If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a sultanate established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. It later expanded into the Levant and Arabia.
Establishment
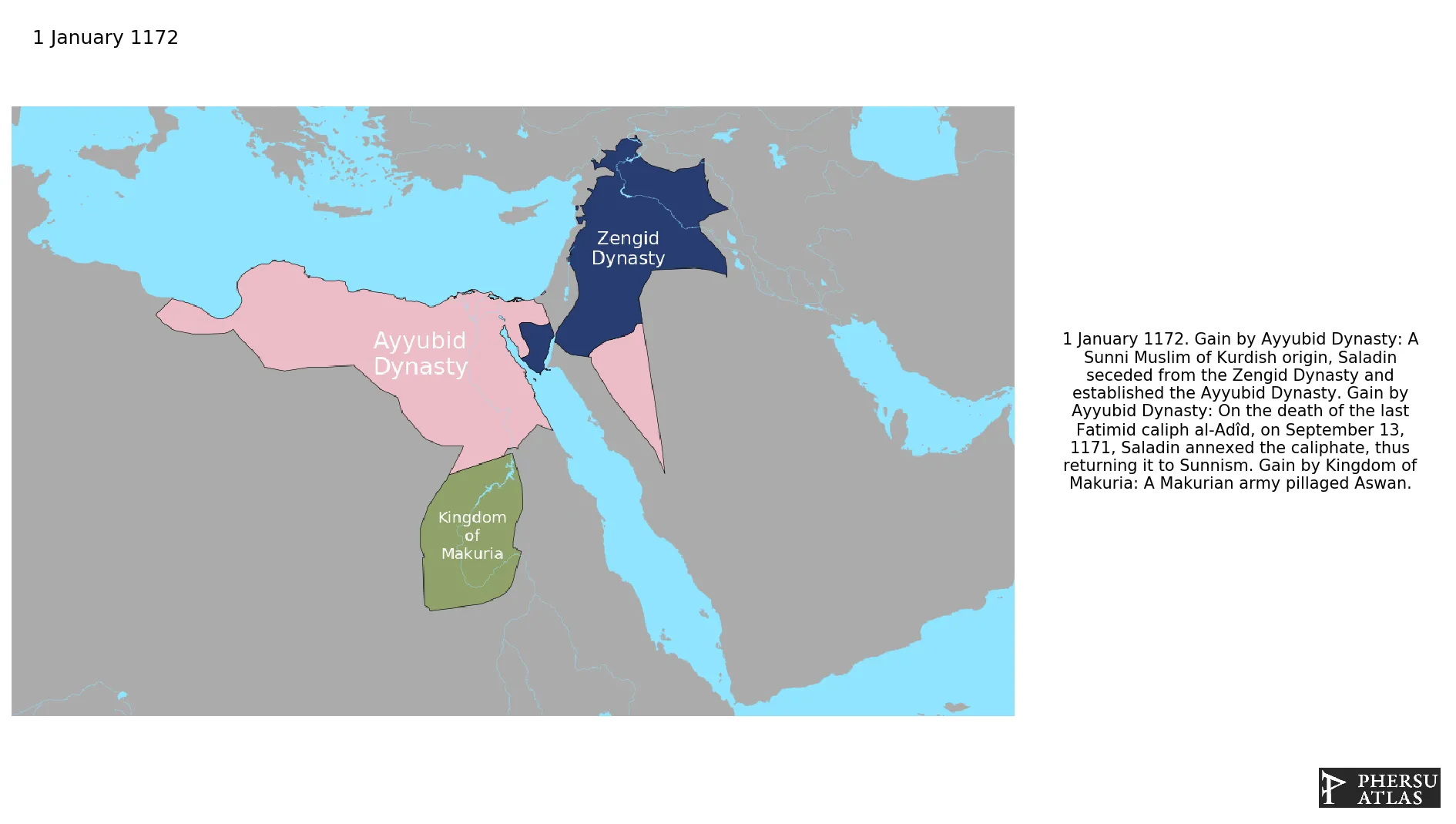
January 1172: A Makurian army pillaged Aswan.
January 1172: A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladin seceded from the Zengid Dynasty and established the Ayyubid Dynasty.
January 1172: On the death of the last Fatimid caliph al-Adîd, on September 13, 1171, Saladin annexed the caliphate, thus returning it to Sunnism.
February 1172: The Makurians leave Aswan.
November 1172: In late 1172, Aswan was besieged by former Fatimid soldiers from Nubia and the governor of the city, Kanz al-Dawla (a former Fatimid loyalist) requested reinforcements from Saladin who complied. The reinforcements had come after the Nubians had already departed Aswan, but Ayyubid forces led by Turan-Shah advanced and conquered northern Nubia after capturing the town of Ibrim.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the Medieval period. The best known of these military expeditions are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291.
