This article is about the specific polity Ethiopian Empire and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an Empire in the Horn of Africa, emerged in precolonial times. It expanded considerably in the XIX century by conquering neighboring petty kingdoms. In 1936 it was one of the few African countries not under European influence, but was conquered by Italy that established the Colony of East Africa. It was restored during World War II, after the British conquered Italian East Africa.
Establishment
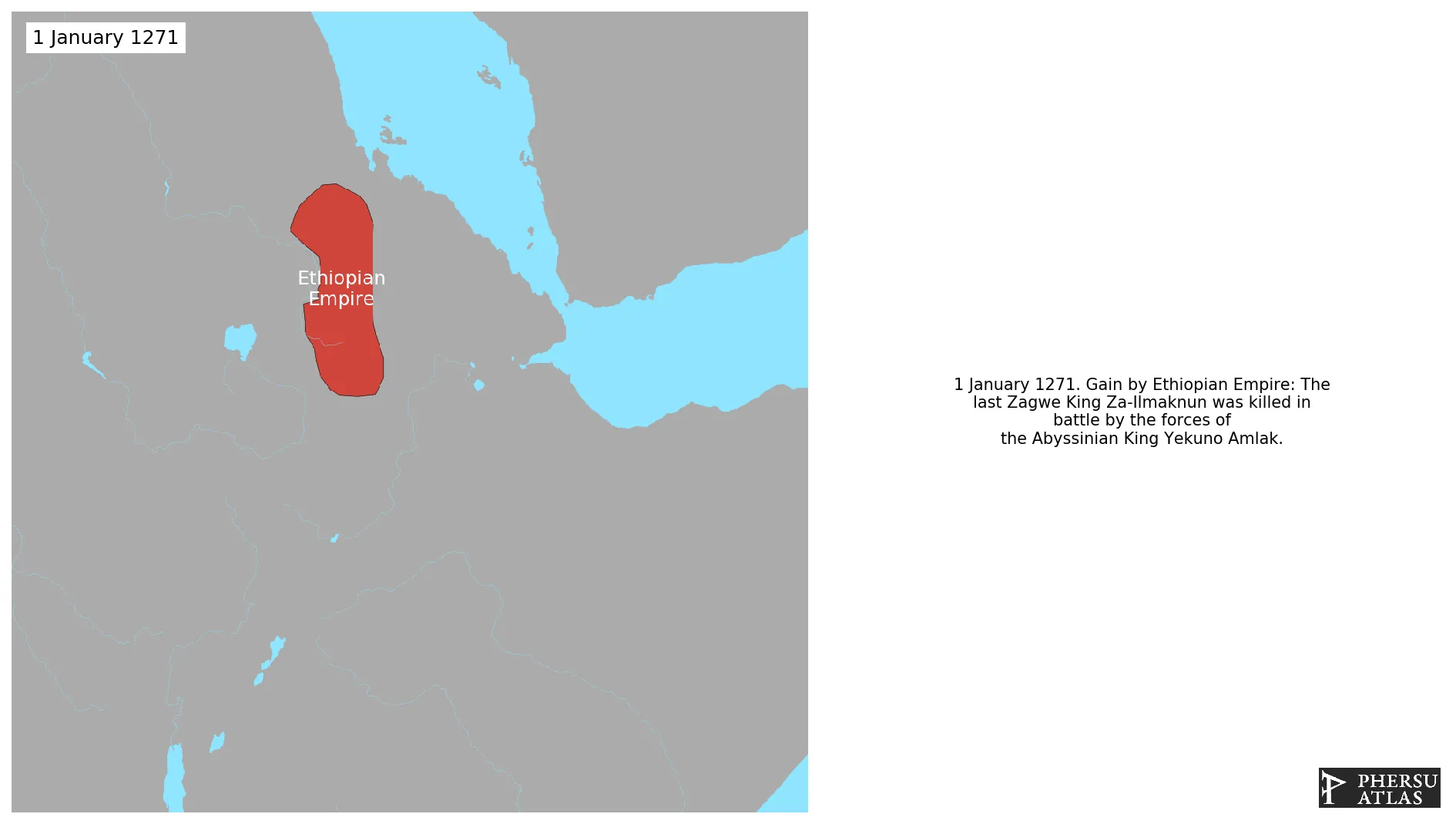
January 1271: The last Zagwe King Za-Ilmaknun was killed in battle by the forces of the Abyssinian King Yekuno Amlak.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a military conflict between the Christian Ethiopian Empire and the Muslim Adal Sultanate from 1529 to 1543.
