This article is about the specific polity Confederate States of America and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an unrecognized Republic in the Southern United States that seceded from the United States in 1861. Its secession started the American Civil War which ended with the victory of the Union, and therefore with the reconquest of the seceded territories by the United States.
Establishment
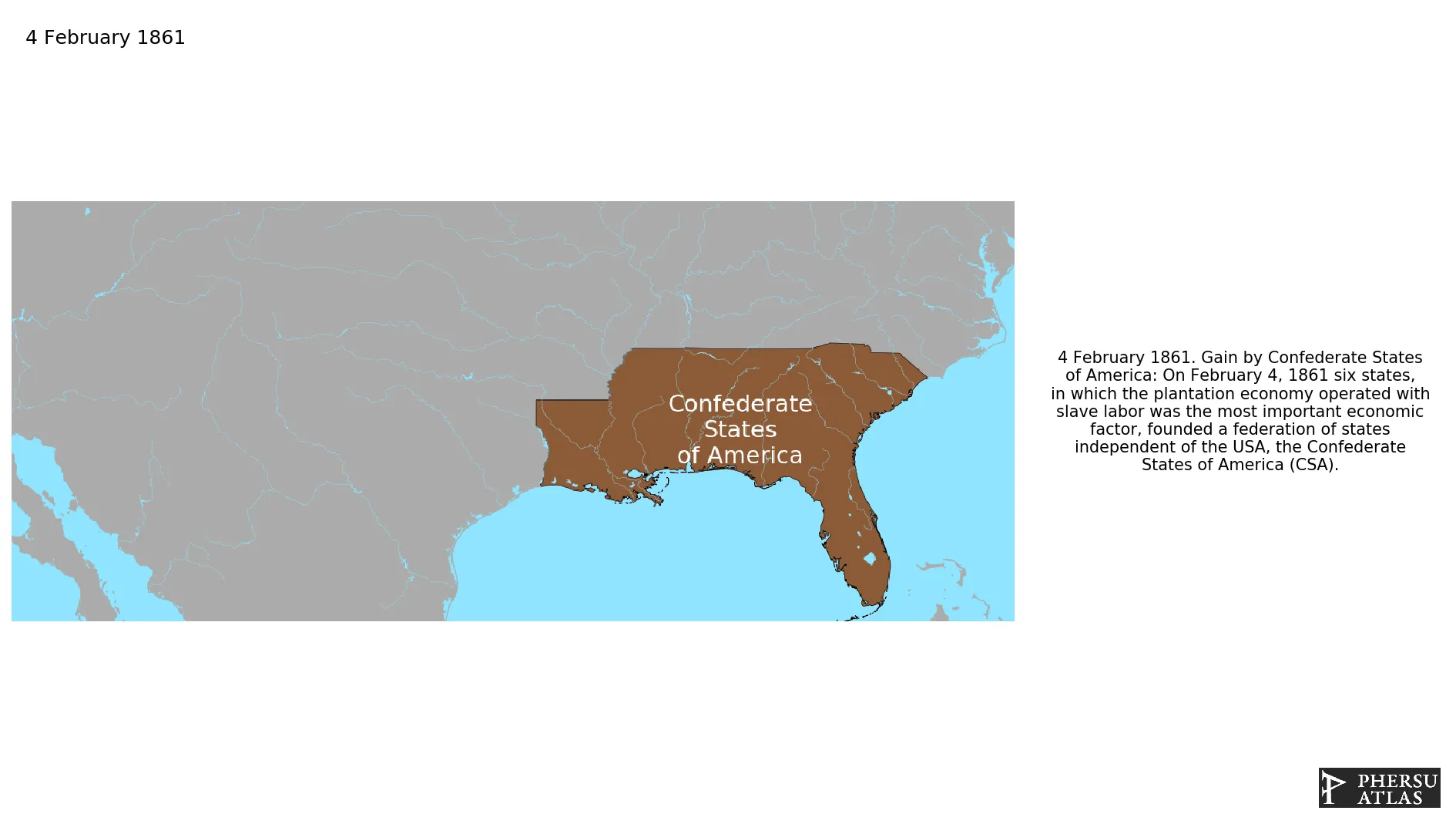
February 1861: On February 4, 1861 six states, in which the plantation economy operated with slave labor was the most important economic factor, founded a federation of states independent of the USA, the Confederate States of America (CSA).
March 1861: Texas proclaimed its secession from the Union and was admitted to the Confederate States.
May 1861: Virginia was admitted to the Confederate States.
May 1861: Arkansas was admitted to the Confederate States.
May 1861: North Carolina was admitted to the Confederate States.
June 1861: Battle of Philippi (West Virginia). Union forces rout a small Confederate detachment in Western Virginia.
July 1861: Battle of Hoke's Run. Robert Patterson defeats Jackson's Confederates but fails to capitalize on his victory.
July 1861: Tennessee was admitted to the Confederate States.
July 1861: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Rich Mountain.
July 1861: Battle of Corrick's Ford: Control of western Virginia was now firmly in Union hands and it stayed that way for the rest of the war.
July 1861: First Battle of Mesilla. Confederate victory secures the southern part of the New Mexico Territory for the CSA.
July 1861: Confederate forces from Texas advance into New Mexico. Federal forces abandon Fort Fillmore.
August 1861: Arizona was officially proclaimed a territory on August 1, 1861, following the Confederate victory at the Battle of Mesilla.
August 1861: Battle of Kessler's Cross Lanes. Confederates under John B. Floyd surprise and defeat Union forces under Erastus B. Tyler.
August 1861: Battle of Hatteras Inlet Batteries: Two forts on the Outer Banks (Fort Clark and Fort Hatteras) had been built by the Confederates. The Union retained both forts.
September 1861: Confederate General Leonidas Polk occupied Columbus.
September 1861: Battle of Carnifex Ferry. Union victory. Confederates withdraw by night after several hours of fighting.
September 1861: Battle of Barbourville. Onfederate Brigadier General Zollicoffer raided a Federal recruitment camp and brought a counter-thrust.
October 1861: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Greenbrier River. Confederates withdraw after inconclusive battle.
October 1861: Battle of Cockle Creek. Union victory.
October 1861: Santa Rosa Island (Florida) is occupied by the union.
October 1861: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Camp Wildcat. Confederates chased from Cumberland Gap.
October 1861: A splinter government in Neosho, Missouri, declared the secession of the state from the United States.
November 1861: Battle of Port Royal. Union fleet under S. F. Du Pont capture Confederate forts at Hilton Head, South Carolina.
