This article is about the specific polity Mughal Empire (Maratha Protectorate) and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
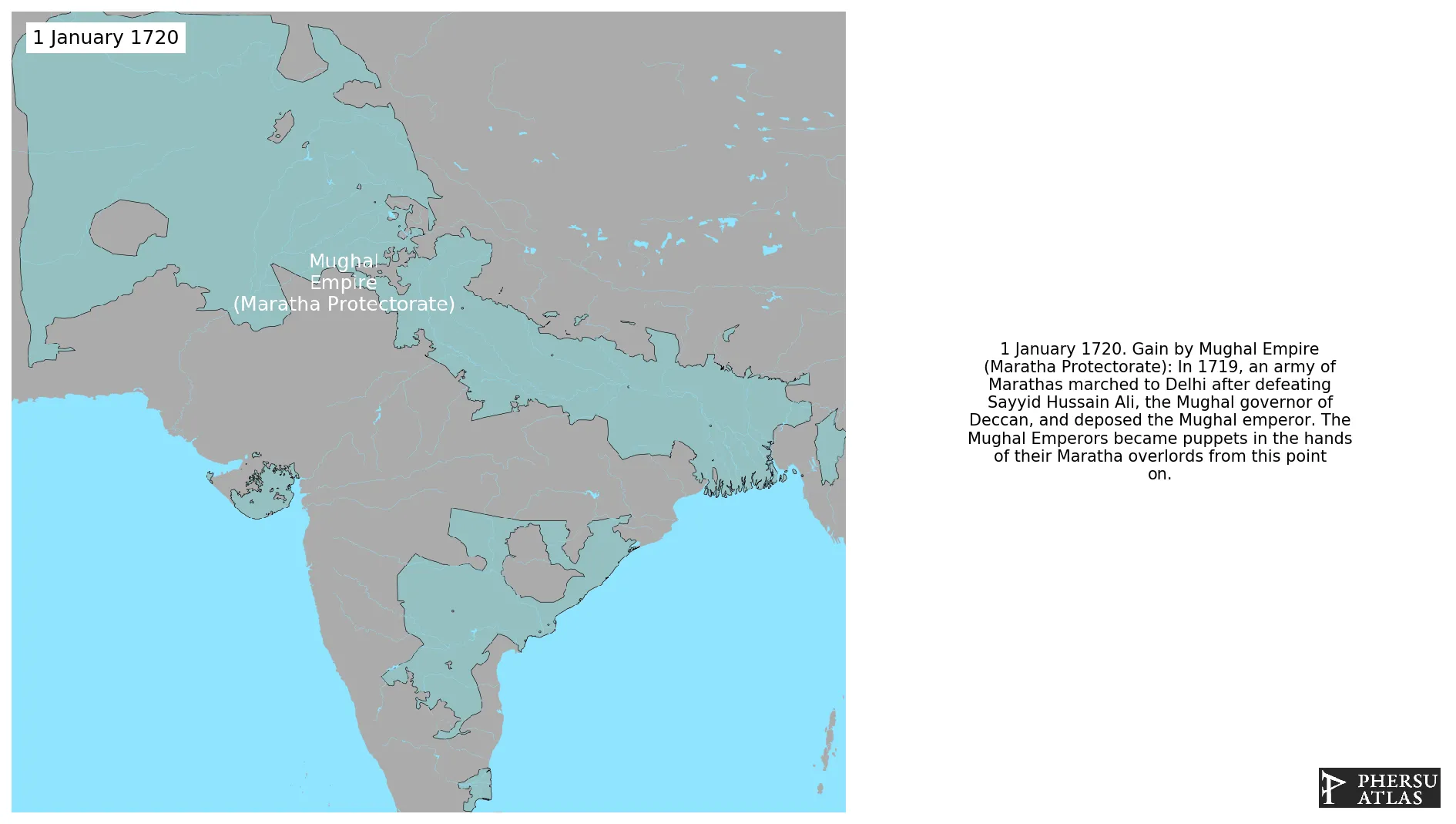
Was an empire that at its heigth controlled most of the Indian Subcontinent and nearby regions. In 1719, an army of Marathas marched to Delhi and deposed the Mughal emperor. The Mughal Emperors became puppets in the hands of their Maratha overlords from this point on.
