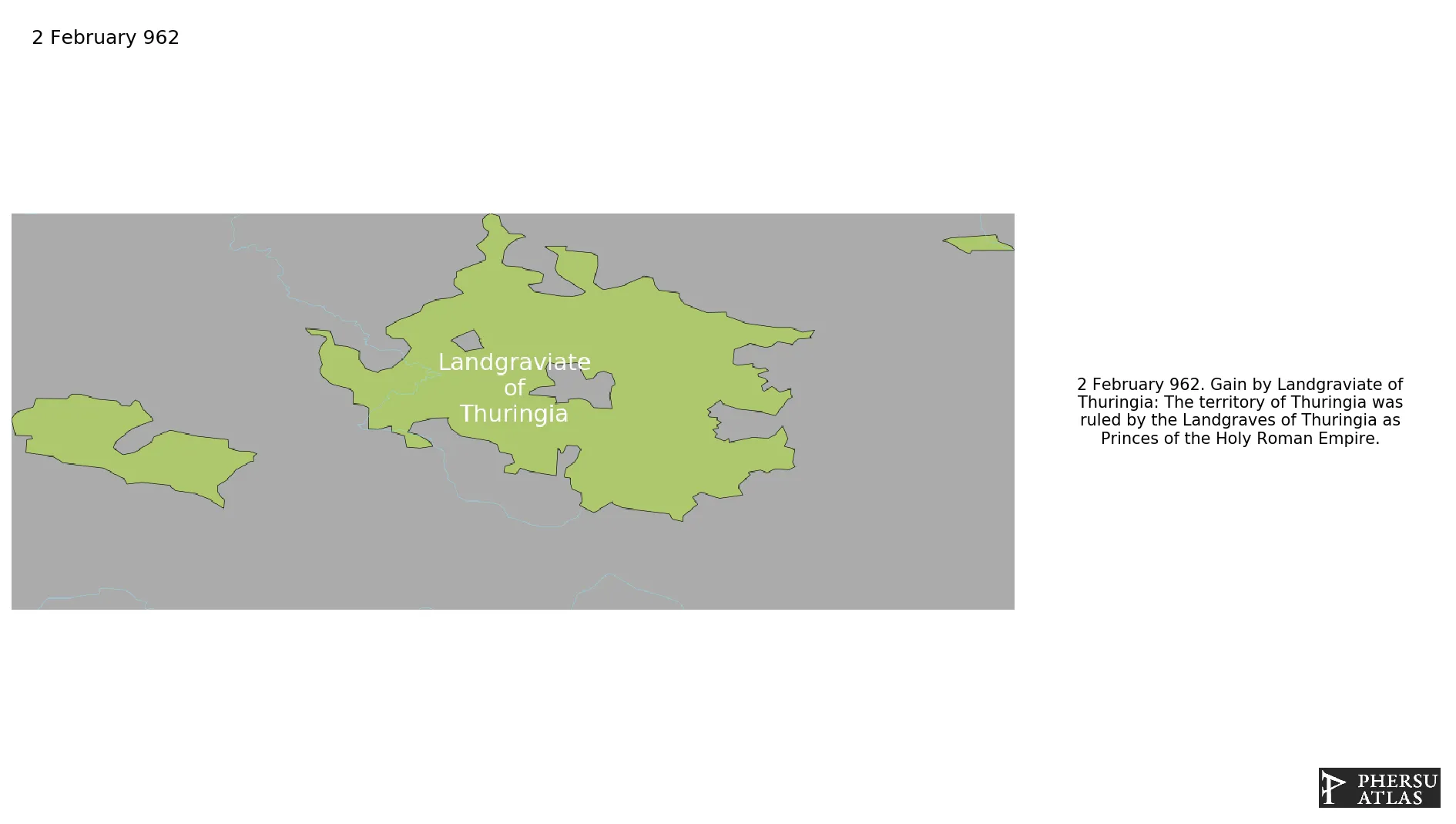
Landgraviate of Thuringia
Landgraviate of Thuringia
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was a Landgraviate of the Holy Roman Empire located in esatern Germany.
Establishment
February 962: The territory of Thuringia was ruled by the Landgraves of Thuringia as Princes of the Holy Roman Empire.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
The Frankish Kingdom was partitioned and reuinited several times as the Frankish rulers used to divide their territories equally among their heirs. This lead also to a number of wars and revolts.
