This article is about the specific polity Duchy of Benevento and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Lombard duchy, and later a principality, in southern Italy centered on Beveneto. It was was annexed by the Normans.
Establishment
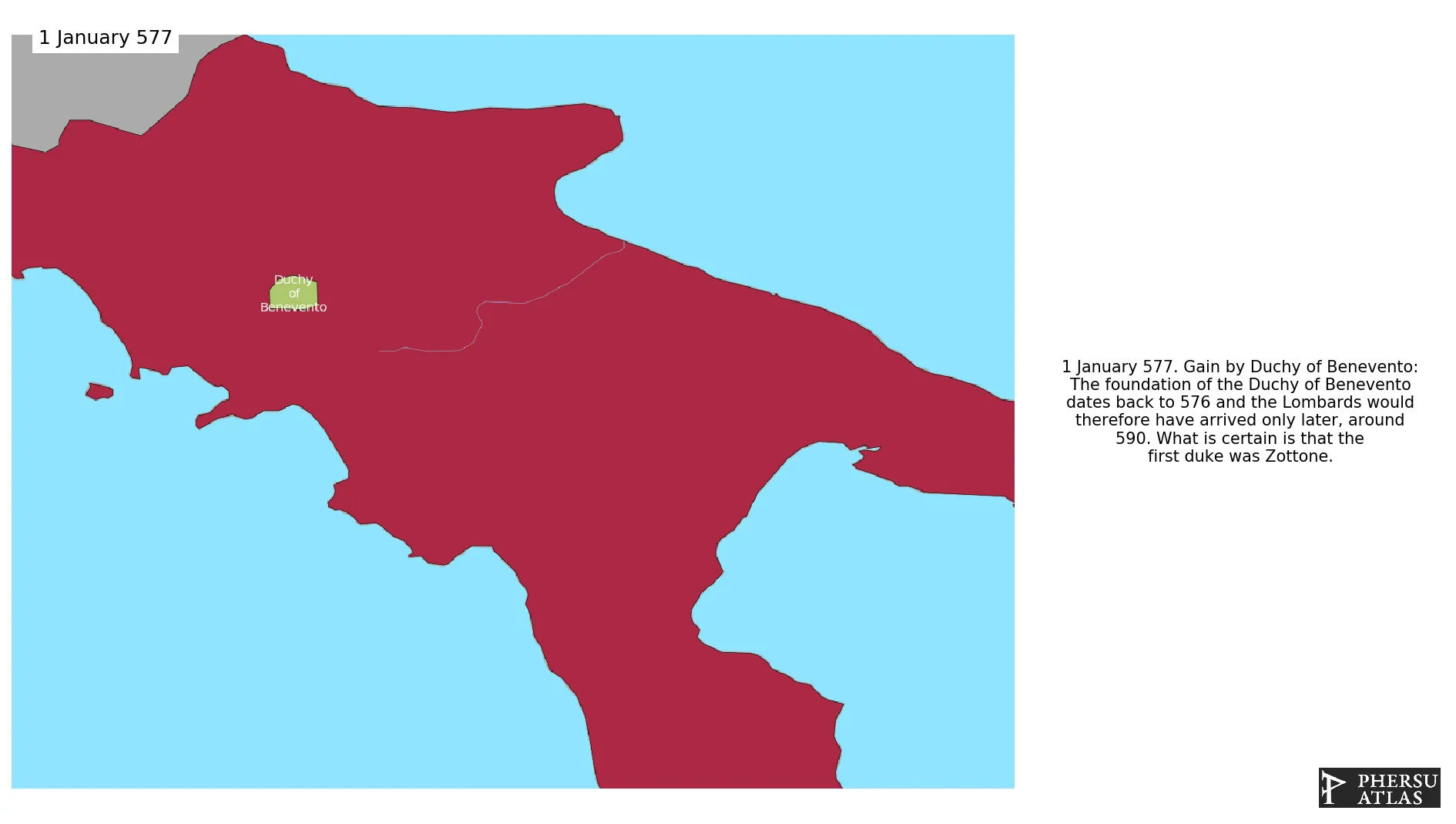
January 577: The foundation of the Duchy of Benevento dates back to 576 and the Lombards would therefore have arrived only later, around 590. What is certain is that the first duke was Zottone.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the invasion of the italian Peninsula, recently reconquered by the Eastern Romans from the Ostrogoths, by the Germanic people of the Lombards.