Establishment
January 1720: In 1719, an army of Marathas marched to Delhi after defeating Sayyid Hussain Ali, the Mughal governor of Deccan, and deposed the Mughal emperor. The Mughal Emperors became puppets in the hands of their Maratha overlords from this point on.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Expansion during the rule of Shahu I in the Maratha Empire.
January 1723: Establishment of the Danish outpost of Eddowa.
January 1729: Yanaon (Yanam) was a French colony in India. It was abandoned from 1728 to 1731 during a period of conflict between the French and the Mughal Empire.
January 1731: The Dutch abandoned their post in Draksharama in favour of Jaggernaikpoeram.
January 1734: In 1733 the British and Dutch convinced the Mughal general at Hugli to attack Bankipur. He attacked Bankipur and the garrison of only fourteen soldiers escaped and set sail for Europe.
February 1734: After a month it was destroyed by the British and the French.
Expansion during the rule of Nader Shah of the Afsharid Dynasty.
January 1741: In 1740, the Khanate of Bukhara was conquered by Nadir Shah, the Shah of Iran.
2.1.Nader Shah's invasion of the Mughal Empire
Was the invasion of India by the Afsharid ruler Nader Shah.
November 1738: Nader advanced to the river Indus before the end of year.
January 1739: The Afsharids advanced onto the Punjab and captured Lahore.
February 1739: Battle of Karnal.
March 1739: Nader Shah, the ruler of the Afsharid Dynasty, captured Delhi in 1739 after defeating the Mughal Empire. The keys to the capital were surrendered to him as a sign of submission and victory.
May 1739: Persian troops left Delhi in early May 1739.
Expansion during the rule of Prithvi Narayan Shah in the Gorkha Kingdom.
January 1747: Expansion of the Gorkha Kingdom under Prithvi Narayan Shah by 1746.
January 1749: Expansion of the Gorkha Kingdom under Prithvi Narayan Shah by 1748.
Expansion during the rule of Ahmad Shah Durrani in the Durrani Empire.
January 1748: In 1747, Peshawar was taken by Ahmad Shah Durrani, also known as Ahmad Shah Abdali, who was the founder of the Afghan Durrani Empire. Ahmad Shah Durrani was a prominent military leader who established the empire in the region.
January 1748: Kasur, a town in present-day Pakistan, was captured by Ahmad Shah Durrani, the founder of the Durrani Empire.
January 1750: In 1749 the Mughal ruler ceded sovereignty over much of north-west India to the Afghans.
January 1752: In 1751, the Afghan ruler Ahmad Shah Durrani of the Durrani Empire gained control of Kashmir. This marked the beginning of Durrani rule in the region, which lasted until the early 19th century.
January 1761: Shah Durrani, who was the founder of the Durrani Empire, sent an army to conquer the areas north of the Hindu Kush mountains, successfully uniting various tribes under his rule.
January 1762: The Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II (1759-1806) made futile attempts to reverse the Mughal decline but ultimately had to seek the protection of the Emir of Afghanistan, Ahmed Shah Abdali, which led to the Third Battle of Panipat between the Maratha Empire and the Afghans (led by Abdali) in 1761.
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
5.1.Indian Theatre (Seven Years' War)
Was the theatre of war of the Seven Years' War in the Indian Subcontinent.
5.1.1.Capture of Calcutta
The Mughal Empire captured British-held Calcutta during the Seven Years' War.
June 1756: The Siege of Calcutta was a battle between the Bengal Subah and the British East India Company on 20 June 1756. The Nawab of Bengal, Siraj ud-Daulah, aimed to seize Calcutta to punish the Company for the unauthorised construction of fortifications at Fort William.
5.1.2.Third Carnatic War
The outbreak of the Seven Years' War in Europe in 1756 resulted in renewed conflict between French and British forces in India.
January 1761: British occupation of Pondichéry.
Were a series of wars fought by the British East India Company in the Indian Subcontinent that resulted in the British conquest and colonial rule of the region.
6.1.Anglo-Mysore Wars
Were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company, Maratha Empire, Kingdom of Travancore, and the Kingdom of Hyderabad on the other. The fourth war resulted in the dismantlement of Mysore to the benefit of the East India Company, which took control of much of the Indian subcontinent.
6.1.1.Second Anglo-Mysore War
Was a conflict between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company from 1780 to 1784.
