If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this event you can find it here:All Statistics
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
January 1803: In 1802, the territory of Heilbronn was transferred to the Duchy of Württemberg. This decision was part of the territorial changes that occurred in Germany during the Napoleonic Wars, with Württemberg gaining control over various regions previously under different rulers.
January 1807: In 1806 Weingarten Abbey became part of the Kingdom of Württemberg.
January 1804: Adelsheim was never one of the major ecclesiastical or secular principalities in the area, but was owned by the Imperial Knights until the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss in 1803. Then it came to the Grand Duchy of Baden.
January 1807: The March of Mulazzo is mediatizated by Napoleon.
February 1803: Reichsdeputationsschluss: the Imperial Recess of 1803, was a resolution passed by the Reichstag (Imperial Diet) of the Holy Roman Empire. The law secularized nearly 70 ecclesiastical states and abolished 45 imperial cities to compensate numerous German princes for territories to the west of the Rhine that had been annexed by France as a result of the French Revolutionary Wars.
January 1808: Hanau was detached from Hesse-Kassel and given to Karl Theodor von Dalberg.
April 1803: The Electorate of Baden was created on April 27, 1803 with the entry into force of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss.
February 1810: In 1810, Dalberg, who was the Prince of Regensburg and Archchancellor of the Holy Roman Empire, merged Frankfurt with the Principality of Aschaffenburg, the County of Wetzlar, Fulda, and Hanau to form the Grand Duchy of Frankfurt.
April 1802: On 9 April 1802, Benevento officially returned to the possession of the Holy See.
January 1803: Salm was created in 1802 as a state of the Holy Roman Empire in order to compensate the princes of Salm-Kyrburg and Salm-Salm, who had lost their states to France in 1793-1795. The new territory was not near most of the old territories of the princes, but instead extended the County of Anholt, which had been a minor possession of the prince of Salm-Salm. Most of the area was taken from the dissolved Bishopric of Münster.
February 1803: By the German Mediatisation of 1803, Oldenburg acquired the Oldenburg Münsterland and the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck.
January 1803: In 1802, the territory of Zwiefalten was secularized and suppressed, leading to its transfer to the Duchy of Württemberg. This decision was part of the secularization process in Germany, which aimed to transfer ecclesiastical territories to secular rulers.
January 1804: The Corvey Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Nassau-Orange-Fulda Principality.
January 1807: In 1806, the territorial sovereignty of the Schlitz lordship fell to the newly formed Grand Duchy of Hesse (Hessen-Darmstadt) as part of the formation of the Confederation of the Rhine and the mediatization of the Counts of Schlitz.
January 1804: The Principality of Regensburg (German: Fürstentum Regensburg) was a principality of the Holy Roman Empire created in 1803. The principality was initially created as an ecclesiastical electorate for Archbishop Karl Theodor von Dalberg, the Elector-Archchancellor of the Empire and the former Archbishop of Mainz, due to the annexation of Mainz itself by the French following the Treaty of Lunéville. Most of the new principality consisted of the territory of the former Prince-Bishopric of Regensburg. The principality also included the Lordships of Donaustauf, Wörth, and Hohenburg, the former free imperial city of Regensburg, St. Emmeram's Abbey, and the abbeys Obermünster and Niedermünster located within the city of Regensburg. Dalberg also acquired the newly-created Principality of Aschaffenburg along the Main river.
May 1804: Declaration of the First Empire in 1804 under Napoleon.
January 1803: In the year 1802, Dinkelsbühl lost its status as an imperial city and became part of the Electorate of Bavaria.
December 1807: In 1807, Napoleon dissolved the kingdom of Etruria and integrated it into France, turning it into three French départements: Arno, Méditerranée and Ombrone.
January 1805: The County of Rothenfels briefly became part of Austria in 1804 with around 13,000 inhabitants and an area of around 450 square kilometers.
March 1805: Establishment of the Kingdom of Italy.
January 1804: Gelnhausen was annexed to Hesse-Cassel.
January 1807: In the year of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss in 1803, the 475 square kilometer Principality of Waldburg was formed, which, however, was mediated as early as 1806 and fell mostly to the Kingdom of Württemberg and a smaller part to the Kingdom of Bavaria.
January 1807: In 1806, Hesse-Homburg was incorporated within Hesse-Darmstadt.
January 1807: The imperial fief of Fosdinovo is mediatizated by Napoleon.
January 1808: After the Peace of Pressburg in 1805, the territory of the Republic of Ragusa was occupied by France under Napoleon Bonaparte (May 27, 1806). The Republic was ultimately abolished by decree issued by General Marmont on January 31, 1808.
January 1810: From 1526 to 1809 Mergentheim was the headquarters of the Teutonic Order [...] Since 1809 the city belonged to the Kingdom of Württemberg and became the seat of the Württemberg Oberamt of the same name.
February 1803: With the German Mediatisation of 1803, Oldenburg acquired the Oldenburg Münsterland and the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck.
January 1811: In 1810, the Alpine territories surrounding Sillian and Lienz were added to the First French Empire under the rule of Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte.
February 1803: In 1803, Buchhorn (Ravensburg) was transferred to the Duchy of Württemberg. This decision was part of the territorial rearrangements in Germany following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire.
January 1811: In 1810, the Duchy of Arenberg was mediatised, leading to France annexing Dülmen and Meppen, while the Grand Duchy of Berg annexed Recklinghausen.
January 1798: The citizens of Parga, a town in western Greece, revolted against French rule in 1815. They sought protection from the British, who had military occupation of the territory since 1797.
January 1804: The Trento Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Habsburgs.
January 1811: Parts of Bavaria are transferred to Württemberg.
January 1804: With the secularization of the Archbishopric of Mainz in 1803, Karl Theodor Anton Maria von Dalberg was compensated by receiving the newly created principalities of Aschaffenburg and Regensburg and the County of Wetzlar.
February 1810: In 1810 Napoleon granted Dalberg's Principality of Regensburg to the Kingdom of Bavaria and compensated him with Hanau and Fulda. Dalberg merged his remaining territories of Aschaffenburg, Frankfurt, Wetzlar, Hanau, and Fulda into the new Grand Duchy of Frankfurt, with the Principality of Aschaffenburg becoming a department of the new grand duchy.
January 1811: In 1810, the city of Lübeck in Germany was annexed by the First French Empire under the rule of Napoleon Bonaparte.
January 1804: In 1803, the princes of the Leiningen-Dagsburg-Hardenburg line were compensated for their lost possessions in the Palatinate on the left bank of the Rhine with a new territory, which became part of the Principality of Leiningen. This territory was located in present-day Germany.
January 1811: Trento is annexed by the Kingdom of Italy.
January 1799: On December 10, 1798, the Piedmontese Republic was established in Turin, recognized by the French who had occupied the city.
January 1804: In 1803, Napoleon Bonaparte elevated the Duchy of Württemberg to the Electorate of Württemberg, granting it the highest status within the Holy Roman Empire. This change in status was significant for the ruling family of Württemberg, the House of Württemberg.
February 1803: Salzburg was secularized as an Electorate for Ferdinand III of Tuscany.
January 1804: In 1803, the right-bank territory of Speyer (at the time also spelled Spayer) was transferred to the Electorate of Baden. This decision was part of the territorial changes following the Treaty of Lunéville, which aimed to reorganize the territories of the Holy Roman Empire after the Napoleonic Wars.
January 1807: Establishment of the Kingdom of Westphalia.
October 1806: In September 1802, the city of Nuremberg lost its imperial freedom and came under the control of Electoral Bavaria. In 1804, it was transferred to Prussia before finally becoming part of the Kingdom of Bavaria in 1806.
January 1807: Ostfriesland and Ravenstein are annexed by Holland.
January 1807: In 1806, the territory of Isny (Rst.) was transferred to the Kingdom of Württemberg. This decision was a result of the Treaty of Pressburg, signed between Napoleon Bonaparte and Emperor Francis II of Austria.
January 1807: In 1806, the city of Augsburg was transferred to the Kingdom of Bavaria as part of the territorial changes brought about by the Napoleonic Wars. This decision was made by the Treaty of Pressburg, signed by Emperor Francis II of Austria and Emperor Napoleon I of France.
January 1799: On April 12, 1798, 121 cantonal deputies proclaimed the Helvetic Republic under the auspices of the French occupying forces. The Helvetic Republic was a centralized state based on the ideas of the French Revolution.
January 1799: The Parthenopean Republic emerged during the French Revolutionary Wars after King Ferdinand IV of Naples fled before advancing French troops.
January 1803: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Germany during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic periods.
January 1803: The Imperial City of Aalen is acquired by the Duchy of Württemberg.
January 1803: Napoleonic occupation of Zibello.
February 1803: With the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss in 1803, she came to the newly formed Electorate of Baden.
February 1803: With the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss 1803 in the course of the reorganization of the Holy Roman Empire, Tarasp fell to the Helvetic Republic as the last Austrian enclave in Switzerland.
February 1803: Since the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss of 1803, the town of Irsee has belonged to Bavaria.
January 1807: Several scattered territories of other German polities were added to the Grand Duchy of Berg, including Berg, Dortmund, Steinfurd, Werden, and Wildenburg.
March 1806: On 15 March 1806, the French emperor created the Granduchy of Berg and put it under the rule of his brother-in-law Joachim Murat. The Grand Duchy was a Napoleonic creation on territories formally part of several German states. Its capital was Düsseldorf.
January 1808: In 1807, Napoleon conquered the County of Carpegna and the County of Scavolino, annexing them to the Kingdom of Italy, a French client state ruled by Napoleon's brother-in-law, Eugène de Beauharnais. This expansion was part of Napoleon's efforts to consolidate his control over Italy.
January 1799: France annexes Geneva and creates the department of Léman.
January 1811: Regensburg and Windesheim are acquired by Bavaria.
January 1806: Establishment of the Granduchy of Würzburg.
January 1807: The city of Leiningen is annexed to the Grand Duchy of Hesse-Darmstadt from 1810.
February 1803: The Imperial City of Biberach is acquired by the Margraviate of Baden as a result of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss.
January 1808: In 1806, William I, Elector of Hesse, was dispossessed by Napoleon Bonaparte for supporting Prussia. Kassel became the capital of the new Kingdom of Westphalia, ruled by Napoleon's brother Jerome.
January 1806: Pyrmont County is partitioned from Waldeck and Pyrmont.
June 1806: The principality of Pontecorvo was a tiny sovereign state forming part of the Napoleonic Empire and established in 1806.
June 1806: The Kingdom of Holland was created by Napoleon Bonaparte in March 1806 in order to strengthen control over the Netherlands by replacing the republican government with a monarchy.
August 1806: The Duchy of Nassau, named for its historical core city, Nassau, was founded in 1806.
January 1807: The Limpurg County is acquired by the Kingdom of Württemberg.
January 1807: Napoleon awarded Massa and Carrara to the Principality of Lucca and Piombino.
January 1807: The domains of all Fuggers (Prince of Fugger-Babenhausen, Count of Fugger-Glött, Count of Fugger-Kirchberg-Weissenhorn, Count of Fugger-Kirchheim, Count of Fugger-Nordendorf) fell to Bavaria.
January 1807: The Kurpfalz-Bayern came to the Kingdom of Württemberg in 1806 through an exchange of territory.
January 1808: Bentheim was mediatized to the Grand Duchy of Berg in 1808.
October 1802: In September 1802, Weissenburg in Bayern lost its imperial freedom and became part of Electoral Bavaria. In 1804, it was transferred to Prussia before finally becoming part of the Kingdom of Bavaria in 1806.
January 1809: Bestowed with the grit and instinct of survival, making self-preservation a priority the Raja of Patiala entered into a treaty with the British against Ranjit Singh in 1808, thus becoming collaborators in the empire building process of the British in the sub-continent of India.
January 1809: The Rheda Lordship is acquired by the Granduchy of Berg.
January 1803: The Augsburg Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Bavaria-Palatinate.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Offenburg is mediatized to Baden.
January 1804: The Hildesheim Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia.
February 1803: In 1803, Reutlingen was transferred to the Duchy of Württemberg. This decision was part of the territorial rearrangements in Europe following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire.
January 1804: The Konstanz Prince-Bishopric is mediatized to Baden.
January 1804: The Passau Prince-Bishopric is divided between Bavaria and Salzburg.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Pfullendorf is mediatized to Baden.
February 1810: In 1810, Karl Theodor von Dalberg, who was the Prince of Regensburg and Archchancellor of the Holy Roman Empire, merged Frankfurt with the Principality of Aschaffenburg, the County of Wetzlar, Fulda, and Hanau to form the Grand Duchy of Frankfurt.
January 1807: In 1806, during the Napoleonic Wars, the Kingdom of Prussia annexed the territory of Hannover. This decision was made as a result of the Treaty of Tilsit.
February 1803: Instability in the Republic reached its peak in 1802-03—including the Stecklikrieg civil war of 1802. Together with local resistance, financial problems caused the Helvetic Republic to collapse. On 19 February 1803, the Act of Mediation restored the cantons. In 1803 Napoleon's Act of Mediation partially restored the sovereignty of the cantons, and the former subject territories of Aargau, Thurgau, Vaud, and Ticino became cantons with equal rights. the Three Leagues, formerly an associate (Zogewandter Ort) but not a full member of the confederacy, became a full member as the canton of Graubünden. In contrast, the territories of Biel, Valais, the former Principality of Neuchâtel (the later canton of Neuchâtel), of the Bishopric of Basel (the later Bernese Jura), and of Geneva did not become part of the Swiss confederacy until the end of the Napoleonic era.
January 1803: In the course of secularization, the monastery and imperial abbey of Weingarten were dissolved in 1802 and initially belonged to the House of Orange-Nassau.
January 1806: The Kingdom of Bavaria had its origins in the Peace of Pressburg on December 26, 1805 between the representatives of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the German and Austrian (double) Emperor Franz II./I. concluded peace treaty. On January 1, 1806, King Maximilian I Joseph was proclaimed in Munich.
April 1807: Schaumburg-Lippe is raised to the rank of principality.
January 1804: The Berchtesgaden Provostry is acquired by the Salzburg Electorate.
January 1799: On January 1799 the french troups capture Lucca.
January 1806: Principality of Waldeck is partitioned from Waldeck and Pyrmont.
January 1804: The Swedish rule over Wismar ended de facto in 1803, when Sweden pledged the city to the Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin for 99 years with the Malmö Pledge Agreement. Formally, Wismar reverted to Germany in 1903 and Sweden waived the redemption of the deposit.
January 1811: The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen is annexed to the First French Empire.
January 1807: After the imperial period, Bremen became the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen from 1806 and then in 1815 as a sovereign state in the German Confederation.
January 1803: In 1802, the territory of Paderborn was transferred to the Kingdom of Prussia. This decision was made as part of the secularization process in the Holy Roman Empire, which aimed to redistribute ecclesiastical lands to secular rulers.
April 1798: After the occupation of Rome by French troops on February 10, 1798, Benevento found itself politically isolated, so Ferdinand IV of Bourbon decided to occupy it.
January 1803: Several exclaves of the Mainz Archibishopric, including Erfurt, are given to the Kingdom of Prussia.
February 1803: The Ellwangen Imperial Monastery is secularised to Württemberg.
February 1803: In 1803, as a result of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss, territories of Hall, Gmünd and Giengen were transferred to the Duchy of Württemberg. This decision was part of a series of territorial reorganizations in the Holy Roman Empire led by Napoleon Bonaparte.
January 1803: In 1802, the territory of Esslingen was transferred to the Duchy of Württemberg. This decision was made as part of the territorial reorganization in Europe following the Napoleonic Wars.
January 1803: The Reichsdeputationshauptschluss assigned Schweinfurt to Bavaria in 1802.
January 1808: In 1807, Heligoland was seized by the United Kingdom during the Napoleonic Wars. It was strategically important for controlling access to the North Sea. The territory was eventually returned to Germany in 1890 in exchange for Zanzibar.
January 1808: Former territories of Nassau were added to the Kingdom of Westphalia.
January 1803: Friedberg annexed by Hesse-Darmstadt.
January 1811: In 1810 the coastal and northern départements North (capital: Stade) and Lower Elbe (capital: Lunenburg) of the Kingdom of Westphalia were ceded to the French Empire.
September 1792: The monarchy was abolished in 1792 during the French Revolution.
January 1803: As part of the mediatisation following the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss, Memmingen fell to the Electorate of Bavaria in 1803.
January 1811: Between 1810 and 1814, Oldenburg was occupied by Napoleonic France. Its annexation into the French Empire, in 1810, was one of the causes for the diplomatic rift between former allies France and Russia.
January 1802: The Cisalpine Republic is renamed Italian Republic.
November 1802: As part of the secularization, ownership of the Rottenmuenster monastery was taken over by Württemberg on November 23, 1802.
January 1803: In 1802, the territory of Mühlhausen (Thuringia) was transferred to the Kingdom of Prussia. This decision was made as part of the territorial reorganization following the Napoleonic Wars.
January 1803: The city and bishopric of Bamberg were promised to the Electorate of Bavaria as compensation for the loss of the Palatinate to France in the Treaty of Lunéville. Even before the final determination of borders in the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss (Imperial Recess) of 1803, Bavaria began to militarily occupy the territory of the bishopric on September 2, 1802, and declared the area a Bavarian province on November 29, definitively.
January 1803: In 1802, Bopfingen lost its imperial immediacy and came under the control of Bavaria.
January 1803: As part of the mediatisation, Wangen lost its status as an imperial city in 1803 and became part of the Electorate of Bavaria.
January 1803: In the course of mediatisation in 1802, Windsheim lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1803: Rottweil acquired by the Duchy of Württemberg.
January 1803: On September 11, 1802 (24 Fructidor, Year X), the French Senate took an "organic senatus-consultum, bringing together the departments of Po, Dora, Marengo, Sésia, Stura and Tanaro in the territory of the French Republic ". A part is annexed by Italy.
January 1803: In 1802Ulm lost its independence and was incorporated into the Electorate of Bavaria.
February 1803: Simultaneously with the conclusion of the main imperial deputation in 1803 and the secularization of the clergy, the Landgrave of Hesse-Kassel, Wilhelm IX, became elector.
February 1803: In 1803 the prince bishopric of Brixen was abolished by the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss and incorporated into the Austrian sovereignty.
February 1803: The Imperial City of Nördlingen is acquired by the Bavaria-Palatinate as a result of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss.
February 1803: In 1803, the imperial city of Weil was transferred to the Duchy of Württemberg. This decision was part of the territorial rearrangements in Europe following the Treaty of Lunéville, which aimed to compensate various German states for territories lost to France.
June 1806: Establishment of the Kingdom of Holland.
January 1804: The right bank of the Strassburg Prince-Bishopric fell to Baden.
January 1804: Some Palatine right-bank territories of the Rhine River were transferred to the Electorate of Baden as part of the territorial changes brought about by the Napoleonic Wars.
