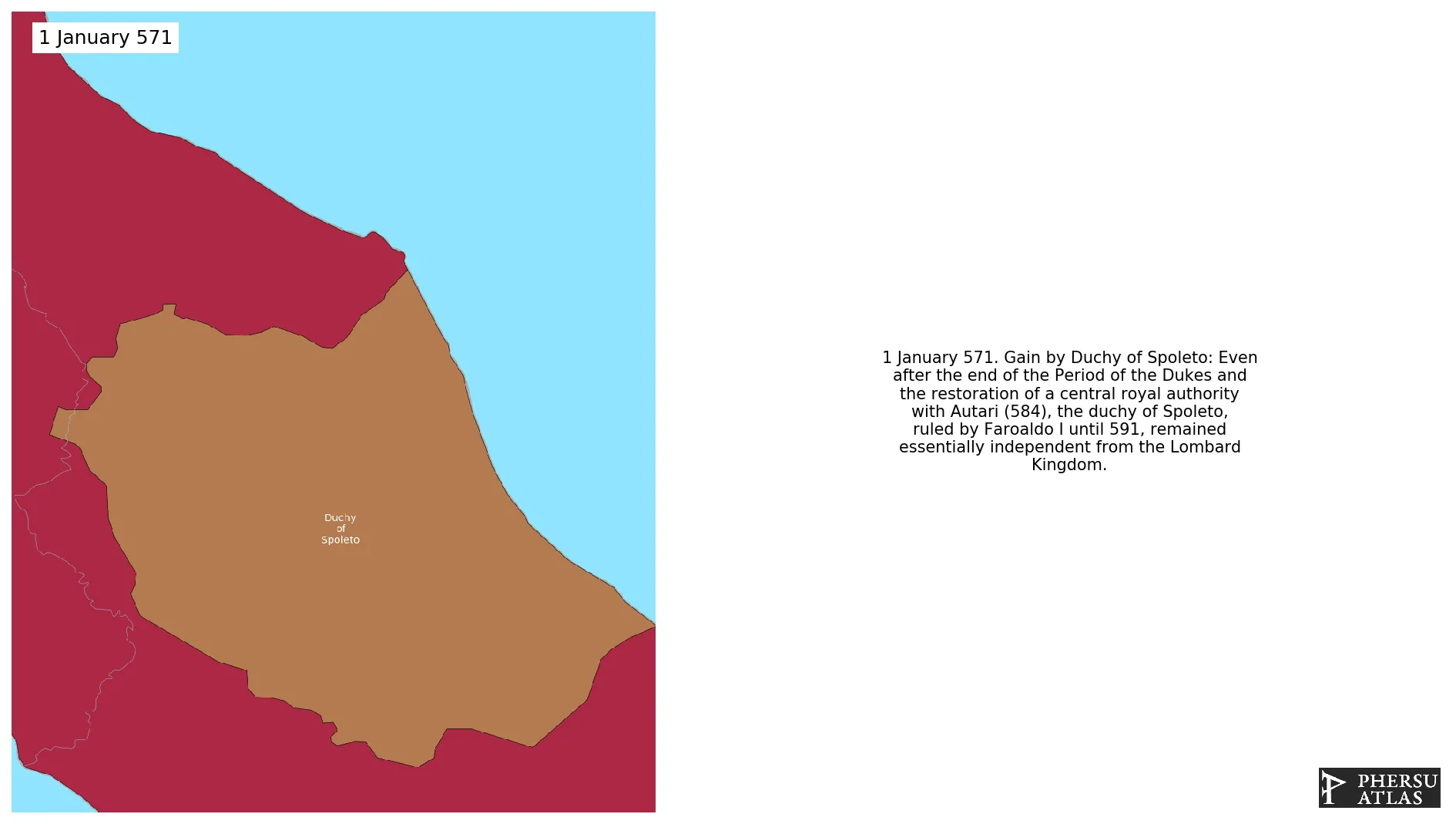
Duchy of Spoleto
Duchy of Spoleto
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Lombard Duchy in southern Italy.
Establishment
January 571: Even after the end of the Period of the Dukes and the restoration of a central royal authority with Autari (584), the duchy of Spoleto, ruled by Faroaldo I until 591, remained essentially independent from the Lombard Kingdom.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the invasion of the italian Peninsula, recently reconquered by the Eastern Romans from the Ostrogoths, by the Germanic people of the Lombards.
1.1.Restitution of Classis
The Lombards gave back Classis to the Byzantines.
January 714: Classis is reconquered by the Byzantines.
1.2.Campaigns of Liutprand
Were a series of military campaigns by Lombard king Liutprand against the Byzantine Empire.
January 718: The Duchy of Spoleto occupied Narni.
Was the cession, made in 728 by the Lombard King Liutprand to Pope Gregory II, of some castles in Latium important for the defense of Rome, the largest of which was that of Sutri.
January 729: Pope Gregory II (715-731) directly addressed the Lombard king Liutprand, asking him to renounce the territories already conquered and to return them to the Byzantine exarch as legitimate owner. Liutprand, on the other hand, donated the castrum of Sutri to the pontiff. According to historians, with the "Donation of Sutri" the pontiff acquired formally recognized temporal power for the first time.
Were a series of wars between the Frankish and Lombard Kingdoms. Charlemagne finally incorporated the Kingdom of the Lombards in the Frankish Kingdom.
3.1.Frankish Invasion of Italy (775)
Was the second military campaign of Frankish king Charles the Great against the Kingdom of the Lombards, which was annexed to the Frankish possessions.
January 775: In 776, Charlemagne, the King of the Franks, conquered the Duchy of Spoleto, adding it to his expanding Carolingian Empire. This conquest came two years after the fall of Pavia, another significant victory for Charlemagne.
January 775: In 774 the pontiff gave him the title of patricius Romanorum. Charles donated Roman Tuscia (with the centers of Ronciglione, Viterbo, Tuscania, Soana) together with some centers of Longobard Tuscia (Populonia, Rusellae and Castrum Felicitatis) and to Ancona, Numana and Osimo: a total of ten cities;.
January 776: Passed under the control of the francs together with the Longobardia Maior.
January 777: In 776, Charlemagne, the King of the Franks, conquered Spoleto, a territory in Italy. This victory came two years after the fall of Pavia, another significant conquest for Charlemagne and his Carolingian Empire.
January 713: During the reign of Liutprand, king of the Lombards from 712, Faroald, Duke of Spoleto, occupied the port of Classe. This event marked a significant power struggle between the Lombards and the Byzantine Empire in Italy.
January 729: Borders of the Duchy of Spoleto in 728 AD.
January 743: In 742 Transemund was forcibly retired to a monastery by Liutprand, who conferred the duchy that he had rewon by force of arms upon Agiprand (742).
January 757: Aistulf capitulated and had to suffer even harsher peace conditions (Second Peace of Pavia, June 756). Pepin donated the conquered lands to the Apostolic See.
January 757: On Astolfo's death, the Spoleto population acclaimed the new duke Alboino, also supported by Pope Stephen II (752-757) who, having ascertained the breaking of the truce with the Lombards.
January 759: In 758 Alboin was attacked and defeated by the new king Desiderius (756-774).
Disestablishment
January 777: In 776, Charlemagne, the King of the Franks, conquered Spoleto, a territory in Italy. This victory came two years after the fall of Pavia, another significant conquest for Charlemagne and his Carolingian Empire.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany)
 Duchy of Spoleto
Duchy of Spoleto