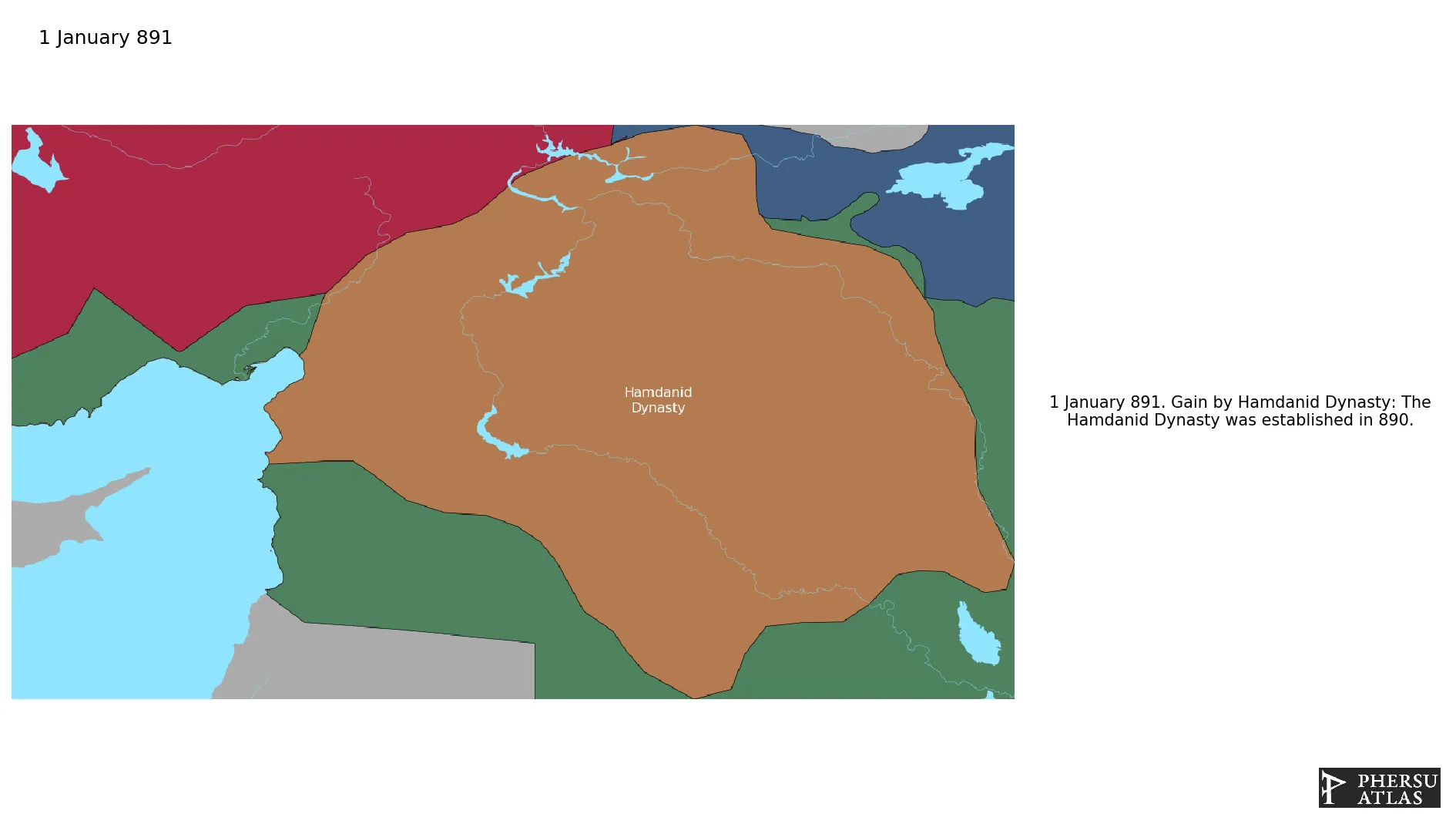
Hamdanid Dynasty
Hamdanid Dynasty
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was an Islamic Arab dynasty of Northern Mesopotamia and Syria.