January 1804: The Lübeck Prince-Bishopric is secularised to Oldenburg.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Kempten is acquired by Bavaria-Palatinate.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Wetzlar is acquired by the Regensburg Principality.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Regensburg is acquired by the Regensburg Principality.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Überlingen is mediatized to Baden.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Wimpfen is acquired by the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Kaufbeuren lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Rothenburg lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1804: In 1803, the Prince-Bishopric of Würzburg was secularized by the Electorate of Bavaria.
January 1804: Establishment of the Bretzenheim Lordship.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Goslar is acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia.
January 1804: The Werden Abbey is acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia.
January 1804: Eichstädt is acquired by the Salzburg Electorate.
January 1804: Kempten was annexed to the Electorate of Bavaria in the course of the German mediatization in 1803.
January 1804: In 1803, Lahr and its environs came under Baden and the town became the seat of a Baden office.
January 1804: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Germany during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic periods.
August 1804: The Principality of Transylvania was founded on August 11, 1804 as a hereditary monarchy by Archduke Franz of Austria, who, as Franz II, was the last Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire. The territory went to the Austrian Empire (Territories outside HRE).
August 1804: The territory of the Austrian Empire was founded on August 11, 1804 as a hereditary monarchy by Archduke Franz of Austria, who, as Franz II, was the last Emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
October 1804: In 1804 Weißenburg in Bayern was annexed by Prussia.
March 1805: The Principality of Lucca and Piombino was a state created from the union of the Principality of Piombino with Lucca and assigned by Napoleon I to his sister Elisa and brother-in-law Felice Baciocchi on March 18, 1805.
June 1805: The last, and only, doge of the Ligurian Republic was Girolamo Luigi Durazzo, appointed by Bonaparte on August 10, 1802, who was deposed on May 29, 1805 with the annexation of Liguria to the French Empire (June 4).
June 1805: Napoleon creates the Principality of Lucca-Piombino and assigns it to his sister Elisa Bonaparte and her husband Felice Baciocchi. End of the ancient Republic of Lucca.
January 1806: The former Imperial Citiy of Konstanz is ceded to Baden.
January 1806: Schramberg was incorporated into the Electorate of Württemberg in 1805 in the course of mediatization.
January 1806: The Salzburg Electorate is acquired by the Austrian Empire.
May 1806: In April 1806, Alexius Friedrich Christian von Anhalt-Bernburg became the first of the princes of Anhalt to become duke.
August 1806: The grand duchy originally formed on the basis of the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1806 as the Grand Duchy of Hesse.
August 1806: Established.
January 1807: In 1806, the territory of castell was transferred to the Kingdom of Bavaria as a result of the Treaty of Pressburg.
January 1807: Wertheim County is divided between Baden and Bavaria.
January 1807: French occupation of Jever.
January 1807: The Imperial City of Frankfurt am Main is acquired by the Regensburg Principality.
January 1807: Solms is divided between the Grand Duchy of Hesse (Hesse-Darmstadt) and Nassau.
January 1807: The Fuerstenberg County is acquired by the Granduchy of Baden.
January 1807: In 1806, the city of Nuremberg was transferred to the Kingdom of Bavaria as part of the territorial changes brought about by the Napoleonic Wars. This decision was made as a result of the Treaty of Pressburg, signed between Napoleon Bonaparte and Emperor Francis II of Austria.
January 1807: The Principality of Öttingen is acquired by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
January 1807: The Erbach County is acquired by the Granduchy of Hesse.
January 1807: The majority of the Leiningen principality fell to the Grand Duchy of Baden.
January 1807: Sayn-Wittgenstein-Karlsburg passes to the Grand Duchy of Hesse.
January 1807: In 1806, the various Hohenlohe territories were divided between the Kingdom of Württemberg and the Kingdom of Bavaria. This decision was made as part of the territorial reorganization following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire.
January 1807: In 1806, the different Hohenlohe territories, ruled by the Hohenlohe family, were divided between the Kingdom of Württemberg and the Kingdom of Bavaria as a result of the territorial changes brought about by the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire.
January 1807: Kurfuerstentum Baden annexed to Wurttemberg.
January 1807: In 1806 the rule of Gimborn-Neustadt passed to the Grand Duchy of Berg.
January 1807: In 1806, due to the Rhine Confederation Act, Scheer came to the Kingdom of Württemberg and was assigned to the Oberamt Saulgau.
January 1807: The Homburg Lordship is acquired by the Granduchy of Berg.
January 1807: In 1806, Count Philip Francis of Adendorf was raised to a Prince, and his lands were renamed to the 'Principality of Leyen'.
January 1807: In 1806, in the reorganization of Germany occasioned by the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation, Maximilian I Joseph, now King of Bavaria, ceded Berg to Napoleon in return for the Principality of Ansbach.
January 1807: Pappenheim County was annexed ot Bavaria in 1806.
January 1807: The March of Tresana is mediatizated by Napoleon.
January 1808: In 1807, the territory of Nassau-Orange-Fulda was transferred to the Duchy of Nassau.
January 1808: Jever is annexed by the Kingdom of Holland.
January 1808: Brunswick was occupied from 1807 to 1813 by the French and became part of the Kingdom of Westphalia.
January 1808: In 1806, in the reorganization of Germany occasioned by the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation, Maximilian I Joseph, now King of Bavaria, ceded Berg to Napoleon in return for the Principality of Ansbach.
May 1808: The Metauro department was constituted on 11 May 1808, with the separation of the Marches from the State of the Church and their annexation to the Kingdom of Italy.
January 1809: The Abbey of Werden is annexed by Westphalia.
January 1809: The Kingdom of Westphalia was created received territories ceded by the Kingdom of Prussia in the Peace of Tilsit, among them the region of the Duchy of Magdeburg west of the Elbe River, the Brunswick-Lüneburg territories of Hanover and Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, and the Electorate of Hesse.
May 1809: On May 17, 1809, Napoleon Bonaparte decreed the suppression of the temporal power of the Pope, annexing the territories of Umbria and Latium to the First French Empire. This move was part of Napoleon's efforts to expand his control over Italy and weaken the influence of the Papal States.
July 1810: King Louis did not perform to Napoleon's expectations—he tried to serve Dutch interests instead of his brother's—and the kingdom was dissolved in 1810, after which the Netherlands were annexed by France.
January 1811: Bopfingen, Leutkirch, Ravensburg, Ulm and Wangen are annexed by the Kingdom of Württemberg.
January 1811: The Imperial City of Hamburg is annexed to the First French Empire.
January 1811: Schweinfurth is annexed by the Granduchy of Würzburg.
April 1811: French annexation of the part of Berg north of the Lippe.
January 1812: The Salm Principality was annexed by France in 1811.
January 1812: French troops occupied Swedish Pomerania to end the illegal trade with the United Kingdom from Sweden.
January 1813: Following Napoleon's failed invasion of Russia, the Free City of Danzig was occupied by Prussian and Russian troops. The duchy was under the control of King Frederick William III of Prussia and Tsar Alexander I of Russia.
January 1813: Following Napoleon's failed invasion of Russia, the Duchy of Warsaw, established by Napoleon in 1807, was occupied by Prussian forces under General Ludwig Yorck and Russian troops led by General Mikhail Barclay de Tolly in 1812.
January 1804: The Imperial City of Dortmund is acquired by the Nassau-Orange-Fulda Principality.
January 1807: The imperial fief of Sorbello is mediatizated by Napoleon.
January 1803: In 1802, the Prince-Bishopric of Eichstätt was secularized by the Electorate of Bavaria.
October 1806: The Electorate of Baden became the much-enlarged Grand Duchy of Baden through the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1803-1806.
January 1804: The Freising Prince-Bishopric is acquired by Bavaria-Palatinate as a result of the Reichsdeputationshauptschluss.
March 1799: The Helvetic Republic annexed the Three Leagues and created the Canton of Raetia.
January 1804: Establishment of the Thurn und Thaxis Principality.
January 1805: The Bretzenheim Lordship is acquired by the Austrian Empire.
January 1807: The March of Aulla-Podenzana is mediatizated by Napoleon.
January 1808: In 1807, the territory of Rietberg was transferred to the Kingdom of Westphalia.
January 1808: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Germany during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic periods.
January 1804: The Osnabrück Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Electorate of Hanover (England).
January 1804: The Fulda Prince-Bishopric is secularised to Nassau.
January 1804: In 1803 the rule of Freising ended, and "Bayrisch Waidhofen", one of the exclaves of the Bishopric, became part of the Habsburg Domains.
January 1807: The Sternstein County is acquired by the Kingdom of Bavaria.
June 1806: In February 1806 the kingdom of Naples was assigned to Giuseppe Bonaparte and the principalities of Benevento and Pontecorvo were created.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Leutkirch lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
January 1804: In the course of mediatisation in 1803, Ravensburg lost its status as an Imperial City and was assigned to Bavaria.
Was the succesful insurrection by self-liberated slaves of the colony of Saint-Domingue (modern-day Haiti) against French rule leading to the creation of the independent country of Haiti, the first independent nation of Latin America and the Caribbean.
September 1793: About 600 British soldiers from Jamaica landed at Jérémie.
September 1793: On 22 September 1793, Mole St. Nicolas, the main French naval base in Saint-Domingue, surrendered to the Royal Navy peacefully. Everywhere the British went, they restored slavery, which made them hated by the mass of common people.
October 1793: In 1793, Captain-General Joaquin Garcia y Moreno led a Spanish force into the Northern Province, which was under military occupation by Spain. This marked a significant event in the history of the region, as it changed the political landscape and control of the territory.
June 1794: In 1794, General Whyte, a British military leader, captured Port-au-Prince during the military occupation of Great Britain in Haiti. This event was part of the larger conflict between Britain and France during the French Revolutionary Wars.
January 1795: The French stormed and retook Tiburon in a surprise attack.
November 1803: The Haitian rebels finally managed to decisively defeat the French troops at the Battle of Vertières on 18 November 1803, leading the first ever group of enslaved peoples to successfully create an independent state through a slave revolt.
May 1798: In 1798, British General Maitland met with Toussaint Louverture, the leader of the slave rebellion in Haiti, to negotiate an armistice. As a result, the British forces left Port-au-Prince on May 18th, marking a significant moment in the Haitian Revolution.
April 1792: A coalition of whites and conservative free blacks and forces under French commissaire nationale Edmond de Saint-Léger put down the Trou Coffy uprising in the south.
May 1794: Toussaint Louverture betrayed his Spanish allies and ambushed them as they left a church in San Raphael.
January 1804: From the city of Gonaïves, Dessalines officially declared the former colony's independence, renaming it "Haiti" after the indigenous Arawak name.
October 1791: In the south, beginning in September, thirteen thousand slaves and rebels led by Romaine-la-Prophétesse, based in Trou Coffy, took supplies from and burned plantations and freed slaves and occupied (and burned) the area's two major cities, Léogâne and Jacmel.
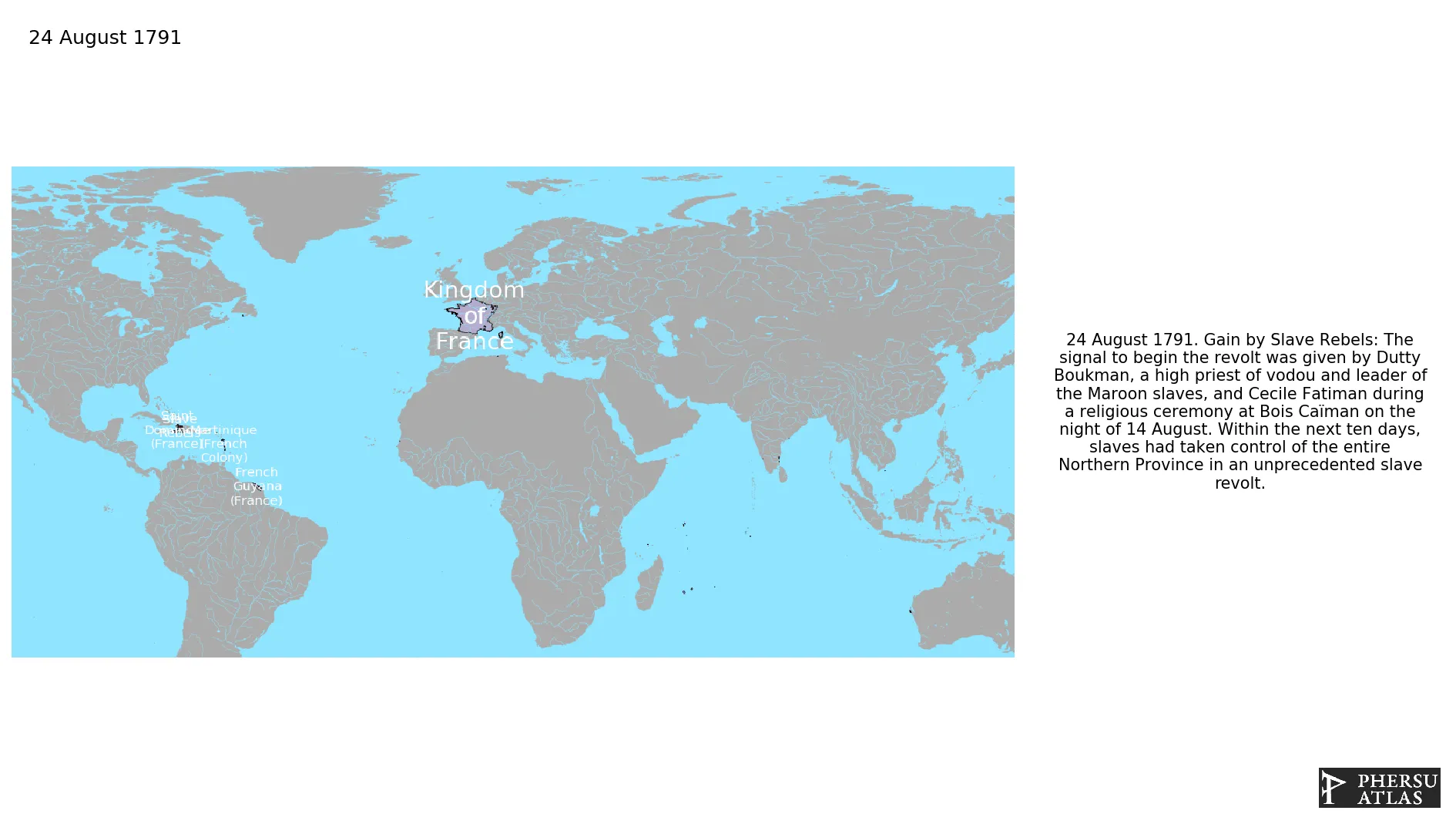
August 1791: The signal to begin the revolt was given by Dutty Boukman, a high priest of vodou and leader of the Maroon slaves, and Cecile Fatiman during a religious ceremony at Bois Caïman on the night of 14 August. Within the next ten days, slaves had taken control of the entire Northern Province in an unprecedented slave revolt.
1.1.War of Knives
Was a civil war from June 1799 to July 1800 between the Haitian revolutionary Toussaint Louverture, a black ex-slave who controlled the north of Saint-Domingue (modern-day Haiti), and his adversary André Rigaud, a mixed-race free person of color who controlled the south.
June 1799: Rigaud struck first; after slaughtering many whites in South Province to secure his rear, on June 16-18, 1799, Rigaud sent 4,000 troops to seize the southern border towns of Petit-Goâve and Grand-Goâve.
September 1800: By August, 1800, Toussaint Louverture was ruler of all Saint-Domingue.
March 1800: Toussaint Louverture, a former slave who became a leader of the Haitian Revolution, took control of the town of Jacmel.
1.2.Invasion of Santo Domingo
Was the Haitian invasion of the Spanish colony of Santo Domingo, which occupied the eastern half of the island of Hispanola.
January 1801: In December 1800, Toussaint ordered an invasion of the Spanish colony of Santo Domingo, which occupied the eastern half of the island of Hispanola. Although Spain had technically ceded Santo Domingo to France in the 1795 Peace of Basel, the colony was still controlled by a Spanish administration at the time.
1.3.Saint-Domingue expedition
Was the unsuccesful invasion of Haiti, a rebellious French colony, ordered by Napoleon.
March 1802: The Haitian rebeles abandoned the fort of Crête-à-Pierrot.
May 1802: Louverture, a former slave who led the Haitian Revolution, agreed to surrender to French forces. At this point France controlled the whole Island of Hispaniola.
February 1802: The Battle of Ravine-à-Couleuvres, also known as the Battle of Snake Gully, was a major battle of the Haitian Revolution on 23 February 1802. After the battle, France controllled a territory between Fort-Liberté and Lacroix (Artibonite)
February 1802: The French arrived on 2 February 1802 at Le Cap with the Haitian commander Henri Christophe being ordered by Leclerc to turn over the city to the French. When Christophe refused, the French assaulted Le Cap and the Haitians set the city afire rather than surrender it.
Were a series of wars between the Kingdom of France (later the French Republic) and several European Monarchies. The French Revolution had deteriorated the relations of France with the other European countries, that tried several times to invade France in order to crash the revolutionary government.
October 1797: The March of Aulla-Podenzana is occupied by France.
October 1797: The March of Tresana is occupied by France.
February 1798: In February 1798 the ephemeral Roman Republic was proclaimed, closely linked to France.
January 1795: The French armies drove the Austrians, British, and Dutch beyond the Rhine, occupying Belgium, the Rhineland, and the south of the Netherlands.
March 1794: In the Caribbean, the British fleet landed in Martinique in February, taking the whole island by 24 March.
May 1794: Guadeloupe conquered by great britain.
July 1794: The Battle of Trippstadt was a relatively minor French military action in 1794. This victory gave the French control of the mountain passes across the lower Vosges ( Kaiserslautern, Trippstadt, Schänzel, Neustadt and along the banks of the Speyerbach River).
April 1795: In 1795, Sint Eustatius, a Dutch colony, was occupied by the French military.
May 1795: In 1795, Saba was occupied by the French military. This period of French occupation would last until April 1801.
May 1795: The Treaty of Den Haag was signed on May 16, 1795 between representatives of the French Republic and the Batavian Republic. The Batavian Republic ceded to France the territories of Maastricht, Venlo, and Zeelandic Flanders. Moreover, the accord established a defensive alliance between the two nations.
March 1797: On 9 December 1797, Frédéric-César de La Harpe, a member of the Helvetian Club from Vaud, asked France to invade Bern to protect Vaud. Seeing a chance to remove a feudal neighbor and gain Bern's wealth, France agreed. By February 1798, French troops occupied Mulhouse and Biel/Bienne. Meanwhile, another army entered Vaud, and the Lemanic Republic was proclaimed.
October 1797: In 1797, the districts of Chiavenna, Valtellina, and Bormio, dependencies of the Three Leagues (an associate of the Confederation), revolted under the encouragement of France. They were quickly invaded and annexed to the Cisalpine Republic on 10 October 1797.