November 1861: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Ivy Mountain.Union forces routed Confederate forces.
November 1861: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Santa Rosa Island. Union forces repel Confederate attempt to capture island.
November 1861: Battle of Round Mountain. Opothleyahola's Unionist Creeks and Seminoles defeated near present-day Stillwater.
November 1861: Battle of Camp Wildcat. Confederates chased from Cumberland Gap.
December 1861: In 1861, during the American Civil War, General John E. Wool led 4,000 Federal troops to secure the Eastern Shore of Virginia for the Union. This strategic move helped solidify Union control over the region and prevent Confederate forces from gaining a foothold.
December 1861: Battle of Chusto-Talasah. Opothleyahola's Unionist Creeks and Seminoles defeated near present-day Tulsa.
December 1861: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Ivy Mountain.
December 1861: In 1861, pro-Confederate members of the Kentucky legislature, including Richard Hawes and George W. Johnson, established a separate government in Russellville. This government was recognized by the Confederate States of America during the Civil War.
December 1861: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Rowlett's Station. Union soldiers hold area, but do not launch any counter thrusts. Confederates and Texas Rangers retreat.
December 1861: Skirmish at Blackwater Creek. Union forces under General Pope capture a newly recruited Missouri State Guard regiment.
December 1861: Battle of Dranesville. Union defeats Confederate forces under J.E.B. Stuart.
December 1861: In 1861, the Confederate States of America ratified treaties with the Osage, Seneca, and Shawnee tribes in what is now Oklahoma. The treaties were negotiated by Confederate Commissioner Albert Pike and aimed to secure alliances with Native American tribes during the Civil War.
December 1861: In 1861, the Confederate States ratified treaties with the Cherokee and Seminole tribes, granting them representation in the Confederate Congress. This move aimed to secure the support of Native American tribes during the American Civil War.
December 1861: Battle of Mount Zion Church: The resulting Union victory here and elsewhere in central Missouri ended Confederate recruiting activities in the region and pushed conventional Confederate forces out of the area.
December 1861: The Confederate States ratified treaties with the Choctaw and Chickasaw, granting them a delegate in the Congress of the Confederate States; with the Comanche; with the Creek, granting them a delegate to be shared with the Seminole; and the Quapaw.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a civil war in the United States of America between the central government (Unionists) and the secessionist Confederate States of America that occupied the southern States. The main cause of the war was the different economic system of the northern and southern states: the northern states were industrialized and had abolished slavery, whereas the southern states relied on slavery to run its plantation agriculture based economy. At the end of the war the Union occupied the southern states and slavery was abolished. .
January 1862: Area under Union control by the end of 1861.
July 1862: Arizona was occupied by Union forces led by General James H. Carleton. The territory was officially transferred to the New Mexico Territory.
January 1863: Area under Union control by the end of 1862.
January 1864: Area under Union control by the end of 1863.
January 1865: Area under Union control by the end of 1864.
1.1.Secession Phase
The election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860 caused a wave of southern states secessions in the United States. The secessionist states soon formed an independent country, the Confederate States of America.
1.2.Trans-Mississippi Theatre
Was the theatre of war west of the Mississippi River during the American Civil War.
July 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Camden Point. Union victory.
July 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Fort Smith. Union victory. Federal troops maintain control of western Arkansas
August 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Camden Point.
August 1864: Confederate retreat after the Battle of Fort Smith.
May 1865: Battle of Palmito Ranch. Confederate victory. Last battle in Texas during final phases of the Civil War. Southernmost battle on land in Civil War.
May 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Palmito Ranch.
1.2.1.Missouri Front (American Civil War)
Were a series of battles between the Missouri State Guard and the Union during the American Civil War.
1.2.2.Confederate Arizona
Was the conquest of Arizona by the Confederate Army during the American Civil War.
1.2.3.Trail of Blood on Ice
Was a December 1861 campaign in the American Civil War in which pro-Union Native Americans, led by Upper Creek Chief Opothleyahola, fought their way north from Indian Territory.
1.2.4.New Mexico campaign (American Civil War)
Was the military invasion of New Mexico by Confederate Brigadier General Henry Hopkins Sibley during the American Civil War.
March 1862: The Confederate forces reached Albuquerque.
March 1862: Confederate forces captured Santa Fe on March 13, 1862.
March 1862: Battle of Glorieta Pass. Tactical retreat of Union forces.
April 1862: Battle of Peralta. Union forces defeat the 5th Texas Mounted Volunteers.
1.2.5.Pea Ridge Campaign
Was a battle near Leetown, northeast of Fayetteville, Arkansas during the American Civil War. By defeating the Confederates, the Union forces established Federal control of most of Missouri and northern Arkansas.
March 1862: Battle of Pea Ridge or Elkhorn Tavern: By defeating the Confederates, the Union forces established Federal control of most of Missouri and northern Arkansas.
1.2.6.California Column
Was a military campaign of Union forces started from California to fight against the Confederates in Arizona.
March 1862: The California Column arrives at Stanwix Station.
May 1862: The California Column captures Tucson (1862).
August 1862: The California Column captures Franklin (modern-day El Paso, Texas).
1.2.7.Operations Near Cache River (Arkansas)
Were a series of military operation part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
July 1862: Battle of Cotton Plant. Union victory.
1.2.8.Operations to Blockade the Texas Coast
Were a series of military operations part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
September 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Sabine Pass.
January 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Galveston. Confederate victory.
September 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Sabine Pass. Confederate victory.
October 1863: Union troop retreat after being defeated in the Second Battle of Sabine Pass.
1.2.9.Operations North of Boston Mountains
Were a series of military operations part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
October 1862: Battle of Old Fort Wayne. Confederate forces go into Full retreat under Douglas H. Cooper, with the Union gaining control of the Indian territory.
November 1862: Battle of Clark's Mill. Union force surrenders to larger Confederate force.
November 1862: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Old Fort Wayne.
1.2.10.Vicksburg Campaign
Was a military campaign by the Union to conquer Vicksburg, Mississippi, during the American Civil War.
December 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Chickasaw Bayou. Confederate General John C. Pemberton defeats William Tecumseh Sherman.
January 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Chickasaw Bayou.
May 1863: Battle of Port Gibson. General Grant defeats the Confederates.
May 1863: Battle of Snyder's Bluff. Union feint during Vicksburg Campaign.
May 1863: Battle of Raymond. Failed Confederate attempt to protect Vicksburg from approaching Federals.
