This article is about the specific polity Hungary (Germany) and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
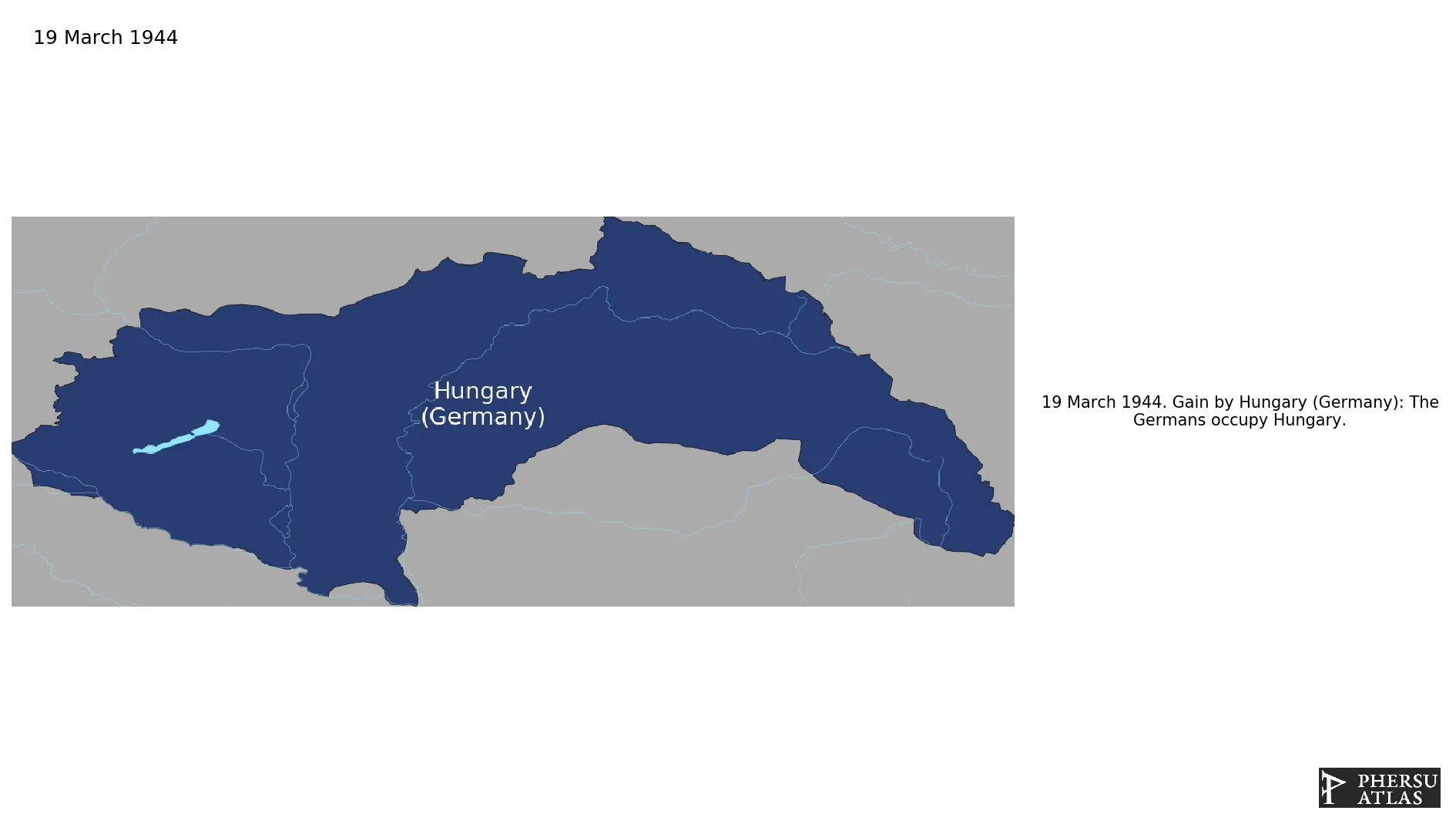
Due to fears that Hungary would seek to negotiate a separate peace with the Allies, Germany occupied the country and established a puppet regime. It ended when Hungary was occupied by the Red Army.
Establishment
March 1944: The Germans occupy Hungary.
August 1944: Soviet advances during Operation Bagraton and Šiauliai Offensive.
August 1944: Troops of the USSR 7th Guards Army stormed Bacău and the 40th Army took Târgu Neamț.
