.svg.png.webp)
Data
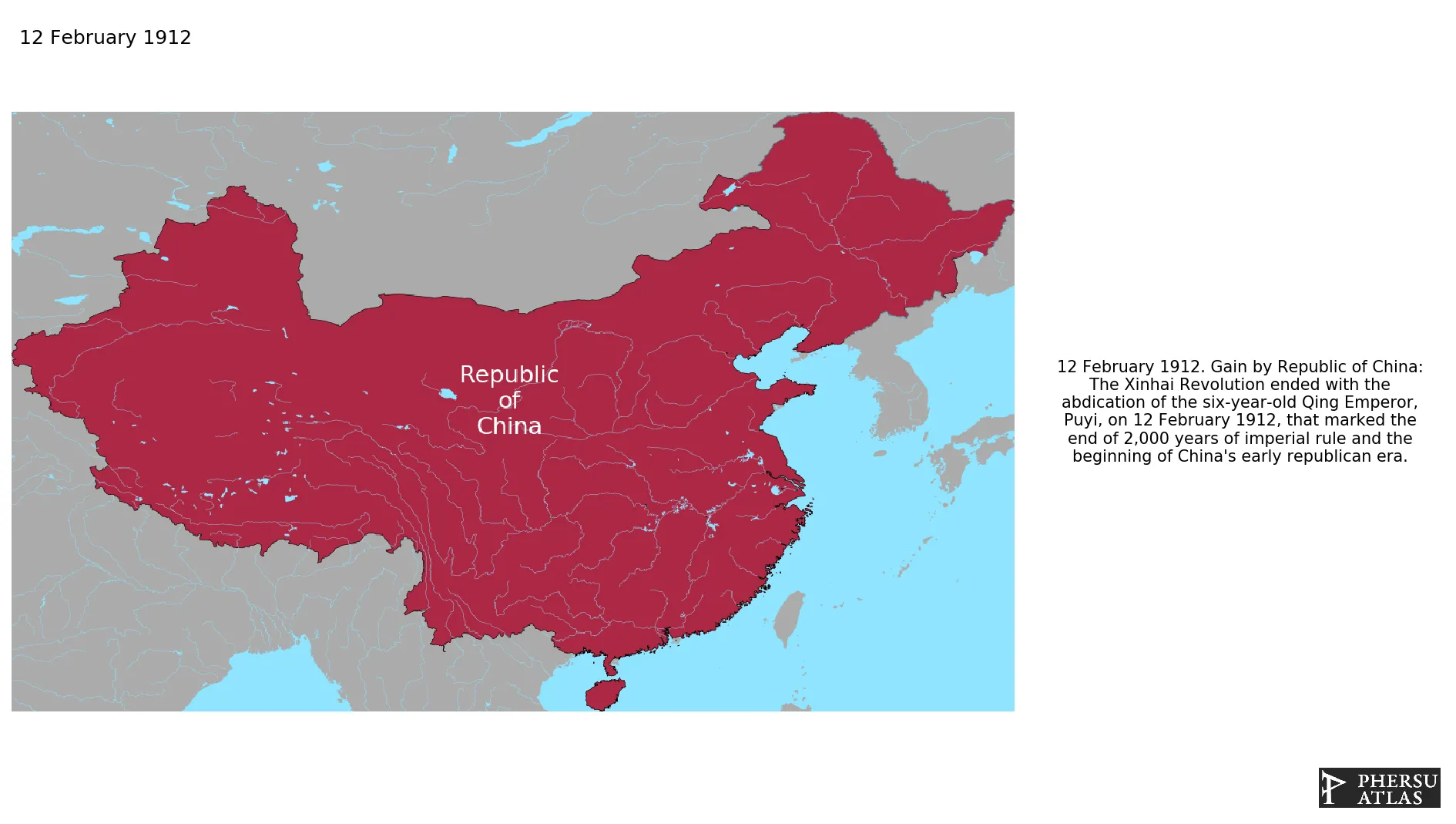
Name: Republic of China
Type: Polity
Start: 1912 AD
End: 1916 AD
Nation: china
Statistics
All Statistics: All Statistics
 Republic of China
Republic of China
This article is about the specific polity Republic of China and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the official designation of the successor state ot Qing China. Nominally, it was the name of the state existing in mainland China from 1912 to 1949 and of the still existing Republic of China whose control is limited to the territory of Taiwan since 1949. In order to show the factual situations arisen from the different historical periods of China in the XX century, the Republic of China in our model only refers to the period immediately following the Qing Dynasty. From 1916 mainland China is treated as a patchwork of war lord-controlled polities, the "Warlords (Chinese Warlord Era)" polity. After this period, the conservative party in the long Chinese Civil War is treated directly as "Kuomintang" and the state founded by the Kuomintang in Taiwan is called simply "Taiwan" to clearly distinguish it from the the People's Republic of China that controls mainland China.
Establishment
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
1. Xinhai Revolution
Was a revolt in Chin that ended China's last imperial dynasty, the Manchu-led Qing dynasty, and led to the establishment of the Republic of China.
2. Sino-Mongolian War of 1913-1915
Was a war between China and Mongolia. It was initiated by a Mongolian invasion of China.
3. Chinese Warlord Era
Was a period in the history of the Republic of China when control of the country was divided among former military cliques of the Beiyang Army and other regional factions.