October 1797: Following the Treaty of Campo Formio, where Napoleon Bonaparte decreed the final dissolution of the Venetian Republic, Preveza - like other Venetian possessions in Greece and Albania - was ceded to Revolutionary France.
February 1793: French control of the Principality of Monaco during the French revolution from 1793 to May 17, 1814, as part of the département of Alpes-Maritimes.
October 1798: In 1798 small Venetian territories that were not ceded to the Austrian Empire were conquered by the Ottoman Empire.
February 1798: In February 1798, the ephemeral Roman Republic was proclaimed in Rome, Italy. The republic was closely linked to France.
January 1793: In 1792, revolutionary France annexed several territories of the Holy Roman Empire, including Worms, Speyer, and territories of the Flanders region.
September 1794: In mid-September 1794, the Prussians, led by Frederick William II, attacked the weakened French forces, commanded by General Lazare Hoche, in the north-eastern frontier and reoccupied Kaiserslautern, which was part of the territory of Bavaria-Palatinate at the time.
June 1794: In 1794, the British were driven out of Guadeloupe by Victor Hugues, a French politician and revolutionary.
October 1797: The Duchy of Milan remained an Austrian possession until 1796, when a French army under Napoleon Bonaparte conquered it, and it ceased to exist a year later as a result of the Treaty of Campo Formio, when Austria ceded it to the new Cisalpine Republic.
January 1793: Marie-Galante, which was Republican, separated itself from the royalist government of Guadeloupe.
March 1793: The Rauracian Republic was annexed by the First French Republic and became the department of Mont-Terrible.
January 1796: Wied-Runkel was annexed by France.
October 1797: The March of Mulazzo is occupied by France.
November 1797: The so-called Republic of Ancona was a revolutionary municipality which was proclaimed by the Army of Italy of the young general Bonaparte on 19 November 1797, among the other Jacobin republics. It was based in Ancona and included the territories which, in the Papal State, were part of the Marca of Ancona with the capital Macerata, or the current territory of the Marches.
March 1798: After only 117 days, on March 7, 1798, the Anconine Republic was united with the Roman Republic.
February 1798: The Tiberina Republic was a provisional government which was proclaimed on February 4, 1798, when the Jacobins took power in the city of Perugia.
April 1795: The French occupy the entire island of Saint Martin.
April 1796: The colony was on 22 April 1796 again captured by Britain, however who now remained in possession of the colony until 27 March 1802, when Berbice was restored to the Batavian Republic under the terms of the Treaty of Amiens.
March 1797: The Republic of Crema was created in March 1797 following the occupation of the city of Crema (Italy) by French troops.
December 1792: Secession of the Rauracian Republic, partly composed of territories belonging to the Abbey of Basel.
January 1794: In 1794, during the War of the First Coalition, the French armies, led by generals such as Jean-Charles Pichegru and Jacques François Dugommier, were defending the border regions in the Pyrenees against the Spanish and British forces. The territory ultimately went to the First French Republic.
March 1802: Great Britain held Martinique until the Peace of Amiens.
October 1797: The Republic of Noli is annexed to the Ligurian Republic.
January 1796: In 1795, the territory of Ligny was annexed by the First French Republic.
January 1796: In 1795 the area of Stablo-Malmedy became part of the French department of Ourthe, and from 1796 the abbeys and monasteries were secularized.
January 1793: With an unauthorized plebiscite, under pressure from French revolutionaries, the Comtat Venaissin was annexed by France.
August 1793: Counter-revolutionary forces turned Toulon over to Britain and Spain.
December 1793: Toulon was not retaken by Dugommier (with the assistance of the young Napoleon Bonaparte) until 19 December.
January 1794: In 1793, the territory of Dachstuhl was annexed by the First French Republic.
January 1794: In 1793, the territory of Moempelgard was annexed by the First French Republic.
January 1794: Salm-Salm annexed to France.
January 1795: The Imperial City of Cologen (German: Köln) is annexed by France.
August 1795: Peace of Basel of 1795 at the end of the War of the First Coalition between the Kingdom of Prussia and the French Republic. France gained the left bank of the Rhine.
January 1796: In 1795, the territory of Rochefort was annexed by the First French Republic.
January 1796: Salm-Salm annexed to France.
January 1796: Between 1798 and 1814, Schleiden County was part of France after being conquered in the First Coalition War and through the French annexation of the left bank of the Rhine and through the Peace of Campo Formio and Lunéville.
April 1796: The Republic of Alba was established in 1796 as a sister republic of the First French Republic. It was created during the French Revolutionary Wars and lasted only from April 26 to April 28 of that year. The territory of Alba was located in present-day Italy.
April 1796: The Republic of Alba was established by Napoleon Bonaparte after the French army conquered the region. It was a sister republic of the First French Republic and only existed for a brief period from 26 to 28 April 1796 before being annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia.
May 1797: Before the French Revolutionary Wars, the Ionian Islands had been part of the Republic of Venice. When the 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio dissolved the Republic of Venice, they were annexed to the French Republic.
October 1797: Campo Ligure becomes part of the Ligurian Republic.
October 1797: The March of Fosdinovo is occupied by France.
October 1797: The March of Sorbello is occupied by France.
March 1798: The Tiberina Republic became part of the Napoleonic Roman Republic.
October 1798: The Battle of Nicopolis in 1798 took place in the Venetian possession of Greece. The Ottoman troops, led by Ali Pasha and his son Mukhtar, decisively defeated the Venetian forces, leading to the territory being transferred to the Ottoman Empire.
January 1799: In 1797, the districts of Chiavenna, Valtellina, and Bormio, dependencies of the Three Leagues (an associate of the Confederation), revolted under the encouragement of France. They were quickly invaded and annexed to the Cisalpine Republic on 10 October 1797.
2.1.Belgian front
Was the Belgian theatre of the War of the First Coalition.
June 1792: In 1792, during the French Revolutionary Wars, General Luckner led a 20,000 strong French force to invade the Austrian Netherlands. They successfully captured Menen and Kortrijk on 19 June.
June 1792: The French forces, led by General Charles François Dumouriez, withdrew back to Lille on 30 June 1792 after facing resistance from Austrian and Dutch troops in Menen and Kortrijk.
2.2.Battle of Valmy
Was a battle between France and an alliance of European states led by Prussia that attempted an invasion of the French territory.
September 1792: First Coaltion leaves conquered territory in the Rhineland.
September 1792: In July 1792 an Austro-Prussian force assembled at Coblenz in the Rhineland with the aim of marching on Paris, rescuing King Louis XVI, and ending the revolution. The coalition forces met with the French army in Valmy on September 20, 1792 but were defeated.
August 1792: In 1792, during the French Revolutionary Wars, the First Coalition forces, led by Duke Charles William Ferdinand of Brunswick, conducted a slow march to besiege the city of Verdun. The city eventually fell to the Coalition forces, marking a significant event in the early stages of the war.
August 1792: Coalitionary forces captured Longwy.
September 1792: In 1792, during the French Revolutionary Wars, the Duke of Brunswick, leading the First Coalition forces, decided not to attack and instead camped for three days at Landres. This delay allowed the French revolutionary forces, led by General Dumouriez, to regroup and prepare for the Battle of Valmy.
September 1792: Verdun surrendered on 2 September 1792.
2.3.Piedmontese front
Was the Piedmontese theatre of the War of the First Coalition.
January 1794: In 1794, during the French Revolutionary Wars, a French invasion of Piedmont led by General Jean-Charles Pichegru failed in the border regions. The territory ultimately went to the Kingdom of Sardinia, ruled by King Victor Amadeus III.
September 1792: In 1792, during the French Revolution, the County of Nice was attacked and forced to surrender by the French revolutionary forces under the command of General Jacques Bernard d'Anselme. This resulted in the territory of Savoy and Nice being occupied by France.
2.4.Rhineland campaign of 1792
Was a French military campaign in the Rhineland.
September 1792: The French attacked Speyer on 29 September and conquered it the next day.
October 1792: French troops occupy Worms and Philippsburg without a fight.
October 1792: French general Custine captured Mainz on 21 October 1792.
October 1792: The French army penetrated as far as Frankfurt, which surrendered.
2.5.Battle of Jemappes
Was a battle between France and Austria in modern-day Belgium during the War of the First Coalition.
October 1792: Advancing French forces reach Mons.
2.6.Flanders Campaign
Was a French military campaign in the Flanders.
February 1793: The Republican French army stopped near Aldenhoven.
January 1795: On 10 January French general Pichegru ordered a general advance across the frozen river between Zaltbommel and Nijmegen and the allies were forced to retreat behind the Lower Rhine.
February 1793: The French Armée du Nord commanded by general Charles-François Dumouriez advanced from Antwerp and invaded Dutch Brabant.
February 1793: A French army under Francisco de Miranda laid siege to Maastricht.
June 1795: Territory evacuated by the French at the end of the Flanders Campaign. The surrender of Luxembourg on 7 June 1795 concluded the French conquest of the Low Countries, thus marking the end of the Flanders Campaign.
October 1793: In mid October French officer Vandamme laid siege to Nieuport. At the same time French marshal MacDonald took Werwicq.
January 1794: Spanish armies crossed the Pyrenees.
April 1794: French generals Jean-Charles Pichegru and Lazare Hoche defeated Austrian General Clerfayt at the Battle of Mouscron. As a result, they were able to retake the territories of Courtrai (Kortrijk) and Menen, which had been under Austrian control.
June 1794: Ypres surrendered to French General Charles Pichegru.
July 1794: After suffering defeats at the hands of French revolutionary forces, Austrian General Coburg retreated to Tienen in 1794.
July 1794: Brussels is conquered by French troops led by general Jean-Charles Pichegru on 11 July 1794.
September 1794: Antwerp was evacuated by the Austrian forces on the 24th of November 1794. Three days later, General Pichegru, a prominent French military leader during the French Revolutionary Wars, occupied the city.
November 1794: After a brief siege, Nijmegen was found to be untenable and the city was abandoned to the French.
November 1794: The French army occupies Liège.
December 1794: By 28 December the French had occupied the Bommelwaard and the Lands of Altena.
January 1795: On 16 January, the city of Utrecht surrendered to the French.
January 1795: The Batavian Republic was established after the French revolutionary forces invaded the Netherlands, leading to the overthrow of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands. The proclamation of the Batavian Republic on 19 January 1795 marked the beginning of a new era in Dutch history.
October 1793: Dumonceau (France) drove the Hanoverians from Menen.
January 1795: Dutch revolutionaries led by Cornelius Krayenhoff put pressure on the city council of Amsterdam to hand over the city to the invading French army.
October 1794: General Jean-Baptiste Jourdan led the French forces to capture the city of Namur in present-day Belgium.
July 1793: Valenciennes conquered by First Coalition.
January 1794: In 1793, during the French Revolutionary Wars, General Charles François Dumouriez led French forces into Brabant, a territory that was part of the Austrian Netherlands. This military occupation was part of France's campaign to expand its territory and spread revolutionary ideals.
August 1794: Mechelen, a city in present-day Belgium, fell to French forces on the 15th of January, 1794.
October 1793: Marchiennes on 29 October 1793 was the site of a battle between the French Revolutionary Army, led by General Jean-Baptiste Jourdan, and the First Coalition forces. The First Coalition was a group of European nations united against revolutionary France during the French Revolutionary Wars.
September 1793: Coalitionary forces captured Le Quesnoy, a strategic town in northern France.
September 1793: In 1793, during the French Revolutionary Wars, the Austrian general Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany, began besieging the French-held city of Maubeuge as part of the First Coalition's efforts to defeat the revolutionary government in France.
October 1793: Cysoing conquered by First Coalition.
April 1794: Landrecies fell on 30 April 1794 to the First Coalition forces, led by Austrian General Prince Josias of Coburg and British General Sir William Erskine. The capture of Landrecies was part of the larger War of the First Coalition, a conflict between revolutionary France and a coalition of European powers.
July 1793: During the French Revolutionary Wars, the Prussians, led by Duke of Brunswick, besieged Mainz, held by French revolutionary forces under General Custine. The siege lasted from 14 April to 23 July 1793.
July 1793: Condé-sur-l'Escaut conquered by First Coalition.
January 1795: The Batavian Republic (Dutch Bataafse Republiek, Nine Dutch: Bataafsche Republiek) was a daughter republic established by the French Revolutionary Export, formed from the Republic of the Seven United Provinces. It was proclaimed on January 19, 1795.
September 1793: Maubege is conquered by coalitionary forces.
2.7.British Invasion of Corsica
British forces invaded and succesfully occupied Corsica during the War of the First Coalition.
February 1793: The French forces, led by General Napoleon Bonaparte, withdrew from San Fiorenzo in 1793 after facing military occupation by Great Britain. This event marked a strategic victory for the British forces in the Mediterranean region during the French Revolutionary Wars.
August 1794: In 1794, during the Anglo-Corsican Kingdom, negotiations between British commander Stuart and French commander Raphaël de Casabianca in Calvi, Corsica, resulted in a truce and eventual capitulation on August 10th.
May 1794: In 1794, during the French Revolutionary Wars, the city of Bastia in Corsica surrendered to British Admiral Samuel Hood offshore. This marked the beginning of Great Britain's military occupation of the territory, which lasted until 1796.
2.8.War of the Pyrenees
Was the Pyrenean front of the First Coalition's war against the First French Republic.
July 1795: Spanish general Cuesta recaptured Puigcerdà and Bellver from the French on 26 and 27 July.
April 1793: In 1793, Spanish General Antonio Ricardos invaded the Cerdagne region and captured the town of Saint-Laurent-de-Cerdans during the War of the Pyrenees between France and Spain. This military occupation marked a significant event in the conflict between the two countries.
September 1793: Eustache Charles d'Aoust rallied the French to win the Battle of Peyrestortes on 17 September. This represented the farthest Spanish advance in Rousillon.
December 1793: In 1793, during the French Revolutionary Wars, Spanish General Gregorio García de la Cuesta led the successful military occupation of Collioure and Port-Vendres, seizing control of the ports from the French.
February 1794: In 1794, during the War of the Pyrenees, Jacques Lefranc, a French general, led 2,000 Republican troops to capture the strategic Izpegi Ridge in the Basque Country, which was under Spanish control at the time. This victory marked a significant military occupation by France in the region.
August 1794: Moncey, a French general during the French Revolutionary Wars, captured San Sebastián in 1794 without facing any opposition. This marked the beginning of French military occupation in the region.
September 1794: The fortress of Bellegarde fell on 17 September 1794 after the Spanish garrison, led by Captain General Alejandro O'Reilly, was starved out by the French forces under General Dugommier during the War of the Pyrenees. This marked a significant victory for France in their military occupation of the region.
November 1794: Figueres and its Sant Ferran Fortress fell to the French with 9,000 prisoners.
July 1795: Vitoria, a city in northern Spain, fell to the French forces led by General Jean-Charles de Bailleul on 17 July 1795 during the War of the Pyrenees.
July 1795: Bilbao conquered by france.
July 1795: The Peace of Basel ends the War of the Pyrenees on July 22, 1795 In the treaty, it was established that France returned the occupied territories to Spain. Spain, in compensation for the recovery of the territories of the Pyrenees, ceded to revolutionary France the eastern part of Santo Domingo. The French already controlled the western part of the island, Santo Domingo, since the signing of the Treaty of Rijswijk in 1697.
August 1793: In 1793, Luc Siméon Auguste Dagobert, a French military leader, defeated a Spanish force led by Manuel la Peña at Puigcerdà in the Cerdagne region. This victory led to the territory of Puigcerdà and Bellver being occupied by France.
October 1794: From 15 to 17 October, French marsha Bon-Adrien Jeannot de Moncey, launched a broad front offensive from the Baztan valley and the Roncevaux Pass to the south in the direction of Pamplona. The Battle of Orbaitzeta saw clashes at Mezkiritz (Mezquiriz), Orbaitzeta, Lekunberri, and Villanueva (Hiriberri).
June 1793: The Siege of Bellegarde was part of the War of the First Coalition, with the French garrison surrendering to the Spanish forces led by Captain General Antonio Ricardos. This marked a significant victory for Spain in the conflict.
February 1795: Pierre François Sauret was a French general who led the successful Siege of Roses in 1795. The Siege of Roses was a military operation during the War of the Pyrenees, where French forces occupied the town of Roses in Catalonia, Spain.
2.9.Peace of Basel
Were a series of Treaties between the French Republic and Prussia, Spain and Hesse-Kassel that ended the War of the First Coalition with these countries.
April 1795: Peace of Basel of 1795 at the end of the War of the First Coalition between the Kingdom of Prussia and the French Republic. France gained the left bank of the Rhine.
April 1795: The Peace of Basel of 1795 consisted of three peace treaties involving France during the French Revolution. The first was with Prussia (represented by Karl August von Hardenberg) on 5 April. France returned all of the lands east of the Rhine captured during the war.
2.10.Italian theatre (War of the first coalition)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the First Coalition.
March 1797: Archduke Charles of Austria was defeated at the Tagliamento on 16 March, and Napoleon proceeded into Austria, occupying Klagenfurt.
June 1796: The Bolognese Republic was a French client republic established when Papal authorities escaped from the city of Bologna in June 1796.
February 1797: Frecnh forces besiege Mantua.
November 1795: In northern Italy the victory at the Battle of Loano in November gives France access to the Italian peninsula.
April 1796: Battle of Mondovì.
May 1796: French forces occupy Lodi and Milan.
May 1796: The Duchy of Milan was ruled by the Habsburgs and became the Transpadane Republic after being occupied by Napoleon's French forces in 1796. This marked the end of Habsburg rule in the region and the establishment of a new republic.
September 1796: In September, Napoleon Bonaparte marched north against Trento in Tyrol. Bonaparte overran the holding force at the Battle of Rovereto.
September 1796: French victory at the Battle of Bassano on 8 September 1796.
November 1796: The Austrians defeated the French at Calliano.
November 1796: Napoleon defeated the Venetians led by Alvinczi in the Battle of Arcole southeast of Verona.
January 1797: The Duchy of Milan remained an Austrian possession until 1796, when a French army under Napoleon Bonaparte conquered it, and it ceased to exist a year later as a result of the Treaty of Campo Formio, when Austria ceded it to the new Cisalpine Republic.
January 1797: In 1797, during the Napoleonic Wars, French troops under Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Venetian state up to the Adige River. The Austrians controlled Vicenza, Cadore, and Friuli as part of the ongoing conflict in the region.
February 1797: French troops advanced directly toward Austria over the Julian Alps. General Barthélemy Joubert invaded Tyrol.
April 1797: The French advanced as far as Judenburg by the evening of April 7th.
June 1797: In 1797, Napoleon Bonaparte deposed Giacomo Maria Brignole, the last doge of the Republic of Genova. This marked the end of the Republic of Genova and the territory was incorporated into the Ligurian Republic.
June 1797: In June 1797, the territories of Bologna, Ferrara, and Romagna were annexed to the Cisalpine Republic through the Treaty of Tolentino. This agreement was signed between Napoleon Bonaparte, who was leading the French forces in Italy, and representatives of the Papal States.
