This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of the Netherlands and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
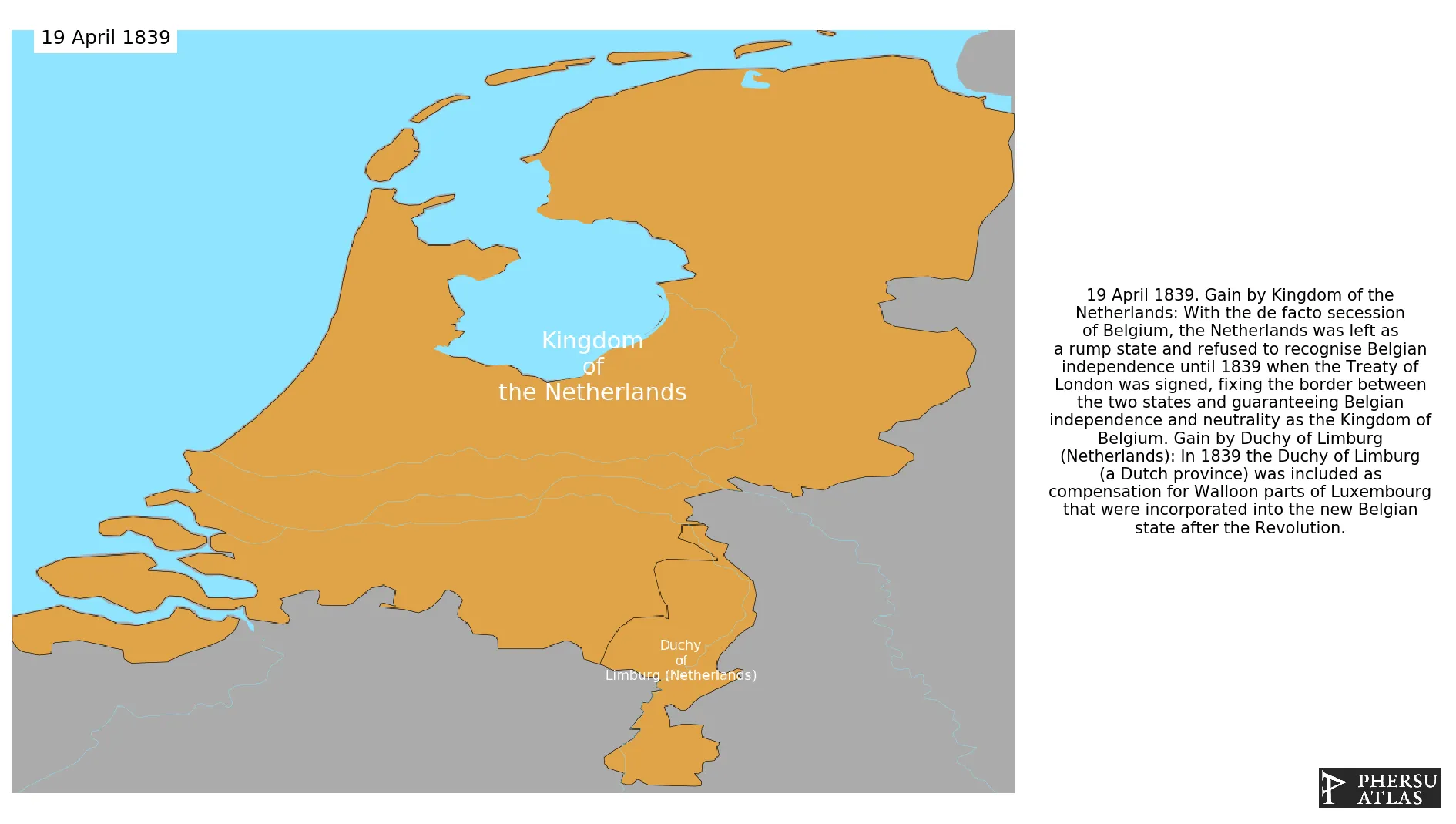
With the de facto secession of Belgium, the Netherlands was left as a rump state and refused to recognise Belgian independence until 1839 when the Treaty of London was signed, fixing the border between the two states and guaranteeing Belgian independence and neutrality as the Kingdom of Belgium.
