If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
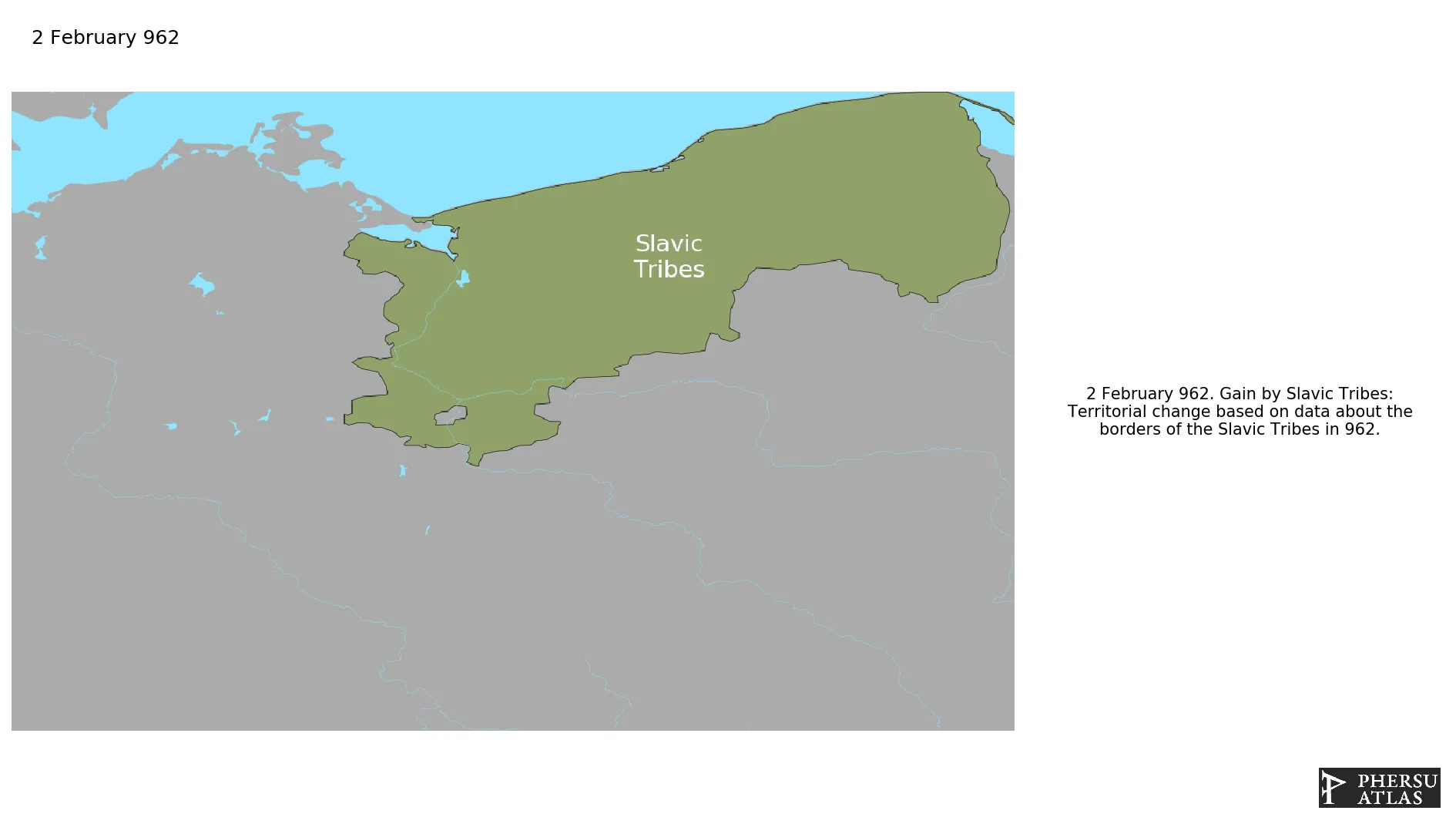
Was the tribal territory the Slavs in eastern Germany and western Poland (mainly Polabian Slavs). It is unclear how organized the polity was, or even whether it was a polity.
Establishment
February 962: Territorial change based on data about the borders of the Slavic Tribes in 962.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the Medieval period. The best known of these military expeditions are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291.
1.1.Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades (or Baltic Crusades) were Christian colonization and Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Christian military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the pagan Baltic, Finnic and West Slavic peoples around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea.
1.1.1.Wendish Crusade
Was a military campaign in 1147, one of the Northern Crusades and a part of the Second Crusade, led primarily by the Holy Roman Empire and directed against the Polabian Slavs (or "Wends") in present-day northeast Germany and Poland.
January 1145: A diocese is again established in Havelberg, after it had been destroyed by the local Slavic tribes.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
2.1.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
2.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Germany
Was a Mongol raid in the Holy Roman Empire.
May 1241: The Mongols invaded the Holy Roman Empire without major clash of arms.The army invaded eastern Germany, and crossed the March of Moravia in April-May 1241.
June 1241: The Mongols left eastern Germany and Moravia.
January 984: The rebellion of 983, initiated by the Lutici, led to a factual disestablishment of the Northern and Billung marches as well as the corresponding bishoprics.
January 984: In 983, Zeitz was overrun by the Sorbs and the marcher territory fell into the hands of the Slavs.
January 993: The region of Neumark came under the sovereignty of the first Polish state during the 10th-century rule of Mieszko I (died 992) and Bolesław I (ruled 992-1025), Dukes of the Polans. Polish rulers incorporated the future Neumark territory as the Lubusz Land.
January 999: The North March is conquered by Saxony.
January 1001: Around the year 1000, German settlers came to the area of today's Vogtland. The German Emperor appointed the bailiffs as ministerials to administer newly developed areas that had previously only been sparsely populated by Sorbs.
January 1122: The Duchy of Pomerania was established as a vassal state of Poland in 1121.
January 1135: In 1134 Emperor Lothair of Supplinburg bestowed the Northern March on the Ascanian count Albert the Bear.
January 1148: The Burggraviate of Altenburg was founded in 1147 under King Konrad III in the course of the German colonization of the East. built in Pleissenland.
January 1148: The Wendish Crusade of 1147, concurrent to the Second Crusade, was largely unsuccessful, resulting in devastation to the Liutizi lands and forced baptisms. The campaign did secure Saxon control of Wagria and Polabia, however.
January 1158: For further one-and-a-half centuries, the lands east of the Elbe defied German control, until in 1134 Emperor Lothair of Supplinburg bestowed the Northern March on the Ascanian count Albert the Bear. Albert signed an inheritance contract with the Slavic Hevelli prince Pribislav and in 1150 succeeded him in his eastern territory around the fortress of Brandenburg an der Havel, which became the nucleus of his newly established Margraviate of Brandenburg in 1157.
January 1166: Establishment of the Brand Prince-Bishopric.
January 1221: Conquests of Albert II, Margrave of Brandenburg, by 1222.
Disestablishment
January 1246: Between 1230 and 1245, Brandenburg acquired the remaining part of Barnim and the southern Uckermark up to the Welse river.
Selected Sources
Strakosh-Grassmann, G. (1893): Der Einfall der Mongolen in Mitteleuropa in den Jahren 1241 und 1242, Innsbruck (Austria), pp. 53-67
 Slavic Tribes
Slavic Tribes