October 1531: Battle of Amba Sel.
February 1543: The Bahr negus also joined Emperor Gelawdewos and the Portuguese in the decisive Battle of Wayna Daga, where Imam Ahmad was killed. The death of Imam Ahmed and the victory in the Battle of Wayna Daga caused a semi-collapse of Ahmed forces and forced a Somali retreat from Ethiopia.
Expansion during the rule of Selim II in the Ottoman Empire.
January 1568: Özdemir Pasha, a deputy of the Ottoman Empire admiral, conquered the west bank of the Red Sea in 1567 during the reign of Selim II. This territory roughly corresponds to a narrow coastal strip of Sudan and Eritrea.
January 1571: The Ottoman Turks made multiple advances further inland conquering Eritrea. The sanjak of Ibrim was established in the 1560s.
2.1.Ottoman conquest of Habesh
Was an Ottoman military campaign in modern-day Eritrea.
January 1580: Ethiopian emperor Sarsa Dengel retook Debarwa.
Was a punitive expedition by the armed forces of the British Empire against the Ethiopian Empire whose emperor had imprisoned several missionaries and two representatives of the British government.
October 1867: The British troops occupied the area from the dry bed of the Kumayli River to the Suru Pass. At the pass the engineers were busy at work building a road to Senafe 101 km long, rising to 2,300 m for the elephants, gun-carriages, and carts.
October 1867: In 1867, the advance guard of engineers, led by British military officer General Robert Napier, landed at Zula on the Red Sea. This marked the beginning of Great Britain's military occupation of the territory, as part of their efforts to expand their influence in the region.
February 1868: Emperor Tewodros II of Ethiopia accepts the submission of the inhabitants of Delanta. The area was quickly overran by the British.
March 1868: In 1868, British forces, led by General Robert Napier, undertook a grueling three-month trek over 640 km of mountainous terrain to reach Emperor Tewodros II's fortress at Magdala in Antalo, Ethiopia. This military campaign resulted in the British occupation of the territory.
March 1868: On 17 March, the British army reached Lake Ashangi.
April 1868: British force reached the Bashilo.
April 1868: Battle of Magdala.
April 1868: Having first blown up the fortress and burned Amba Mariam (then known as Magdala), Brtish officer Robert Napier commenced the return march.
June 1868: By June 2, the British base camp in Abyssinia had been dismantled. The British forces evacuated Ethiopia and set sail for England on June 10.
Was a war by Mahdist Sudan against Egyptian rule. The Mahdista were finally defeated by Egyptian and British forces, and Sudan became an Anglo-Egyptian condominium.
4.1.Mahdist Attacks to Ethiopia
Was the invasion of Ethiopia by Mahdist Sudan during the Mahdist War.
January 1869: Bogos occupied by Egypt.
October 1884: According to the Hewett Treaty of 3 June 1884, Ethiopia agreed to facilitate the evacuation of Egyptian garrisons in southern Sudan. In September 1884, Ethiopia reoccupied the province of Bogos, which had been occupied by Egypt.
February 1887: King Tekle Haymanot of Gojjam led a successful counteroffensive as far as Gallabat in the Sudan in January 1887.
February 1888: In January 1888, the Mahdists defeated Ethiopian Emperor Tekle Haymanot at Sar Weha and sacked the city of Gondar.
March 1888: Mahdist forces leave Sar Weha and Gondar.
Was a war between the Ethiopian Empire and the Khedivate of Egypt caused by the expansionistic aims of the latter after having occupied Sudan.