January 1780: By 1779, Mysore ruler Haider Ali had captured parts of modern Tamil Nadu and Kerala in the south, extending the Kingdom's area to about 80,000 mi2 .
Expansion during the rule of Rana Bahadur Shah in the Kingdom of Nepal.
January 1787: Based on the border of Nepal in 1782.
January 1721: In 1720, Mahmud Hotak, the ruler of the Hotak Empire, led his Afghan forces across the deserts of Sistan and successfully captured the territory of Kerman. Mahmud Hotak was a prominent leader of the Hotak Empire, which was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire established in parts of present-day Afghanistan and Iran.
January 1721: Mazulipatam becomes a French possession.
January 1722: The Baroda State was founded in 1721, when the Maratha general Pilaji Gaekwad conquered Songadh from the Mughals.
October 1722: The siege of Isfahan in 1722 was led by Mahmud Hotak, who defeated Sultan Husayn and took control of Persia, establishing the Hotak Empire. Sultan Husayn abdicated after the six-month siege, recognizing Mahmud as the new Shah of Persia.
January 1723: Bankipur was an ancient village on the Hugli river located in what is now West Bengal, north of Barrackpore, a little north of Ishapore.
January 1724: Yanaon (Yanam) became a French possession.
January 1724: In 1722-1723, forces led by Khanthaji Kadani and Pilaji Gaekwad attempted to raid Sihor but were repelled by Maharaja Bhavsinhji Gohil. After the war Bhavsinhji realised the reason for repeated attack was the location of Sihor. In 1723, he established a new capital near Vadva village, 20 km away from Sihor, and named it Bhavnagar after himself.
January 1725: Hyderabad State was founded by Mir Qamar-ud-din Khan who was the governor of Deccan under the Mughals from 1713 to 1721.
January 1725: The fourth Nizam Salabat Jang, a son of the Nizam al Mulk, who was indebted for his elevation to the throne to the French East India Company, granted the district of Kondavid (in the Guntur district) to the French in return for their services, and soon afterwards granted the other circars as well.
January 1728: Bahawalpur state was founded in 1727 AD by Nawab Sadiq Muhammad Khan Abbasi, who was a descendant of the Abbasid Caliphs. He established the state after breaking away from the Durrani Empire, establishing a prosperous and independent kingdom in the region.
January 1731: Mohammad Khan Bahadur Khanji I declared independence from the Mughal governor of Gujarat subah, and founded the state of Junagarh in 1730.
January 1731: Cambay was founded as a state in 1730 by the penultimate Nawab of the Mughal Empire, Mirza Ja‘far Mu’min Khan I, the last of the Mughal governors of Gujarat, at the time of the dismemberment of Mughal rule in India.
January 1731: Jigni State was founded as a jagir in 1730 by Rao Padam Singh, a Rajput of the Bundela clan.
January 1731: Establishment of Chaudandi.
January 1732: Jaitpur state was founded in 1731 by Jagat Rai, son of the famous Bundela leader Chhatrasal, as a division of Panna State.
January 1732: Gwalior state was a semi-autonomous Maratha state. It was centered in modern-day Madhya Pradesh, arising due to the rise of the Maratha Empire and fragmentation of the Mughal Empire.
January 1732: Yanaon (Yanam) is re-occupied by the French.
January 1732: Panna was the capital chosen by a leader Chhatar Sal, the founder of Panna State, after leading a revolt against the Mughal Empire.
January 1733: As the Mughal Empire declined and decentralized, local governors in Oudh began asserting greater autonomy, and eventually Oudh matured into an independent polity governing the fertile lands of the Central and Lower Doab.
January 1734: Malneta state founded.
January 1734: Bantva is described as Bantva Choryashi is Ain-i-Akabari. Bantva was bestowed by Nawab Bahadur Khan (Sher Khan Babi) of Junagadh State, on his brothers Diler Khan Salabat Muhammed Khan Babi and Sher Zaman Khan in 1733 after their expulsion from Ghogha by Sohrab Khan.
January 1740: Ballabhgarh, is a town and a tehsil (subdistrict) in Faridabad District of Haryana, India, and is part of the National Capital Region. The town was founded by Raja Balram Singh, in 1739, who also built the Nahar Singh Mahal palace in the same year.