1.1.Battle of Marj Ayyun
Was a battle between the Christian crusaders of the Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Ayyubids.
June 1179: Marjayoun is conquered by Ayyubid troops led by Saladin against the Christians.
1.2.Siege of Jacob's Ford
A victory of the Muslim Sultan Saladin over the Christian King of Jerusalem, Baldwin IV.
August 1179: A victory of the Muslim sultan Saladin over the Christian King of Jerusalem, Baldwin IV, resulted in the conquest of Jacob's Ford.
1.3.Battle of Cresson
Was a small battle between Frankish and Ayyubid forces on 1 May 1187.
May 1187: Battle of Cresson: Muzzafar al-Din annihilates an army of Hospitallers and Templars.
1.4.Battle of Hattin
Was a battle between the Christian Crusader states and the Ayyubid Sultan Saladin.
September 1187: After the Battle of Hattin, 52 towns and fortifications were captured by Saladin's forces. By mid-September, Saladin had taken Acre, Nablus, Jaffa, Toron, Sidon, Beirut, and Ascalon.
September 1187: The Siege of Jerusalem was a siege on the city of Jerusalem that lasted from September 20 to October 2, 1187, when Balian of Ibelin surrendered the city to Saladin.
October 1187: The Siege of Jerusalem was a siege on the city of Jerusalem that lasted from September 20 to October 2, 1187, when Balian of Ibelin surrendered the city to Saladin.
November 1187: Tyre was saved by the arrival of Conrad of Montferrat, resulting in Saladin's siege of Tyre.
January 1188: The Siege of Tyre ended on January 1, 1188.
1.5.Siege of Safed (1188)
Was part of Saladin's invasion of the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
January 1189: Siege of Safed (1188).
1.6.Third Crusade
Was an attempt led by three European monarchs of Western Christianity to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by the Ayyubid sultan Saladin in 1187.
August 1189: Siege of Acre (1189-1191).
July 1191: Siege of Acre (1189-1191).
September 1191: Battle of Arsuf: Richard I of England overcomes Saladin.
September 1191: The Crusaders, now under the unified command of Richard I of England, defeated Saladin at the Battle of Arsuf, allowing for the Crusader conquest of Jaffa and much of coastal Palestine.
January 1192: The crusaders seized the abandoned Ascalon.
June 1192: The crusaders march as far as Bayt Nuba near Jerusalem.
July 1192: In July 1192 Saladin, at the head of thousands of men, took Jaffa.
July 1192: The city of Jaffa was reconquered by Richard I of England.
1.6.1.Treaty of Jaffa (1192)
A treaty between the Muslim ruler Saladin and Richard the Lionheart, King of England, restoring the Kingdom of Jerusalem to a coastal strip between Jaffa and Beirut.
September 1192: Richard I of England signed a treaty with Saladin in 1192, restoring the Kingdom of Jerusalem to a coastal strip between Jaffa and Beirut.
1.7.Crusade of 1197
Was a crusade launched by the Hohenstaufen emperor Henry VI.
October 1197: A substantial German army under the command of Archchancellor Conrad of Mainz and Marshal Henry of Kalden landed at Acre. They captured the wealthy and important city of Sidon.
October 1197: Archchancellor Conrad of Mainz and Marshal Henry of Kalden entered Beirut.
1.8.Frankish conquest of Sidon, Lydda and Ramla
Frankish conquest of Sidon, Lydda and Ramla, in the Holy Land.
October 1204: Aimery and Al-Adil conclude a six-year truce. The Franks take full control of Sidon, Lydda and Ramla.
1.9.Fifth Crusade
Was a Crusade initiated by Pope Honorius III. The military actions took place in Palestine and Egypt.
December 1217: The crusaders capture Beisan.
August 1218: In 1218, the fortress of Damietta in the Nile Delta was besieged by the Crusaders. After two failed attempts, the fortress eventually capitulated on 25 August.
January 1222: Al-Kamil forced the Crusaders to retreat from Damietta and Egypt altogether.
1.10.Sixth Crusade
Was a military expedition to recapture Jerusalem and the rest of the Holy Land. The diplomatic maneuvering of the Holy Roman Emperor and King of Sicily, Frederick II, resulted in the Kingdom of Jerusalem regaining some control over Jerusalem.