April 1796: Napoleon defeated an Austro-Sardinian force at the Battle of Millesimo.
August 1797: On August 5, 1797 Napoleon's troops occupied the Principality of Torriglia, and annexed it to the Ligurian republic.
May 1796: On 28 April, the Piedmontese signed an armistice at with the French at Cherasco. On 18 May they signed a peace treaty in Paris, ceding Savoy and Nice and allowing the French bases to be used against Austria.
April 1796: Napoleon won at the Second Battle of Dego, driving the Austrians northeast, away from their Piedmontese allies.
December 1796: The Bolognese Republic was absorbed by the Cispadana Republic within a few months.
January 1797: The Rocchetta-Suvero Marquisate became part of the territories of the Cispadana Republic.
February 1797: Carpi is annexed to the Cisalpine Republic.
October 1796: Spain signed the Second Treaty of San Ildefonso with France on 19 August 1796, entering the war against Britain on the side of France in return for concessions in Italy. In response, Britain withdrew from Corsica. On 19 October 1796, the French reconquered Bastia and Corsica became a French département.
July 1797: The Cispadane Republic is merged into the Cisalpine Republic.
November 1796: The Austrians were victorious over the French at Bassano.
January 1797: The March of Castevoli and the March of Villafranca were unified in the Castevoli and Villafranca Marquisate.
October 1796: The Duchy of Modena-Reggio was occupied by Napoleon and entered the Cispadan Republic.
October 1796: Constitution of the Cispadane Republic.
June 1797: The Cispadane Republic was merged with the Transpadane Republic (formerly the Duchy of Milan until 1796) to form the Cisalpine Republic.
July 1797: The Republic of Crema entered then into the Cisalpine Republic in July 1797.
July 1797: The 1797 Republic of Aste was a Jacobin municipality fruit of the political events that led, between June and July of that same year, to the proclamation of popular self-government in the city of Asti.
August 1796: The Reggiana Republic was an ephemeral republican municipality born from the secession of the Reggio territories from the Duchy of Modena and Reggio proclaimed on 26 August 1796.
2.11.Rhine campaign of 1796
Were a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
July 1796: On 5 July 1796, French general Desaix defeated Austrian general Latour at the Battle of Rastatt.
June 1796: The French army occupies Renchen.
September 1796: End of Mainz blockade.
June 1796: French General Kléber defeated the Duke of Württemberg in the Battle of Altenkirchen.
July 1796: French forces occupied the city of Giessen.
July 1796: French forces occupy the city of Friedberg.
July 1796: Neuwied conquered by france.
July 1796: French conquest of Cannstadt.
August 1796: French forces occupy Neresheim.
August 1796: On 17 August the French took Sulzbach.
June 1796: A division of French general Kléber's troops seized a bridge over the Sieg from Michael von Kienmayer's Austrians at Siegburg.
July 1796: Ettlingen conquered by france.
2.12.Rhine campaign of 1797
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
September 1796: Wiesbaden conquered by france.
2.13.Rhine campaign of 1799
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
September 1796: The Austrians established a strong cordon that forced General Jean Victor Marie Moreau to shift his forces southward to the remaining bridgehead at Hüningen.
2.14.Rhine campaign of 1798
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
September 1796: On 16-18 September Charles of Brunswick defeated the French Army of Sambre & Meuse in the Battle of Limburg.
2.15.Rhine campaign of 1800
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
October 1796: The French retreated across the rivers Rhine and Elz, destroying all the bridges.
October 1796: French forces occupy Schliengen.
2.16.Rhine campaign of 1801
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
January 1797: The French besieged Kehl from 10 November 1797.
2.17.Rhine campaign of 1802
Was one of a series of battles in the Rhineland during the War of the First Coalition.
February 1797: The French handed over the east-bank bridgehead at Hüningen.
2.18.Treaty of Campo Formio
Was a treaty between France and Austria that ended the War of the First Coalition.
January 1798: The Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI). The treaty transferred the Austrian Netherlands to France. The territories of Venice were partitioned, most were acquired by Austria. Austria recognized the Cisalpine Republic and the newly created Ligurian Republic. Extension of the borders of France up to the Rhine, the Nette, and the Roer.
October 1797: The Treaty of Campo Formio was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI). The treaty transferred the Austrian Netherlands to France. The territories of Venice were partitioned, most were acquired by Austria. Austria recognized the Cisalpine Republic and the newly created Ligurian Republic. Extension of the borders of France up to the Rhine, the Nette, and the Roer.
January 1798: In 1797, the territory of St. Hubert was ceded to the First French Republic. This decision was made as part of the Treaty of Campo Formio, signed by Napoleon Bonaparte and Austrian foreign minister Count Ludwig von Cobenzl.
The theatre of war in the overseas colonies during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.
May 1815: End of British occupation of Bonaire.
June 1793: Karikal conquered by great britain.
July 1793: Yanaon (Yanam) conquered by great britain.
July 1793: Mahé, a French colony, was occupied by British forces on 16 July 1793.
August 1793: In 1793, Pondichéry was occupied by the British military. This event was part of the larger conflict between Great Britain and France during the French Revolutionary Wars. Pondichéry was a French colonial territory in India, and its capture by the British was a significant blow to French influence in the region.
August 1814: On 13 August 1814, the British combined the colonies of Demerara and Essequibo into the colony of Demerara-Essequibo.
August 1814: The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814 restored Bengal to Dutch rule.
January 1796: British occupation of Malacca during the Napoleonic Wars (1795-1818).
January 1797: Eseequibo annexed by the British.
January 1797: The British forces, led by Sir Ralph Abercromby and Lieutenant Colonel Alured Clarke, recaptured the territories of Demerara, Essequibo, and Berbice from the Dutch in 1796 during the French Revolutionary Wars. This military occupation solidified British control over the region.
April 1816: 5 Jun 1815 - 28 Apr 1816: British occupation of Martinique.
August 1816: 18 September 1811 - 19 August 1816: the Dutch Dejima Factory was occupied by the British.
November 1816: After the British occupation during the Napoleonic Wars, the French Saint-Martin administration resumed control of the territory in 1816.
August 1814: Essequibo became official British territory on 13 August 1814 as part of the Treaty of London and was merged with the colony of Demerara.
January 1797: In 1796, the British colony of Saint Peter (located in present-day Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada) was sacked by French troops during the French Revolutionary Wars. This event was part of the military occupation of the territory by France.
June 1793: Chandernagore was a French colony in India. In 1793, during the French Revolutionary Wars, the British East India Company captured the territory.
February 1809: 24 Feb 1809 - 9 Dec 1814: British occupation of Martinique.
February 1796: In the period 1788 - 1795 there was no cordiality between the Dutch and the British. The British had planned after their conquest of India to take over a dozen Dutch possessions in the region, with Ceylon as the biggest prize. Their chance came when in the winter of 1794/95 Holland was overrun by the French army. On 14 February 1796, the Dutch forces surrendered with minimal bloodshed.
April 1817: Yanaon was given back to the French on 12 Apr 1817.
August 1810: In 1810, British forces led by Admiral Robert Stopford occupied the Maluku Islands, also known as the Spice Islands, as part of the Napoleonic Wars. This military occupation was part of the British strategy to control key trading ports in the Dutch East Indies.
September 1800: Curaçao was occupied by the British from 13 September 1800 to 13 January 1803.
January 1804: During the Napoleonic Wars, Great Britain captured Gorée in 1803.
January 1802: During the French occupation of the Netherlands between 1810 and 1814, the Dutch possessions on the Gold Coast held the rather unusual position—together with the island of Deshima in Japan—of being the only Dutch territories not occupied by either France or Great Britain.
November 1802: 21 April 1801 - 21 November 1802: British occupation of Sint Estatius.
December 1802: Great Britain leaves the Island of Saint Martin where the French (northern part of the Island) and the Dutch (southern part of the Island) resume control.
March 1803: 20 Mar 1803 - 22 Jun 1816: British occupation of Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
December 1807: British occupation of the Saint Croix island.
January 1809: The Royal Navy took possession of Marie-Galante to stop French privateers using its port.
January 1809: Portuguese conquest of French Guiana.
February 1810: The British occupy the entire island of Saint Martin.
February 1810: 21 February 1810 - 1 February 1816: British occupation of Sint Estatius.
January 1808: 1807-1815: British occupation of the Danish West Indies during the Napoleonic Wars.
May 1814: Under the Treaty of Paris Article VIII France ceded to Britain the islands of "Tobago and Saint Lucia, and of the Isle of France and its dependencies, especially Rodrigues and Les Seychelles.
May 1814: The Treaty of Paris ceded Tobago to the British in 1814.
January 1803: In 1802, Puerto Rico was reconquered by the Spanish, led by Governor Toribio Montes. This marked the return of the territory to Spanish America after a brief period of British occupation.
January 1795: British conquest of the island of Marie-Galante.
November 1815: Danish reconquest of the Saint Croix island.
February 1816: 21 February 1810 - 1 February 1816: British occupation of Sint Estatius.
December 1816: Pondichéry and Chandernagore restored to France.
November 1817: After Napoleon's abdication in 1814, it was decided to return French Guyana to French control, but it was only on 8 November 1817, when a French expedition arrived with Cayenne's new governor, Claude Carra Saint-Cyr, that the French took formal possession of the territory.
July 1795: British troops occupied Dutch Coromandel to prevent it from being overrun by the French. Dutch governor Jacob Eilbracht capitulated to the British on 15 July 1795.
April 1797: Sir Ralph Abercromby was a British Army officer who led the invasion of Puerto Rico in 1797. The military occupation by Great Britain lasted only a few months before the island was returned to Spanish control as part of the Treaty of Amiens in 1802.
February 1797: In 1796, French troops led by General Victor Hugues sacked the British colony of Saint Peter in present-day Guyana. This event marked a significant moment in the conflict between France and Great Britain during the late 18th century.
July 1816: After being occupied by the British during the Napoleonic Wars, the Iles des Saintes were returned to French control on 22 July 1816.
January 1808: For more than a century, the succession of Cirebon lineages was conducted without any significant problems. However, by the end Sultan Anom IV reign (1798-1803), Keraton Kanoman faces succession disputes. One of the prince, Pangeran Raja Kanoman, demand his share of throne and separate the kingdom by forming his own, Kesultanan Kacirebonan.
January 1816: In 1816, the southern part of Saint Martin was returned to the Dutch.
April 1809: During the Napoleonic Wars, Admiral Sir Alexander Forrester Inglis Cochrane led the British armada to reconquer the Iles des Saintes from French control on 14 April 1809. This strategic victory helped secure British dominance in the Caribbean region.
June 1816: The Treaty of Paris (1814) gave the islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon back to France.
February 1805: Aruba was occupied by the British from 12 February 1805 to 20 November 1805.
January 1807: Curaçao was occupied by the British from 1 January 1807 to 4 March 1816.
March 1801: In 1801, the island of Saint Martin in France was occupied by the British from March 24.
March 1801: 20 March 1801 - 10 July 1802: British occupation of Saint Barthélemy.
April 1801: 21 April 1801 - 21 November 1802: British occupation of Sint Estatius.
January 1802: Britain occupied the Danish West Indies in 1801-02.
February 1803: 16 April 1801 - January 1803: British occupation of Saba.
November 1805: Aruba was occupied by the British from 12 February 1805 to 20 November 1805.
March 1813: In 1810, the British captured Guadeloupe from France during the Napoleonic Wars. In 1813, the island was handed over to Sweden under the Treaty of Stockholm, marking a shift in colonial control in the Caribbean.
December 1814: 24 Feb 1809 - 9 Dec 1814: British occupation of Martinique.
June 1815: 5 Jun 1815 - 28 Apr 1816: British occupation of Martinique.
July 1815: After Napoleon's defeat at the Battle of Waterloo, the French-controlled Les Saintes islands were annexed by Great Britain on 6 July 1815.
August 1815: The British re-occupied the French part of Saint Martin in the Caribbean.
January 1816: 1807-1815: British occupation of the Danish West Indies during the Napoleonic Wars.
March 1816: End of British occupation of Aruba.
July 1802: 20 March 1801 - 10 July 1802: British occupation of Saint Barthélemy.
September 1811: 18 September 1811 - 19 August 1816: the Dutch Dejima Factory was occupied by the British.
January 1797: The British expelled the Dutch from Ceylon in 1796 and included Maldives as a British protected area.
January 1802: British forces left the Maluku Islands in 1801.
January 1803: Britain occupied the Danish West Indies in 1801-02.
April 1801: 16 April 1801 - January 1803: British occupation of Saba.
January 1817: Karikal was a French colonial territory in India. The territory was restored to French control on January 14, 1817, after being temporarily occupied by the British during the Napoleonic Wars.
May 1793: In 1793 the British landed in Saint-Pierre and, the following year, again expelled the French.
May 1793: Dutch control over the entire island of Saint Martin.
January 1794: The name of Île Bourbon was changed into Île de la Réunion in 1793 by a decree of the Convention Nationale (the elected revolutionary constituent assembly) with the fall of the House of Bourbon in France.
May 1794: The British frigate "Orpheus" commanded by Captain Henry Newcome arrived at Mahé on 16 May 1794, during the War of the First Coalition. Terms of capitulation were drawn up and the next day Seychelles was surrendered to Britain.
July 1795: British occupation of Dutch Bengal.
January 1796: As a result of the Kew Letters, Dutch settlements on the Malabar Coast were surrendered to the British in 1795, in order to prevent them from being overrun by the French.
October 1797: French Guyana is organized as a département of France.
January 1804: The British again occupied Essequibo during the Napoleonic Wars.
February 1805: On 25 February 1805, Jean-Jacques Dessalines, the leader of the First Empire of Haiti, led 30,000 troops to capture Santiago, a city in present-day Dominican Republic.
January 1807: French conquest of El Kala in 1806.
March 1816: Curaçao was occupied by the British from 1 January 1807 to 4 March 1816.
February 1810: In 1810, the British captured the island of Guadeloupe again.
January 1811: Britain assumed full control of the Seychelles including Aldabra, Farquhar and Desroches upon the surrender of Mauritius in 1810.
January 1815: The British leave northern Saint Martin.
October 1815: Organised settlement of Ascension Island began in 1815, when the British garrisoned it as a precaution after imprisoning Napoleon on Saint Helena to the southeast. On 22 October the Cruizer-class brig-sloops Zenobia and Peruvian claimed the island for King George III.
January 1816: Ile Bourbon was restored to France by the Congress of Vienna in 1815.
January 1816: The British returned Marie-Galante Island to France.
February 1816: 22 Feb 1810 - 22 Feb 1816: British occupation of Saba.
August 1816: The formal annexation of the Islands of Refreshment was made on August 14, 1816, partly as a measure to ensure the French could not use the islands as a base for a rescue operation to free the deposed Napoleon I of France from his prison on Saint Helena.
January 1797: British forces captured the Maluku Islands in 1796.
January 1802: Establishment of French Guyana.
December 1802: On 31 Dec 1802, Dharampur State, under the rule of Raja Rajendra Singh, became a British protectorate. This decision was made as part of the Treaty of Bassein between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire.
January 1803: Curaçao was occupied by the British from 13 September 1800 to 13 January 1803.
January 1804: British occupation of Saint Lucia.
January 1804: Birtish reconquest of the Demerara territories.
February 1810: 22 Feb 1810 - 22 Feb 1816: British occupation of Saba.
March 1805: Three frigates and two French brigantines arrived in Santo Domingo. Dessalines abandoned the siege of Santo Domingo and retreated to Haiti.
October 1803: In September 1803 the British occupied Berbice again, this time for good.
3.1.Newfoundland expedition
Was a French-Spanish military expedition to occupy Newfoundland during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796-1808).
3.2.French India (Treaty of Amiens)
Restoration of French rule in French India according to the Treaty of Amiens.
In 1795 the dissatisfaction towards the Dutch East India Company (and against British Rule) caused a revolt of the Boers, who founded several secessionist states.
May 1799: The rebels of Graaff-Reinet surrendered to British forces in April 1799.
November 1795: The Republic of Swellendam was ended on 4 November 1795 when the Cape was occupied by the Kingdom of Great Britain.
June 1795: By 1795, the dissatisfaction towards the Dutch East India Company caused the burghers of Swellendam to revolt, and they declared themselves a Republic.
January 1796: In 1795, the burghers of Graaff-Reinet, who were annoyed by company taxation, proclaimed themselves to be the independent.
February 1796: Before the authorities at Cape Town could take decisive measures against the rebels of Graaff-Reinet, they were compelled to capitulate to the British who had invaded and occupied the Cape Colony.
February 1799: In January 1799, Marthinus Prinsloo, a leader of the 1795 independence movement, led a rebellion against British rule in Graaff-Reinet.
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
September 1799: In 1799, during the French Revolutionary Wars, the Austrians, led by Archduke Charles, occupied the Legations and the Marches in Italy. Meanwhile, the British forces, under the command of Admiral Nelson, landed in Civitavecchia and expelled the French. Subsequently, they set up military administrations in different cities in the region.
June 1799: The Parthenopean Republic existed from 21 January to 13 June 1799, collapsing when Ferdinand returned to restore monarchial authority. Sicily reverted to a dependency of Naples.
January 1801: On June 20, 1799, Austro-Russian troops reconquer Turin and restore Charles-Emmanuel IV to his throne.
January 1801: In 1797, the districts of Chiavenna, Valtellina, and Bormio, dependencies of the Three Leagues (an associate of the Confederation), revolted under the encouragement of France. They were quickly invaded and annexed to the Cisalpine Republic on 10 October 1797.
March 1801: The Kingdom of Etruria was created by the Treaty of Aranjuez, signed at Aranjuez, Spain on 21 March 1801. It was established for the House of Bourbon-Parma, with Louis, Duke of Parma, becoming King of Etruria. The territory was formed from the Grand Duchy of Tuscany.
January 1799: After the French occupation of the west bank of the Rhine around 1798 (Treaty of Campo Formio and Treaty of Lunéville), the Duke of Arenberg received new lands: the county of Vest Recklinghausen, the county of Meppen, and the lordship of Dülmen.
September 1799: In 1799, during the Roman Republic (Napoleonic), the Austrians, led by Archduke Charles, occupied the Legations and the Marches. Meanwhile, the British forces, under the command of Sir Ralph Abercromby, landed in Civitavecchia and expelled the French. Subsequently, they set up military administrations in different cities in the region.
January 1799: The County of Vernio is abolished by Napoleon.
June 1800: Battle of Marengo. Melas promptly entered into negotiations which led to the Austrians evacuating Northern Italy west of the Ticino, and suspending military operations in Italy.
March 1802: In 1802, Britain and France signed the Treaty of Amiens, ending the war of the War of the Second Coalition. Britain returned most of occupied Dutch Guiana to the Batavian Republic.
January 1799: In 1799, Napoleon conquered Naples, forcing King Ferdinand and the court to flee to Sicily, where Ferdinand established a separate state on the island.