March 1876: The Egyptians, established forts in Eritrea: "Gura" fort and "Khaya Khor" fort.
March 1876: Battle of Gura.
Expansion during the rule of Menelik II in the Ethiopian Empire.
March 1889: The Kingdom of Shewa is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
March 1889: Expansion of Ethiopia by the end of the reign of Yohannes IV.
January 1890: Konta is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1890: Dauro is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1891: Amarro is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1891: In 1893, the integration of Kambata, occupied since 1890, was completed.
January 1892: In 1891, Ras Wolde Giyorgis Abboye, a prominent Ethiopian military leader, conquered the territories of Konta and Kulo.
January 1892: Ethiopian conquest of Sidamo.
January 1892: Ethiopian conquest of Balé.
January 1895: Ethiopian conquest of Harer.
January 1895: The Ras Gobena Dachi is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1895: The Wolde Giyorgis Abboye is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1895: The Kingdom of Janjero is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1897: Walo is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1898: Ethiopia's expansion under Menlik II until 1897.
January 1898: The Kingdom of Kaffa is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1898: Ethiopian expedition in Borana.
January 1899: Ethiopia's expansion under Menlik II until 1898.
January 1899: Sheka is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
June 1899: Territorial change based on available maps.
January 1900: Sidamo conquered by Ethiopian Empire.
January 1903: The Kingdom of Gumma is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1905: Expansion of the Ethiopian Empire in 1904.
Were two invasion of Ethiopia by the Kingdom of Italy whose goal was to make Ethiopia a colony. The first invasion was not succesful, but after the second invasion Ethiopia became part of of Italian East Africa.
7.1.First Italo-Ethiopian War
Was an ultimately unsuccesful Italian invasion of Ethiopia.
January 1895: In 1893, judging that his power over Ethiopia was secure, Menelik repudiated the treaty with Ital. In response the Italians ramped up the pressure on his domain in a variety of ways, including the annexation of small territories bordering their original claim under the Treaty of Wuchale, and finally culminating with a military campaign and across the Mareb River into Tigray (on the border with Eritrea) in December 1894.
October 1895: Amba Alagi is temporarily occupied, as part of the Italian invasion of Tigray, on 13 October 1895 by a contingent of troops under the command of General Giuseppe Arimondi.
December 1895: Battle of Amba Alagi.
December 1895: In 1895, during the First Italo-Ethiopian War, Italian General Giuseppe Arimondi led his troops to the unfinished Italian fort in Mekele, Ethiopia. This marked Italy's military occupation of the territory.
January 1896: Battle of Mekelle.
March 1896: Battle of Adwa.
7.2.Second Italo-Ethiopian War
Was the second Italian military invasion of Ethiopia. At the end of the war the country became part of Italian East Africa.
7.2.1.Northern Front (Second Italo-Ethiopian War)
Was the northern front of the Second Italo-Ethiopian war.
7.2.1.1.De Bono Offensive
Was a military offensive by Italian general Emilio De Bono during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
October 1935: The Italian I Corps took the city of Adigrat.
October 1935: Adua was captured by the Italian II Corps.
October 1935: Dejazmach Haile Selassie Gugsa and 1,200 of his men surrendered to the Italian command near Adagmos.
October 1935: From October 15, the forces under the command of De Bono moved from Adua towards Axum to occupy the city.
November 1935: The Italian avant-gardes entered Macallè.
7.2.1.2.Ethiopian Christmas Offensive
Was an Italian military offensive during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
December 1935: Italian military occupation of Abbi Addi.
January 1936: The Ethiopians reoccupied all of southern Tembien.
7.2.1.3.Badoglio Offensive
Was a military offensive by Italian general Pietro Badoglio during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
February 1936: Battle of Amba Aradam.
February 1936: Second Battle of Tembien.
March 1936: Battle of the Scirè.
April 1936: Italian march on Gondar resulting in the occupation of Gondar and the Lake Tana area.
April 1936: Battle of Lake Ascianghi.
April 1936: The Italian army corps entered Dessié on April 15, 1936.