February 1229: Even with the military orders on board, Frederick of Sicily's force was a mere shadow of the army that had amassed when the crusade had originally been called. He realised that his only hope of success in the Holy Land was to negotiate for the surrender of Jerusalem as he lacked the manpower to engage the Ayyubid sultanate in battle. He hoped that a token show of force, a threatening march down the coast, would be enough to convince al-Kamil, the sultan of Egypt, to honor a proposed agreement that had been negotiated some years earlier, prior to the death of al-Muazzam, the governor of Damascus. The Egyptian sultan, occupied with the suppression of rebellious forces in Syria, agreed to cede Jerusalem to the Franks, along with a narrow corridor to the coast. In addition, Frederick received Nazareth, Sidon, Jaffa, and Bethlehem.
1.11.Barons' Crusade
Was a crusade to the Holy Land that, in territorial terms, was the most successful crusade since the First Crusade.
December 1239: An-Nasir Dawud of Transjordan, whose caravan had been seized by Peter, marched on Jerusalem, which was largely undefended. After a month of being holed up in the Tower of David, the garrison of the citadel surrendered to Dawud on 7 December.
March 1241: The Ayyubid signed a treaty with the crusaders. Galilee and the hinterland of Jaffa were restored to the Kingdom of Jerusalem which reaches its greatest territorial extent after 1187.
1.12.Siege of Jerusalem (1244)
The 1244 Siege of Jerusalem took place after the Sixth Crusade, when roaming Khwarazmians clans conquered the city on July 15, 1244.
July 1244: The 1244 Siege of Jerusalem took place after the Sixth Crusade, when roaming Khwarazmians clans conquered the city on July 15, 1244.
1.13.Ayyubid campaign against the crusaders (1247)
Was a military campaign of the Ayyubids that led to the conquest of important cities controlled by the Crusader states, like Ascalon.
June 1247: Ayyubids occupies Tiberias.
June 1247: Mount Tabor and Belvoir surrendered to Ayyub's troops.
October 1247: In 1247, the Ayyubid Dynasty, led by the Egyptian sultan As-Salih Ayyub, captured the city of Ascalon from the Crusaders.
1.14.Seventh Crusade
Was a Crusade led by Louis IX of France against the Ayyubids of Egypt.
June 1249: Damietta was taken by the French with little resistance from the Egyptians.
Georgia's king Tamar the Great invaded and conquered the cities of Tabriz, Ardabil, Khoy, Qazvin.
January 1208: Georgian King Tamar the Great invaded and conquered the cities of Tabriz, Ardabil, Khoy, Qazvin.
January 1209: Georgian King Tamar the Great invaded and conquered the cities of Tabriz, Ardabil, Khoy, Qazvin.
January 1210: Georgian King Tamar the Great invaded and conquered the cities of Tabriz, Ardabil, Khoy, Qazvin.
January 1211: Georgian King Tamar the Great invaded and conquered the cities of Tabriz, Ardabil, Khoy, Qazvin.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
January 1259: In 1258, the Kesun area was incorporated into the Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia, which was a Christian state established by Armenian refugees fleeing the Seljuk invasion.
January 1259: The Ayyubids lost Diyar Bakr to the Mongols.
3.1.Mongol-Mamluk Wars
Were a series of wars between the Mongols and the Muslim Dynasties of the Ayyubids and Mamluks.
January 1260: The Mongols besieged Aleppo from 18 January to 24 January 1260.
March 1260: The Christian Mongol general Kitbugha captured Damascus.
March 1260: The last Ayyubid ruler, al-Nāṣir Yūsuf, was captured by the Mongols near Gaza that same year.
January 1174: Tūrānshāh arrived in Yemen and subdued the country. The rule of the Sulaymanids was thus effectively ended.
May 1174: The Ayyubid troops quickly overran the bulk of Yemen and took Zabid.
June 1174: When the Ayyubids conquered Aden, the rule of the Zurayids ended.
September 1174: When the Ayyubids reached the outskirts of San'a, Ali bin Hatim fled to a mountain fortress, leaving San'a to be captured in August 1174. This ended the rule of Fatimid-affiliated dynasties in San'a.
November 1174: Saladin set out to conquer Syria from the Zengids, and on November 23 he was welcomed in Damascus by the governor of the city.
January 1175: In 1174, Sharaf al-Din Qaraqush, a commander under al-Muzaffar Umar, conquered Tripoli from the Normans.
January 1175: The Banu Kanz entered into conflict with the Ayyubids in 1174, during which they were defeated and forced to migrate southward into northern Nubia.
January 1176: Hama and Homs conquered by Ayyubid Dynasty.
January 1176: The Ayyubid garrison in Ibrim withdrew to Egypt in 1175, leaving the are to Nubian kings.
June 1176: The Ayyubids proceeded to conquer other Syrian cities in the north, namely Ma'arat al-Numan, A'zaz, Buza'a, and Manbij, but failed to capture Aleppo.