June 1799: The Parthenopean Republic collapsed when Ferdinand IV of Naples returned with the help of the British to restore his monarchial authority.
June 1800: During the Siege of Genoa, the Austrian forces led by General Michael von Melas besieged and captured the city, which was defended by the French under General André Masséna. This event was part of the Second Coalition, a military alliance against France during the Napoleonic Wars.
June 1800: After the Battle of Mareng, the Austrians evacuated Northern Italy west of the Ticino, and suspended military operations in Italy.
June 1800: Napoleon defeated the army of the Second Coalition at Marengo and refounded the Cisalpine Republic. The legations of Bologna, Ferrara and Romagna were once again taken away from the Holy See.
March 1801: By the Treaty of Florence of 28 March 1801, the king of Naples ceded the Presidi to the French Republic, which then ceded them to the new Kingdom of Etruria.
5.1.Malta during the War of the Second Coalition
During the War of the Second Coalition, Malta, at the time controlled by the Knights Hospitalier, was conquered by France but shortly after occupied by Great Britain.
October 1798: The island of Gozo, which is today a part of Malta, was independent for nearly three years between 1798 and 1801 during the French Revolutionary Wars. During the revolt on september 3 the French garrison held out in the Cittadella and Fort Chambray, until they capitulated on 28 October after negotiations which were made with the help of Sir Alexander Ball.
June 1798: The Maltese troops refused to continue the fight without support from their government and negotiations followed in which Hompesch and the knights agreed to abandon Malta on condition of financial compensation amounting to 3 million Francs. Bonaparte gained the entire Maltese archipelago, including fortresses, military stores and cannon, the small Maltese Navy and Army and the entire property of the Roman Catholic Church in Malta.
September 1800: Malta (proper - without Gozo island) conquered by great britain.
August 1801: Cassar continued to rule Gozo independently until 20 August 1801, when the British Civil Commissioner, Charles Cameron, removed him from the position.
5.2.Mediterranean campaign of 1798
Was a French military campaign in Egypt led by Napoleone Bonaparte. The French Republic sought to capture Egypt as the first stage in an effort to threaten British India and force Great Britain to make peace.
August 1798: In 1798, Napoleon Bonaparte led the French military occupation of Upper Egypt, defeating Ibrahim Bey at the Battle of Salahie and driving him out of the territory.
July 1798: French general Louis Desaix marched across the desert with his division and two cannon, arriving at Demenhour, 24 kilometres from Alexandria, on 18 Messidor (6 of July).
July 1798: The village of Chebreiss, located in modern-day Lebanon, was captured by French forces in 1798 after two hours of fierce fighting led by General Napoleon Bonaparte during the French campaign in Egypt and Syria.
July 1798: Battle of the Pyramids, also known as the Battle of Embabeh. It was a major engagement fought during the French Invasion of Egypt. The French army, under Napoleon Bonaparte, scored a decisive victory against the forces of the local Mamluk rulers, wiping out almost the entire Ottoman army located in Egypt. The victory effectively sealed the French conquest of Egypt as Murad Bey chaotically fled to Upper Egypt. Napoleon entered Cairo after the battle and created a new local administration under his supervision.
June 1801: Cairo conquered by Ottoman Empire.
March 1799: French forces managed to capture Jaffa.
March 1799: The French captured Haifa and the munitions and provisions stored there, along with the castle at Jaffa, the castle at Nazareth and even the town of Tyre much farther up the coast. Also the siege of Acre began on 18 March but the French were unable to take it.
May 1799: Napoleon Bonaparte retreated from Acre on 21 May after a failed final assault on 10 May, and withdrew to Egypt.
July 1798: In 1798, Napoleon Bonaparte led the French army to victory in the Battle of Alexandria, securing the city during the French military occupation of Egypt. This was part of Napoleon's campaign to disrupt British trade routes and establish French dominance in the region.
July 1798: In 1798, French forces under the command of Napoleon Bonaparte marched to Rahmanié in Egypt during the French campaign in the country. The fleet was expected to arrive with much-needed provisions for the troops.
September 1801: After Napoleon's failed campaign in Egypt, French General Menou was left in charge. He was eventually besieged in Alexandria by the British forces led by General Abercromby. Menou surrendered on September 2, 1801, marking the end of French rule in Egypt.
February 1799: Bonaparte's French forces left Egypt on 5 February 1799 and, seven days after leaving Cairo, Bonaparte arrived at Arish and bombarded one of the castle towers. The garrison surrendered two days later.
July 1798: On 2 Thermidor (20 July) 1798, French General Napoleon Bonaparte's army arrived 800 meters from the village of Embabé in Egypt during his military campaign in the region.
April 1801: In April 1801, Fort Julien, Egypt, surrendered to the Ottoman Empire.
5.3.Russian and Turkish expedition in the Ionian Islands
A joint Russian and Turkish expeditionary force occupied the French-held Ionian Islands.
October 1798: A joint Russian and Turkish expeditionary force, which included ten Russian ships of the line, numerous smaller Russian vessels and approximately 30 assorted Turkish ships, rapidly invaded and seized the islands of Paxi, Santa Maura, Theaki, Cephalonia, Zante and Cerigo, capturing 1,500 French prisoners by 10 October.
5.4.German Front (War of the Second Coalition)
Was the German theatre of the War of the Fifth Coalition.
May 1800: After French general Claude Lecourbe had captured Stockach, the Austrians led by general Paul Kray retreated to Messkirch, where they enjoyed a more favourable defensive position.
May 1800: French forces movement to fight at nearby Biberach an der Ris.
December 1800: Austria was defeated by France in the Battle of Hohenlinden (3 December 1800). By december, 25th the French forces were 80 km from Vienna. The Austrians requested an armistice, which French general Moreau granted on 25 December.
December 1800: The French army occupied Salzburg.
March 1799: On 1 March 1799, the French Army of Observation, in an order of battle of approximately 30,000 men in four divisions, crossed the Rhine at Kehl and Basel.
March 1799: At the intensely fought Battle of Ostrach, 21-22 March 1799, French suffered significant losses and were forced to retreat from the region, taking up new positions to the west at Messkirch.
June 1800: After being defeated by the French at the Battle of Höchstädt, Hungarian General Paul Kray retreated to Munich.
December 1800: French General of Division Claude Lecourbe's Right Wing brushed aside Riesch at Rosenheim.
May 1800: The French army forced the Austrians to retreat to Ulm.
December 1800: The French victory in the Battle of Hohenlinden ended the War of the Second Coalition against France.
5.5.Suvorov Italian campaign
Was a military campaign led by Russian general Alexander Suvorov against France that took place in Italy.
June 1799: On June 20, 1799, Austro-Russian troops reconquer Turin and restore Charles-Emmanuel IV to his throne.
April 1799: Napoleon Bonaparte entered Milan on 29 April 1799.
June 1799: In 1799, during the Second Coalition, the Allies, led by Russian General Alexander Suvorov and Austrian Archduke Charles, defeated the French at the Trebbia River. They continued to push the French forces back into the Alps and Genoa, ultimately reaching Fiorenzuola.
July 1799: Coalition forces took the key fortress of Mantua.
April 1799: On 27 April, Russian feldmarshal Suvorov defeated French general Jean Victor Moreau at the Battle of Cassano.
June 1799: The Russian army led by Suvorov moved on to Turin, having defeated Moreau yet again at Marengo.
August 1799: In 1799, French General Joubert was defeated and killed in battle with Russian General Suvorov at Novi, during the Second Coalition War. The battle took place to the north of Genoa, in present-day Italy.
5.6.Suvorov Swiss campaign
Was a military campaign led by Russian general Alexander Suvorov against France that took place in Switzlerand.
October 1799: The Russian troops were forced by the French to abandon their hold on the left bank of the Rhine.
September 1799: In 1799, during the Second Battle of Zürich, the French army led by André Masséna defeated the Russian forces commanded by Alexander Korsakov. This victory forced Korsakov to retreat to Schaffhausen in the territory of the Helvetic Republic.
May 1799: French army defeated at the Battle of Winterthur.
5.7.Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland
An expeditionary force of British and Russian troops invaded the North Holland peninsula in the Batavian Republic.
August 1799: In August 1799, the Duke of York led a combined Anglo-Russian army to invade the northern tip of Holland, which was then a French vassal state known as the Batavian Republic (1795-1806). This invasion was part of the Second Coalition against France.
November 1799: The defeat at Castricum in 1799 marked the end of the Anglo-Russian invasion of Holland during the French Revolutionary Wars. British General Ralph Abercromby and Russian General Herman Willem Daendels were involved in the conflict. The Batavian Republic, a French client state, regained control of the northern tip of Holland after the British and Russian troops were forced to retreat.
5.8.Treaty of Lunéville
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.
February 1801: The Treaty of Lunéville was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville between the French Republic and Holy Roman Emperor Francis II. Certain Austrian holdings within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire were relinquished, and French control was extended to the left bank of the Rhine, "in complete sovereignty" but France renounced any claim to territories east of the Rhine. Contested boundaries in Italy were set. The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was awarded to the French.
March 1801: The Duchy of Parma-Piacenza is occupied by France after the Traety of Lunéville (2/9/1801).
April 1801: In accordance with the Treaty of Lunéville (1801) that ended the War of the Second Coalition. As part of the settlement of the war, Duke Ercole received the rest of the Breisgau and the Principality of Heitersheim annexed the neighbouring county of Bonndorf, thus greatly expanding in size.
February 1801: After the French occupation of the west bank of the Rhine around 1798 (see Treaty of Campo Formio and Treaty of Lunéville), the Duke of Arenberg received new lands: the county of Vest Recklinghausen, the county of Meppen, and the lordship of Dülmen.
5.9.War of the Oranges
Was a brief conflict in 1801 in which Spanish forces, instigated by the government of France, and ultimately supported by the French military, invaded Portugal.
June 1801: Campo Maior was a Portuguese town near the Spanish border. Lieutenant-Colonel Dias Azevedo was a military leader in the Portuguese garrison who successfully defended the town against a Spanish assault for 17 days in 1801 during the War of the Oranges.
June 1801: The Treaty of Badajoz was signed by Spain and Portugal on 6 June 1801. Portugal ceded the border town of Olivença and Almeda to Spain and closed its ports to British military and commercial shipping. The Spanish abandoned the remaining occupied territory.
May 1801: The Spanish attack to Portugal started on the early morning of the 20 May, and focused on the Portuguese border region that included the main Garrison Town and Fortifications of Elvas and the smaller fortified towns of Campo Maior, Olivença and Juromenha.
August 1801: To minimise the impact of the ban on using Portuguese ports, in July a British force occupied the island of Madeira.
June 1801: The Treaty of Badajoz was signed by Spain and Portugal on 6 June 1801. Portugal ceded the border town of Olivença and Almeda to Spain and closed its ports to British military and commercial shipping.
June 1801: Portugal signed a second Treaty of Badajoz with France, represented by Napoleon's younger brother Lucien Bonaparte, granting France substantial territorial gains in South America. The modern border between French Guiana and Brazil is the Oyapock River, which was agreed in 1713. The proposed Treaty moved it south to the Araguari or Amapá River, taking in large parts of Northern Brazil.
5.10.Treaty of Amiens
Was a treaty between France and Great Britain that ended the War of the Second Coalition.
March 1802: In 1802, Britain and France signed the Treaty of Amiens, ending the war of the War of the Second Coalition. Britain returned the Cape Colony to the Dutch.
March 1802: In 1802, Britain and France signed the Treaty of Amiens, ending the war of the War of the Second Coalition. Britain returned the Island of Menorca to Spain.
March 1802: At the Peace of Amiens (1802), the Netherlands received the Essequibo colony for a short time.
March 1802: The Treaty of Amiens in 1802 restored the island of Marie-Galante to France. With the restoration, slavery too was reinstated .
January 1806: The outbreak of the Napoleonic Wars (18 May 1803) invalidated the Peace of Amiens. In January 1806, the British occupied the colony for a second time after the Battle of Blaauwberg.
5.10.1.Saint Pierre and Miquelon (Treaty of Amiens)
The Treaty of Amiens of 1802 returned Saint Pierre and Miquelon to France.
August 1802: The Treaty of Amiens of 1802 returned the Saint Peter islands to France.
Was a war between Spain and Great Britain fought intermittently during the Coalition Wars.
November 1798: A British expedition captured the island of Menorca (historically called "Minorca" by the British) from Spain.
November 1798: In 1798, during the French Revolutionary Wars, a British expedition led by Admiral John Duckworth captured the island of Menorca from Spain. The British occupation of Minorca lasted until 1802 when it was returned to Spain under the Treaty of Amiens.
6.1.Invasion of Trinidad (1797)
Was the British invasion of Trinidad during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796-1808).
February 1797: In 1797, a fleet of 18 warships led by Sir Ralph Abercromby invaded and captured the Island of Trinidad. This marked the beginning of British colonial rule in Trinidad, which was previously under Spanish control. Abercromby was a British Army officer known for his successful military campaigns during the French Revolutionary Wars.
6.2.British invasions of the River Plate
Was the British invasion of modern-day Argentina during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796-1808).
October 1807: The occupation of Montevideo by the British army lasted until September 1807, when troops were withdrawn in compliance with the agreement signed following the surrender of British forces in Buenos Aires in July 1807.
August 1806: Beresford surrendered to Spanish forces on 14 August.
June 1806: The British took Quilmes, near Buenos Aires.
June 1806: In 1806, British forces led by Sir Home Popham occupied Buenos Aires during the British invasions of the River Plate.
February 1807: British forces captured the city of Montevideo.
French invasion of the Old Swiss Confederacy.
January 1798: French troops under general Ménard invaded Vaud.
April 1798: On April 12, 1798, 121 cantonal deputies proclaimed the Helvetic Republic under the auspices of the French occupying forces. The Helvetic Republic was a centralized state based on the ideas of the French Revolution.
Was an uprising against British rule in Ireland.
May 1798: 24 May - 12 October 1798: there was an uprising against British rule in Ireland.
8.1.Connacht Republic (Irish Rebellion of 1798)
Was a major uprising against British rule in Ireland.
August 1798: The Irish Republic of 1798, more commonly called the Republic of Connacht, was a short lived puppet state proclaimed during the Irish Rebellion of 1798 that resulted from the French Revolutionary Wars. In theory the republic was to cover the whole island of Ireland, but its functional control was limited to only very small parts of the Province of Connacht. The rebel republic was a puppet state of the French Republic and was very short lived.
September 1798: The British army then slowly spread out into the rebel held Province of Connacht in a brutal campaign of killing and house burning which reached its climax on 23 September 1798 when Killala was stormed and retaken with much slaughter.
8.2.Acts of Union of 1800
Were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland (previously in personal union) to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The acts came into force on 1 January 1801.
January 1801: There were parallel acts of the Parliament of Great Britain and the Parliament of Ireland which united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland (previously in personal union) to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The acts came into force on 1 January 1801.
Was a secret agreement signed on 1 October 1800 between the Spanish Empire and the French Republic by which Spain agreed to exchange its North American colony of Louisiana for territories in Tuscany.
October 1800: The treaty of San Ildefonso (October 1, 1800) between France and Spain provided for the transfer of the island of Elba, then part of Tuscany, under French sovereignty.
October 1800: In the secretly negotiated Third Treaty of San Ildefonso in 1800, Spain returned the colonial territory of Louisiana to France. This was done under the rule of King Charles IV of Spain and First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte of France.
A rebellion which originated in Central Switzerland and was centered around the cities of Zürich and Bern, as well as rural parts of the Swiss plateau in the cantons Aargau and Solothurn. It resulted in the collapse of the Helvetic Republic, the renewed French occupation of Switzerland and ultimately the Act of Mediation dictated by Napoleon on 19 February 1803.
September 1802: August – October 1802: rebellion which originated in Central Switzerland and was centered around the cities of Zürich and Bern, as well as rural parts of the Swiss plateau in the cantons Aargau and Solothurn.
Was a European conflict spanning the years 1805 to 1806. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, made up of the United Kingdom, the Holy Roman Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily, and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war.
February 1806: The assignment treaties of Paris in 1806 involved Napoleon Bonaparte and King Frederick William III of Prussia. As a result of these treaties, the territory of Neuchatel Principality was transferred from Prussia to Napoleon's control.
February 1806: The assignment treaties of Paris in 1806 involved the transfer of territory to the Grand Duchy of Berg.
11.1.Ulm Campaign
Was a series of French and Bavarian military maneuvers and battles to outflank and capture an Austrian army in 1805 during the War of the Third Coalition. It took place in the vicinity of and inside the city of Ulm.
October 1805: The French army crossed the Danube at Donauwörth.
December 1805: French forces seized Vienna in November 1805.
October 1805: By 10 October French officer Loison's division held Elchingen.
October 1805: Battle at Wertingen between the Austrians led by Auffenburg troops and the French of Murat and Lannes.
11.2.Venetian front or Italian campaign of 1805
Was the Venetian theatre of the War of the Third Coalition.
November 1805: By November 14th, 1805 the French armies had reached the Isonzo but the army of Archduke Charles of Austria prevented them to cross the river.
October 1805: The French managed to gain a bridgehead over the Adige river at Verona.
October 1805: Between 29 and 31 October, the outnumbered French defeated the superior Austrian army in the battle of Caldiero.
11.3.Peace of Pressburg
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Third Coalition.
December 1805: On December 16, 1805, the area of Königsegg-Rothenfels went to the Kingdom of Bavaria through the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: The Fricktal passed to the Swiss Confederation with the Napoleonic Acts of Mediation.
December 1805: In exchange for providing France with a large auxiliary force, Napoleon allowed Frederick to raise Württemberg to a kingdom on 26 December 1805.
December 1805: French evacuation of occupied territories after the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: Territorial changes after the Peace of Pressburg.
December 1805: The Kingdom of Bavaria was a state in Central Europe. It had its origins in the Peace of Pressburg on December 26, 1805 between the representatives of the French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and the German and Austrian (double) Emperor Franz II./I. concluded peace treaty. On January 1, 1806, King Maximilian I Joseph was proclaimed in Munich.
December 1805: After the Austrian defeat at the Battle of Austerlitz and the Peace of Pressburg in 1805, Further Austria was entirely dissolved and the former Habsburg territories were assigned to the Grand Duchy of Baden (Breisgau), the Kingdom of Württemberg (Rottenburg and Horb) and the Kingdom of Bavaria (Weitnau Günzburg, Weißenhorn). Minor estates passed to Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and the Grand Duchy of Hesse.
11.4.French invasion of Naples
In 1806 the French army invaded the Kingdom of Naples, which was soon conquered. The Bourbon King of Naples, Ferdinand IV fled to Sicily.
July 1806: Gaeta surrendered, concluding the invasion with a decisive French victory.
March 1806: The Napoleonic Kingdom of Naples (formally the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies) was a state founded by Napoleon Bonaparte in December 1805, when French troops occupied the Bourbon Kingdom of Naples.