September 1944: Soviet advance in Romania on 8 September 1944.
September 1944: By 24 September 1944, nearly all of Romania was under Allied control.
October 1944: With support from the 5th Air Army, Pliyev's group took the town.
October 1944: With support from the Soviet 5th Air Army, Pliyev's group took the town of Hajdúszoboszló.
October 1944: On 11 October 1944, Soviet troops reached the outskirts of Debrecen.
October 1944: By 14 October 1944, the German eastern line had fallen back 14 kilometers, with Oradea occupied by Malinovsky's forces.
October 1944: Germans are forced from Debrecen
October 1944: General Ivan Pliyev's Soviet forces captured Nyíregyháza in Hungary.
October 1944: The German 23rd Panzer Division recaptured Nyíregyháza.
October 1944: The Red Army started its offensive against the city of Budapest.
October 1944: Nyíregyháza was captured by the Red Army.
December 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the eastern front of World War II in that date.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
1.1.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
January 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
1.1.1.German invasion of Hungary
Was the occupation of Hungary by German Nazi troops during World War II.
1.1.2.Operation Bagration
Was the Soviet offensive against German-occupied Belarus during World War II.
1.1.2.1.Šiauliai Offensive
Was an operation of the Soviet forces of the 1st Baltic Front, commanded by General Hovhannes Bagramyan, conducted from 5 July to 29 August 1944. It drove German troops from much of Lithuania, with the main tactical objective being the city of Šiauliai.
1.1.3.Battle of Romania
The Soviet Operations to drive out the Axis powers from Romania during World War II.
1.1.3.1.Jassy-Kishinev Offensive
Was a Soviet offensive against Axis forces in Eastern Romania during World War II.
1.1.4.Battle of Debrecen
Was a battle taking place 6-29 October 1944 on the Eastern Front in Hungary during World War II.
1.1.5.Soviet Invasion of Hungary
Was the Soviet invasion of German-occupied Hungary during World War II.
April 1945: Soviet operations in Hungary ended on 4 April 1945, when the last German troops were expelled.
1.1.5.1.Battle of Budapest
Was the 50-day-long encirclement by Soviet and Romanian forces of the German-occupied Hungarian capital of Budapest.
1.1.5.2.Operation Spring Awakening
Was the last major German offensive of World War II. It took place in Western Hungary on the Eastern Front and lasted from 6 March until 15 March, 1945. The objective was to secure the last significant oil reserves still available to the European Axis powers and prevent the Red Army from advancing towards Vienna. It was a failure for Nazi Germany.
March 1945: German occupation of Balaton lake region (line of 15 march).
March 1945: Soviet counterattack in Hungary.
March 1945: Soviet forces continue to advance in Hungary towards Austria.
1.1.6.Soviet Invasion of Slovakia
Was the Soviet invasion of Slovakia near the end of World War II.
March 1945: In Czechoslovakia, troops of Second Ukrainian Front take communications center of Banska Bystrica.
1.1.7.Vienna Offensive
Was an offensive launched by the Red Army in order to capture Vienna, Austria, during World War II. .
March 1945: The German bridgehead at Komárom was eliminated by Soviet forces.
Disestablishment
January 1945: Frontline of the Soviet offensive to the Oder in that date.
March 1945: German occupation of Balaton lake region (line of 15 march).
March 1945: Soviet counterattack in Hungary.
March 1945: Soviet forces continue to advance in Hungary towards Austria.
March 1945: In Czechoslovakia, troops of Second Ukrainian Front take communications center of Banska Bystrica.
March 1945: The German bridgehead at Komárom was eliminated by Soviet forces.
April 1945: Soviet operations in Hungary ended on 4 April 1945, when the last German troops were expelled.
Selected Sources
Ian Kershaw (trad. de l'anglais), La Fin : Allemagne, 1944-1945, Paris, Seuil, 2012, p.137
Operation Bagration, 22 June-19 August 1944. United States Military Academy of West Point. Retrieved on 6 April 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope30.jpg
Russian Balkan And Baltic Campaigns, 19 August-31 December 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope31.jpg
Soviet Offensive To The Oder, 12 January-30 March. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope32.jpg
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 455
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.182
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.300
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.307
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.473
.svg.png.webp)
.png.webp)
 Hungary (Germany)
Hungary (Germany)