January 1182: Kyrrhos and Gaziantep (Ayntab) area conquered by Ayyubid Dynasty.
January 1183: Marash Area conquered by Ayyubid Dynasty.
January 1184: Saladin conquered Aleppo, ending Zengid rule in Syria.
July 1187: The Crusader stronghold of Acre was captured by Saladin.
July 1187: Ayyubid brigades took Haifa, Caesarea, Sebastia and Nablus.
July 1187: In 1187, the Ayyubid Dynasty, led by Al-Adil, conquered the cities of Mirabel and Jaffa.
July 1187: Saladin received the surrender of Sarepta, Sidon, Beirut, and Jableh.
September 1187: In August, the Ayyubids conquered Ramla, Darum, Gaza, Bayt Jibrin, and Latrun.
September 1187: Ascalon conquered by Ayyubid Dynasty.
September 1187: Saladin captures Jaffa, Arsuf, Caesarea, Haifa, Sidon and Ascalon.
November 1187: Karak and Mont Real in Transjordan soon fell, followed by Safad in the northeastern Galilee. By the end of 1187 the Ayyubids were in control of virtually the entire Crusader kingdom in the Levant with the exception of Tyre.
January 1188: On 1 January 1188, Saladin agreed to withdraw from Tripoli.
December 1188: Saladin's troops capture Kerak.
January 1189: The Ayyubid wrested control of Kairouan from the Almohads in 1188.
January 1189: Belvoir surrenders to Saladin's troops.
June 1189: Saladin's troops capture Montreal. Only Tyre and Belfort remain under Frankish rule in the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
January 1191: Sharaf al-Din Qaraqush was an Armenian mamluk in the service of the Ayyubid prince al-Muzaffar, who engaged in a series of campaigns of conquest in Tripolitania.
January 1193: From 1192 the Ayyubids ruled only over the town of Erzen and its surroundings.
September 1197: Al-Adil captures Jaffa.
November 1197: German and Frank troops seized Sidon and Beirut.
June 1198: A new truce with Ayyubid Al-Adil, allowed the Kingdom of Jerusalem to retain Jaffa.
January 1202: In 1201 the city and the province of Erzurum were conquered by the Seljuk sultan Süleymanshah II.
January 1205: Kyrrhos and Gaziantep (Ayntab) area conquered by Armenian Kingdom of Cilicia.
January 1207: Kyrrhos and Gaziantep (Ayntab) area conquered by Sultanate of Rum.
January 1208: Jochi subjugated the Siberian forest people, the Uriankhai, the Oirats, Barga, Khakas, Buryats, Tuvans, Khori-Tumed, and Kyrgyz
January 1212: Sharaf al-Din Qaraqush, who engaged in a series of campaigns of conquest in Tripolitania and Ifriqiya in the service of the Ayyubids, was defeated and executed by the Almohads.
January 1227: In 1226, the Khwarazmian Empire, led by Jalal ad-Din Mingburnu, clashed with the Ayyubids and captured the town of Ahlat in the Armenian highlands. This victory further expanded the empire's territory in the region.
January 1233: The Artuqids of Hasankeyf become vassals of the Ayyubids.
January 1233: A Kurdish emirate centered around Hasankeyf and ruled by descendants of the Ayyubid dynasty.
January 1236: The Kurdish Ayyubids had held power in most of Yemen since deposing the Zurayids 1173. The last of the line, al-Malik al-Mas'ud, left Yemen for Syria in 1229 and entrusted governance to an ambitious member of his own mercenary force. This was Umar bin Ali who nominally acknowledged the Ayyubids of Egypt during his first years in power. However, he proclaimed himself ruler in his own right in 1235.
May 1250: The Bahri Mamluks revolted against the sultan and killed him in April 1250. Aybak married Shajar al-Durr and subsequently took over the government in Egypt in the name of al-Ashraf II who became sultan, but only nominally.
May 1250: A group of disgruntled Salihi officers had Turanshah assassinated at his camp in Fariskur.
January 1251: The Zangids of Jazirah submitted to the Ayyubid Dynasty.
May 1253: In April 1253, a treaty was signed whereby the Mamluks would retain control over all of Egypt and Palestine up to, but not including, Nablus, while an-Nasir Yusuf would be confirmed as the ruler of Muslim Syria.
Disestablishment
January 1260: The Mongols besieged Aleppo from 18 January to 24 January 1260.
March 1260: The Christian Mongol general Kitbugha captured Damascus.
March 1260: The last Ayyubid ruler, al-Nāṣir Yūsuf, was captured by the Mongols near Gaza that same year.
Selected Sources
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.115

 Ayyubid Dynasty
Ayyubid Dynasty