February 1806: On 9 February 1806, Masséna invaded the Kingdom of Naples and two days later, the Bourbon king of Naples, Ferdinand IV also fled to Sicily, protected by the British fleet. Naples soon fell into French hands and by the end of February, only two places in the kingdom still held out.
March 1806: French force and the Royal Neapolitan Army was soundly defeated at the Battle of Campo Tenese on 10 March 1806. A day after Campo Tenese, Joseph was installed as the new King of Naples.
Was a war between France and Sweden that took place in Swedish Pomerania.
12.1.Offensive in Hanover (Franco-Swedish War)
Were a series of battles in the region of Lauenburg during the Franco-Swedish War.
December 1806: In 1806, during the Napoleonic Wars, French forces advanced rapidly in western Germany, leading to the retreat of Swedish troops towards Lübeck. The territory of Lauenburg was subsequently taken over by the Electorate of Hanover (England).
September 1806: During the summer of 1806, Prussia, under the leadership of King Frederick William III, formed the Fourth Coalition against France, led by Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. As a result, Sweden, under King Gustav IV Adolf, was granted the right to occupy Lauenburg, a territory located in northern Germany.
December 1806: In 1806, during the Napoleonic Wars, French forces advanced rapidly in western Germany, leading to the retreat of Swedish troops towards Lübeck. This event took place in Lauenburg, which later became part of the Mecklenburg-Schwerin Duchy.
12.2.Offensive in Swedish Pomerania
Were a series of French campaigns were Swedish Pomerania was occupied.
January 1807: On 28 January, French forces commanded by Marshal Mortier crossed the Peene River in an attempt to impose a blockade on Stralsund. To the east, General of Division Charles Louis Dieudonné Grandjean's division crossed the Peene at Anklam, driving back the Swedish outposts. To the west, General of Division Pierre Louis Dupas' division crossed the stream unopposed near Demmin. On the 29th, Mortier's two divisions appeared before the port and on 30 January began the blockade.
May 1809: The Prussian freikorps are defeated by the French who recaptured Stralsund.
May 1809: The French occupation of Stralsund was interrupted when a Prussian freikorps under Ferdinand von Schill seized the city.
September 1807: Rügen conquered by france.
Was a war between the French Empire and a coalition of European monarchies, mainly Prussia and Russia.
February 1807: In 1807, Aruba, a Dutch colony, was occupied by Great Britain.
February 1807: In 1807, Bonaire, a Dutch colony, was occupied by Great Britain.
13.1.Prussian Campaign (War of the Fourth Coalition)
Was a French military campaign in Prussia during the War of the Fourth Coalition.
October 1806: At the double Battle of Jena-Auerstedt on 14 October, Napoleon defeated a Prussian army led by Frederick Louis.
October 1806: French Marshal Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte defeated Eugene Frederick Henry, Duke of Württemberg, at the Battle of Halle and chased his forces across the Elbe River.
December 1806: The Albertines remained electors until the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 and then attained the Saxon royal dignity through an alliance with Napoleon.
October 1806: Napoleon Bonaparte led the Grande Armée to victory in the Battle of Schleiz against the Prussian division on 9 October 1806.
October 1806: Napoleon entered Berlin on 27 October 1806.
October 1806: French Marshal Lannes crushed a Prussian division at Saalfeld.
13.2.Polish, Russian and Swedish campaigns (War of the Fourth Coalition)
Was the theatre of war in Poland, Russia and Sweden during the War of the Fourth Coalition.
August 1807: However, Swedish refusal to join the Continental System led to a second invasion of Swedish Pomerania led by Marshal Brune. Stralsund fell on 24 August after a second siege and the Swedish army surrendered at Rügen, completing the occupation of Swedish Pomerania.
April 1807: In 1807, during the Napoleonic Wars, France and Sweden agreed to a ceasefire in Stralsund. This led to the withdrawal of all French troops from Swedish Pomerania. The agreement was negotiated by French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte and Swedish King Gustav IV Adolf.
January 1808: In 1807, Swedish Pomerania was occupied by France under Marshal Brune. The peace treaty negotiated by Brune and Swedish general Johan Christopher Toll allowed the Swedish army to withdraw with their weapons and ammunition.
February 1807: The Battle of Eylau was fought between Napoleon's Grande Armée and the Imperial Russian Army led by General Levin August von Bennigsen. It was one of the bloodiest battles of the Napoleonic Wars, with heavy casualties on both sides. The battle ended inconclusively, with neither side achieving a decisive victory.
June 1807: In 1807, Napoleon Bonaparte defeated the Russian army at the Battle of Friedland. This victory led to the Treaty of Tilsit, where Russia ceded territory to France and solidified Napoleon's dominance in Europe.
January 1807: In order to safeguard the Russian border against a possible French attack, a 40,000-strong Russian contingent advanced into Moldavia and Wallachia.
January 1807: The Siege of Stralsund in 1807 was a military conflict between French forces under Marshal Brune and Swedish defenders led by Count von Schill. The city eventually fell to the French, leading to its occupation by Napoleon's troops.
13.3.Peace of Tilsit
Were a series of treaties that ended the War of the Fourth Coalition.
July 1807: The treaty signed between Prussia and France at Tilsit, following the War of the Fourth Coalition, was highly disadvantageous to Prussia. As a result of this agreement, the Kingdom lost most of its Polish territories to the newly created Duchy of Warsaw. Additionally, it ceded most of its territories in central Germany and the Rhineland to France, the Grand Duchy of Berg, and the Kingdom of Westphalia. The remnant territories occupied by France in Germany were evacuated.
July 1807: After the defeat of King Frederick William III of Prussia at the 1806 Battle of Jena-Auerstedt, according to the Franco-Prussian Treaty of Tilsit of 9 July 1807, the territory of the free state was carved out from lands that made up part of the West Prussia province.
July 1807: The second of the Treaties of Tilsit was signed by France with Prussia on 9 July 1807 and awarded the left bank of the Elbe to the newly created Kingdom of Westphalia.
July 1807: With the second Treaty signed in Tilsit, Prussia lost Cottbus to Saxony.
July 1807: The Treaties of Tilsit were two agreements signed by Napoleon I of France in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland. The first was signed on 7 July, between Emperor Alexander I of Russia and Napoleon I of France.
July 1807: The Treaties of Tilsit were two agreements signed by Napoleon I of France in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland. The first was signed on 7 July, between Emperor Alexander I of Russia and Napoleon I of France. The Russian tsar agreed to evacuate Wallachia and Moldavia.
July 1807: Peace of Tilsit.
July 1807: The Peace of Tilsit was signed in 1807 between Emperor Napoleon I of France and Tsar Alexander I of Russia. The treaty divided Europe into spheres of influence, with the Duchy of Warsaw being created out of Prussian territory as a French client state.
July 1807: The Duchy of Warsaw was a Polish state established by Napoleon in 1807 from the Polish lands ceded by the Kingdom of Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit.
July 1807: Towards the end of 1806, the French entered Poland and Napoleon created a new Duchy of Warsaw.
July 1807: The second of the Treaties of Tilsit was signed by France with Prussia on 9 July 1807. It awarded the left bank of the Elbe to the newly created Kingdom of Westphalia. In addition, Białystok was given to Russia (which led to the creation of the Belostok Oblast).
Was a war between Great Britain and the Ottoman Empire caused by the agreement of the Ottomans to open the Dardanelles exclusively to French warships. .
March 1807: The Alexandria expedition of 1807 was led by General Alexander Mackenzie Fraser and Admiral John Thomas Duckworth. The British troops occupied Alexandria in response to the French occupation of Egypt and to secure British interests in the region.
September 1807: End of the British occupation of Alexandria.
Was a naval conflict between Denmark-Norway and the British during the Napoleonic Wars. The war's name is derived from the Danish tactic of employing small gunboats against the materially superior Royal Navy.
February 1808: The Danish possessions at Tranquebar was taken over by the British East India Company.
May 1809: The island of Anholt was captured by British forces.
January 1814: The Treaty of Kiel was signed in 1814, ending the Napoleonic Wars. Denmark-Norway ceded Heligoland to Britain and Norway to Sweden. Denmark regained control of Anholt island as part of the agreement.
September 1807: The British were instead more successful on 11 September when HMS Carrier brought to the British Admiralty the despatches from Admiral Thomas McNamara Russell announcing the capitulation of the small island of Heligoland to the British.
Was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars.
April 1814: The Battle of Toulouse took place in April 1814 during the Napoleonic Wars. It was fought between the French army, led by Marshal Soult, and the Allied forces of Spain and Great Britain, commanded by the Duke of Wellington. The battle resulted in a victory for the Allies, leading to the occupation of Toulouse.
January 1813: In 1812-1813, the First French Empire annexed Catalonia during the Peninsular War (Guerra Peninsular) and divided the region into four départements, with Andorra as a part of the district of Puigcerdà.
March 1814: French retreat t Tarbes. End of the Napoleonic Kingdom of Spain.
May 1814: The British left Madeira after the End of the Peninsular War.
16.1.French Campaigns in Spain and Portugal (1807-1812)
Were a series of military campaigns by the French army in Spain and Portugal during the Peninsular War.
December 1809: The city of Girona fell on 12 December 1809 during the Peninsular War, when French forces captured the city from the Spanish defenders.
March 1809: A French army led by Victor invaded southern Spain and routed Gregorio de la Cuesta's army at Medellín.
January 1812: During the Peninsular War, French Marshal Louis Gabriel Suchet trapped Spanish General Joaquin Blake's army in Valencia, forcing its surrender in January 1812. This victory was part of Napoleon's efforts to control Spain during the Napoleonic Wars.
May 1808: In 1808, under French pressure, King Charles IV and his son, Ferdinand VII, both abdicated their claims to Napoleon. This led to the establishment of the Kingdom of Spain under Napoleonic rule.
January 1810: Ellermann marched on Del Parque's position at Salamanca, who promptly abandoned it and retreated south.
February 1808: Between 9 and 12 February, the French divisions of the eastern and western Pyrenees crossed the border and occupied Navarre and Catalonia, including the citadels of Pamplona and Barcelona.
December 1808: Napoleon struck with overwhelming strength and the Spanish defense evaporated at Burgos, Tudela, Espinosa and Somosierra.
December 1808: Madrid surrendered on 1 December 1808 to French forces.
November 1807: In 1807, French General Junot invaded Portugal, leading to the occupation of Lisbon on November 30. The Portuguese Prince Regent John fled with his family, courtiers, and valuables aboard a fleet, seeking refuge in Brazil.
March 1808: In early March 1808, Marshal Joachim Murat, a French military leader and brother-in-law of Napoleon Bonaparte, established his headquarters in Vitoria, Spain. This marked the beginning of the French military occupation of the territory during the Napoleonic Wars.
March 1808: On 23 March 1808, French Marshal Joachim Murat entered Madrid.
February 1809: French forces captured the city of Zaragoza.
June 1811: Catalonia fell to a surprise attack on 29 June.
December 1808: Laurent Gouvion Saint-Cyr's 17,000-strong VII Corps besieged and captured Roses from an Anglo-Spanish garrison.
December 1808: In 1808, during the Peninsular War, French Marshal Soult captured the city of León in Spain as part of Napoleon's invasion. This event was significant in the struggle for control of the Iberian Peninsula between the French forces and the Spanish resistance.
January 1809: The British troops escaped to the sea after fending off a strong French attack at Corunna. The French occupied the most populated region in Spain, including the important towns of Lugo and La Corunna.
August 1809: The French withdrew for the last time from Galicia in July 1809.
October 1811: The Spanish defenders of Sagunto capitulated on 25 October.
August 1809: Allied forces withdrew from Talavera, Spain, on 4 August.
January 1811: General Suchet, a French military leader under Napoleon Bonaparte, captured the town of Tortosa from the Spanish in Catalonia during the Napoleonic Wars in 1811. This victory was part of the French conquest of the Iberian Peninsula.
January 1810: The Junta Central decided to flee to the safety of Cádiz.
16.2.Iberia in revolt
Were a series of uprisings against the French rule in the Iberian Peninsula.
May 1808: Zaragoza and Murcia conquered by Kingdom of Spain.
July 1808: In 1808, Portugal erupted in revolt in June against French occupation led by Napoleon Bonaparte. The Portuguese royal family, including Queen Maria I and Prince Regent John, fled to Brazil, transferring the kingdom's capital to Rio de Janeiro.
May 1808: In 1808, the first wave of uprisings against French occupation of Spain occurred in Cartagena and Valencia.
May 1808: The province of Asturias cast out its French governor on 25 May and declared war on Napoleon.
June 1808: By 1 June the main French army of 80,000 held a narrow strip of central Spain from Pamplona and San Sebastián in the north to Madrid and Toledo in the centre.
July 1808: At the Battle of Medina de Rioseco on 14 July, Bessières defeated Cuesta and Old Castile returned to French control.
August 1808: Joseph Bonaparte evacuated the capital for Old Castile, while ordering Verdier to abandon the siege of Zaragoza and Bessières to retire from Leon.
16.3.Second Portuguese campaign
Was a French military campaign in Portugal during the Peninsular War.
May 1809: After the Battle of Grijó (10-11 May) and the Second Battle of Porto (12 May), the French lost all their conquests in Portugal.
March 1809: First Battle of Porto.
March 1809: In 1809, during the Peninsular War, Marshal Soult's French troops attacked Braga, Portugal. The Portuguese forces, led by General Francisco Silveira, were unprepared and suffered heavy losses. Approximately 4,000 Portuguese soldiers were killed, while the French lost around 200 men in the battle.
16.4.Coalition campaigns in the Iberian Peninsula
Ware a series of military campaigns by Great Britain, Spain and Portugal against the French forces in the Iberian Peninsula. The French were finally expelled.
February 1814: During the Peninsular War in 1814, British General Hill successfully pushed the French forces back to Joyeuse after defeating them in the Battle of Garris.
June 1813: In 1813, during the Peninsular War, Burgos was seized by the French forces.
June 1813: At the Battle of Vitoria, Joseph Bonaparte's 65,000-man army were defeated decisively.
July 1813: Battle of Roncesvalles.
August 1813: The Allies chased the retreating French, reaching the Pyrenees in early July, and began operations against San Sebastian and Pamplona.
July 1813: In 1813, during the Napoleonic Wars, Marshal Soult of the Kingdom of Spain launched a counter-offensive against the Allies in the Battle of the Pyrenees. The Allies were defeated at the Battle of Maya, marking a significant victory for the Kingdom of Spain.
March 1814: In 1814, during the Napoleonic Wars, French Marshal Suchet's division of 9,661 men retreated to Figueras, leaving most of Catalonia. The territory was then occupied by Spain and Great Britain. Suchet was a prominent French military leader known for his campaigns in Spain.
April 1814: French General Pierre-Joseph Habert surrendered Barcelona to Spanish forces on 25 April 1814.
January 1812: French conquest of Catalonia.
April 1812: The town of Badajoz was stormed on 6 April 1812 during the Peninsular War. The assault was led by British General Arthur Wellesley, also known as the Duke of Wellington, and resulted in a bloody battle with heavy casualties on both sides. The town ultimately fell to the British and Portuguese forces, marking a significant victory in the war against the French.
June 1812: The allied army took Salamanca.
December 1813: Wellington occupied the right as well as the left bank of the Nive.
January 1812: The border fortress town of Ciudad Rodrigo was captured with an assault led by the Duke of Wellington and his British and Portuguese forces during the Peninsular War in 1812. The territory was then returned to the Kingdom of Spain.
August 1813: The French forces of Suchet, after the Battle of Vitoria, evacuated Tarragona.
September 1813: The Citadel of San Sebastián surrendered to Spanish forces on 9 September.
16.5.French Autumn counterattack
Was a French counterattack against the military campaign by the Coalition in the Iberian Peninsula.
July 1812: As a consequence of the Salamanca campaign, the French were forced to evacuate the provinces of Andalusia and Asturias.
Was the theatre of war in the Adriatic Sea during the Napoleonic Wars.
May 1814: The abdication of Napoleon in early April 1814 brought the War of the Sixth Coalition to a close. Corfu, the longest-held French territory in the Adriatic surrendered and was added to the United States of the Ionian Islands under British protection.
February 1814: By 16 February 1814 every French harbour in the Illyrian provinces had been captured by British or Austrian troops. Over 700 French merchant ships had been seized and the only remaining French outpost in the region was Corfu.
January 1808: In 1807, the Royal Navy, under the command of Admiral William Hoste, seized the Dalmatian Island of Lissa from the French forces. This strategic move was part of the Napoleonic Wars, with Lissa serving as a key naval base in the Mediterranean.
January 1814: Ragusa conquered by Sixth Coalition.
October 1809: In 1809, during the Napoleonic Wars, HMS Warrior, commanded by Captain William Hoste, successfully landed on the island of Cephalonia and forced the Neapolitan garrison to surrender. This marked the beginning of Great Britain's military occupation of the territory.
October 1809: The islands of Zante and Ithaca surrendered to the British forces led by Sir James St. Clair-Erskine.
October 1809: In 1809, the detached frigate HMS Spartan, commanded by Jahleel Brenton, successfully invaded Cerigo, which was under Ottoman control at the time. This military occupation was part of the British efforts during the Napoleonic Wars to control strategic locations in the Mediterranean.
December 1813: Surrender of the strategic port of Zara to the British.
April 1810: The island of Santa Maura, also known as Lefkada, surrendered to the British forces on 16 April 1810.
January 1814: Cattaro, a strategic port city in modern-day Montenegro, was captured by Austrian forces in collaboration with Montenegrin ground troops in 1814 during the Napoleonic Wars. This victory was part of the Sixth Coalition's efforts to defeat Napoleon Bonaparte.
Was a war between the Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire fought during the Napoleonic Wars. Sweden lost Finland, which became the Grand Duchy of Finland within the Russian Empire.
March 1808: Helsinki conquered by russia.
January 1810: The Treaty of Paris in 1810 ended the war between France and Sweden after Sweden's defeat by Russia in the Finnish War. Swedish Pomerania was ceded to the Kingdom of Sweden as a result of this treaty.
September 1808: Oravais conquered by russia.
February 1808: In 1808, during the Finnish War, 24,000 Russian troops led by General Friedrich Wilhelm von Buxhoevden invaded Finland and captured the town of Lovisa.
March 1808: The Russian army took Åbo.
March 1809: The Russians entered Umeå on 24 March.
November 1808: By November 1808, Russian forces had overrun all of Finland. On 19 November, the Convention of Olkijoki was signed and the Swedish army was forced to leave the Finnish countryside.
March 1809: Bagration's corps of 17,000 men occupied the strategic Åland Islands.
August 1808: Swedish landing in Pori.
January 1810: The Treaty of Paris in 1810 ended the war between France and Sweden after Sweden's defeat by Russia in the Finnish War. As a result, Swedish Pomerania was ceded to France.
March 1808: A small Russian detachment was sent to Åland. Before the end of March 1808 even Vasa was taken by the Russians.
