If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Were the Portuguese possessions in the Indian Subcontinent that lasted from the XV century to the loss of Goa in 1961.
Establishment
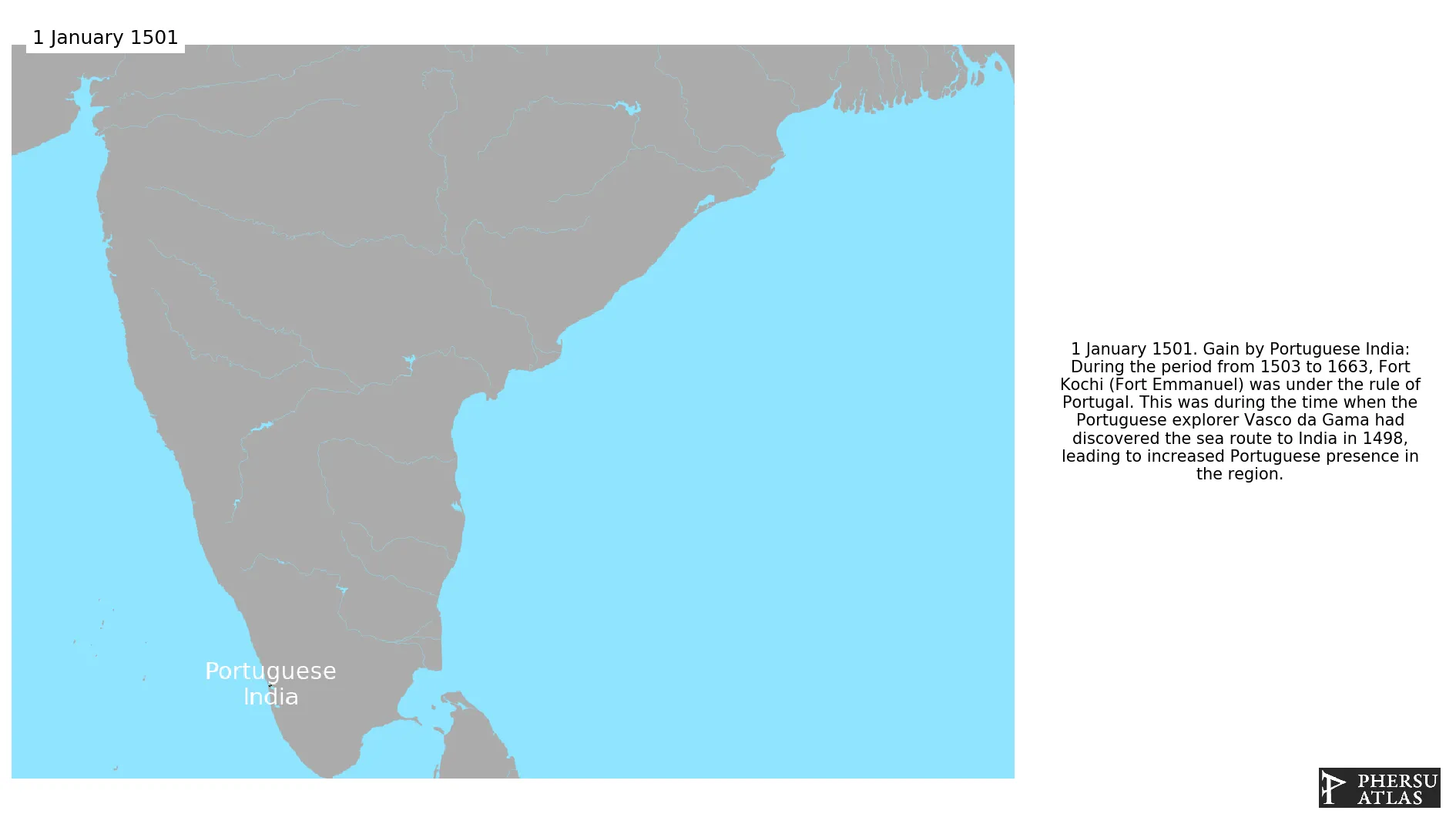
January 1501: During the period from 1503 to 1663, Fort Kochi (Fort Emmanuel) was under the rule of Portugal. This was during the time when the Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama had discovered the sea route to India in 1498, leading to increased Portuguese presence in the region.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Portuguese conquest of Goa occurred when the governor of Portuguese India Afonso de Albuquerque captured the city in 1510.
