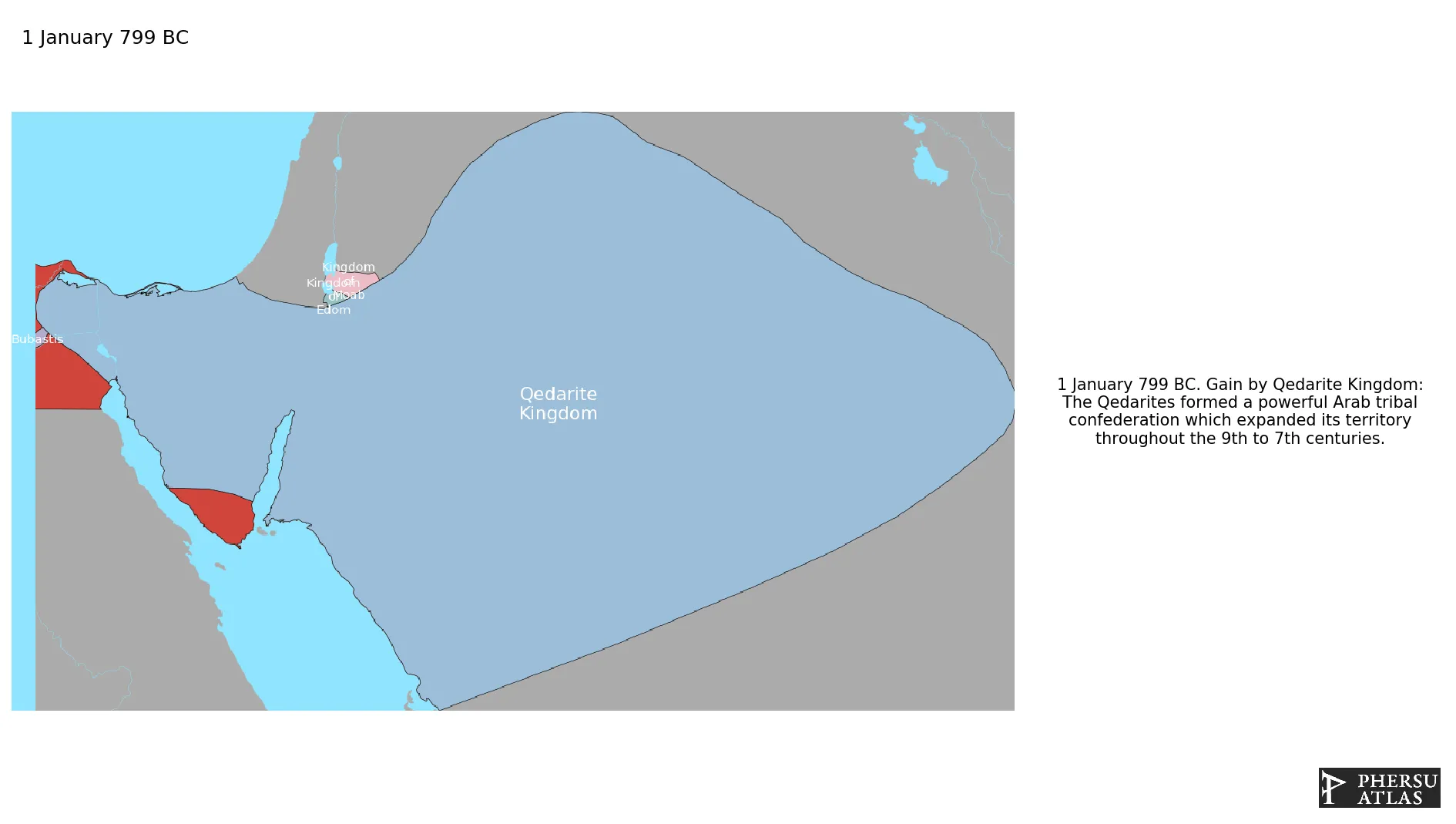
Qedarite Kingdom
Qedarite Kingdom
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a largely nomadic, ancient Arab tribal confederation.