May 1936: Occupation of Addis Ababa by Italian forces.
7.2.2.Southern Front (Second Italo-Ethiopian War)
Was the southern front of the Second Italo-Ethiopian war.
7.2.2.1.Graziani Offensive
Was an Italian military offensive commanded by General Rodolfo Graziani during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
October 1935: Italian general Graziani authorized the execution of the "Milan Plan": a series of small offensive attacks along the entire front to eliminate the annoying enemy garrisons and to test their resistance. In about twenty days Graziani occupied the villages of Dolo, Oddo, Ualaddaie, Bur Dodi, Dagnerei, Callafo, Scivallè and Gherlogubi, after they had been cleared following the preventive aerial bombardments ordered by the general.
November 1935: First attack with chemical agents of the Second Italo-Ethiopian War against the village of Gorrahei, which was subsequently the main objective of the "Plan Gorizia" which began on October 28. However, it fell into Italian hands only on 6 November.
January 1936: Battle of Ganale Doria.
April 1936: El Fud conquered by italy.
April 1936: Segàg conquered by italy.
April 1936: Battle of the Ogaden.
May 1936: The Italian columns, led by General Rodolfo Graziani, began their advance towards Harar in 1936 during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War. The city was occupied by Italian forces in the early afternoon of 6 May.
May 1936: Italian general Graziani entered Dire Daua, a few hours before the arrival by train from Addis Ababa of the men of Badoglio. With this last formal act, the war on the southern front also ended.
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
8.1.World War I African Theatre
Was the African Theatre of World War I.
8.1.1.Somaliland campaign
Was a long guerrilla conflict which took place between 1900 and 1920 in the territories corresponding to present-day Somalia and in the border areas between Somalia and present-day Ethiopia. The Somali Islamist leader Mohammed Abdullah Hassan succeeded in uniting various clans and tribes in his country in a unitary movement of opposition to Italian and British colonial rule.
October 1908: The Dervishes resumed the conflict. A column invaded the Sultanate of Obbia and attacked the Mudugh region.
February 1913: After various raids, in June 1912 the Dervish Mullah moved further south and created an independent Somali national state. The core of his territory was protected by a chain of forts to the west, and went from Mount Shimbiris on the coast to the village of Gid Ali in the interior.
December 1920: On December 21, 1920 (the precise date is not clear) Abdullah Hassan, who was the leader of the Dervish movement, died after six days of illness (also unspecified, malaria or pneumonia). The Mullah's death effectively ended the Dervish Revolt.
Following the death of Abba Jifar II, King of Jimma, Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie seized the opportunity to finally annex Abba's Kingdom.
May 1932: Following the death of Jimma ruler Abba Jifar II, Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie seized the opportunity to finally annex Jimma. On 12 May, 400 soldiers and a team of administrators descended upon Jimma and brought the kingdom to an end.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
10.1.World War II (East African Theatre)
Was the East African theatre of World War II.
10.1.1.British invasion of Italian East Africa
Was the British invasion and occupation of Italian East Africa during World War II.
December 1941: The Anglo-Ethiopian Agreement was a joint effort between Ethiopia and the United Kingdom at reestablishing Ethiopian independent statehood following the ousting of Italian troops by combined British and Ethiopian forces in 1941 during the Second World War.
January 1318: In 1317, the Kingdom of Damot was conquered by Emperor Ámeda-Sion I of the Ethiopian Empire. Damot had previously been an independent entity until this conquest, after which it fell under the influence of the Solomonic dynasty's power.
January 1330: The Sultanate of Dawaro was subjugated by Emperor Amda Seyon I in the early 14th century.
January 1345: During the reign of Emperor Amda Seyon I, Arbabni was conquered and annexed by Abyssinia.
January 1401: Ennarea became independent from the kingdom of Damot in the 14th century.
January 1416: Isaak (Yeshaq) of Ethiopia conquered and annexed the Sultanate of Ifat in 1415.