November 1510: The Portuguese conquest of Goa occurred when the governor of Portuguese India Afonso de Albuquerque captured the city in 1510.
The fall of Calicut occurred in 1526, when the Zamorin, the local Indian ruler, captured the fort of Calicut from the Portuguese.
July 1526: The fall of Calicut in 1526 occurred when the Zamorin, the ruler of the Kingdom of Vursut, captured the fort from the Portuguese, marking a significant event in the history of Portuguese-Indian relations.
July 1526: The fall of Calicut in 1526 occurred when the Zamorin, the ruler of the Kingdom of Calicut in India, captured the fort from the Portuguese, who had established a trading post in the region. This event marked a significant shift in power dynamics in the region, with the territory eventually coming under the control of the Bengal Sultanate.
Was a succession crisis caused by the death of the King of Portugal without heirs. The conflict saw two main claimants to the Portuguese throne: António, Prior of Crato, proclaimed in several towns as King of Portugal, and his first cousin Philip II of Spain, who eventually succeeded in claiming the crown, reigning as Philip I of Portugal.
October 1580: Philip II of Spain succeeded in claiming the Portuguese crown, reigning as Philip I of Portugal.
Was a revolution organized by the Portuguese nobility and bourgeoisie sixty years after the crowning of Philip I (Philip II of Spain), the first "dual monarch", that ended the Iberian Union.
November 1640: A revolution organized by the nobility and bourgeoisie on 1 December 1640, sixty years after the crowning of Philip I (Philip II of Spain), the first "dual monarch", ended the Iberian Union between Portugal and Spain.
Were a series of wars between the native kingdoms of modern-day Sri Lanka and the Portuguese Empire.
5.1.Dutch intervention 1638-1658
Was a Dutch military operation in Sri Lanka against the Portuguese Empire.
January 1659: Tuticorn captured by the Dutch in 1658.
January 1659: In 1658, the Dutch made an agreement with Nayaka of Thanjavur, by which ten villages were transferred from the Portuguese to the Dutch Nagapattinam Port, Puthur, Muttam, Poruvalancheri, Anthanappettai, Karureppankadu, AzhingiMangalam, Sangamangalam, Thiruthinamangalam, Manjakollai, Nariyankudi.
Was a global conflict between the Portuguese Empire and the Dutch Empire. The conflict primarily saw the Dutch companies invading Portuguese colonies in the Americas, Africa, and the East Indies.
6.1.Operations in the Pacific and Indian Oceans
Were the military operations of the Dutch in the Pacific and Indian Oceans during the Dutch-Portuguese War.
January 1664: The Dutch settled in the Malabar coast in 1663.
Expansion during the rule of Aurangzeb in the Mughal Empire.
January 1667: Mughal annexation of Chittagong.
Expansion during the rule of Shahu I in the Maratha Empire.
January 1738: In 1737 the island was captured by the Marathas,.
May 1739: The fort was taken over by the Maratha Army in 1739, ending the Battle of Vasai.
September 1740: After the capture of Baçaim in 1740, a peace treaty was concluded, and on 18 September 1740, Chaul was ceded by treaty to the Marathas.
Were a series of wars fought by the British East India Company in the Indian Subcontinent that resulted in the British conquest and colonial rule of the region.
