This article is about the specific polity Japanese Empire and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
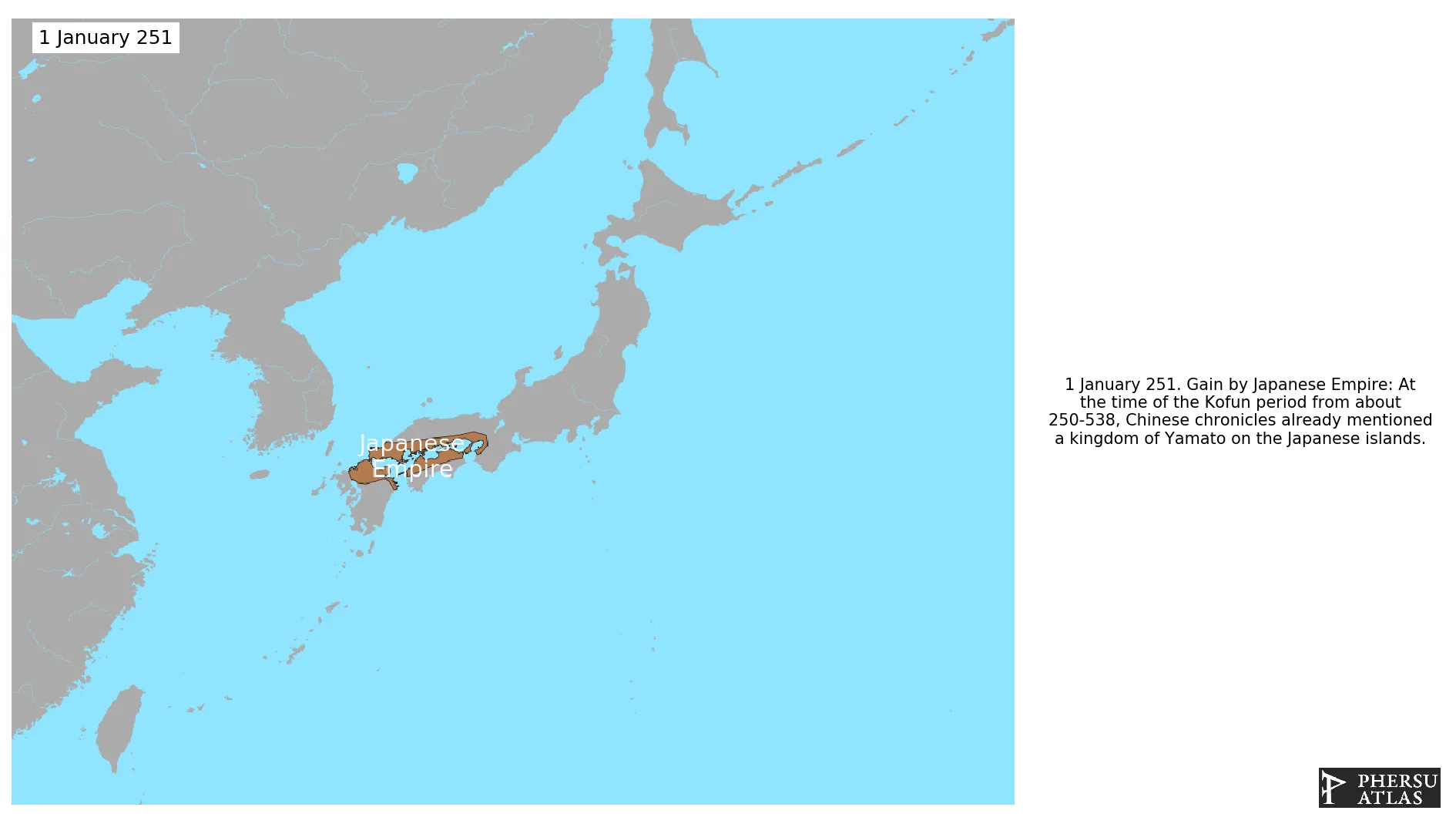
The state of Japan emerged as an ethnically Yamato polity already in 250 AD, during the Kofun period, and over the centuries colonized the entire Japanese Archipelago. From the end of the XIX century Japan became a regional power in South Asia and subjugated large territories, like Korea, Taiwan and Manchuria. During World War II it extended its domain to most of East and Southeast Asia but was defeated by the Allies and occupied by United States until 1952.
