If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
A Greek polis in the ancient region of Ionia.
Establishment
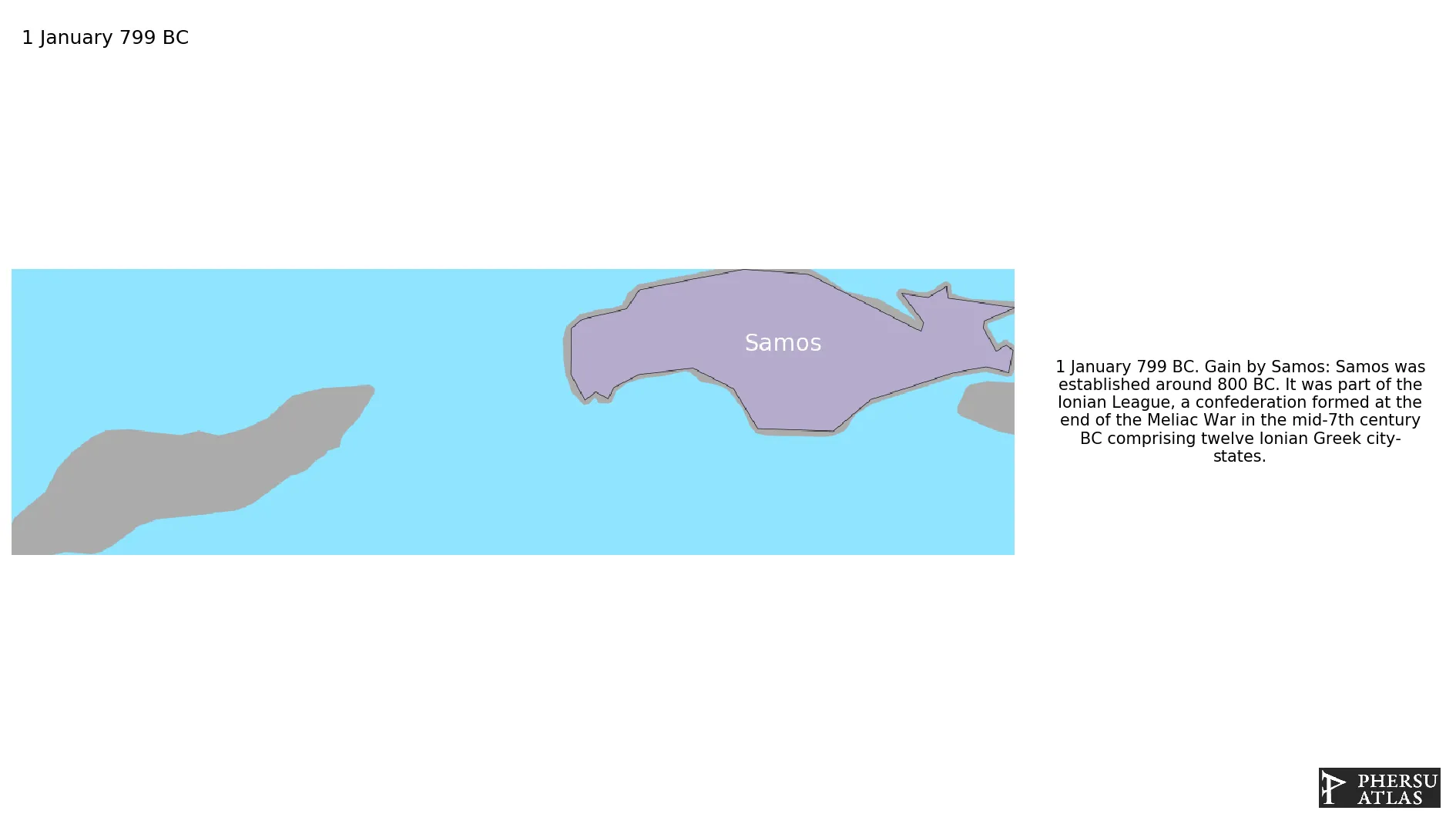
January 799 BC: Samos was established around 800 BC. It was part of the Ionian League, a confederation formed at the end of the Meliac War in the mid-7th century BC comprising twelve Ionian Greek city-states.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Conquests by Achaemenid ruler Cambyses II.
January 521 BC: Samos, having lost its charismatic leader, was easily conquered by the Persians in 522 BC.
Were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire and Greek city-states.
2.1.Greek reconquests after the Second Persian Invasion of Greece
The final defeat of the Persians at Mycale during the Second Persian Invasion of Greece encouraged the Greek cities of Asia to revolt, and the Persians lost all of their territories in Europe.
August 479 BC: The immediate result of the victory at Mycale was a second revolt amongst the Greek cities of Asia Minor. The Samians and Milesians had actively fought against the Persians at Mycale, thus openly declaring their rebellion.
2.2.Wars of the Delian League
Were a series of campaigns fought between the Delian League of Athens and her allies (and later subjects), and the Achaemenid Empire of Persia.
January 477 BC: Samos joined the Delian League. The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states founded in 478 BC under the leadership of Athens.
Was an Ancient Greek military conflict between Athens and Samos. The war was initiated by Athens's intervention in a dispute between Samos and Miletus.
January 439 BC: A group of oligarchs opposing Athenian influence, collaborating with allies in the city, invaded Samos with 700 mercenaries of Pissuthnes, and defeated the democrats. Samos left the Athenian sphere of influence.
January 438 BC: Athenian siege of Samos, at the end of which the Samians surrendered and were forced to become a member of the Athenian Empire.
Was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world.
4.1.Second Phase - Deceleian War
Was the second phase of the Peloponnesian War, where Sparta allied with Persia against Athens, which capitulated and lost its empire.
January 403 BC: The Delian League was dissolved upon the conclusion of the Peloponnesian War with the defeat of Athens (404 BC).
Was a conflict in ancient Greece which pitted Sparta against a coalition of city-states comprising Thebes, Athens, Corinth and Argos, backed by the Achaemenid Empire.
5.1.The King's Peace / Peace of Antalcidas
Was a peace treaty guaranteed by the Persian King Artaxerxes II that ended the Corinthian War in ancient Greece.
January 386 BC: At the conclusion of the Corinthian War, under the terms of the Peace of Antalcidas in 387 BC, the coast of asia minor was annexed to Persia.
January 549 BC: During the 6th century BC, Oenoe, a city in Icaria, was incorporated into the maritime empire of Polycrates, the tyrant of Samos. Polycrates was known for his naval power and successful rule over the Aegean Sea.
January 549 BC: During the 6th century BC, the territory of Therma was conquered by Polycrates, the tyrant of Samos. This expansion of the Samian sea empire included the incorporation of Oenoe and the rest of Icaria into Polycrates' domain.
Disestablishment
January 386 BC: At the conclusion of the Corinthian War, under the terms of the Peace of Antalcidas in 387 BC, the coast of asia minor was annexed to Persia.
Selected Sources
Malczynski, R (2009): Die griechische Welt im Zeitalter des Aristoteles, Düsseldorf (Germany), pp. 5-6
Plutarch: Parallel Lives, Pericles: 26.1
Roisman, J. / Yardley, J. C. (2011): Ancient Greece From Homer to Alexander: The Evidence, Hoboken (USA), pp. 96, 105–106
Spence, I. (2002): Historical Dictionary of Ancient Greek Warfare, Scarecrow Press, p. XXVII
Xenophon: Hellenica, 5.1.31
 Samos
Samos