1.1.Rule of the Dukes
Was an interregnum in the Lombard Kingdom of Italy during which Italy was ruled by the Lombard dukes of the old Roman provinces and urban centres.
1.1.1.Siege of Naples (582)
Lombard siege of Naples.
January 582: Zotto, also known as Zotto I, was the Duke of Benevento who attempted to conquer Naples in 581 but was unsuccessful and had to abandon the siege. This event marked a failed military campaign by the Duchy of Benevento to expand its territory.
February 582: During the siege of Naples in 582, the Lombard king Zotto attempted to conquer the city but was ultimately unsuccessful. As a result, Naples remained under the control of the Eastern Roman Empire.
1.2.Campaigns of Liutprand
Were a series of military campaigns by Lombard king Liutprand against the Byzantine Empire.
February 718: The Duchy of Benevento took possession of Cuma.
January 719: The Byzantine duke of Naples, John I, reconquered Cumae.
Was the siege of Byzantine-controlled Naples by the Lombard Duke of Spoleto.
January 593: Siege of Naples by Lombards from Benevento together with Ariulfo Duke of Spoleto.
February 593: The tribune Costantium, sent to Naples by Pope Gregory the Great, managed to repel the besiegers from Naples.
Capua was conquered by the Lombards.
January 595: In 594, the city of Capua fell into the hands of the Lombards, specifically the Duchy of Benevento, during the Lombard invasion of Italy. The Lombards were a Germanic tribe that ruled much of Italy during the Early Middle Ages.
Venafro was conquered by the Lombards.
January 596: The Longobard conquest of Venafro in 595 resulted in the territory coming under the control of the Duchy of Benevento. This event marked the end of the ability to elect a bishop in Venafro, as the Longobards imposed their own governance and control over the region.
Were the military campaigns of Arechi I, the Lombard duke of Beveneto, that led to the conquest of Nola and Crotone.
January 597: Fall of Nola to Lombard forces from the Duchy of Benevento.
January 600: Arechi I of Benvento conquers Atella.
January 601: A Byzantine fleet conquered back Crotone.
January 602: Lombard forces of the Duchy of Benevento conquer Nuceria Alfaterna.
January 642: At his death, the Byzantine garrisons in the South were greatly reduced. Only Naples, Amalfi, Gaeta, Sorrento, part of Calabria and the seaside cities of Puglia (Trani, Bari, Brindisi, Otranto) remained in Byzantium.
5.1.Lombard conquest of Crotone
The Lombard duke of Beveneto conquered Crotone.
January 597: Fall of Nola and threat against Amalfi (the Longobards made many prisoners, who were ransomed by the pope) and also the conquest of Crotone, however too exposed to the attacks of the Byzantine fleet and soon lost again.
In 646, Slavic invadors landed near Siponto on the Adriatic and plundered southern Italy.
January 647: In 646, Slavic plunderers landed near Siponto on the Adriatic. Aiulf personally led his forces against the intruders, but his horse fell into a pit dug by the Slavs around their camp and he was surrounded and killed.
February 647: In 646, Slavic plunderers landed near Siponto on the Adriatic. Aiulf personally led his forces against the intruders, but his horse fell into a pit dug by the Slavs around their camp and he was surrounded and killed.
Romuald II of Benevento took the outlying castle of Cumae from John I of Naples in 716.
January 717: Romuald II took the outlying castle of Cumae from John I of Naples in 716 and ignored Pope Gregory II's pleas and offers of compensation for restitution. In 717, the pope funded an expedition of John's which decisively defeated his gastald's army and displaced his men from Cuma.
January 718: Romuald II took the outlying castle of Cumae from John I of Naples in 716 and ignored Pope Gregory II's pleas and offers of compensation for restitution. In 717, the pope funded an expedition of John's which decisively defeated his gastald's army and displaced his men from Cuma.
January 663: Its destinies were closely linked to the Lombard royal crown only during Grimoald's reign.
January 672: Grimoald king of the Lombards: 662-671.
Disestablishment
January 730: Liutprand marched on Spoleto and obtained the submission of the dukes Thrasamund II (Spoleto) and Romualdo II (Benevento), who swore allegiance to him.
.png.webp)
 Duchy of Benevento
Duchy of Benevento