9.1.Anglo-Mysore Wars
Were a series of four wars fought during the last three decades of the 18th century between the Sultanate of Mysore on the one hand, and the British East India Company, Maratha Empire, Kingdom of Travancore, and the Kingdom of Hyderabad on the other. The fourth war resulted in the dismantlement of Mysore to the benefit of the East India Company, which took control of much of the Indian subcontinent.
9.1.1.Second Anglo-Mysore War
Was a conflict between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company from 1780 to 1784.
January 1780: By 1779, Mysore ruler Haider Ali had captured parts of modern Tamil Nadu and Kerala in the south, extending the Kingdom's area to about 80,000 mi2 .
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
10.1.French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars - Theatre of war in the overseas colonies
The theatre of war in the overseas colonies during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
December 1802: On 31 Dec 1802, Dharampur State, under the rule of Raja Rajendra Singh, became a British protectorate. This decision was made as part of the Treaty of Bassein between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire.
Was the occupation of the Portuguese territories of Dadra and Nagar Haveli in India that were subsequently inglobated in the Indian Republic.
July 1954: Liberation of Dadra: the territories of Dadra were integrated into the Republic of India.
July 1954: Liberation of Naroli from Portuguese rule.
August 1954: Indian liberation of Silvassa.
August 1954: In 1954, the Portuguese unit surrendered to the Special Reserve Police (SRP) at Udva in the remnant Dadra and Nagar Haveli territory. This event marked the beginning of the liberation of Dadra and Nagar Haveli from Portuguese colonial rule.
Was an armed action carried out by the Indian Armed Forces to annex the last Portuguese Indian territory of Goa.
December 1961: The "armed action" was code named Operation Vijay (meaning "Victory") by the Indian Armed Forces. It involved air, sea and land strikes for over 36 hours, and was a decisive victory for India, ending 451 years of rule by Portugal over its remaining exclaves in India.
January 1502: For over 450 years, the coastal enclaves of Daman (Portuguese: Damão) and Diu on the Arabian Sea coast were part of Portuguese India, along with Goa and Dadra and Nagar Haveli.
January 1503: The Portuguese were the first Europeans to establish a trading center in Tangasseri, Kollam in 1502.
January 1503: Cannanore/Kolathunadu becomes a Portuguese possession.
January 1503: The Portuguese established a trading post in Pulicat in 1502 with the help of the Vijayanagar rulers.
January 1508: In the early 16th century the Portuguese made commercial contacts with the town and established a commercial centre in Nagapattinam.
January 1510: In 1509, the Portuguese wrested Diu from Gujarat sultanate following the battle of Diu.
January 1512: The Portuguese factory and fort in Kozhikode were established by explorer Afonso de Albuquerque in 1511.
January 1522: The first Portuguese settlement at Chaul, a port town in India, took place in 1521.
January 1524: Mylapore was occupied by the Portuguese in 1523, who established the viceroyalty of "São Tomé de Meliapor" or "Saint Thomas of Mylapore.
January 1524: Fort Cranganore was constructed in Kodungallur by Portuguese in 1523.
January 1527: In 1526, the Portuguese under the viceroyship of Lopo Vaz de Sampaio took possession of Mangalore, a port city in India. This marked the beginning of Portuguese control over the region as part of Portuguese India.
January 1529: In 1528, the Sultan of Bengal permitted the Portuguese to establish factories and customs houses in the Port of Chittagong.
December 1534: The Treaty of Vasai (1534) was signed by Sultan Bahadur of Gujarat and the Kingdom of Portugal on 23 December 1534 while on board the galleon São Mateus. Based on the terms of the agreement, the Portuguese Empire gained control of the city of Vasai.
December 1534: Growing apprehensive of the power of the Mughal emperor Humayun, Sultan Bahadur Shah of Gujarat was obliged to sign the Treaty of Bassein with the Portuguese Empire. According to the treaty, the Seven Islands of Bombay, the nearby strategic town of Bassein and its dependencies were offered to the Portuguese. .
January 1535: In 1534, the Portuguese took the islands of Salsette from Sultan Bahadur Shah of Gujarat.
January 1536: In 1535 Bahadur Shah, the Sultan of Gujarat, concluded a defensive alliance with the Portuguese against the Mughal emperor Humayun and allowed the Portuguese to construct the Diu Fort and maintain a garrison on the island.
January 1538: In 1537 CE, Vikrama Aditya Pandya the heriditary jati talaivan (caste leader) of the Paravar led a delegation to Goa and made a deal with the Portuguese and agreed to embrace christianity and open the doors of the pear fisheries in exchange for protection from the Muslim Marakayyar and Mappila traders. Accordingly, he was rechristened Joao de Cruz and 20,000 of his castemen embraced christianity and became subjects of the king of Portugal. The Portuguese state began to claim rights over the economic resources in the area.
January 1541: Portuguese establish an ouputs in Surat.
January 1546: Arakkal Kingdom was ruled by the Arakkal royal family, who were the only Muslim royal family in Kerala. The kingdom was a prominent maritime power in the region, with control over trade routes and the lucrative spice trade. The territory of Cannanore was strategically important due to its location on the Malabar Coast.
January 1549: Thoothukudi was taken over by the Portuguese in 1548.
January 1560: Damão was conquered by the Portuguese.
January 1580: The Portuguese explorer Vasco da Gama established the town of Hooghly-Chuchura in 1579 as a trading post in the Bengal region of India. The town became an important center for Portuguese trade and influence in the area.
January 1599: The Portuguese establish an outpost in Masulipatnam/Machilipatnam, India.
January 1606: Masulipatnam was the first Dutch factory on the Coromandel Coast of India.
January 1610: The Dutch occupied Pulicat fort.
January 1613: In 1612, England established its first Indian trading factory in Surat.
January 1628: Sawantwadi state was founded in 1627 by Khem Sawant I.
January 1633: The Mughal governor of Bengal expelled the Portuguese from Hugli-Chuchura.
May 1661: On 11 May 1661, the marriage treaty of Charles II of England and Catherine of Braganza, daughter of King John IV of Portugal, placed Bombay in possession of the English Empire, as part of Catherine's dowry to Charles.
January 1662: In 1661, Fort Pallipuram was integrated into Dutch Malabar. The fort was originally built by the Portuguese in the early 16th century and was an important strategic location in the region.
January 1662: Foundation of Fort Quilon.
January 1662: In 1661 the Dutch East India Company took possession of Kollam.
January 1663: The Dutch took the control of Kodungallur fort in 1663.
January 1663: São Tomé de Meliapore was occupied by the Dutch.
September 1674: 25 Jul 1672 - 6 Sep 1674: Sainte Thomé (São Tomé de Meliapore) occupied by France.
January 1742: In 1741, Governor Joseph François Dupleix arrived in India, aiming to establish a French territorial empire. Commanded by Marquis Bussy-Castelnau, Dupleix's forces gained control over the area from Hyderabad to Cape Comorin.
October 1783: The Portuguese were granted the area of Nagar Haveli on 10 June 1783 on the basis of Friendship Treaty executed on 17 December 1779 as compensation towards damage to the Portuguese frigate Santana by Maratha Navy in 1772.
January 1786: Then, in 1785 the Portuguese purchased Dadra, annexing it to Portuguese India.
Disestablishment
December 1961: The "armed action" was code named Operation Vijay (meaning "Victory") by the Indian Armed Forces. It involved air, sea and land strikes for over 36 hours, and was a decisive victory for India, ending 451 years of rule by Portugal over its remaining exclaves in India.
Selected Sources
Fernández Álvarez, M. (1998): Felipe II y su tiempo, cuarta edición, p. 523
de Oliveira Marques , A. H. R.(1972): History of Portugal, Columbia University Press, p. 322-325

 Portuguese India
Portuguese India