May 1863: Battle of Jackson, Mississippi. Union victory.
May 1863: Battle of Champion Hill. Union General Grant defeats Pemberton.
June 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Snyder's Bluff.
June 1863: Battle of Milliken's Bend. In the largest battle fought between Confederate and Black troops, after nearly two days of close combat, the Confederates were defeated in their attempt to raise the siege of Vicksburg.
June 1863: Battle of Lake Providence. Confederates withdraw to Floyd, Louisiana.
July 1863: Siege of Vicksburg: the entire Mississippi area controlled by the union. It cut off the Trans-Mississippi Department (containing the states of Arkansas, Texas and part of Louisiana) from the rest of the Confederate States, effectively splitting the Confederacy in two.
1.2.11.Marmaduke's First Expedition into Missouri
Was a Confederate military campaign in Missouri during the American Civil War.
January 1863: Second Battle of Springfield. Confederates enter town, but are unable to take nearby fort.
February 1863: The Confederates retreated after the Second Battle of Springfield.
1.2.12.Marmaduke's Second Expedition into Missouri
Was a Confederate military campaign in Missouri during the American Civil War.
May 1863: Battle of Chalk Bluff. Confederate victory.
May 1863: Marmaduke suffered considerable casualties and his momentum had been checked, forcing him to abandon his second expedition into Missouri.
1.2.13.Taylor's operations in West Louisiana
Was a Confederate military campaign in western Louisiana during the American Civil War.
June 1863: Battle of LaFourche Crossing. Confederates disengage, and fled to Thibodaux.
June 1863: The Confederate States of America captured Brashear City.
June 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Donaldsonville. Confederate forces failed to take Fort Butler.
July 1863: Battle of Kock's Plantation. Union troops retreat to Fort Butler in Donaldsonville, seized during the Second Battle of Donaldsonville.
July 1863: Confederate troop retreat after the Second Battle of Donaldsonville.
1.2.14.Operations to Control Indian Territory
Were a series of military operations part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War.
July 1863: Battle of Honey Springs. In Indian Territory, two largely Black and American Indian forces meet. Union victory.
February 1864: Battle of Middle Boggy Depot. Union troops massacred Confederate forces as the Confederates burned their encampments.
February 1864: The Confederates retreated 72 km southwest down the Dragoon Trail. The Union advance continued south toward Ft. Washita the next day, but when the expected reinforcements did not arrive Philips' Expedition into Indian Territory stalled on February 15, near old Stonewall.
1.2.15.Quantrill's Raid into Kansas
Was a Confederate raid in Kansas during the American Civil War.
August 1863: Lawrence Massacre.
August 1863: On August 25th, four days after the raid on the city, General Ewing issued his General Order No. 11, in which he ordered the forced evacuation of four Missouri counties along the Kansas border.
1.2.16.Little Rock Campaign
Was a military campaign by the Union to conquer Little Rock, Arkansas, during the American Civil War.
August 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Bayou Meto (Battle of Reed's Bridge). Confederate forces delay the Union advance on Little Rock.
September 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Bayou Meto (Battle of Reed's Bridge).
1.2.17.Red River Campaign
Was a major Union offensive campaign in the Trans-Mississippi theater of the American Civil War.
March 1864: Battle of Fort De Russy. Fort DeRussy fell to the Union and the Red River to Alexandria was open.
April 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Mansfield or Sabine Cross Roads. Banks Union Red River Campaign halted by the Confederates.
April 1864: Battle of Pleasant Hill. Confederate attack fails.
April 1864: Battle of Monett's Ferry. Confederate forces driven back.
May 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Mansfield or Sabine Cross Roads.
May 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Pleasant Hill.
1.2.18.Camden Expedition
Was the final campaign conducted by the Union Army in Arkansas during the Civil War.
April 1864: Battle of Elkin's Ferry. Confederates unable to prevent Union river crossing.
April 1864: Battle of Prairie D'Ane. Union Major General Frederick Steele defeats Sterling Price.
1.2.19.Price's Missouri Expedition
Was a Confederate raid in Arkansas, Missouri, and Kansas during the American Civil War.
September 1864: Battle of Fort Davidson (Battle of Pilot Knob). Union forces detonate their own fort after losing to Confederates.
October 1864: Battle of Glasgow. Union forces surrender.
October 1864: Second Battle of Lexington. Union forces driven out of town.
October 1864: Battle of Little Blue River. Confederate victory.
October 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Independence.
October 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Byram's Ford.
October 1864: Battle of Westport. Union forces win decisive battle to take control of Missouri.
October 1864: Second Battle of Newtonia. Union Major General James G. Blunt defeats Joseph O. Shelby.
1.3.Eastern Theatre (American Civil War)
The eastern theater of the American Civil War consisted of the major military and naval operations in the states of Virginia, West Virginia, Maryland, and Pennsylvania, the District of Columbia, and the coastal fortifications and seaports of North Carolina.
February 1862: Battle of Elizabeth City. Union victory.
February 1862: The town of Edenton in the proximity of Elizabet City (North Carolina) was taken by Union troops without bloodshed.
March 1862: Union general Nathaniel P. Banks occupied Winchester just after Confederate general Stonewall Jackson had withdrawn from the town.
March 1862: Battle of New Bern. Union troops disembark from ships and capture the town.
April 1862: Battle of Fort Macon. Confederate fort surrenders after Union artillery bombardment.
May 1862: Battle of Princeton Court House. Witthdrawal of Union General Jacob Dolson Cox.
June 1862: Although the city of Norfolk was not under attack, it was isolated and increasingly worthless to the Confederate Army. In May, the city was abandoned.
June 1862: Battle of Tranter's Creek. Confederate forces retreat after Colonel Singletary is killed.
June 1862: After suffering a defeat at the Battle of Bull Run in 1862, Union forces under the command of General Irvin McDowell did not pursue the Confederate Army and instead retreated back to their fortifications in Washington.
June 1862: Battle of Gaines' Mill or Chickahominy River. Confederate General Robert E. Lee defeats Union General George B. McClellan.
September 1862: Battle of Charleston. Confederate troops occupy Charleston during Kanawha Valley offensive.
March 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Kelly's Ford.
May 1863: Second Battle of Fredericksburg. Union forces under John Sedgwick defeat Confederate forces left to guard the town by Lee.
May 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Suffolk (Hill's Point). Inconclusive.
May 1863: Battle of Salem Church. Confederate General Lee defeats Sedgwick.
June 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Suffolk (Hill's Point).
July 1863: Battle of Manassas Gap. Indecisive battle by day, Confederates withdraw by night.
August 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Manassas Gap.
October 1863: First Battle of Auburn. Inconclusive.
October 1863: Battle of Bristoe Station. Meade defeats elements of Lee's forces, but Confederates destroy railroad during retreat.
October 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Auburn. Confederates attack Union rearguard, indecisive.
October 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Buckland Mills. Union cavalry caught in ambush, defeated.
November 1863: Second Battle of Rappahannock Station. Union forces surge across river, forcing Lee to retreat.
November 1863: Union troop retreat after the First Battle of Auburn.
November 1863: Union troop retreat after the Second Battle of Auburn.
November 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Buckland Mills.
December 1863: Battle of Mine Run. Meade bombards Lee's Confederates.
January 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Mine Run.
March 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Walkerton. Confederate victory.
April 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Walkerton.
April 1864: Battle of Plymouth. Confederate land forces, supported by naval ram, retake two Union forts near Plymouth, North Carolina.
August 1864: Battle of Smithfield Crossing. Confederate forces routed a small Union detachment, but a Union counterattacked stopped the Confederates; ultimately ending the last engagement in West Virginia of the Civil War.
September 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Smithfield Crossing.
October 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Saltville. Confederates defeat Union Black Cavalry, war crimes committed against captured blacks.
October 1864: Battle of Boydton Plank Road. Union forces take control of road.
November 1864: Union troop retreat after the First Battle of Saltville.
December 1864: Battle of Marion. Union victory.
1.3.1.Western Virginia Campaign
Was a military campaign of Union in the western part of Virginia. The region was conquered and later became the state of West Virginia.
1.3.2.North Carolina coast
Were a series of military operations by the Union in North Carolina during the American Civil War.
February 1862: Battle of Roanoke Island. Union forces under Ambrose E. Burnside capture island from Henry A. Wise
January 1865: Second Battle of Fort Fisher. Union takes fort.
February 1865: Battle of Wilmington (North Carolina). Last Confederate port falls.
1.3.3.Romney Expedition
Was a Confederate raid in Virginia during the American Civil War.
January 1862: Battle of Hancock. Unsuccessful Confederate attack on Maryland town.
February 1862: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Hancock.
1.3.4.Peninsula campaign
Was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March to July 1862 during the American Civil War.
March 1862: Union General George B. McClellan landed his army at Fort Monroe.
April 1862: The IV Corps of Brig. Gen. Erasmus D. Keyes made initial contact with Confederate defensive works at Lee's Mill, an area McClellan expected to move through without resistance.
May 1862: General George B. McClellan’s Army of the Potomac occupies the Yorktown-Warwick River line recently abandoned by Confederate forces.
May 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Williamsburg.
May 1862: Battle of Seven Pines: the union army reached the outskirts of Richmond.
July 1862: After suffering heavy casualties at the Battle of Malvern Hill, General George McClellan ordered the Army of the Potomac to retreat to Harrison's Landing on the James River in Virginia in 1862 during the American Civil War. This move was seen as necessary to regroup and resupply the Union forces.
August 1862: General George B. McClellan received the order to retreat from the Virginia Peninsula in 1862 during the American Civil War.
1.3.5.Jackson's Valley campaign
Was a Confederate campaign through the Shenandoah Valley in Virginia during the American Civil War.
March 1862: First Battle of Kernstown. Union forces defeat Confederates under "Stonewall" Jackson.
May 1862: First Battle of Winchester: Jackson enveloped the right flank of the Union Army under Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks and pursued it as it fled across the Potomac River into Maryland.
1.3.6.Northern Virginia Campaign
Was a series of battles fought in Virginia during August and September 1862 in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.
August 1862: General Stonewall Jackson remained in position until August 12, 1862, when he withdrew to Gordonsville during the American Civil War. This retreat was part of his strategic movements in Virginia against the Union forces.
August 1862: In 1862, during the American Civil War, Union General John Pope withdrew his forces to the Rappahannock River, thwarting Confederate General Robert E. Lee's plans for an offensive. This strategic move led to the Second Battle of Bull Run.
1.3.7.Invasion of Maryland
Was a Confederate campaign in Maryland during the American Civil War.
September 1862: Frederick conquered by Confederate States of America.
September 1862: Battle of Harpers Ferry. Stonewall Jackson captures Union garrison under Dixon S. Miles
September 1862: On September 4 Confederate General Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia
had begun an invasion of the North. Lee hoped to cut key rail lines west and isolate Washington, with Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, as his probable objective. By September 16th Lee's army took position in Sharpsburg, Maryland.
September 1862: Battle of Antietam or Sharpsburg. Union General McClellan ends Lee's first invasion of North, bloodiest single day of the war.
September 1862: Battle of Shepherdstown. Confederate victory.
April 1863: The Chancellorsville Campaign began in 1863 with General Joseph Hooker leading the Union army across the Rappahannock River into Confederate territory in the border regions south to the Rapidan River.
May 1863: Battle of Chancellorsville. Confederate General Lee defeats Hooker's Army of Potomac.
1.3.8.Goldsboro Expedition
Were a series of military operations part of the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.
December 1862: Battle of Kinston. Union forces under John G. Foster defeat Confederates under Nathan Evans.
December 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of White Hall.
December 1862: Battle of Goldsboro Bridge. General Foster defeats Confederates and destroys the bridge.
January 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of White Hall.
1.3.9.Gettysburg Campaign
Was a military invasion of Pennsylvania by the main Confederate army under General Robert E. Lee in summer 1863.
June 1863: On June 26, elements of Confederate Maj. Gen. Jubal Early's division of Ewell's Corps occupied the town of Gettysburg after chasing off newly raised Pennsylvania militia in a series of minor skirmishes.
June 1863: Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart's cavalry reached Fairfax Court House in 1863. They were delayed by a small battle on June 27, part of the Gettysburg Campaign during the American Civil War.
June 1863: CSA forces occupied Westminster, Maryland.
June 1863: General J.E.B. Stuart and an army of 8,000 Confederate cavalrymen occupied Rockville on June 28, 1863, while on their way to Gettysburg.
June 1863: On June 28, 1863, a Civil War skirmish between Confederate and Union armies took place at Wirghtsville, Pennsylvania.
June 1863: General Jubal Early's Confederate Division occupied York, Pennsylvania. This was significant as York was the largest Northern town to fall to the Confederates during the war.
June 1863: By June 29, Confederate General Lee's army was strung out in an arc from Chambersburg (45 km northwest of Gettysburg) to Carlisle (48 km north of Gettysburg) to near Harrisburg and Wrightsville on the Susquehanna River.
June 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Second Battle of Donaldsonville. Inconclusive.
July 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Carlisle. Inconclusive.
July 1863: Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart led his troops to Carlisle, Pennsylvania in June 1863 during the Gettysburg Campaign. After a brief skirmish and burning the Carlisle Barracks, Stuart retreated to Gettysburg where the decisive Battle of Gettysburg would take place.
July 1863: Battle of Fairfield.Cavalry engagement won by the Confederate army during the Gettysburg Campaign secured the important Hagerstown Road.
July 1863: Battle of Gettysburg: The defeat of his massive infantry assault, Pickett's Charge, caused Lee to order a retreat that began the evening of July 4.
July 1863: Battle of Boonsboro. Indecisive action at rearguard of Lee's retreat.
July 1863: General George Meade led the Union Army of the Potomac, while General Robert E. Lee commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia during the American Civil War. Lee's successful retreat across the Potomac River after the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863 marked a turning point in the war.
July 1863: Battle of Williamsport. Indecisive.
August 1863: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Williamsport.
1.3.10.Operations in North Alabama
Were a series of military operations part of the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War.
February 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Morton's Ford. Inconclusive.
March 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Morton's Ford.
1.3.11.Overland Campaign
A series of battles fought in Virginia during May and June 1864, in the American Civil War.
May 1864: General Ulysses S. Grant's forces crossed the Rapidan River.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of the Wilderness. Grant and Lee meet inconclusively.
May 1864: Battle of Yellow Tavern. Union forces win cavalry battle, Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart is mortally wounded.
May 1864: Battle of Spotsylvania Court House. Grant and Lee meet inconclusively, Grant writes to Halleck "I propose to fight it out on this line if it takes all summer".
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of North Anna. Inconclusive.
May 1864: Battle of Haw's Shop. Union advance.
June 1864: Battle of Cold Harbor. Confederate General Lee repulses Grant.
1.3.12.Bermuda Hundred Campaign
Was a series of battles fought at the town of Bermuda Hundred, outside Richmond, Virginia, during May 1864 in the American Civil War.
May 1864: Battle of Port Walthall Junction. Union forces destroy railroad.
May 1864: Battle of Swift Creek. Union forces damage railroad, but are stopped by Confederate forces.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Chester Station. Union forces under Benjamin Butler pushed back.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Proctor's Creek. Confederate Beauregard defeats Butler.
May 1864: Battle of Ware Bottom Church. Confederate victory.
June 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Swift Creek.
June 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Proctor's Creek.
June 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Ware Bottom Church.
1.3.13.Richmond-Petersburg campaign
Was a series of battles around Petersburg, Virginia, fought from June 9, 1864, to March 25, 1865, during the American Civil War.
June 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Petersburg. Confederate Beauregard defeats Butler.
August 1864: Battle of Globe Tavern. Confederate forces lose control of railroads at Petersburg.
October 1864: Battle of Peebles' Farm. Union victory near Petersburg.
1.3.14.Appomattox Campaign
Were a series of American Civil War battles fought March 29 - April 9, 1865, in Virginia that concluded with the surrender of Confederate General Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia to the forces of the Union Army.
April 1865: Third Battle of Petersburg. Union General Grant defeats Lee.
April 1865: Battle of Sutherland's Station. Union victory.
April 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Amelia Springs. Inconclusive.
April 1865: Battle of Rice's Station. Confederate forces are caught off guard by John Gibbon's forces.
April 1865: Battle of High Bridge. Union forces thwart Lee's attempts to burn bridges and to resupply, Grant proposes that Lee surrender, but he refuses.
April 1865: Battle of Appomattox Court House. Confederate General Lee's forces surrounded. He subsequently surrenders.
1.4.Western Theatre of the American Civil War
The western theater of the American Civil War encompassed major military operations in the states of Alabama, Georgia, Florida, Mississippi, North Carolina, Kentucky, South Carolina and Tennessee, as well as Louisiana east of the Mississippi River.
October 1863: Battle of Wauhatchie. Longstreet defeated by Union forces.
November 1863: Battle of Collierville. Abortive Confederate attack on the town.
April 1864: Battle of Salyersville. Confederates were driven into Salyersville with heavy losses.
May 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Salyersville.
1.4.1.Early Operations in Kentucky
Were the battles in Kentucky in the early phases of the American Civil War.
January 1862: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Rowlett's Station.
1.4.2.Federal Penetration up the Cumberland and Tennessee Rivers
Was a military campaign by the Union during the American Civil War.
February 1862: Battle of Fort Henry: surrender of Fort Henry to Unionist forces. Grant and Foote's gunboats gain control of Tennessee River by defeating Lloyd Tilghman
February 1862: Battle of Fort Donelson. Confederate army under Simon Bolivar Buckner surrenders to Grant, Union gains control of Cumberland River
April 1862: Battle of Shiloh or Pittsburg Landing. Grant and reinforcements under Buell repulse Albert Sidney Johnston and P. G. T. Beauregard. A.S. Johnston is killed.
May 1862: Siege of Corinth. Union forces capture town.
1.4.3.Joint Operations Against New Madrid, Island No. 10, and Memphis
Was a military campaign of Union forces started from California to fight against the Confederates in Arizona.
June 1862: Battle of Memphis. Union forces capture the city.
1.4.4.Kentucky Campaign
Was an American Civil War campaign conducted by the Confederate States Army in Tennessee and Kentucky.
June 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the First Battle of Chattanooga.
August 1862: Battle of Richmond (Kentucky). Edmund Kirby Smith routs Union army under Brig. Gen. William "Bull" Nelson.
August 1862: On August 30, 1862, Lexington (Kentucky) was captured and briefly occupied by Confederate troops.
October 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Perryville or Chaplin Hills.
1.4.5.Iuka and Corinth Operations
Were a series of battles in Iuka and Corinth (Missisippi) during the American Civil War.
September 1862: Battle of Iuka. Union victory.
October 1862: Second Battle of Corinth. Confederate attack fails.
November 1862: Confederate troop retreat after the Second Battle of Corinth.
1.4.6.Stones River Campaign
Were a series of military operations in northern Tennessee during the American Civil War.
December 1862: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Hartsville. Disguised in Union uniforms, Confederates infiltrate and defeat Union forces.
January 1863: Battle of Stones River. Confederate army forced to withdraw after losing 11,739 men.
1.4.7.Middle Tennessee Operations
Were a series of military operations in central Tennessee during the American Civil War.
February 1863: Battle of Dover. Failed Confederate attack on town.
March 1863: The Confederates retreated after the Battle of Dover.
March 1863: Battle of Thompson's Station. Confederate Earl Van Dorn defeats John Coburn
March 1863: Battle of Vaught's Hill. Union forces withstand attack by John Hunt Morgan's Confederates.
March 1863: Battle of Brentwood.
March 1863: Battle of Brentwood. Union force surrenders.
April 1863: Battle of Franklin (1863). Confederates withdraw after rearguard defeat.
April 1863: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Vaught's Hill.
1.4.8.Streight's Raid in Alabama and Georgia
Was a military campaign by the Union in northern Alabama during the American Civil War.
April 1863: Battle of Day's Gap. Union victory.
May 1863: Blountsville conquered by USA.
May 1863: Gadsden conquered by USA.
May 1863: Forrest (Union) surrounded Streight's exhausted men (Confederates) 5 km east of Cedar Bluff, Alabama, and forced their surrender.
1.4.9.Tullahoma campaign
Was a military campaign by the Union that drove the Confederate forces out of central Tennesse during the American Civil War.
June 1863: General Braxton Bragg ordered the Confederate Army to withdraw to Tullahoma on June 27, 1863, during the American Civil War. This strategic move was in response to the advance of Union forces led by General William Rosecrans.
July 1863: The Union forces, led by General Joseph Hooker, launched an attack on the Confederates, resulting in the Battle of Lookout Mountain.
1.4.10.Morgan's Raid in Kentucky, Indiana, and Ohio
Was a Confederate raid in Indiana, Kentucky, Ohio, and West Virginia during the American Civil War.
July 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Tebbs Bend. Union infantry defeats Confederate cavalry.
July 1863: Battle of Lebanon (Kentucky).
July 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Buffington Island. Confederates captured after failing to find a secure retreat.
July 1863: Battle of Salineville: The Union victory shattered John Hunt Morgan's remaining Confederate cavalry and led to his capture later that day. The northernmost battle in the Civil War.
1.4.11.Knoxville campaign
Were a series of military operations in eastern Tennessee during the American Civil War.
September 1863: Battle of the Cumberland Gap (1863).
September 1863: Battle of Blountville. Union forces capture town.
October 1863: Battle of Blue Springs. Confederate forces overrun.
November 1863: Battle of Campbell's Station. Union victory.
1.4.12.Chickamauga campaign
Were a series of military operations in northwestern Georgia during the American Civil War.
September 1863: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Chickamauga. Confederarate victory.
October 1863: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Chickamauga.
1.4.13.Chattanooga campaign
Were a series of military operations in Chattanooga, Tennessee during the American Civil War.
November 1863: Battle of Ringgold Gap: The five hour Battle of Ringgold Gap resulted in the Confederate victory of Major General Patrick R. Cleburne and gave the Army of Tennessee safe passage to retreat through the Ringgold Gap mountain pass.
1.4.14.Operations in Dandridge
Were a series of military operations in Tennesse during the American Civil War.
December 1863: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Mossy Creek. Union victory.
January 1864: Battle of Dandridge. Union forces withdraw.
January 1864: Confederate cavalry forced back.after the Battle of Mossy Creek.
1.4.15.Meridian and Yazoo River expeditions
Was an Union military operation leading ot the capture of Meridian (Mississippi) during the American Civil War.
February 1864: Battle of Meridian. Union General Sherman occupies town.
February 1864: Battle of Okolona. Confederate cavalry, commanded by Maj. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest, routed 7,000 cavalry under the command of Brig. Gen. William Sooy Smith.
March 1864: Union forces elave Yazoo City.
March 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Okolona.
1.4.16.Atlanta campaign
Was a series of battles fought in the Western Theater of the American Civil War throughout northwest Georgia and the area around Atlanta during the summer of 1864.
May 1864: Battle of Rocky Face Ridge. Due to a flanking movement by Union troops under Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman, Confederates led by Gen. Joseph E. Johnston were forced to evacuate their strong position near Atlanta.
May 1864: Battle of Resaca: It ended inconclusively with the Confederate Army retreating.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Adairsville.
May 1864: Battle of New Hope Church. Confederate Hooker's forces defeated.
May 1864: Battle of Pickett's Mill. Unsuccessful attack by Union General Sherman on Johnston.
June 1864: Battle of Dallas (Georgia). Confederate withdrawal in Georgia.
June 1864: Battle of Kolb's Farm. Union victory.
June 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of New Hope Church.
June 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Pickett's Mill.
June 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Kennesaw Mountain. Confederate Johnston repulses Sherman.
July 1864: Battle of Marietta. Union victory. Confederates withdrew.
July 1864: Battle of Peachtree Creek. Union victory.
July 1864: Battle of Atlanta. Victory of Union army who reaches the southeast of Atlanta, Georgia.
July 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Kennesaw Mountain.
July 1864: Battle of Ezra Church. Confederate attack on Union army northwest of Atlanta fails to gain element of surprise, finding entrenched Union forces. Union victory.
July 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Brown's Mill. Confederate victory.
August 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Utoy Creek. Indecisive battle on Union right flank near Atlanta.
August 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Lovejoy's Station. Confederates repel Union raiders attacking the station.
August 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Brown's Mill.
September 1864: Battle of Jonesborough. William J. Hardee's Confederates defeated, resulting in Atlanta's fall the following day.
September 1864: Atlanta falls to the Union on September 2, 1864, after a siege.
September 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Utoy Creek.
September 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Lovejoy's Station.
1.4.17.Forrest's Defense of Mississippi
Was a Confederate counteroffensive in Mississippi during the American Civil War.
June 1864: Battle of Brice's Crossroads. Confederate N.B. Forrest routs Union force almost three times as large.
July 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Brice's Crossroads.
August 1864: Second Battle of Memphis.Confederate raid.
August 1864: Second Battle of Memphis. Confederate raid.
September 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Second Battle of Memphis.
1.4.18.Morgan's Raid into Kentucky
Was a Confederate raid in Kentucky during the American Civil War.
June 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Cynthiana. Union Brig. Gen. Stephen Gano Burbridge defeated Confederate Brig. Gen. John Hunt Morgan. Most Confederate soldiers were casualties, though Morgan escaped.
July 1864: Confederae troop retreat after the Battle of Cynthiana.
1.4.19.Operations in Mobile Bay
Was a battle of the American Civil War where the Union conquered Mobile Bay, Alabama.
August 1864: Battle of Mobile Bay. Union General David Farragut takes the port of Mobile.
1.4.20.Franklin-Nashville Campaign
Was a series of battles fought in the Western Theater of the American Civil War in Alabama, Tennessee, and northwestern Georgia.
October 1864: Battle of Allatoona. Union victory.
October 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Decatur. Confederates unable to cross river.
November 1864: Battle of Columbia. Confederate victory.
November 1864: Confederate troop retreat after the Battle of Decatur.
November 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Spring Hill.
December 1864: Battle of Nashville: In one of the largest victories achieved by the Union Army during the war, Thomas attacked and routed Hood's army, largely destroying it as an effective fighting force.
1.4.21.Sherman's March to the Sea
Was a military campaign of the American Civil War conducted through Georgia from November 15 until December 21, 1864 by the Union.
November 1864: Battle of Griswoldville. Sherman's march to the sea continued.
November 1864: Battle of Buck Head Creek. Union victory.
November 1864: Battle of Honey Hill. The third battle of Sherman's March to the Sea was a failed Union Army expedition under Maj. Gen. John P. Hatch that attempted to cut off the Charleston and Savannah Railroad in support of Sherman's projected arrival in Savannah.
December 1864: Battle of Waynesboro, Georgia. Union victory.
December 1864: Second Battle of Fort McAllister. Union General William B. Hazen captures Fort McAllister.
December 1864: Savannah, Georgia, falls to Union forces under General William T. Sherman.
December 1864: Union retreat after defeat in Battle of Honey Hill.
1.4.22.Campaign of the Carolinas
Was an Union military campaign in the Carolinas to link up with the forces in Virginia during the American Civil War.
February 1865: Battle of Rivers' Bridge. Union forces capture river crossing.
February 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Aiken.
February 1865: Battle of Congaree Creek.
February 1865: Columbia, capital of South Carolina, falls to the Union.
March 1865: Battle of Aiken. Confederate victory.
March 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Monroe's Cross Roads. Confederates delayed Federal Cavalry movement towards Fayetteville.
March 1865: Battle of Bentonville. Sherman defeats Confederates
April 1865: Battle of Morrisville. Union victory. Last cavalry battle of the War.
April 1865: When Johnston agreed to purely military terms and formally surrendered his army and all Confederate forces in the Carolinas, Georgia, and Florida.
1.4.23.Wilson's Raid
Was an Union raid in Alabama and Georgia during the American Civil War.
April 1865: Battle of Ebenezer Church (Alabama).
1.4.24.Mobile campaign
Were a series of military operations part of the Western Theater of the American Civil War.
April 1865: Battle of Fort Blakeley. Union forces capture fort east of Mobile.
1.5.Lower Seaboard Theatre
Encompassed major military and naval operations that occurred near the coastal areas of the Southeastern United States: in Alabama, Florida, Louisiana, Mississippi, South Carolina, and Texas, as well as southern part of the Mississippi River.
March 1862: The Union captured St. Augustine.
April 1862: 28 gunboats commanded by Union Commodore Samuel Dupont occupied Fort Clinch at Fernandina Beach.
April 1862: Battle of Fort Pulaski. Union blockade closes Savannah, Georgia. Parrott rifle makes masonry forts obsolete.
April 1862: Two days before the city surrendered in April 1862, Moore and the legislature abandoned Baton Rouge as the state capital, relocating to Opelousas in May.
October 1862: Battle of Georgia Landing. Confederate forces fled to Labadieville.
January 1864: Fort Myers, a strategic location during the Seminole Indian Wars, was abandoned until Union soldiers, led by General John Newton, reoccupied it in December 1863 during the Civil War. This move was part of the Union's efforts to establish control over key points in Florida.
June 1864: Camp Milton was a Confederate stronghold during the American Civil War. It was captured by Union forces on June 2, 1864.
September 1864: Battle of Marianna. Union cavalry raid into Florida panhandle.
March 1865: Battle of Fort Myers: Even though the attack had been repelled, Fort Myers was abandoned by its garrison in early March. Southernmost land battle in Florida of the war.
March 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Natural Bridge. Confederate victory in Florida prevents the capture of Tallahassee.
April 1865: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Natural Bridge.
1.5.1.New Orleans Expedition
Was a military campaign of the Union culminationg in the capture of New Orleans, the major port of the Confederates, during the American Civil War.
April 1862: Battle of Forts Jackson and St. Philip. Decisive battle for possession of New Orleans. Union victory.
May 1862: Union forces under General Butler occupy New Orleans, Louisiana.
1.5.2.Operations in West Louisiana
Were a series of military operations in western Louisiana during the American Civil War.
April 1863: Battle of Fort Bisland. Confederate forces retreat from Fort Bisland.
April 1863: Battle of Irish Bend. Confederate Richard Taylor retreats from Fort Bisland.
April 1863: Battle of Vermillion Bayou. Confederate Richard Taylor, being vastly outnumbered, retreats after an artillery skirmish.
April 1863: Taylor retreated from the Teche region, and Banks was able to capture the Confederate fort at Butte a la Rose and Alexandria.
1.5.3.Siege of Port Hudson
Was the final engagement in the Union campaign to recapture the Mississippi River in the American Civil War.
May 1863: Battle of Plains Store. Union victory.
1.5.4.Union Invasion of Florida
Was a military invasion of Florida by the Union during the American Civil War.
February 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Olustee. Confederate victory.
February 1864: In 1864, during the American Civil War, Union forces led by General Truman Seymour were defeated by Confederate troops commanded by General Joseph Finegan in Jacksonville, Florida. The Union forces were forced to retreat back to their fortifications in the city.
March 1864: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Olustee.
1.6.Secession of the Free State of Jones
During the American Civil War Jones County (Mississippi) formed a separate government.
October 1863: On October 13, 1863, a band of deserters from Jones County and adjacent counties organized to protect the area from Confederate authorities and the crippling tax collections. The company, led by Newton Knight, formed a separate government, with Unionist leanings, known as the "Free State of Jones", and fought a recorded 14 skirmishes with Confederate forces.
1.7.Valley Campaigns of 1864
Were the battles that took place in the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia during the American Civil War.
1.7.1.Lynchburg Campaign
Were a series of battles in the area of Lynchburg, Virginia, during the American Civil War.
May 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of New Market. Confederate forces halt Union army under Franz Sigel from advance up the Shenandoah Valley.
June 1864: Battle of Piedmont. Union forces under David Hunter defeat Confederate defenses on march to Staunton, Virginia, upper Shenandoah Valley.
June 1864: Battle of Lynchburg: Union army forced back through West Virginia.
1.7.2.Early's Incursion
Were a series of Confederate military operations led by Jubal Early in Maryland and Virginia during the American Civil War.
July 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Monocacy. Union Gen. Lew Wallace slows up Jubal Early, saving DC.
July 1864: Battle of Fort Stevens. Failed Confederate attempt to capture Washington, D.C., President Lincoln, observing the battle, comes under Confederate fire.
July 1864: Confederate General Jubal Early unsuccessfully attacked Fort Stevens in Washington D.C. during the Civil War in 1864. After realizing he could not capture the capital, Early retreated back to Virginia.
July 1864: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Cool Spring. Unionist Joseph Thoburn led a full retreat after being surrounded by Confederate forces.
July 1864: Second Battle of Kernstown. Jubal Early defeats Union forces.
1.7.3.Sheridan Valley Campaign
Were a series of battles that took place in the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia during the American Civil War from May to October 1864.
August 1864: Confederate troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Summit Point. Inconclusive.
September 1864: Battle of Opequon. Union General Sheridan defeats Early, several officers killed or wounded on both sides.
September 1864: Battle of Fisher's Hill. Successful Union frontal assault.
October 1864: Battle of Cedar Creek. Union General Sheridan defeats Early, drives Confederates from Shenandoah Valley.
April 1862: New Orleans was captured April 29, 1862 by a combined Army-Navy force under U.S. Flag Officer David Farragut and Major General Benjamin Butler during the American Civil War. The city's fall was a significant victory for the Union, as it gave them control of the Mississippi River and split the Confederacy in two.
Disestablishment
January 1865: Area under Union control by the end of 1864.
January 1865: Second Battle of Fort Fisher. Union takes fort.
February 1865: Battle of Rivers' Bridge. Union forces capture river crossing.
February 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Aiken.
February 1865: Battle of Congaree Creek.
February 1865: Columbia, capital of South Carolina, falls to the Union.
February 1865: Battle of Wilmington (North Carolina). Last Confederate port falls.
March 1865: Battle of Fort Myers: Even though the attack had been repelled, Fort Myers was abandoned by its garrison in early March. Southernmost land battle in Florida of the war.
March 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Natural Bridge. Confederate victory in Florida prevents the capture of Tallahassee.
March 1865: Battle of Aiken. Confederate victory.
March 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Monroe's Cross Roads. Confederates delayed Federal Cavalry movement towards Fayetteville.
March 1865: Battle of Bentonville. Sherman defeats Confederates
April 1865: Battle of Ebenezer Church (Alabama).
April 1865: Third Battle of Petersburg. Union General Grant defeats Lee.
April 1865: Battle of Sutherland's Station. Union victory.
April 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Amelia Springs. Inconclusive.
April 1865: Union troop retreat after the Battle of Natural Bridge.
April 1865: Battle of Rice's Station. Confederate forces are caught off guard by John Gibbon's forces.
April 1865: Battle of High Bridge. Union forces thwart Lee's attempts to burn bridges and to resupply, Grant proposes that Lee surrender, but he refuses.
April 1865: Battle of Appomattox Court House. Confederate General Lee's forces surrounded. He subsequently surrenders.
April 1865: Battle of Fort Blakeley. Union forces capture fort east of Mobile.
April 1865: Battle of Morrisville. Union victory. Last cavalry battle of the War.
April 1865: When Johnston agreed to purely military terms and formally surrendered his army and all Confederate forces in the Carolinas, Georgia, and Florida.
May 1865: Union troop maneuver preceding the Battle of Palmito Ranch.
May 1865: Battle of Palmito Ranch. Confederate victory. Last battle in Texas during final phases of the Civil War. Southernmost battle on land in Civil War.
Selected Sources
1861-1865 - The Civil War 1861-1865. Perry-Castañeda Library
Battle History. Gettysburg Pensylvania Historic Crossroads. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.gettysburgpa.gov/history/slideshows/battle-history
Battle of Adairsville. National Park Service. Retrieved on 31 March 2024 on https://www.nps.gov/civilwar/search-battles-detail.htm?battleCode=GA009
Colton, Ray Charles (1985). The Civil War in the Western Territories. University of Oklahoma Press. pp. 122–123.
Flaherty, M.: California and the Civil War - The California Column and the March to Tucson, 1862. Military Museum. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.militarymuseum.org/CaliforniaColumn.html
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.412
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.429
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.433
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.437
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.456
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.457
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.465
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.466
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.577
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.589
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.594
Fredriksen, J.C. (2010): Chronology of American Military History - Volume 1, Facts On File, p.600
Irvine, D. (1968): Military Operations of the Civil War: A Guide-index to the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies, 1861-1865, U.S. National Archives and Records Service, Vol. 1, pp. 73-74
Lexington National Cemetery. The Historical Marker Database. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.hmdb.org/m.asp?m=202872
List of American Civil War battles. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 31 March 2024 on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_American_Civil_War_battles
Map Collection of the University of Texas and Austin. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://maps.lib.utexas.edu/maps/historical/civil_war_1861-1865.jpg
Rockville. The Historical Marker Database. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.hmdb.org/m.asp?m=174764
SANTA FE NATIONAL CEMETERY. U.S. Department of Veteran Affairs. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.cem.va.gov/pdf/InterpretiveSigns/SantaFeNationalCemetery.pdf
Secession Ordinances of 13 Confederate States. University of Houston. Retrieved on 4 April 2024 on https://www.digitalhistory.uh.edu/disp_textbook.cfm?smtID=3&psid=3953
The Statutes at Large of the Provisional Government of the Confederate States of America, from the Institution of the Government, February 8, 1861, to its Termination, February 18, 1862, Inclusive. Arranged in Chronological Order. Together with the Constitution for the Provisional Government, and the Permanent Constitution of the Confederate States, and the Treaties Concluded by the Confederate States with Indian Tribes. Documenting the American South. Retrieved on 4 April 2024 on https://docsouth.unc.edu/imls/19conf/19conf.html
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.337
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.347
Wrightsville. The Historical Marker Database. Retrieved on 5 April 2024 on https://www.hmdb.org/m.asp?m=171286
.svg.png.webp)
 Confederate States of America
Confederate States of America