January 1501: The Hadiya Sultanate was annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1501: Oral traditions assert its establishment to refugees from the Nubian kingdom of Alodia, after its capital Soba had fallen to Arabs or the Funj in c. 1500, centered around the mountainous region of Fazughli on the Blue Nile.
January 1501: The Kingdom of Janjero was a tiny kingdom located in what is now Ethiopia established c.15th century.
January 1590: Emperor Sarsa Dengel of Ethiopia successfully checked the Ottoman expansion into Ethiopian territories by securing a significant victory and subsequently sacking Arqiqo in 1589. This decisive action restricted the Ottomans to a narrow coastal strip, limiting their influence and control in the region.
January 1591: Emperor Sarsa Dengel of Ethiopia successfully checked the Ottoman expansion into Ethiopian territories by securing a significant victory and subsequently sacking Arqiqo in 1589. This decisive action restricted the Ottomans to a narrow coastal strip, limiting their influence and control in the region.
January 1601: According to oral sources, the Sultanate of Rehayto was founded around 1600, by detachment from the Sultanate of Tadjourah.
January 1701: The Sultanate of Tadjourah was founded in the 15th century by Umar ibn Dunya according to Afar accounts. It was a powerful state in the Horn of Africa, controlling trade routes and coastal regions. In 1700, the territory of Tadjoura and surrounding regions fell under the rule of the Sultanate of Tadjoura.
January 1801: Shewa, located in present-day Ethiopia, became part of the Ethiopian Empire in 1800.
January 1822: Between 1821 and 1841, Muhammad Ali, Pasha of Egypt, came to control Yemen and the sahil, with Zeila included.
January 1840: Kingdom of Shewa (Shoa) established ca. 1839.
January 1857: In 1856, the Kingdom of Shewa was annexed by the Ethiopian Empire under the rule of Emperor Tewodros II.
January 1860: Shewa was annexed by Ethiopia.
December 1860: Walayta is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1872: In 1871, the southern part of East Welega, centered around Nekemte, became part of the newly founded Leqa Naqamte state.
January 1880: Ethiopian occupation of Medri Bahri in 1879.
January 1886: With the help of the British, the city of Massawa came under Italian control and became part of Italy's colony of Eritrea in 1885.
January 1887: The Kingdom of Gomma is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1887: The emirate of Harar would finally be destroyed in 1887, in the battle of Chelenqo, at the hands of the armies of Negus Sahle Maryam of Showa (the future emperor Menelik II), who would later annex the emirate.
July 1887: In 1887, after signing successive treaties with the then ruling Somali Sultans from the Isaaq, Issa, Gadabursi, and Warsangali clans, the British established a protectorate in the region referred to as British Somaliland.
January 1888: The Kingdom of Gera is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
January 1888: Establishment of French Somaliland.
May 1889: The Treaty of Wuchale was signed between Italy and Menelik II, the Emperor of Ethiopia. It established the borders between Italian Eritrea and the Ethiopian Empire in 1889.
January 1933: Jimma Abba Jifar is annexed by the Ethiopian Empire.
September 1948: The British ceded Ogaden to Ethiopia in 1948.
September 1952: The Eritrean-Ethiopian Federation was a coalition between the former Italian colony of Eritrea and the Ethiopian Empire. It was established as a result of the renunciation of Italy’s rights and titles to territorial possessions in Africa.
November 1962: Following pressure from Haile Selassie I on the Assembly of Eritrea, the Federation was officially dissolved and Eritrea annexed by Ethiopia.
March 1975: The Derg, officially the Provisional Military Government of Ethiopia, was the military junta that ruled Ethiopia from 1974 to 1987.
Disestablishment
March 1975: The Derg, officially the Provisional Military Government of Ethiopia, was the military junta that ruled Ethiopia from 1974 to 1987.
Selected Sources
Matteotti, F. (1938): La Formazione de l'impero coloniale italiano, Volume Terzo - L'impero (dall'occupazione di Dessiè all'assetto definitivo dell'impero), Milan (Italy), pp. 9-10
.svg.png.webp)
 Ethiopian Empire
Ethiopian Empire