February 1808: Borgå (Finnish: Porvoo) was captured on 24 February.
March 1808: In Savolax, Russians advanced rapidly and took Kuopio.
March 1808: Abandoned Swedish fortifications on the Hangö Peninsula were taken by Russia and manned on 21 March.
September 1808: In 1808, during the Finnish War, Russian General Nikolay Kamensky led a 11,000-strong corps to achieve important victories at Kuortane, leading to the territory falling under Russian military occupation.
September 1808: After the Russians were driven from Central Finland, their forces stretched along the line of Pori - Tampere - Mikkeli.
June 1808: In May, the Russians suffered further setbacks when they were driven from Gotland and Åland by Swedish forces.
18.1.Treaty of Fredrikshamn
The Treaty of Fredrikshamn or the Treaty of Hamina was a peace treaty concluded between Sweden and Russia on 17 September 1809 that ended the Finnish War. Sweden ceded the whole of Finland and all of its domains east of the Torne River to Russia.
September 1809: The Treaty of Fredrikshamn or the Treaty of Hamina was a peace treaty concluded between Sweden and Russia on 17 September 1809. Sweden ceded the whole of Finland and all of its domains east of the Torne River (the north-eastern parts of what was then called Västerbotten, today Norrbottens län) to Russia. Sweden then joined the Continental System and closed its harbours to British ships.
Was a war between Denmark-Norway and Sweden due to Denmark-Norway's alliance with France and Sweden's alliance with the United Kingdom during the Napoleonic Wars.
19.1.Swedish Offensive (Dano-Swedish War of 1808-09)
Was the main Swedish military offensive against Denmark during the Dano-Swedish War of 1808-09.
April 1808: Fighting in Høland and Aurskog ended with a Norwegian victory, and the Swedish commander, Colonel Schwerin felt so threatened by the Norwegian counterattacks that he ordered a retreat after the defeat at Toverud.
April 1808: Battle of Trangen: The invading Swedish troops, led by Colonel Carl Pontus Gahn, were surrounded and forced to surrender to the Danish.
April 1808: The Swedish main attack in Aurskog-Høland in 1808 was led by General Carl Pontus Gahn and Lieutenant Colonel Carl Johan Adlercreutz. The goal was to secure the territory for Sweden during the ongoing Finnish War against Russia.
April 1808: In 1808, during the Napoleonic Wars, a battle occurred at Lier, near Kongsvinger. The Swedish forces, led by King Charles XIII, defeated the Norwegian army. This victory led to Sweden's military occupation of the territory.
April 1808: After this victory the Swedish troops entrenched themselves at Lier and advanced all the way to the river Glomma.
19.2.Danish Offensive (1808)
Was a Danish offensive against Sweden during the Dano-Swedish War of 1808-1809.
August 1808: On July 24, von Döbeln's Swedish troops increased by 900 units, which allowed an attack against the Norwegians, who were forced to retreat. The resulting armistice required the Norwegians to leave Sweden by 3 August, which they did.
July 1808: Norwegian troops captured the fortress of Hjerpe.
July 1808: Hjerpe conquered by Kingdom of Sweden.
August 1808: Mörsil and Mattmar in Jämtland were occupied by Denmark-Norway.
Was an Anglo-Spanish military expedition that restored Santo Domingo to Spain.
July 1809: The Siege of Santo Domingo of 1808 was a military conflict between French forces led by General Marie-Louis Ferrand and Spanish forces led by Juan Sánchez Ramírez. The siege resulted in the surrender of Santo Domingo to the French, who then controlled the territory until 1809 when it was transferred to Spanish America.
November 1808: Battle of Palo Hincado.
Was a conflict between a colition of European monarchies and Napoleon's French Empire.
July 1809: Battle of Gefrees. After taking the capital, Dresden, and pushing back an army under the command of Napoleon's brother, Jérôme Bonaparte, the Austrians were effectively in control of all of Saxony.
21.1.Dalmatian Campaign (1809)
Was the Dalmatian theatre of the War of the Fifth Coalition.
June 1809: Ljubljana conquered by france.
May 1809: In 1809, Marshal Marmont, a French military commander, achieved a significant victory over the Austrians at Pribudić.
May 1809: French forces under general Marmont take the city of Gospić.
March 1809: In 1809, during the Napoleonic Wars, the French forces led by Marshal Marmont were defeated and driven back to Knin and Zadar by the Austrian Empire under the command of Archduke John of Austria. This marked the beginning of the Austrian military occupation of the territory.
21.2.Danube Campaign (War of the Fifth Coalition)
Was a French military campaign in the Danube area during the War of the Fifth Coalition. The French forces defeated the Austrian army and occupied Vienna.
May 1809: After defeating the Austrian forces led by Archduke Charles, Napoleon Bonaparte occupied Vienna in May 1809.
July 1809: After the Battle of Wagram, Napoleon's forces, led by Marshal Davout, pursued the retreating Austrians under Archduke Charles. The exhausted French troops caught up with the Austrians at Znaim in mid-July 1809, leading to a military occupation of the territory by France.
April 1809: The Austrian advance guard, led by Archduke Charles of Austria, beat back the Bavarians, commanded by Marshal Lefebvre, near Landshut in 1809 during the War of the Fifth Coalition. This victory led to the Austrian Empire occupying the territory.
21.3.Austro-Polish War
Was a war between the Austrian Empire and the Napoleon-allied Duchy of Warsaw.
June 1809: The Austrians took back Sandomierz and Lwów.
May 1809: Lwów conquered by france.
May 1809: In 1809, Sandomierz was incorporated into the Duchy of Warsaw.
June 1809: The Austrian main army under Archduke Ferdinand Karl Joseph, unable to push further on the left bank, and in danger of having its supply lines cut by Poniatowski, was forced to abandon the siege of Toruń.
May 1809: Polish forces took the major cities of Lublin.
May 1809: Zamość conquered by france.
April 1809: After the Battle of Raszyn on 19 April, where Poniatowski's Polish troops brought an Austrian force twice their number to a standstill (but neither side defeated the other decisively), the Polish forces nonetheless retreated, allowing the Austrians to occupy the Duchy's capital, Warsaw.
July 1809: Kielce and Kraków conquered by france.
June 1809: The Austrians abandoned Warsaw on 1 June.
21.4.Walcheren Campaign
Was an unsuccessful British expedition to the Netherlands in 1809, during the War of the Fifth Coalition.
July 1809: The British seized the swampy island of Walcheren at the mouth of river Scheldt, as well as South Beveland island, both in the present-day Netherlands.
September 1809: The British expedition in the Netherlands ("Walcheren Campaign") was called off in early September.
21.5.Treaty of Schönbrunn
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Fifth Coalition.
January 1811: Due to the Peace of Schönbrunn in 1809, Bavaria once again took possession of the Innviertel in 1810.
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna. Austria lost its access to the Adriatic Sea by waiving the Littoral territories of Gorizia and Gradisca and the Imperial Free City of Trieste, together with Carniola, the March of Istria, western ("Upper") Carinthia with East Tyrol, and the Croatian lands southwest of the river Sava to the French Empire (Illyrian provinces).
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna.
October 1809: The Illyrian Provinces (in French: Gouvernement des Provinces Illyriennes) were a French governorate of the Napoleonic era, a sort of exclave of metropolitan France, created with the union of the territories ceded by the Austrian Empire and the Italian Kingdom Napoleonic empire to the French Empire as a result of the Treaty of Schönbrunn (October 14, 1809).
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna. West Galicia was ceded to the Duchy of Warsaw.
October 1809: The Treaty of Schönbrunn was signed between France and Austria at Schönbrunn Palace near Vienna.Austria had to cede the Duchy of Salzburg to Bavaria.
Was a revolt in the County of Tyrol led by Andreas Hofer against French and Bavarian occupation.
April 1809: 8 aprile - dicembre 1809: Under the decisive leadership of Andreas Hofer, the country was liberated from the Bavarian-French occupation in the spring of 1809 and defended until autumn. It was not until November and December 1809 that Napoleon's troops were able to reoccupy the country and reassert their rule.
Was a series of British amphibious operations and naval actions fought to take possession of the French Indian Ocean territories of Isle de France and Île Bonaparte during the Napoleonic Wars.
23.1.Invasion of Île Bonaparte
British invasion of Île Bonaparte (today called Réunion).
July 1810: The island of Ile Bonaparte was invaded by a Royal Navy squadron led by Commodore Josias Rowley in 1810, who used the old name of "Bourbon".
23.2.Invasion of Isle de France
British invasion of Isle de France (today called Mauritius).
December 1810: Invasion of Isle de France: a substantial British military force was landed by the Royal Navy at Grand Baie on Isle de France (now Mauritius). Marching inland against weak French opposition, the British force was able to overwhelm the defenders.
Was a successful British amphibious operation against the Dutch East Indian island of Java that took place between August and September 1811 during the Napoleonic Wars.
September 1811: On 16 September Salatiga fell to the British.
September 1811: In 1811, British forces led by Captain Robert Maunsell suspected the presence of French General Jan Janssen in Cirebon, Indonesia. They landed a force from several ships, including HMS Lion and HMS President, prompting the defenders to surrender quickly. This marked the British military occupation of Cirebon.
January 1811: Captain Christopher Cole was a British naval officer who led the capture of the Banda Islands in 1810. This marked the final conquest of Dutch territories in the Maluku Islands by Great Britain during the Napoleonic Wars.
August 1811: In 1811, during the Napoleonic Wars, the British forces led by Sir Samuel Auchmuty and Sir Robert Gillespie advanced on Batavia, the capital of the Dutch East Indies. The city was left undefended by the Dutch colonial authorities, leading to its occupation by the British.
August 1811: The British forces, led by Lieutenant Colonel Gillespie, attacked Fort Cornelis in Java, which was held by the Dutch. The fort was captured after a fierce battle in 1811, marking the beginning of British military occupation in the region.
January 1811: The Dutch-held islands of Amboyna, Harouka, Saparua, Nasso-Laut, Buru, Manipa, Manado, Copang, Amenang, Kemar, Twangwoo and Ternate had surrendered to a force led by Captain Edward Tucker in 1810.
August 1814: The British returned Java to the Dutch East Indies in 1814 under the Convention of London.
September 1811: With his effective force reduced to a handful of men, Janssens surrendered two days later, on 18 September.
August 1811: British naval forces landed at 14:00 at Cilincing.
January 1811: The Kingdom of Holland was annexed to the First French Empire in 1810, and Java became a titular French colony.
Was a French military campaign in Russia. It was launched by Napoleon to force the Russian Empire back into the continental blockade of the United Kingdom. The campaign proved unsuccesful, and the French Army suffered heavy losses.
June 1812: Eugene de Beauharnais, the stepson of Napoleon Bonaparte and Viceroy of Italy, crossed at Prenn on June 30.
September 1812: The Battle of Borodino took place during Napoleon's invasion of Russia in 1812. It was fought between the French forces under Napoleon Bonaparte and the Russian army commanded by General Mikhail Kutuzov. The battle resulted in heavy casualties on both sides, with neither emerging as a clear victor.
November 1812: Battle of Krasnoi (Krasny) (November 15 to 18, 1812).
August 1812: Following a defeat at Smolensk on August 16-18, Napoleon Bonaparte continued his move east during the French invasion of Russia in 1812. The Battle of Smolensk was a key engagement between the French forces and the Russian army led by General Mikhail Kutuzov.
December 1812: The last French troops left Russian soil.
June 1812: On June the 28th Napoleon entered Vilnius.
June 1812: The 25th of June 1812 found Napoleon Bonaparte's group advancing past the bridge head with Marshal Ney's command approaching the existing crossings at Alexioten in Lithuania during the French military occupation.
September 1812: Napoleon Bonaparte, the French military leader and emperor, moved into Moscow in 1812 during the French invasion of Russia. This marked the beginning of the French military occupation of the city during the Napoleonic Wars.
October 1812: The Second Battle of Polotsk was fought between the French army and the Russian army.
June 1812: Jerome Bonaparte, the younger brother of Napoleon Bonaparte, moved VII Corps to Białystok.
September 1812: The Battle of Borodino, was the largest and bloodiest battle of the French Campaign in Russia.
November 1812: Battle of Vyazma.
Was a war between France and a a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States. The coalition emerged after the decimation of the French army in the French invasion of Russia. The coalition ultimately invaded France and forced Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile.
October 1813: The Swedish Army mobilized and assisted against Napoleon in the Battle of Leipzig in 1813.
November 1813: The Sovereign Principality of the United Netherlands was a short-lived sovereign principality and the precursor of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. The principality was proclaimed in 1813 when the victors of the Napoleonic Wars established a political reorganisation of Europe, which would eventually be defined by the Congress of Vienna.
January 1814: Following Napoleon's defeat at the Battle of Leipzig in 1813, the Congress of Vienna opted to mediatize the Leyen Principality and give it to Austria.
January 1814: After the defeat of Napoleon in Leipzig (Battle of Leipzig), the Papal territories occupied by the French were returned to the Holy See (January 24, 1814).
April 1814: In 1814, the military occupation of the Sixth Coalition ended in France. This marked the withdrawal of foreign troops, including those of Russia, Prussia, Austria, and Sweden, from French territory after the defeat of Napoleon Bonaparte in the War of the Sixth Coalition.
April 1814: The Treaty of Fontainebleau was signed on 11 April 1814. Napoleon was stripped of his powers as ruler of the French Empire. The treaty also established the island of Elba as a separate principality to be ruled by Napoleon.
May 1814: During the French Revolution, the territory of Monaco was under French control from 1793 to May 17, 1814, as part of the département of Alpes-Maritimes. This period ended with the fall of the French Empire.
May 1814: The Marquisate of Sorbello reacquired its independence at the end of the Napoleonic Domain in Italy.
January 1814: Bernadotte invaded Schleswig, swiftly invested and reduced its fortresses and occupied the entire province.
May 1814: The Carpegna County reacquired its independence at the end of the Napoleonic Domain in Italy.
January 1814: Görz and Trient are annexed by Austria.
May 1814: The Duchy of Modena-Reggio is restored.
December 1813: On 16 December 1813, Radhanpur became a British protectorate.
January 1814: In December 1813, Bernadotte's Army, now some 65,000, composed only of Swedish and Russian troops following the secondment of the Prussian troops to Blücher's army, attacked the Danish Army in Holstein.
January 1814: Bremen reverted to an independent Free City in 1813.
January 1814: Kniphausen is annexed by Oldenburg.
January 1814: Ostfriesland is annexed by Russia.
January 1814: The Treaty of Kiel was signed by King Frederick VI of Denmark-Norway and Crown Prince Charles John of Sweden. As a result, Norway was forced to cede to Sweden after being part of Denmark-Norway for centuries.
January 1814: On 25 January Blücher entered Nancy.
February 1814: Napoleon inflicted such heavy punishment upon his adversaries that they fell back precipitately to Bar-sur-Aube.
March 1814: On 13 March Napoleon retook Reims.
April 1814: The French monarchy was restored by the other great powers in 1814.
May 1814: The Norwegians rejected declared independence and adopted their own constitution on 17 May.
May 1814: The Valtellina, formerly owned by Graubunden, was granted to Austria.
November 1813: The Battle of Nivelle.
March 1814: With the occupation of Benevento by Murat, the prince of Talleyrand was removed (February 1814), and the principality became extinct.
May 1814: Louis-Nicolas Davout, a French military commander, was in control of Hamburg during the War of the Sixth Coalition. He eventually surrendered to Russian forces led by General Levin August, Count von Bennigsen in April 1814.
August 1813: In the Battles of Großbeeren and neighboring Blankenfelde and Sputendorf an allied Prussian-Swedish army under Crown Prince Charles John - formerly Marshal of France Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte - defeated the French.
March 1814: Battle of Laon.
February 1814: Blücher himself on the night of 7/8 February was at Sézanne.
April 1813: On 5 April, in the Battle of Möckern, combined Prusso-Russian forces defeated French troops. The French withdrew to Magdeburg.
April 1814: The principality of Elba Island was a small European state, which existed in the 19th century from 1814 to 1815, ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, former emperor of the French and king of Italy.
October 1813: Napoleon is defeated in Leipzig by the Coalition forces. The French Army is forced to leave Germany.
March 1814: After the Congress of Vienna in 1814, the former republic of Lucca became a duchy under the rule of Maria Luisa of Spain. Piombino was annexed to the grand duchy of Tuscany under the control of Ferdinand III, Grand Duke of Tuscany.
December 1813: The Battle of Nive near Bayonne in 1813 involved the forces of French Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte against the Spanish and British armies led by Arthur Wellesley, the Duke of Wellington. The battle resulted in the territory of Bayonne being captured by Spain and Great Britain.
March 1814: The Battle of Paris ended when the French commanders, seeing further resistance to be hopeless, surrendered the city.
January 1814: Cottbus is ccupied by Prussia and later added to the Province of Brandenburg.
October 1813: Napoleon withdrew with around 175,000 troops to Leipzig.
October 1813: The Battle of Leipzig or Battle of the Nations. was fought from 16 to 19 October 1813, at Leipzig, Saxony. The coalition armies of Russia, Prussia, Austria, and Sweden, led by Tsar Alexander I of Russia and Karl Philipp, Prince of Schwarzenberg, decisively defeated the French army of Napoleon I.
October 1813: The Grand Duchy's short existence came to an end when the French forces pulled back in the course of the 1813 Battle of Leipzig. The territory was then administered by Prussia, which officially incorporated the former Grand Duchy according to the Final Act of the 1815 Congress of Vienna.
October 1813: Following Napoleon's defeat in 1813, the elector was restored. The rulers of the Electorate of Hesse became the only Prince-Electors in the German Confederation, even though there was no longer a Holy Roman Emperor for them to elect.
January 1814: Dortmund, Ostfriesland, Gleichenstein, Goslar, Halberstadt, Mark, Nordhausen, Paderborn, Tecklenburg are annexed by Prussia.
January 1814: The Treaty of Kiel was signed by King Frederick VI of Denmark-Norway and Crown Prince Charles John of Sweden. The treaty ended the Napoleonic Wars and resulted in Norway being ceded to Sweden, leading to a period of Swedish military occupation in Norway.
January 1814: Occupied territories in Holstein and Schleswig are reverted to Denmark at the end of the War of the Sixth Coalition.
January 1814: Swedish Pomerania, given to Denmark a year earlier in return for Norway, was ceded by Denmark to Prussia.
January 1814: Between 1035 and 1814, the Faroe Islands were part of the Kingdom of Norway, which was in a personal union with Denmark from 1450. In 1814, the Treaty of Kiel transferred Norway to the King of Sweden, on the winning side of the Napoleonic Wars, whereas Denmark retained the Faroe Islands, along with Greenland and Iceland.
February 1814: Mormant conquered by Sixth Coalition.
February 1814: Montereau conquered by Sixth Coalition.
