japanese retreat from southern Cebu.
May 1945: Major combat operations continued in Dumuguate until 28 May 1945, when the Japanese positions fell and Filipino guerrillas assumed control.
June 1945: By 4 June, the Japanese began a general withdrawal, retreating further into the unexplored mountains of Negros.
August 1945: Negros Island was liberated from Japanese occupation.
1.2.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
1.2.1.The Surrender of Japanese forces
Surrender of Japanese forces at the end of World War II.
September 1945: The Japanese commander in the Philippines, Gen. Yamashita, surrendered to Gen. Wainwright at Baguio.
July 1946: The independent Republic of the Philippines is proclaimed.
Disestablishment
July 1946: The independent Republic of the Philippines is proclaimed.
Selected Sources
Cannon, M. H. (1993): Leyte: The return to the Philippines, Washington D.C. (USA), p. 278
Cannon, M. H. (1993): Leyte: The return to the Philippines, Washington D.C. (USA), p. 329
Cannon, M. H. (1993): Leyte: The return to the Philippines, Washington D.C. (USA), p. 348
Cannon, M. H. (1993): Leyte: The return to the Philippines, Washington D.C. (USA), p. 355
Cannon, M. H. (1993): Leyte: The return to the Philippines, Washington D.C. (USA), p. 356
Flemming, Thomas / Steinhage, Axel / Strunk, Peter (1995): Chronik 1946: Tag für Tag in Wort und Bild, Chronik-Verlag/Bertelsmann Lexikon Verlag,p. 112
U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/books/wwii/MacArthur%20Reports/MacArthur%20V1/Images/p_004.jpg
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 388
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 4
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 408
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 434
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 443
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 455
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 464
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 488
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 499
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 519
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.32
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.347
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.354
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.370
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.423
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.457
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.539
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.7
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.8
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.36-37
.svg.png.webp)
 Commonwealth of the Philippines
Commonwealth of the Philippines