Establishment
January 251: At the time of the Kofun period from about 250-538, Chinese chronicles already mentioned a kingdom of Yamato on the Japanese islands.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the slow colonization of Japanese archipelago by the ethnically Yamato Japanese state.
January 701: Expansion of the Japanese Empire in the Japanese Archipelago by 700 AD.
January 1201: Expansion of the Japanese Empire in the Japanese Archipelago by 1200 AD.
January 1458: Koshamain's War: armed struggle between the Ainu and Wajin that took place on the Oshima Peninsula of southern Hokkaidō, Japan, in 1457. Escalating out of a dispute over a sword, Koshamain and his followers sacked twelve forts in southern Ezo, before being overcome by superior forces under Takeda Nobuhiro.
January 1601: Expansion of the Japanese Empire in the Japanese Archipelago by 1600 AD.
January 1673: Full control of the Japanese island of Hokkaido starting with the end of the Shakushain's revolt.
January 1801: Expansion of the Japanese Empire in the Japanese Archipelago by 1800 AD.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
2.1.Mongol Invasion of Japan
Were two unsuccesful campaigns by Kublai Khan of the Yuan dynasty in 1274 and 1281 to conquer the Japanese archipelago .
2.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Japan
Was the first Mongol invasion of the Japanese Archipelago.
November 1274: The Yuan invasion force set off from Korea on 2 November. Two days later they began landing on Tsushima Island.
November 1274: The Yuan Dynasty secured control of Tsushima Island.
November 1274: The Yuan fleet departed Tsushima on 13 November and attacked Iki Island. Kagetaka, the governor of Iki, gave a spirited defence with 100 samurai and the local armed populace before falling.
November 1274: In 1274, the Mongolian army, led by Kublai Khan, attacked the base of the Sashi Clan on Hirato Island, Taka Island, and Nokono Island. This was part of the Yuan Dynasty's efforts to expand their territory in Japan.
November 1274: The Yuan fleet crossed the sea and landed in Hakata Bay.
November 1274: The Yuan troops withdrew and took refuge on their ships after only one day of fighting with the Japanese. A typhoon that night, said to be divinely conjured wind, threatened their ships, persuading them to leave Japan and return to Korea.
2.1.2.Second Mongol Invasion of Japan
Was the first Mongol invasion of the Japanese Archipelago.
June 1281: The Eastern Route army set sail first from Korea on 22 May and attacked Tsushima Island on 9 June.
June 1281: Iki Island conquered by Yuan Dynasty.
June 1281: In 1281, during the Mongol invasions of Japan, the Eastern Route army led by Kublai Khan split their forces and attacked Hakata Bay and Nagato Province. The invasion force, unable to land, occupied the islands of Shiga and Noko, furthering their campaign against Japan.
June 1281: The Mongolian army was again defeated by the fierce Japanese attacks on the Islands of Shiga and Noko.
July 1281: In 1281, Ryōzōji Iekiyo, a Japanese samurai, successfully defended Iki Island against the Mongolian army during the Mongol invasions of Japan. This victory forced the Mongolian army to retreat to Hirado Island, marking a significant turning point in the conflict.
July 1281: In 1281, Ryōzōji Iekiyo, a powerful Japanese warrior, successfully repelled the Mongolian army from Iki Island. The Mongolian army retreated to Hirado Island.
August 1281: In 1281, during the Mongol invasions of Japan, the Japanese army, led by samurai generals like Kusunoki Masashige and Sasaki Takatsuna, took advantage of the disarray in the Mongol forces and launched a successful attack on the 100,000 soldiers left without commanders. This decisive move ultimately led to the repulsion of the Mongol forces from Japan.
A civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. A dispute between Hosokawa Katsumoto and Yamana Sōzen escalated into a nationwide civil war involving the Ashikaga shogunate and a number of daimyō in many regions of Japan.
January 1468: The Onin war was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. A dispute between Hosokawa Katsumoto and Yamana Sōzen escalated into a nationwide civil. During the war the two clans were de-facto independent entities.