January 1741: As the Mughal suzerainty weakened, the Benares zamindari estate became Banaras State, thus Balwant Singh of the Narayan dynasty regained control of the territories and declared himself Maharaja of Benares in 1740.
January 1741: Vala (Vallabhipura) princely state was founded in 1740 by Thakore Sahib Akherajji of nearby Bhavnagar (also in Gohelwar prant; later a salute state under a Maharaja), a Gohil Rajput of the Suryavanshi clan, for his twin brother Visaji, who became the first Thakore.
January 1742: In 1741, Governor Joseph François Dupleix arrived in India, aiming to establish a French territorial empire. Commanded by Marquis Bussy-Castelnau, Dupleix's forces gained control over the area from Hyderabad to Cape Comorin.
January 1751: Beri State was founded in the mid eighteenth century by Diwan Acharju (Achharaj) Singh, a jagirdar who was the son of Diwan Mahma Rai of Karaiha in Gwalior State .
January 1751: Independence of the Suket State from Mughal Empire.
January 1751: Bhajji state founded at an uncertain date before the 19th century.
January 1751: Kothi State was founded in 1750 by Raja Keshri Singh, a Rajput ruler who expelled the former Bharr ruler of the area. The territory was located in present-day Himachal Pradesh, India.
December 1754: The Governor of French India, Charles Godeheu, signed a treaty with the British on December 26, 1754, agreeing to evacuate all the territories in India conquered by his predecessor, Joseph Dupleix. The British also agreed to leave the territories of French India that they had occupied.
January 1756: Establishment of the Danish outpost of Frederiknagore (today Serampore) in Bengal.
January 1757: The region of Rajputana came under Maratha domination during this time.
June 1757: British Lieutenant Colonel Robert Clive defeated Indian and French forces in the Battle of Plassey.
January 1758: Delhi was captured by the Maratha army under Raghunath Rao in August 1757, defeating the Afghan garrison in the Battle of Delhi. This laid the foundation for the Maratha conquest of North-west India.
August 1758: In Lahore, as in Delhi, the Marathas were now major players. After the Battle of Attock, 1758, the Marathas captured Peshawar defeating the Afghan troops in the Battle of Peshawar on 8 May 1758.
January 1759: The maximum extent of the Kingdom of Travancore was reached at the end of Marthanda Varma's reign.
January 1759: The British East India Company, seeking an overland connection between its holdings at Madras and Bengal, sought to gain access to the Northern Circars, a series of coastal territories held by the French until 1758, when they were ousted with British military support.
January 1759: Tenganapatnam was abandoned by the Dutch in favour of Parangippettai (Porto Novo) in 1758.
April 1760: Karikal is occupied by British forces on 15 Apr 1760.
January 1772: In 1771, the Maratha leader Mahadji Scindia recaptured Delhi from Afghan control, restoring Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II to power. In 1784, the Marathas officially became the protectors of the emperor in Delhi, solidifying their influence in the region.
January 1801: With his fourth descendant Kumbhoji IV, the State raised itself, by acquiring the parganas of Dhoraji, Upleta, Sarai, and Patanvav.
January 1802: In 1801, the territories of Nawab of the Carnatic (ruler of Arcot and Nellore), Nawab of Junagarh, and Rohilkhand of Lower Doab were annexed by the British East India Company.
January 1806: British conquests in India until 1805.
January 1810: In 1809 Tripura became a British protectorate and in 1838 the Rajas of Tripura were recognised by the British as sovereigns.
May 1819: In 1819, the British East India Company completed its conquest of the Maratha Empire. This marked the end of Maratha rule and the consolidation of British control over much of the Indian subcontinent.
Disestablishment
May 1819: In 1819, the British East India Company completed its conquest of the Maratha Empire. This marked the end of Maratha rule and the consolidation of British control over much of the Indian subcontinent.
Selected Sources
Die Dänen in Indien, Südostasien und China (1620-1845), Wiesbaden (Germany), p. 236
Larsen, K. (1940): Guvernører, Residenter, Kommadanter og Chefer samt enkele andre fremtradende personer i de tidligere Danske Tropokolonier, Copenhagen (Denmark), p. 20
Rennell, J. (1782): Map of Hindustan, London (UK)
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.235-237

.png.webp)
 Mughal Empire (Maratha Protectorate)
Mughal Empire (Maratha Protectorate)