March 1814: After the Congress of Vienna in 1814, the former republic of Lucca was transformed into a duchy under the rule of Maria Luisa of Spain. Piombino was annexed to the Grand Duchy of Tuscany, which was ruled by Ferdinand III.
March 1814: After the Congress of Vienna in 1814, the former republic of Lucca was transformed into a duchy under the rule of Maria Luisa of Spain. Piombino, on the other hand, was annexed to the Grand Duchy of Tuscany under the control of Ferdinand III.
May 1814: Republic's revival in Genoa.
May 1814: The Scavolino County reacquired its independence at the end of the Napoleonic Domain in Italy.
May 1814: The Vernio County reacquired its independence at the end of the Napoleonic Domain in Italy.
May 1814: The Duchy of Massa in 1814, following the Congress of Vienna, at the time of its maximum expansion after the acquisition of some of the former Malaspina fiefdoms of Lunigiana, assigned the following year to the Duchy of Modena and Reggio.
May 1814: The Marquisate of Fosdinovo reacquired its independence at the end of the Napoleonic Domain in Italy.
February 1814: Méry-sur-Seine conquered by Sixth Coalition.
January 1814: The Austrian advanced near La Rothière on the afternoon.
26.1.Treaty of Paris (1814)
Was the treaty that ended the war between France and the Sixth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.
May 1814: In the 1814 Treaty of Paris, Sweden ceded Guadeloupe to France.
May 1814: By the Treaty of Paris, May 30, 1814, the House of Savoy was restored to its rights.
May 1814: Lingen and Ravensberg are acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia.
May 1814: Oldenburg administration in Jever.
May 1814: The Duchy of Massa and Carrara is restored after the Napoleonic Wars.
May 1814: Jever is occupied by Russia.
May 1814: Vechta and part of the Bishopric of Lübeck are acquired by Oldenburg.
May 1814: Restoration of the Duchy of Parma-Piacenza, wich is assigned for life to Napoleon's wife Maria Luisa d'Austria, who will rule on the duchy until her death in 1847.
Was a war initiated by Norway to gain independence from Sweden. The war resulted in a compromise, with Norway being forced into the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, a union with Sweden under the Swedish king Charles XIII, but with Norway having its own constitution and parliament.
July 1814: The hostilities opened on 26 July with a swift Swedish naval attack against the Norwegian gunboats at Hvaler.
July 1814: The town of Fredrikstad in Norway surrendered to Swedish force.
August 1814: The Norwegian forces withdrew over the Glomma river at Langnes in Askim.
August 1814: Convention of Moss, was signed on 14 August 1814. Norway agreed to enter into a personal union with Sweden as a separate state with its own constitution and institutions, except for the common king and foreign service.
Was a series of international diplomatic meetings after the end of the Napoleonic wars whose aim was a long-term peace plan for Europe. It redraw the borders of Europe and partially restored the Monarchies of the pre-revolutionary period.
October 1814: The Kingdom of Hanover was established in 1814 at the Congress of Vienna as the successor state to the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg. This territory was given to the Kingdom of Hanover, which was ruled by the House of Hanover, a British royal family.
October 1814: After the fall of Napoleon in 1814, George III regained his lands in Hanover and acquired additional territories from Prussia, becoming the King of Hanover.
January 1815: The Granduchy of Würzburg is partitioned between Baden and Bavaria.
October 1814: The "Electorate of Hanover" (the core duchy) was enlarged with the addition of other lands and became the kingdom of Hanover in 1814 at the peace conferences (Congress of Vienna) settling the future shape of Europe in the aftermath of the Napoleonic wars.
June 1815: At the Congress of Vienna, sovereignty of the island of Elba was returned to the Grand Duchy of Tuscany.
June 1815: After the downfall of France in 1814 and the Congress of Vienna in 1815, the Grand Duchy of Tuscany was restored.
June 1815: With the Congress of Vienna, the Kingdom of prussia acquired a large territory in the Rhineland which formed the Grand Duchy of the Lower Rhine, a new province of the Kingdom of Prussia.
June 1815: According to the Congress of Vienna, the March of Sorbello is incorporated in the Granduchy of Tuscany.
June 1815: In addition, Oldenburg received the Principality of Birkenfeld an der Nahe as a further exclave alongside the Principality of Lübeck, so that the national territory now comprised three parts.
January 1815: Tirol is annexed by Austria.
March 1815: The United Kingdom of the Netherlands was formed, which added the former territory of the low countries that had been ruled by the Austrian Empire to the Netherlands, and had William I as its king. His son William joined the fighting at Waterloo, whose battle site was located in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. Though the Dutch initiated their request to William I, the great powers of the Napoleonic wars had made a secret pact to support a strong nation on that border with France with William as its king.
June 1815: Prussia received three-fifths of Saxony with the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: In 1815, the Congress of Vienna returned the principalities of Pontecorvo and Benevento to the Holy See.
June 1815: Lingen fell to Hanover with the Congress of Vienna.
September 1814: On September 12, 1814, Neuchâtel became the capital of the 21st canton, but also remained a Prussian principality.
June 1815: According to the Congress of Vienna, the March of Fosdinovo enters the Duchy of Modena-Reggio.
September 1814: Valais, Neuchâtel and Geneva were raised to full members of the Swiss Confederation.
January 1815: In 1814, an imperial decree reestablished the independence and economy of Andorra.
March 1815: The United Netherlands was created in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars, with William I of Orange-Nassau becoming the first King of the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1815. This marked the unification of the Northern and Southern Netherlands under one sovereign principality.
March 1815: On 20 March 1815 Bern was given the town of Biel/Bienne and much of the land that had been owned by the Bishop of Basel as compensation for lost territories.
June 1815: In the 1815 Congress of Vienna, Poland was formally partitioned between Russia, Prussia and Austria.
June 1815: According to the Congress of Vienna, Lucca maintains its indipendence from Tuscany as a Duchy.
June 1815: Territories awarded to the Kingdom of Saxony by the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: In 1815, the Congress of Vienna compelled the state to recognize the independence of Hesse-Homburg, which was expanded by adding Meisenheim. This decision was significant for the Landgraviate of Hesse-Homburg and its ruler, Frederick VI.
January 1815: The region of Frankfurt was annexed by Bavaria in 1814.
November 1815: The British gradually took control of the islands, and following the Treaty of Paris, the islands were formally organised into the United States of the Ionian Islands under British protection.
June 1815: Establishment of the free city of Hamburg after the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: According to the Congress of Vienna, the Marches of Tresana, Mulazzo, Castevoli-Villafranca, Rocchetta-Suvero and Aulla-Podenzana are ceded to the Duchy of Modena-Reggio.
January 1815: In 1814 the Kingdom of Hanover bartered Saxe-Lauenburg against Prussian East Frisia.
June 1815: With the Congress of Vienna, the Duchy of Nassau received: from Mainz, Höchst, Königstein, Cronberg, Lahnstein and the Rheingau; from Cologne some districts on the east bank of the Rhine; from Bavaria, the sub-district of Kaub; from Hesse-Darmstadt, the lordship of Eppstein, Katzenelnbogen, and Braubach; from Prussia, Sayn-Altenkirchen, Sayn-Hachenburg; and several cloisters were received from Mainz.
June 1815: Territories awarded to the Kingdom of Bavaria by the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: Not all Austrian territories became part of the German onfederation.
June 1815: Establishment of the free city of Lübeck after the Congress of Vienna.
September 1814: On 29 December under pressure from Austria, the Diet abolished the 1803 constitution which had been created by Napoleon in the Act of Mediation. On 6 April 1814 the so-called Long Diet met to replace the constitution. The Diet remained dead-locked until 12 September when Valais, Neuchâtel and Geneva were raised to full members of the Confederation.
February 1815: Geona was eventually annexed by the Kingdom of Sardinia in 1815.
June 1815: The Austrian Empire receives the Tarnopol district from Russia.
June 1815: The Congress of Vienna was a meeting of European powers to reorganize the continent after the Napoleonic Wars. The principality of Pontecorvo was ruled by Napoleon's brother-in-law, Marshal Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte. The return of Pontecorvo to the Papal States was part of the restoration of territories taken by Napoleon during his reign.
June 1815: According to the Congress of Vienna and because of the end of the Principality of Lucca-Piombino, the Duchy of Massa/Principality of Carrara is restored under the rule of Maria Beatrice d'Este.
June 1815: After the Congress of Vienna in 1815, the territory of Nain went to the Kingdom of Prussia, specifically outside the German Confederation. This decision was made by the European powers to reorganize the political landscape of Europe after the Napoleonic Wars.
June 1815: According to the Congress of Vienna, the March of Mulazzo is ceded to the Duchy of Modena-Reggio.
June 1815: The County of Vernio, according to the Congress of Vienna, is annected to the Granduchy of Tuscany.
June 1815: Establishment of the free city of Frankfurt after the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: Some minor territories de facto fell under the control of the Ottoman Empire in 1815.
June 1815: Fulda fell to Hanover with the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: Territories awarded to the Duchy of Anhalt by the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: Territories awarded to the Granduchy of Hesse by the Congress of Vienna.
June 1815: Rieneck is ceded to Bavaria.
June 1815: In 1815, the Congress of Vienna recognized the independence of Hesse-Homburg, which was expanded by adding Meisenheim.
June 1815: The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg was a territory reestablished by the Congress of Vienna in 1815.
June 1815: Luxembourg existed as an independent Grand Duchy from 1815 and was therefore not part of the Kingdom of the United Netherlands. However, from 1815 to 1890 it was ruled by the Dutch king, who was also the Grand Duke of the sovereign Luxembourg.
June 1815: The "Electorate of Hanover" was enlarged with the addition of other lands and became the kingdom of Hanover in 1814 at the peace conferences of Vienna.
June 1815: This decision was confirmed at the Congress of Vienna. The lands of the principality were divided between the Grand Duchy of Hesse-Darmstadt and the Electorate of Hesse-Kassel (or Hesse-Cassel).
June 1815: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Germany during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic periods.
June 1815: Territorial change based on available maps.
June 1815: By the Congress of Vienna in 1815, both parts of the now sovereign Duchy of Mecklenburg became the Grand Duchy.
June 1815: The Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz is elevated to the rank of grand duchy.
October 1815: Prussia agreed to exchange Swedish Pomerania with the cession of the duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg to Denmark and assumed the Danish war debt to Sweden. The delivery via the Swedish governor to the Prussian plenipotentiary minister took place in October 1815.
Napoleon escaped the exile he had been forced after the War of the Sixth Coalition and reorganized the French army. He was defeated by a coalition that included Great Britain, Austria, Prussia and Russia and sent into permanent exile on the island of Saint Helena.
June 1815: French retreat after being defeated in the Battle of Waterloo (18 June 1815).
July 1815: The French King, Louis XVIII, made his public entry into Paris, amidst the acclamations of the people, and again occupied the throne.
July 1815: After the defeat of Napoleon at the Battle of Waterloo on June 18, 1815, the Seventh Coalition forces, led by Prussian Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, advanced towards Paris. By July 2, Blücher had positioned his troops with his right at Plessis-Piquet, left at Meudon, and reserves at Versailles, preparing to besiege the city.
June 1815: In 1815, during the Napoleonic Wars, the advanced guards of Napoleon Bonaparte's army were stationed at Saint-Denis and Gonesse. This marked the beginning of the Battle of Waterloo, where Napoleon's forces faced the Seventh Coalition led by the Duke of Wellington and Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher.
June 1815: In 1815, during the Napoleonic Wars, the Prussians, led by Field Marshal Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher, were stationed at Crépy, Senlis, and La Ferté-Milon. This strategic positioning played a crucial role in the Seventh Coalition's efforts to defeat Napoleon Bonaparte at the Battle of Waterloo.
March 1815: Napoleon arrived in Paris, and re-established the Empire.
June 1815: The British took Cambrai.
June 1815: To secure a central position at the Battle of Waterloo Napoleon secured Charleroi.
June 1815: A French army hoccupies Genappe before the Battle of Quatre Bras.
June 1815: From Beaumont the Prussians advanced to Avesnes, which surrendered to them.
June 1815: The castle of Guise surrendered to the Prussian army.
June 1815: Aubervilliers conquered by Seventh Coalition.
July 1815: The two Coalition armies, with Graf von Zieten's Prussian I Corps as the vanguard, entered Paris. .
29.1.Neapolitan War
Was a conflict between the Napoleonic Kingdom of Naples and the Austrian Empire during the War of the Seventh Coalition. Naples, which was still ruled by the Napoleonic general Joachim Murat, decided to side with Napoleon. The Austrian won the war and reinstated Ferdinand IV as King of Naples and Sicily.
May 1815: Murat's joint campaign was definitively wrecked on 4 May 1815, after the Austrians defeated him in the battle of Tolentino: finally, with the Treaty of Casalanza, signed at Capua on 20 May 1815 by the Austrian and Murat generals, the kingdom of Naples thus returned to the crown Bourbon, with King Ferdinand who returned to Naples on 7 June.
29.1.1.Neapolitan attack (Neapolitan War)
Was the invasion of central and northern Italy launched by the Neapolitan armies during the Neapolitan War.
March 1815: Leaving behind a reserve Army of the Interior in case of an invasion from Sicily, Murat sent his two elite Guard Divisions through the Papal States, forcing the Pope to flee to Genoa. With the remainder of his army, Murat established his headquarters at Ancona and advanced on the road towards Bologna. On 30 March, Murat had arrived in Rimini, where he gave the famous Rimini Proclamation, inciting all Italian nationalists to war.
April 1815: Battle of the Panaro.
April 1815: The Austrian advance guard under the command of General Bianchi was beaten back at an engagement near Cesena. Bianchi retreated towards Modena and took up a defensive line behind the River Panaro, allowing Murat to take Bologna on 3 April.
April 1815: The two Guard Divisions Murat had sent into the Papal States passed unmolested into Tuscany and by 8 April had occupied Florence, the capital of the Grand Duchy of Tuscany.
29.1.2.Austrian counterattack (Neapolitan War)
Was the Austrian invasion of Italy during the Neapolitan War.
April 1815: Battle of Pesaro.
April 1815: General Nugent had continued to advance from Florence. Having arrived in Rome.
May 1815: The Austrian armies united near Calvi and began the march on Naples.
May 1815: Neapolitan Generals Pepe and Carrascosa sued for peace and concluded the Treaty of Casalanza with the Austrians, bringing the war to an end.
April 1815: Carrascosa, who was in command of the Neapolitan troops around Modena, saw the Austrian trap and ordered a retreat to a defensive line behind the Panaro where he was joined by the remainder of his division, which had been evacuated from Reggio Emilia and Modena.
April 1815: Neipperg's corps was still in pursuit and by 29 April, his advanced guard had arrived in Fano, just two days' march away.
April 1815: Murat hurried his retreat and by late April, his main force had arrived safely in Ancona, where he was reunited with his two Guard Divisions.
April 1815: Ferrara was attacked by Neapolitan troops.
April 1815: In Tuscany Murat's two Guard Divisions also inexplicably retreated without being harassed in any way by Nugent. By 15 April, the Austrians had retaken Florence.
April 1815: On 14 April, Frimont attempted to force a crossing of the Panaro, but was repelled. However, only two days later, Murat and his army retreated from Bologna, which was quickly retaken by the Austrians.
April 1815: Battle of Cesenatico.
April 1815: The Austrians reached Foligno.
May 1815: A joint Anglo-Austrian fleet began a blockade of Ancona, eventually taking the entire garrison of the city as prisoners.
May 1815: By 12 May, Bianchi, who was now in command of both his and Neipperg's corps, had taken the town of L'Aquila.
May 1815: Nugent intercepted Murat at San Germano (now Cassino).
29.1.3.King Ferdinand restored
On 23 May, at the end of the Neaopolitan War, the main Austrian army entered Naples and restored King Ferdinand to the Neapolitan throne.
May 1815: The main Austrian army entered Naples and restored King Ferdinand to the Neapolitan throne.
Selected Sources
Addington, L. (1994): The Patterns of War Since the Eighteenth Century, Bloomington (USA), p.24
Ader, J.J. (1826): Histoire de l'expédition d'Égypte et de Syrie, A. Dupont et cie, pp. 186-207
Alison, A. (1835): History of Europe, W. Blackwood and Sons, pp. 86-90.
Articles secrets et convention additionelle du traité de Campo Formio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2024 on https://books.google.de/books?id=SStJAAAAcAAJ&dq=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&hl=de&pg=PA1#v=onepage&q=Trait%C3%A9%20de%20paix%20de%20Campo%20Formio&f=false
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), p. 26-49
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), p. 48
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 48-49.
Fournier. A (1913): Napoleon I. Eine Biographie, Vienna (Austria), p. 255
Frieden von Campoformio. Retrieved on March, 24th 2014 on https://books.google.de/books?id=UbGMtENHaBIC&pg=PA9#v=onepage&q&f=false
Gagliardo, J. (1980): Reich and Nation: The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Bloomington (USA), p. 192
Guthrie, W. (1798): A New geographical, historical and commercial grammar and present state of the several kingdoms of the world, printed for Charles Dilly and G.G. and J. Robinson, p. 473
Günther Cordes: Grafschaft Schleiden. In: Gerhard Taddey (Hrsg.): Lexikon der deutschen Geschichte. Personen, Ereignisse, Institutionen. Von der Zeitwende bis zum Ausgang des 2. Weltkrieges. 2., überarbeitete Auflage. Kröner, Stuttgart 1983, ISBN 3-520-80002-0, S. 1106.
Jorio, M. (2002): Basel, Frieden von (1795). Historisches Lexikon der Schweiz. https://hls-dhs-dss.ch/de/articles/044887/2002-05-01/
Kreins, J. (2003): Histoire du Luxembourg, Paris (France), p. 63
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, Munich (Germany), p. 248
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, Munich (Germany), p. 281
Köbler, G. (2014) Historische Enzyklopädie der Länder der Deutschen, Munich (Germany), pp. 791-792
Oberfinanzrath von Memmingen (1837): Beschreibung des Oberamts Biberach, Stuttgart and Tübingen (Germany), p. 95
Phillipson, C. (2008): Termination of War and Treaties of Peace, Clark (USA), p. 273
Poole, R.L. (1902): Historical Atlas of Modern Europe, Oxford (United Kingdom), Plate XI
Schneid, F. (2002): Napoleon's Italian campaigns, 1805-1815, Greenwood (USA), pp. 41-42
Smith, D. (1998): Napoleonic Wars Databook, London (UK), p. 178
Smith, D. (1998): The Napoleonic Wars Data Book, London: Greenhill, p. 104
Spindler, M. / Kraus, A. (2011): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts (Handbuch der bayerischen Geschichte. Band 3: Franken, Schwaben, Oberpfalz bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts.), Munich (Germany), p. 384ff.
Swiss campaign of Suvorov and his wonder-heroes. Top War. 30 September 2011. https://en.topwar.ru/7227-shveycarskiy-pohod-suvorova-i-ego-chudo-bogatyrey.html
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.260
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.274
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.287
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.296
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.302
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.308
 French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars