If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
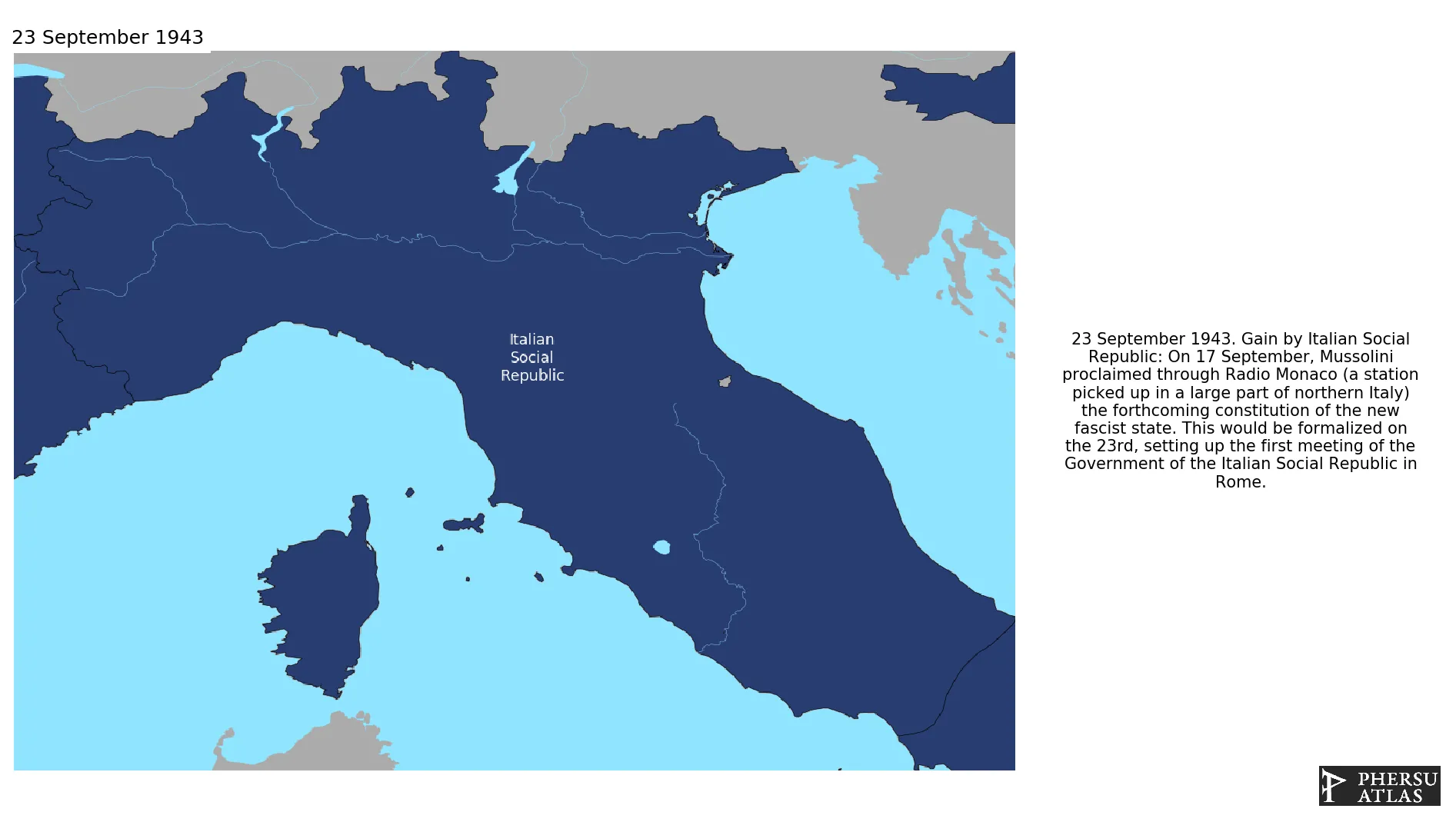
Aftet the allied invasion of Sicily, Italy signed the Armistice of Cassabile and arrested Mussolini. The Germans occupied most of Italy and freed Mussolini who created the Italian Social Republic, a puppet state that ruled over the Italian territories occupied by Germany (with the exception of parts of northeastern Italy, under direct German military control). The Italian Social Republic was slowly occupied by the allies and fell in 1945.
Establishment
September 1943: On 17 September, Mussolini proclaimed through Radio Monaco (a station picked up in a large part of northern Italy) the forthcoming constitution of the new fascist state. This would be formalized on the 23rd, setting up the first meeting of the Government of the Italian Social Republic in Rome.
September 1943: The Four Days of Naples were a historic episode of popular insurrection that took place during the Second World War, between 27 and 30 September 1943. During the insurrection, civilians, with the contribution of soldiers loyal to the Southern Kingdom, managed to free the city of Naples from the occupation of the Wehrmacht forces.
October 1943: The German troops resisted as per Albert Kesselring's order, until 16 October, and then began to withdraw slowly from the Barbara Line, in order to buy time for the conclusion of the work on the Gustav Line.
November 1943: The German forces, led by Field Marshal Albert Kesselring, were pressured by the Allies to abandon the Barbara Line in Italy. They retreated to the Bernhardt Line.
November 1943: By mid-November, the Allies had reached Sangro, in front of the Gustav Line.
December 1943: The main American attack began on 8 December: after days of bloody fighting in the mountains, the Germans had to evacuate Monte Lungo.
December 1943: Battle of Montelungo. By December 16th Mignano Monte Lungo is cleared by the U.S. Fifth Army.
December 1943: Allied conquest of San Pietro.
December 1943: Germans are cleared from Ortona by British forces.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
1.1.World War II (Western Front)
Was the Western European theatre of World War II.
1.1.1.Colmar Pocket
Was an Allied military operation to liberate central Alsace from German forces.
January 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
1.2.World War II (Italian Front)
Was the Italian Front of World War II.
1.2.1.Italian Campaign (World War II)
Was the military operation of the Allies to free italy from the forces of Germany and its puppet state, the Italian Social Republic.
January 1944: The Bernhardt Line underwent the first attacks by the US 5th Army starting on November 5, 1943, while the fight lasted until late December, when it was conquered.
May 1944: Allied forces conquer Mount Maio and the town of Castelforte, as well as Monte Girofano and Monte Feuci.
May 1944: In Italy, the Germans retreated to the Hitler line.
May 1944: On 22 May the II Army Corps had reached Terracina in the coastal sector.
May 1944: The French conquered the Ausoni mountains.
May 1944: U.S. operations At Anzio And Cassino, 11-30 May 1944.
June 1944: Allied forces take Rome.
June 1944: Some garrisons had also remained in Orsogna, which was only liberated on 8 June 1944 by the paratroopers of the Nembo belonging to the Italian Liberation Corps (C.I.L.) after the breakthrough of the Gustav Line at Cassino.
June 1944: Allied offensive to liberate Italy up to the river Arno (1944).
July 1944: Allied offensive to liberate Italy up to the river Arno (1944).
July 1944: By July 3rd, Allied forces reach Siena, which falls to 3rd Algerian Division.
July 1944: Allied forces break through to Ancona on Adriatic coast.
July 1944: Leghorn falls to American 34th Division without serious opposition, but retreating Germans have carried out a thorough demolition program within the city and on harbor facilities.
August 1944: Allied offensive to liberate Italy up to the river Arno (1944).
August 1944: The Allies crossed the Arno at Pontassieve and entered Florence.
August 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the allied offensive in Italy.
September 1944: Lucca was liberated on 5 September.
September 1944: Allied conquest of Pistoia.
September 1944: Battle of Gemmano.
September 1944: Battle of Rimini.
December 1944: Faenza area cleared by the Allied forces.
December 1944: Battle of Garfagnana.
December 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the allied offensive in Italy.
1.2.1.1.Battle of Anzio
Was a battle of the Italian Campaign of World War II.
January 1944: Landing of the VI Army Corps at Anzio and Nettuno on 22 January 1944. British and American forces advance several miles inland.
January 1944: U.S. operations At Anzio And Cassino, 11-30 May 1944.
February 1944: After heavy fighting and heavy losses on both sides, the Germans managed to recapture Aprilia on 9 February.
February 1944: U.S. operations At Anzio And Cassino, 11-30 May 1944.
1.2.1.2.Spring 1945 offensive in Italy
Was the final Allied attack during the Italian Campaign in the final stages of the Second World War.
April 1945: Allied spring offensive in northern Italy (April-May 1945).
April 1945: Battle of Bologna. The city is liberated by Allied forces.
April 1945: US armored forces headed for Milan on 29 April.
April 1945: In the Truscott sector, La Spezia and Genoa were reached by allied troops.
May 1945: The surrender of Caserta was the formal and final act which sanctioned the end of the Italian campaign and the definitive defeat of the Nazi-fascist forces in the peninsula during the Second World War. The act was signed by Representatives of
German General Vietinghoff and became operational starting from 2 May.
May 1945: Allied spring offensive in northern Italy (April-May 1945).
1.2.2.War in the German Operational Zones of northern Italy
Were the events in the operational zones created by Germany in northern Italy during World War II.
1.2.3.Four Days of Naples
Was an uprising in Naples, Italy, against Nazi German occupation forces from September 27 to September 30, 1943, immediately prior to the arrival of Allied forces in the city.
Disestablishment
January 1945: The Porto Viro cut was a major hydraulic project carried out in the Po Delta by the Republic of Venice, begun in 1600, and completed in 1604. From 1200 to 1600 alluvial soils advanced 25 meters a year; 70 in the 16th and 17th centuries. If before 1600 the Delta expanded by about 53 hectares a year, from 1604 to 1840 it passed to 135 hectares a year. The formation of new territories continued further. In the 19th century, with the introduction of steam pumps, large reclamation works were carried out which, accompanied by the construction of imposing embankments, definitively subtracted large tracts of land from the marsh.
January 1945: Allied operations in the Colmar Pocket (January-February 1945).
April 1945: Allied spring offensive in northern Italy (April-May 1945).
April 1945: Battle of Bologna. The city is liberated by Allied forces.
April 1945: US armored forces headed for Milan on 29 April.
April 1945: In the Truscott sector, La Spezia and Genoa were reached by allied troops.
May 1945: Allied spring offensive in northern Italy (April-May 1945).
May 1945: The surrender of Caserta was the formal and final act which sanctioned the end of the Italian campaign and the definitive defeat of the Nazi-fascist forces in the peninsula during the Second World War. The act was signed by Representatives of
German General Vietinghoff and became operational starting from 2 May.
Selected Sources
Allied Offensives In Italy, 5 June- 31 December 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope51.jpg
Delta del Po - Storia, retrieved November, 11th, 2020 on https://web.archive.org/web/20140505001813/http://www.atuttascuola.it/contributi/scienze/delta_del_po6.htm
Operations At Anzio And Cassino, 11-30 May 1944 United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope50.jpg
Operations At Anzio And Cassino, 11-30 May 1944. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope50.jpg
Preti, V. (1997) Martin Mistère e i segreti del Po (CD-ROM), Leonardo Studio, Italy, animation of the evolution of Po delta
Rome-Arno 1944. U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/brochures/romar/72-20.htm
U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/brochures/ardennes/p49(map).jpg
U.S. Army Center of Military History. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://history.army.mil/brochures/po/map2.JPG
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 192
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 196
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 202
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 223
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 233
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 355
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 509
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 523
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.153
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.154
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.155
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.157
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.164
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.269

 Italian Social Republic
Italian Social Republic