If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
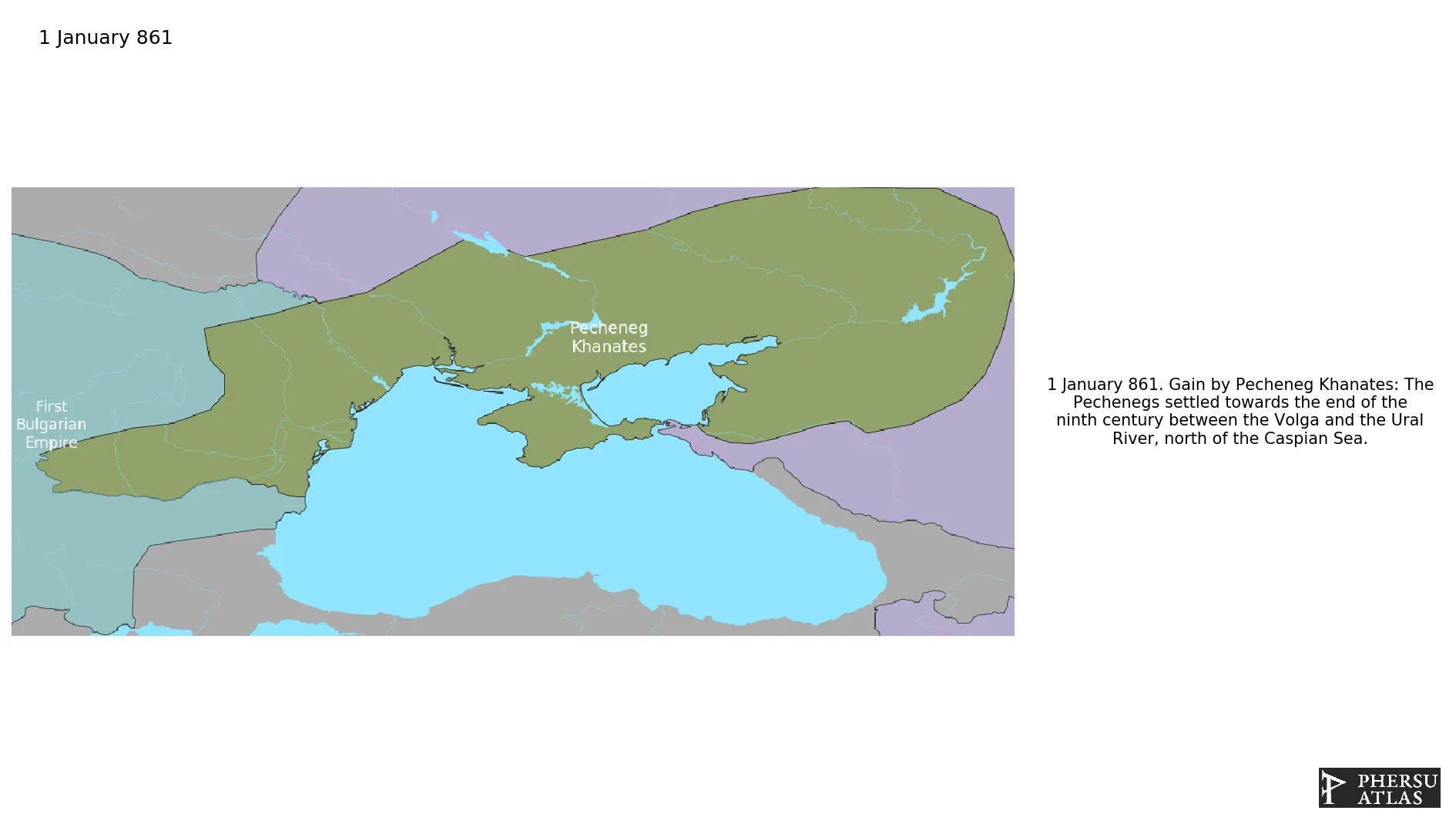
The Pechenegs settled towards the end of the ninth century between the Volga and the Ural River, north of the Caspian Sea.
Establishment
January 861: The Pechenegs settled towards the end of the ninth century between the Volga and the Ural River, north of the Caspian Sea.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of expansionistic military campaigns by Oleg, ruler of the Kievan Rus'.
January 886: In 885, Oleg of Novgorod, subjugated the Poliane people, a Slavic tribe.
The Magyars (or Hungarians) successfully conquered the Carpathian Basin (corresponding to the later Kingdom of Hungary) by the end of the ninth century, and launched a number of plundering raids thoughout Europe.
January 896: The Hungarians conquer the eastern parts of the Carpathian Basin after defeating the Bulgarians in Southern Transylvania and Tiszántúl.