Summary
The Burgundian dukes in the 15th century were able to unite many of these Dutch territories under their rule, laying the foundations for a more centralized state. Under the Habsburg rulers Charles V and Philip II, the Netherlands were integrated into the vast Spanish Empire, though tensions grew over issues of religion and governance. This led to the Eighty Years' War of Dutch independence, culminating in the establishment of the Dutch Republic in 1581.
The Dutch Republic flourished as a major commercial and naval power during the 17th century "Golden Age", producing renowned artists and philosophers. However, the 18th century saw the decline of Dutch global influence, with the country becoming embroiled in conflicts with Britain and France. The French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars led to the end of the Republic and the creation of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815.
Under the House of Orange, the new kingdom initially included both the Netherlands and Belgium, but Belgian independence was achieved in 1830 after a revolt. The 19th and 20th centuries saw the Netherlands consolidate as a modern constitutional monarchy, weathering periods of neutrality, occupation, and reconstruction to emerge as a prosperous, democratic state within the European Union.
Establishment
April 1839: In 1839 the Duchy of Limburg (a Dutch province) was included as compensation for Walloon parts of Luxembourg that were incorporated into the new Belgian state after the Revolution.
April 1839: With the de facto secession of Belgium, the Netherlands was left as a rump state and refused to recognise Belgian independence until 1839 when the Treaty of London was signed, fixing the border between the two states and guaranteeing Belgian independence and neutrality as the Kingdom of Belgium.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
1.1.World War II (Western Front)
Was the Western European theatre of World War II.
1.1.1.German Invasion of Netherlands
Was the German Invasion of the Netherlands during World War II.
May 1940: Battle of Maastricht.
May 1940: Battle of Mill.
May 1940: Battle of the Grebbeberg.
May 1940: Battle of Rotterdam.
May 1940: After the bombing of Rotterdam, the Dutch surrendered in the late afternoon of 14 May, signing the capitulation early the next morning.
May 1940: Battle of Zeeland.
1.1.2.German Invasion of France
The Battle of France was the German invasion of France during World War II that ended with the French Armistice of Compiègne on 22 June 1940.
1.1.2.1.Central Front of the German Invasion of France (World War II)
Was the front of the Meuse Line during the German invasion of France in World War II.
May 1940: The German advance forces reached the Meuse line late in the afternoon.
May 1940: German advance in Belgium.
1.1.3.Siegfried Line campaign
Was a phase in the Western European campaign of World War II which involved actions near the German defensive Siegfried Line.
September 1944: Territorial changes based on the known frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
1.1.3.1.Battle of the Scheldt
Was a series of military operations led by the First Canadian Army, with Polish and British units attached, to open up the shipping route to Antwerp so that its port could be used to supply the Allies in north-west Europe.
October 1944: Allied advances by October 16th in the Low Countries and Belgium, during the Battle of the Scheldt.
November 1944: Allied advances by November 10th in the Low Countries and Belgium, during the Battle of the Scheldt.
1.1.4.Liberation of Netherlands
Was the Allied liberation of the Netherlands from the German occupying forces.
September 1944: Maastricht, Gulpen, Meerssen are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Simpelveld is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Sint-Oedenrode, Veghel, Son en Breugel are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Eindhoven is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Veldhoven is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Nijmegen, Geldrop, Someren, Terneuzen are liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Weert is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Deurne is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Mook is liberated by the Allies of World War II
September 1944: Helmond,Oss are liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Kerkrade is liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Venray is liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Den Bosch, Tilburg, Bergen op Zoom are liberated by the Allies of World War II
October 1944: Tholen,Goes are liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Vlissingen,Westkapelle are liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Wissenkerke,Zoutelande are liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Middelburg is liberated by the Allies of World War II
November 1944: Veere,Koudekerke are liberated by the Allies of World War II
December 1944: Blerick is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Doetinchem,Borculo,Eibergen,Enschede are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Hengelo is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Almelo is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Westerbork,Brummen,Deventer are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Assen,Diepenveen,Olst are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Arnhem, Zwolle are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Zutphen, Leeuwarden, Zoutkamp are liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Groningen is liberated by the Allies of World War II
April 1945: Apeldoorn is liberated by the Allies of World War II
1.1.4.1.Battle of Nijmegen
Was the liberation of the Dutch city of Nijmegen from German occupation during World War II.
September 1944: The Battle of Nijmegen or Liberation of Nijmegen occurred from 17 to 20 September 1944.
1.1.4.2.Battle of Overloon
As a battle fought during the Second World War between Allied forces and the German Army which took place in and around the village of Overloon in the south-east of the Netherlands .
October 1944: Overloon is liberated by the Allies of World War II
1.1.5.Western Allied invasion of Germany
Was the invasion of the western territories of Germany mainly by the United States, United Kingdom, France and Canada at the end of World War II.
March 1945: Frontline of the western front of World War II in that date.
April 1945: Allied military operations during the encirclement of the Ruhr area (March-April 1945).
April 1945: Allied advance in Germany in that date.
April 1945: Allied reduction of Ruhr Pocket.
April 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
May 1945: Final allied military operations in the European theatre of World War II (April-May 1945).
1.1.5.1.German Offensive on the Western Front during the Allied invasion
Was a offensive of Germany against the Allies that were invading German-occupied Europe during World War II.
December 1944: Territorial changes caused on December 16th 1944 by the German Ardenne Offensive of 1944 ("Unternehmen Wacht am Rhein").
1.1.5.2.Operation Veritable
Was an Allied military operation in the Reichswald Forest, in Germany, towards the end of World War II.
February 1945: Territorial changes based on the known frontline during the Rhineland campaign.
1.1.5.3.Operation Grenade
Was the crossing of the Roer river between Roermond and Düren by the U.S. Ninth Army which marked the beginning of the Allied invasion of Germany.
1.2.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
May 1945: After the End of World War II the Western European countries of Germany are reverted to their pre-war borders.
April 1949: An area of Germany of a total size of 69 km2 was allocated to the Netherlands.
August 1963: Almost all of the German territories annexed by the Netherlands at the end of WWII were returned to West Germany in 1963 after Germany paid the Netherlands 280 million German marks. The territory was returned to West Germany on 1 August 1963, except one small hill (about 3 km2) near Wyler village, called Duivelsberg/Wylerberg.
May 1867: Because the Austro-Prussian war had ended the German Confederation, the Treaty of London (1867) dissolved the Duchy of Limburg and annexed it directly to the Netherlands.
Selected Sources
Battle of the Scheldt. Canadiansoldiers.com. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://www.canadiansoldiers.com/history/campaigns/northwesteurope/scheldt.htm
Chronologisch overzicht van de bevrijding van Nederlandse plaatsen in de Tweede Wereldoorlog. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 12 september 2020 on https://nl.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chronologisch_overzicht_van_de_bevrijding_van_Nederlandse_plaatsen_in_de_Tweede_Wereldoorlog
Crossing Of The Rhine, 22-28 March 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope79.jpg
Encirclement Of The Ruhr, 29 March-4 April 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope80.jpg
Final Operations, 19 April-7 May 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope82.jpg
NORTHWESTERN EUROPE, 1940 - CAMPAIGN IN THE WEST, 1940 Situation 16 May and Operations - Since 10 May. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://westpoint.edu/sites/default/files/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe/WWIIEurope11.pdf
Pursuit To The West Wall, 26 August-14 September 1944 United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope66.jpg
Reduction Of Ruhr Pocket And Advance To the Elbe And Middle Rivers, 5-18 April 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope81.jpg
Sullivan, G.R.: Ardennes-Alsace p.23. U.S. Army Center of Military Hisotry. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://www.history.army.mil/brochures/ardennes/aral.htm
The Rhineland Campaign, Operations 8 February-5 March & Operations 6-10 March 1945. United States Military Academy West Point. Retrieved on March, 26th, 2024 on https://s3.amazonaws.com/usma-media/inline-images/academics/academic_departments/history/WWII%20Europe%20Med/WWIIEurope76combined.jpg
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 530
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, pp.276-282

 Kingdom of the Netherlands
Kingdom of the Netherlands