Establishment
January 891: The Hamdanid Dynasty was established in 890.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars between a number of Muslim Arab dynasties and the Byzantine Empire from the 7th to the 11th century. Conflict started during the initial Muslim conquests, under the expansionist Rashidun and Umayyad caliphs, in the 7th century and continued by their successors until the mid-11th century.
January 962: Saif al-Daula of the Hamdanid dynasty, the Emir of Aleppo, had taken 30,000 men into Imperial territory, attempting to take advantage of the army's absence in Crete.
December 962: The Phokas brothers, Nikephoros and Leo, were Byzantine generals. They led the siege of Aleppo in 962, capturing the city except for the citadel. The Emir's soldiers fiercely defended the citadel against the Byzantine forces.
January 963: The Phokas brothers, Nikephoros and Leo, were Byzantine generals. The Emir of Aleppo at the time was Sayf al-Dawla, a prominent ruler of the Hamdanid Dynasty. The Byzantine siege of Aleppo in 963 resulted in the city being partially destroyed, with only the citadel remaining under the control of the Emir's soldiers.
January 968: Said had not fully recovered from the sack of Aleppo, which became an imperial vassal shortly thereafter.
January 970: In 969, the city of Antioch was retaken by the Byzantines.
1.1.Byzantine reconquest of Edessa
Byzantine reconquest of Edessa.
January 943: Byzantine reconquest of Edessa.
1.2.Byzantine occupation of Aleppo
Was the Byzantine Sack of Aleppo. At the time the city was controlled by the Hamdanid Dynasty.
January 964: Sack of Aleppo (962).
February 964: The Sack of Aleppo in 962 was carried out by the Byzantine Empire under the command of Nikephoros Phokas. The city was captured and looted, leading to the transfer of control to the Hamdanid Dynasty in 964.
Expansion during the rule of Malik Shah I in the Seljuk Empire.
January 1074: Within two years the Turkmens had established control as far as the Aegean Sea under numerous beghliks.
January 1080: The great sultan of the Seljuk Empire, Malik Shah I, occupied Syria, removing it from the control of the local Arab princes and Turkish lords who had already settled there.
Were a series of conflicts in the Middle Ages between the Byzantine Empire and the Seljuk Empire.
January 1079: While the Seljuks strengthened themselves in Anatolia thanks to Suleyman, general Filareto Bracamio, who remained isolated from Constantinople, led a long resistance that led to the formation of a principality under Byzantine nominal authority but in fact almost autonomous, which controlled Cilicia (including Tarsus, Mamistra and Anazarbe) and Edessa.
3.1.Seljuk invasion of Asia minor
Was the invasion of Asia Minor by the Seljuq Turks.
January 1068: The Anatolian Seljuks took Aintab in 1067.
January 963: In 962, the Kyrrhos and Gaziantep (Ayntab) areas were recaptured by the Byzantines.
January 968: With the death of Ashot Bagratuni of Taron in 967 (not to be confused with Ashot III), his sons Gregory and Bagrat were not able to withstand the pressure from the empire, which annexed their principality outright and converted it to a theme.
January 980: Jazira conquered by Buyid Dynasty.
January 984: With the weakening of the buyid power after the death of Adud ad-Daula after 983, the Kurdish Marwan tribe under Badh, a former shepherd, gained control of Mayyafariqin and the areas of Amida and Nusaybin.
January 991: Independence of the Numayrid Dynasty from the Hamdanids.
January 1001: During his early reign, Waththab, a member of the Numayrid Dynasty, annexed Edessa from the Hamdanids.
January 1041: The Byzantines conquered Edessa in the early 1030s.
January 1059: A revolt by Turcoman forces in Baghdad against the Seljuqs, led to the loss of the city to the Fatimids Caliph in 1058.
January 1061: Seljuk Sultan Tughril reconquered Baghdad and personally strangled his foster brother İbrahim Yinal who had defected to th Fatimids.
January 1065: Seljuk sultan Alp Arslan marched into Armenia and Georgia, conquering these regions.
Disestablishment
January 1080: The great sultan of the Seljuk Empire, Malik Shah I, occupied Syria, removing it from the control of the local Arab princes and Turkish lords who had already settled there.
 Hamdanid Dynasty
Hamdanid Dynasty