January 903: The Hungarians conquer the eastern parts of Great Moravia, ending with this the Hungarian Conquest of the Carpathian Basin, while the Slavs from West and North to this region, start to pay tribute to them.
January 938: In 937, the Hungarians raided France as far west as Reims, Lotharingia, Swabia, Franconia, the Duchy of Burgundy and Italy as far as Otranto in the south.
January 938: The Hungarians attacked Bulgaria and the Byzantine Empire, reaching the walls of Constantinople.
February 938: The Hungarians attacked Bulgaria and the Byzantine Empire, reaching the walls of Constantinople.
February 938: In 937, the Hungarians raided France as far west as Reims, Lotharingia, Swabia, Franconia, the Duchy of Burgundy and Italy as far as Otranto in the south. After the ride they left these territories.
Were a series of conflicts fought between the Byzantines and Bulgarians which began when the Bulgars first settled in the Balkan peninsula in the 5th century, and intensified with the expansion of the Bulgarian Empire to the southwest after 680 AD.
3.1.Byzantine-Bulgarian War of 894-896
Was a war between the Bulgarian Empire and the Byzantine Empire.
January 897: Battle of Southern Buh: great Bulgarian victory which forced the Magyars of the Etelköz realm to abandon the steppes of southern Ukraine.
3.2.Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria
Was the invasion of the Bulgarian Empire by the Kievan Rus'.
September 971: Byzantine Emperor John I Tzimiskes and Sviatoslav I of Kiev agreed to a peace treaty: The Rus' army left the occupied territories, and their trading rights were re-affirmed in exchange for an oath to never again attack imperial territory.
3.2.1.Kievan Offensive
Was a military campaign by the invading Kievan Rus' in the Bulgarian Empire.
June 968: In August 967 or 968, the Rus' crossed the Danube into Bulgarian territory, defeated a Bulgarian army of 30,000 men in the Battle of Silistra, and occupied most of the Dobruja.
September 969: In summer 969, Sviatoslav returned to Bulgaria in force, accompanied by allied Pecheneg and Magyar contingents. Sviatoslav stormed the city. Thereafter Boris and Roman capitulated, and the Rus' rapidly established control over eastern and northern Bulgaria, placing garrisons in Dorostolon and the Bulgarian capital of Preslav.
Was a Byzantine military campaign under commander Isaac Komnenos (future emperor) against the Pechenegs.
January 1054: Thy Bzantines defeat the Pechenegs who had crossed the Danube and progressed inside the Byzantine Empire after a war with the Russians.
On April 29, 1091, an invading force of Pechenegs was crushed by the combined forces of the Byzantine Empire under Alexios I Komnenos and his Cuman allies.
January 1092: An invading force of Pechenegs was crushed by the combined forces of the Byzantine Empire under Alexios I Komnenos and his Cuman allies.
January 970: In 969, territories of the Khazar Khanate were absorbed into Kievan Rus' under the rule of Grand Prince Sviatoslav I.
January 981: Expansion of the Kievan Rus' by 981 AD.
January 989: It is believed that the conquest of Tmutarakan by the Old Russian state happened either during the eastern campaign of Svyatoslav in 965, or during the campaign of Vladimir in Korsun in 988.
January 1001: The Cuman-Kipchak confederation was a Turkic confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries.
February 1092: An invading force of Pechenegs was crushed by the combined forces of the Byzantine Empire under Alexios I Komnenos and his Cuman allies.
January 1123: In 1122, the Pechenegs invaded the Danube area, leading to a conflict with the Byzantine Empire.
February 1123: The Byzantine Emperor John II Komnenos successfully defeated the Pechenegs in 1123, securing the Danube area for the Byzantine Empire.
Disestablishment
January 1123: In 1122, the Pechenegs invaded the Danube area, leading to a conflict with the Byzantine Empire.
February 1123: The Byzantine Emperor John II Komnenos successfully defeated the Pechenegs in 1123, securing the Danube area for the Byzantine Empire.
Selected Sources
Haldon, John F. (2001), The Byzantine Wars, Stroud: Tempus, p.104
Leyser, K. (1982): Medieval Germany and its neighbours, 900-1250, London (UK), p. 50
Lowe, S. (30 May 2011). The Magyars of Hungary. https://web.archive.org/web/20091027151814/http://www.geocities.com/egfrothos/magyars/magyars.html
Reuter, T. (1995): The New Cambridge Medieval History: c. 900-c. 1024, Cambridge (UK), p. 543
Stephenson, Paul (2000), Byzantium's Balkan Frontier: A Political Study of the Northern Balkans, 900–1204, Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press, p.53
Атлас. 6 класс. История России с древнейших времен до XVI века (Atlas. 6th grade. History of Russia from ancient times to the 16th century.) , Дрофа Publisher (2015), Moscow (Russia), p. 5-8
 Pecheneg Khanates
Pecheneg Khanates