If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a county of the Holy Roman Empire.
Establishment
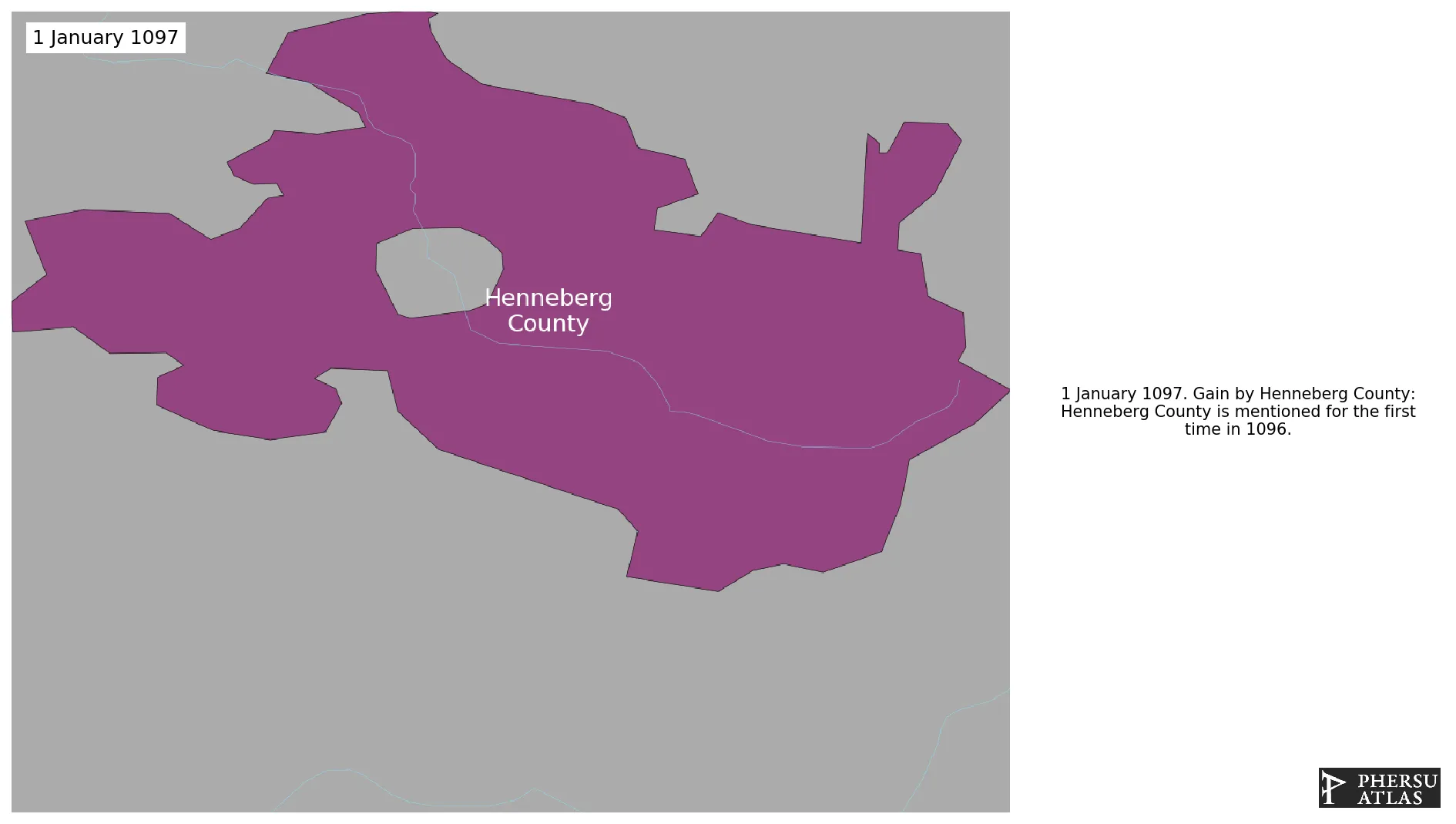
January 1097: Henneberg County is mentioned for the first time in 1096.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
1.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
1.1.1.Swedish Period
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
September 1631: On September 17, 1631, the Swedish army under Gustav Adolf met the troops of the Catholic League under Tilly in the Battle of Breitenfeld north of Leipzig.
December 1631: Gustav Adolf II of Sweden crosses the Rhine with his army and besieges Mainz.
1.1.2.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
1.1.2.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
November 1637: After the death of Swedish King Ferdinand II, his son and successor Ferdinand III brought the Swedish troops back to Pomerania, leaving the territories occupied by Sweden in Germany.
August 1640: In 1640, the Swedes led by field marshal Banér moved through Thuringia via Saalfeld into Hesse and further near the town of Fritzlar, which was reached on August 31, 1640.
October 1640: When 14 regiments arrived to reinforce the imperial army at the end of September 1640, the Swedish army left the territories it occupied in Germany (with the exception of Pomerania).
June 1648: In May 1648, there was the last major field battle of the Thirty Years' War between French-Swedish and Imperial-Bavarian armies near Augsburg.
1.1.3.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
October 1648: With the Peace of Westphalia Sweden received Western Pomerania (henceforth Swedish Pomerania), Wismar, and the Prince-Bishoprics of Bremen and Verden as hereditary fiefs. Sweden evacuated the remnant territories it had occupied in the Holy Roman Empire.
January 1235: The castle of Bodenlauben is sold to the Bishopric of Würzburg.
January 1306: Count Konrad von Wildberg, the last Wildberger, married Margarete von Henneberg. When Count Konrad died, Wiltdber was thus inherited by the Henneberg Dynasty.
January 1354: Hildburghausen came to the Landgraviate of Thuringia.
January 1379: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XIV century.
January 1401: Since 1400, Königsberg in Bayern belonged to the Wettin duchies.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
January 1543: In 1542, the town of Meiningen came to the Counts of Henneberg.
January 1577: Würzburg Prince Bishop Julius Echter von Mespelbrunn made Hofheim a town in 1576, thereby confirming its central importance for the surrounding area.
January 1586: Half of the town of Schmalkalden had belonged to Hesse since 1360, and all of it from 1584.
Disestablishment
January 1661: In 1660, the county of Henneberg was partitioned among various lines of the Wettin family.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 30-31
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Schmidt, G. (2006): Der Dreißigjährige Krieg, Munich (Germany), p. 65
Spindler, M. (2017): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, Munich (Germany), p. 266
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.191-195
Westfälischer Friede - Vertrag von Osnabrück, https://de.wikisource.org/wiki/Westf%C3%A4lischer_Friede_%E2%80%93_Vertrag_von_Osnabr%C3%BCck
.png.webp)
 Henneberg County
Henneberg County