Establishment
January 799 BC: The Qedarites formed a powerful Arab tribal confederation which expanded its territory throughout the 9th to 7th centuries.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a period of political instability that followed the death of Pharaoh Ramesses XI and coincided with the Late Bronze Age collapse.
1.1.Assyrian conquest of Egypt
Were a series of Assyrian military campaigns that led to the conquest of Egypt.
1.1.1.Esarhaddon's second invasion
Was a military campaign of Assyrian King Esarhaddon in Egypt that resulted in the conquest of the northern part of the Egyptian Kingdom.
January 670 BC: In -671 BC, King Esarhaddon of the Assyrian Empire launched a second conquest attempt in Egypt. This time, he successfully occupied key cities like Memphis and Thebes, forcing Taharqa, the ruler of Egypt, to retreat to Nubia after a severe defeat.
Military campaign of Median king Cyaxares.
2.1.Medo-Babylonian conquest of the Assyrian Empire
Was a war fought between Media and Babylon against the Neo-Assyrian Empire that led to the fall of the latter.
2.1.1.Necho´s first campaign in syria
Was a military campaign by Egyptian Pharaoh Necho II that invaded the Levant to help the Assyrian in their war against Media and Babylon.
June 609 BC: Egyptian Pharaoh Necho led a sizable force to help the Assyrians. He soon captured Kadesh on the Orontes and moved forward, joining forces with Assyrian ruler Ashur-uballit and together they crossed the Euphrates and laid siege to Harran. Although Necho became the first pharaoh to cross the Euphrates since Thutmose III, he failed to capture Harran, and retreated back to northern Syria.
January 608 BC: Egyptian Pharaoh Necho led a sizable force to help the Assyrians. He soon captured Kadesh on the Orontes and moved forward, joining forces with Assyrian ruler Ashur-uballit and together they crossed the Euphrates and laid siege to Harran. Although Necho became the first pharaoh to cross the Euphrates since Thutmose III, he failed to capture Harran, and retreated back to northern Syria.
After the collapse of the Babylonian Empire Tyam became an independent kingdom.
January 538 BC: The last Babylonian king, Nabonidus (ruled c. 556-539 BC), conquered Tayma and for ten years of his reign retired there to worship and search for prophecies.
January 555 BC: Labashi-Marduk left the capital and travelled to campaign in the Levant and also conquered the desert oasis city of Tayma in the north Arabia early in his reign.
January 399 BC: The Nabataean Arabs emerge as a political power. The 4th century BC was marked by the growth of Nabataean control over trade routes and various tribes and towns.
January 249 BC: The Zenon papyri, a collection of documents from the time of Ptolemy II Philadelphus, provide evidence of the Nabataeans expanding into the Hauran region around -250 BC. This marked the Nabatean Kingdom's territorial expansion and influence in the area during this period.
January 199 BC: Kindah was a tribal kingdom in central Arabia established by the Kindah tribe which emigrated from its homeland in Hadramout. The tribe's existence dates back to the 2nd century BC.
Disestablishment
January 99 BC: The Qedarite Kingdom was absorbed into the Nabataean state during the 2nd century BC.
Selected Sources
Bernd Schipper, 2010, Egypt and the Kingdom of Judah under Josiah and Jehoiakim, p. 218
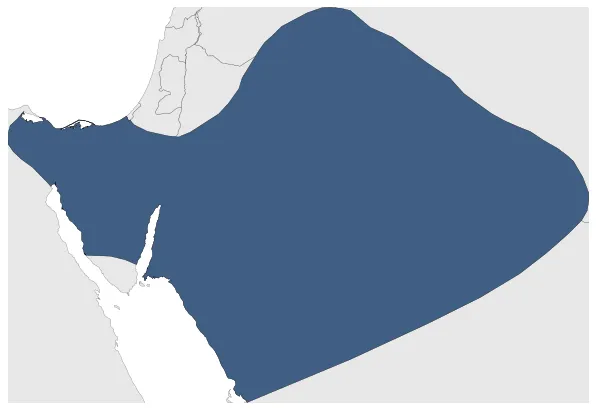
 Qedarite Kingdom
Qedarite Kingdom