January 1468: The Ōnin War was a civil war that lasted from 1467 to 1477, during the Muromachi period in Japan. Katsumoto and Yamana Sōzen escalated into a nationwide civil war involving the Ashikaga shogunate and a number of daimyō in many regions of Japan.
January 1478: At the end of the Onin war, Japan was again a united state.
Was a global conflict between the Portuguese Empire and the Dutch Empire. The conflict primarily saw the Dutch companies invading Portuguese colonies in the Americas, Africa, and the East Indies.
4.1.Operations in the Pacific and Indian Oceans
Were the military operations of the Dutch in the Pacific and Indian Oceans during the Dutch-Portuguese War.
January 1640: The 1639 expulsion of the Jesuit order (Sakoku) and subsequently the Portuguese, from Nagasaki, also doomed the economic viability of Macau.
Were a series of military and exploration campaigns where Russia gradually extended into the territories of northeastern Asia.
January 1698: The Tsardom of Russia expands into Kamchatka through the colonization or voluntary entry of Asian tribes and tribal unions.
January 1783: Ainu tribal unions brought to Russian citizenship by 1782.
February 1855: Under the treaty of 1855, the South Kuriles went to Japan.
May 1875: The Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1875) stipulated that Japan cedes to Russia the part of Sakhalin island it then owned in exchange for the group of the Kuril Islands owned by Russia. Japan thus acquired the northern Kuriles.
Was a civil war in Japan fought from 1868 to 1869 between forces of the ruling Tokugawa shogunate and a clique seeking to seize political power in the name of the Imperial Court.
January 1868: The western domains of Satsuma, Chōshū and Tosa (in red) joined forces to defeat the shogunate forces at the Battle of Toba-Fushimi.
February 1868: The Tokugawa-held Osaka Castle was captured by pro-Imperial "Kangun" forces led by Imperial loyalists such as Saigō Takamori and Ōkubo Toshimichi. This event marked a significant turning point in the Boshin War, ultimately leading to the collapse of the Tokugawa shogunate.
March 1868: Battle of Kōshū-Katsunuma.
March 1868: Battle of Hokuetsu.
May 1868: Battle of Utsunomiya Castle.
July 1868: The city of Edo was fully under control of the Imperial Faction in July 1868.
October 1868: Battle of Bonari Pass.
November 1868: Battle of Aizu.
November 1868: Battle of Noheji.
January 1869: Following defeat on Honshū, Enomoto Takeaki fled to Hokkaidō with the remnants of the navy and his handful of French advisers. Together they organized a government, with the objective of establishing an independent island nation dedicated to the development of Hokkaidō. They formally established the Republic of Ezo on the American model, Japan's only ever republic.
June 1869: Battle of Hakodate.
A period (1839-1949) of foregin interventions in China resulting in the occupation, conquest or lease of large territories by foregin countries.
7.1.Sino-Japanese Wars
Were two major wars between China and Japan in the XIX and XX centuries.
7.1.1.First Sino-Japanese War
Was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea.
7.1.1.1.Treaty of Shimonoseki
Was a treaty signed in Shimonoseki, Japan on April 17, 1895, between the Empire of Japan and Qing China, ending the First Sino-Japanese War.
April 1895: They Qings ceded the Liaodong Peninsula, Taiwan and Penghu Islands to Japan.
7.2.Japanese invasion of Taiwan (1895)
After the First Sino-Japanese War, Qing China had officially ceded the island of Taiwan to Japan. However, the people of Taiwan led by Chiu Feng-chia proclaimed an independent Republic, which caused the Japanese invasion, and ultimately its annexion, by Taiwan.
May 1895: The Treaty of Shimonoseki was signed on 17 April 1895, and contained a clause requiring the cession of Taiwan and the Pescadores. When the news of the treaty's contents reached Taiwan, a number of notables from central Taiwan led by Chiu Feng-chia decided to resist the transfer of Taiwan to Japanese rule. On 23 May, these men proclaimed the establishment of a free and democratic Republic of Formosa.
May 1895: The first troops of the Imperial Guards Division went ashore on the northern coast of Taiwan at Samtiao Point near the village of Audi.
June 1895: The first major engagement in 1895 at Sui-hong (Ruifang) involved the Japanese Empire and the Chinese forces led by General Ye Zhichao. The defending Chinese forces were ultimately defeated in this battle, leading to the territory falling under Japanese control.
June 1895: The Japanese captured the port city of Keelung.
June 1895: The first Japanese troops entered Taipei at dawn.
June 1895: In 1895, during the First Sino-Japanese War, 18 Japanese cavalry troopers led by General Goro Shiba advanced northwards from Taipei and occupied Tamsui, a strategic port town in northern Taiwan.
June 1895: The Japanese captured Hsinchu with little trouble.
August 1895: The Japanese columns were led by General Katsura Taro and General Nogi Maresuke. The resistance in Beipu was part of the wider conflict known as the Japanese invasion of Taiwan, which aimed to bring the island under Japanese control.
August 1895: During the First Sino-Japanese War, the Japanese Empire, led by General Yamagata Aritomo, fought against Chinese insurgents in a significant battle on 8 and 9 August 1895 to capture the heights of Cha-pi-shan.
August 1895: On 11 August the Japanese occupied Aulang.
August 1895: On 14 August the Japanese entered Miaoli county.
August 1895: Japanese occupation of the large village of Koloton.
August 1895: The Japanese fought all day to clear the insurgents from their line of advance, but the village was not completely cleared until the morning of 26 August.
August 1895: Battle of Baguashan.
September 1895: Talibu was securely occupied by the Japanese.
October 1895: Japanese at Yunlin.
October 1895: A Japanese division fought the second-largest battle of the Taiwan campaign, the Battle of Chiayi.
October 1895: The Japanese 17th Infantry Regiments landed at Pa-te-chui.
October 1895: In 1895, during the First Sino-Japanese War, 5,460 troops under the command of Prince Fushimi Sadanaru of the Japanese Empire landed at Po-te-chui in Budai.
October 1895: The larger task force, 6,330 troops under the command of Lieutenant-General Nogi Maresuke, landed at Pang-liau (Fangliao).
October 1895: Battle of Chiatung.
October 1895: Engagement between Japanese and Taiwanese forces near Kiu-sui-kei on 16 October.
October 1895: Battle to capture the fortified village of Shau-lan.
October 1895: The Japanese reached the village of Ji-chang-hang, only a few miles south of Tainan.
October 1895: Tainan capitulated to the Japanese on 21 October.
Was a war between the Japanese Empire and the Russian Empire over the control of Manchuria and Korea.
8.1.Treaty of Portsmouth
The Treaty of Portsmouth formally ended the 1904-05 Russo-Japanese War. Manchuria was given back to Qing China. The southern portion of Sakhalin island was gained by Japan.
September 1905: The Treaty of Portsmouth formally ended the 1904-05 Russo-Japanese War. Russia had to cede the south of the island of Sakhalin to Japan. Japanese forces evacuated the remaining occupied territories of Russia.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
9.1.World War II (Asia & Pacific)
Was the East Asian, South Asian and Pacific theatre of World War II.
9.1.1.Volcano and Ryukyu Islands campaign
Was an Allied military campaign in the Volcano Islands and Ryukyu Islands during World War II.
March 1945: After a final attack by Japanese forces, Iwo Jima is captured and occupied. At 08:00 of 26 March 1945 American General Chaney assumes title of Island Commander.
June 1945: U.S. Tenth Army completes capture of Okinawa.
9.1.2.Soviet-Japanese War
Was a conflict during World War II that started when Soviet forces invaded the Japanese puppet state of Manchukuo.
9.1.2.1.Invasion of South Sakhalin
Was the Soviet invasion of the Japanese portion of Sakhalin Island during World War II.
August 1945: Keton conquered by russia.
August 1945: Toro conquered by russia.
August 1945: Maoka conquered by russia.
August 1945: Tayohara conquered by russia.
August 1945: Otomari conquered by USSR.
9.1.2.2.Seishin Operation
Was an amphibious assault on northern Korea between 13-17 August 1945, carried out by the forces of the Soviet Union.
August 1945: The Soviet 13th Naval Infantry brigade (in total 181 men under command of Colonel A. Z. Denisin) entered the city of Chongjin.
9.1.2.3.Invasion of the Kuril Islands
Was the World War II Soviet military operation to capture the Kuril Islands from Japan in 1945.
August 1945: Shimushu conquered by russia.
August 1945: Paramushiru conquered by russia.
August 1945: Matsuwa conquered by russia.
August 1945: Etorufu conquered by russia.
August 1945: Uruppu conquered by russia.
September 1945: Kunashiri conquered by russia.
September 1945: Shikotan conquered by russia.
9.1.3.Japanese Surrender (World War II)
Were the evacuation of the Japanese forces from occupied territories after the formal surrender of the Empire of Japan.
August 1945: After the dropping of Atomic Bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan accepts the Allied unconditional surrender terms (14 August 1945). The Japanese archipelago was effectively placed under the authority of the Supreme Commander of the Allied Powers.
August 1945: Japanese Taiwan and the Spratly Islands are placed under the authority of China.
February 1946: After World War II, the Soviet Union gained control of the southern part of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands from Japan. This territorial transfer was confirmed in the Treaty of San Francisco in 1951.
Was a series of withdrawals from territories occupied by the Allies during World War II in the aftermath of the war.
10.1.Division of Korea between USA and URSS
Was the occupation and subsequent partition of Japanese-held Korea by the USSR and the USA.
August 1945: USSR declares war on Japan on 8 August. Some days after the declaration, Soviet troops move into Korea.
September 1945: US Lieutenant General John R. Hodge arrived in Incheon to accept the Japanese surrender south of the 38th Parallel.
January 301: Nakoku conquered by Japanese Empire.
January 401: Kibi was eventually annexed by the Japanese Empire in 400.
January 1489: Kaga ikki was a theocratic feudal confederacy that emerged in Kaga Province. The Kaga ikki was a faction of the Ikkō-ikki, mobs of peasant farmers, monks, priests, and jizamurai.
January 1551: In 1550, the Portuguese established a trading post in Hirado, Japan.
January 1562: The Portuguese trading post in Hirado operated from 1550 to 1561.
January 1572: In 1571 a Portuguese trading post is established at Nagasaki.
January 1583: Kaga ikki is overrun by the forces of Oda Nobunaga in a series of campaigns lasting from 1573 to 1582.
September 1609: Dutch factory established at Hirado by the Dutch East India Company (VOC). The factory was subordinated to Java.
July 1613: In June 1613, the English East India Company established a trading post in Hirado, Japan.
January 1624: The English East India Company established a trading post at Hirado in June 1613, which operated until December 1623.
January 1637: Portuguese trading post established in Deshima.
January 1640: In 1639 the Shogun exiles the Portuguese from Japan.
June 1641: In 1641, the Dutch East India Company moved ist Japanese factory from Hirado to Deshima Island in the Nagasaki Bay.
January 1854: Japanese colonists began moving to the Bonin Islands and Nanpō Islands in 1853 and Japan claimed the islands in 1861, annexing them in 1891 as part of Tokyo Prefecture.
February 1860: Deshima is abandoned by the Dutch.
January 1873: In 1872, Emperor Meiji unilaterally declared the Ryukyu Kingdom annexed to Japan.
January 1890: The Volcano Islands were uninhabited until 1889 when the two northern islands were settled by Japanese settlers from the Izu Islands. They were officially annexed by Japan in 1891.
January 1908: Pratas Island was occupied by Japan in 1907.
January 1910: In 1909 Japan left Pratas island.
August 1910: In 1910 Korea was fully annexed by the Japanese Empire.
January 1940: And from 1939 to 1945 the Pratas Islands were occupied by Japan.
Disestablishment
February 1946: After World War II, the Soviet Union gained control of the southern part of Sakhalin and the Kuril Islands from Japan. This territorial transfer was confirmed in the Treaty of San Francisco in 1951.
Selected Sources
La conquête de l'archipel par les Japonais, larousse.fr. Retrieved on February 16th, 2021 on https://www.larousse.fr/encyclopedie/images/La_conqu%C3%AAte_de_larchipel_par_les_Japonais/1011363
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.548
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p.551
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp. 455-456
応仁の乱(読み)おうにんのらん. Koto Bank. Retrieved on 5 April on https://kotobank.jp/word/応仁の乱-38826
.svg (1).png.webp)
 Japanese Empire
Japanese Empire