1.1.Incoronation of Otto I
East Frankish King Otto I was crowned first Holy Roman Emperor.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
2.1.Mongol Invasions of Germany
Were a series of Mongol raids in Germany.
2.1.1.First Mongol Invasion of Germany
Was a Mongol raid in the Holy Roman Empire.
May 1241: The Mongols invaded the Holy Roman Empire without major clash of arms.The army invaded eastern Germany, and crossed the March of Moravia in April-May 1241.
June 1241: The Mongols left eastern Germany and Moravia.
Was a military conflict over the succession in the Landgraviate of Thuringia.
3.1.Peace of Langsdorf
Was a treaty which ended the War of the Thuringian succession. Thuringia was divided in two: Thuringia and Hesse.
September 1264: Granted Henry I of Hesse, the son of Sophie von Brabant, the county of Hesse in the War of the Thuringian-Hessian Succession (1247-1264).
January 1015: The Beichlingen Lordship is first mentioned in 1014.
January 1033: Establishment of Orlamünde County.
January 1090: In the area around Tonna north of Gotha, there is evidence that the Counts of Tonna and later Counts of Gleichen ruled from the end of the 11th century. Their headquarters was the castle chain Castle in Graefentonna. Count Erwin I († 1116) was mentioned in 1089 as the first regent, who called himself "Count of Tonna" after the ancestral seat of Tonna.
January 1100: The Counts of Gleichen near Erfurt in Thuringia are first documented in 1099.
January 1101: In the area around Tonna north of Gotha, there is evidence that the Counts of Tonna and later Counts of Gleichen ruled from the end of the 11th century. Their headquarters was the castle chain Castle in Graefentonna. Count Erwin I († 1116) was mentioned in 1089 as the first regent, who called himself "Count of Tonna" after the ancestral seat of Tonna.
January 1104: Schwarzburg County is mentioned for the first time in 1103.
January 1104: The Counts of Kevernburg, the Counts of Schwarzburg and the Counts of Rabenswalde-Wiehe have the Sizzonen as a common ancestor. Their eponymous headquarters was the Kevernburg, today's Käfernburg near Arnstadt. In the early Middle Ages, the counts belonged to the Thuringian high nobility. Sizzo III. (* ca. 1093; † 1160) was first mentioned in 1103 and called himself both Count of Kevernburg and Count of Schwarzburg.
January 1105: Treffurt was first mentioned in a document from Archbishop Ruthard of Mainz in 1104. Friedrich von Treffurt was hired as an advisor to Heinrich Raspe IV.
January 1132: The Hessian counties (Maden/Gudensberg, Marburg area, up to the Westerwald) passed through marriage to the Counts of Ludowinger, who were raised to the ranks of Landgraves of Thuringia in 1131.
January 1138: Establishment of the Walkenried Abbey.
January 1167: The Lobdaburg family established itself in the 12th century as part of the expansion of the state on the Limes Sorabicus in eastern Thuringia and can be traced back to 1166, based in Camburg an der Saale.
January 1188: Klettenberg Castle was probably built around 1087. The county of Klettenberg was first mentioned in 1187.
January 1195: In 1194 the village of Sangerhausen was granted city rights.
January 1199: Ebeleben was first mentioned in 1198. In the western part of the town center there was a medieval castle. The lords of Ebeleben were ministers of the Thuringian landgrave. In 1198 a knight from Ebeleben was mentioned.
January 1201: In the 13th century, the Frankensteins ruled over an extensive area, partly still uninhabited land, which Emperor Heinrich II had transferred to the Hersfeld monastery as a wild ban for use.
January 1211: Establishment of the Stolberg County.
January 1214: In the 13th century, "marshals of Sondershausen" are known, who were feudal to the Thuringian landgrave from 1213 and from 1287 to the Archdiocese of Mainz.
January 1221: Nordhausen is declared a Free Imperial City.
January 1221: Based on Gustav Droysen's Holy Roman Empire Map at the time of the Hohenstaufen dynasty.
January 1250: After the death of the first Meranian Duke in 1159, his son Konrad III. was his successor. He is only mentioned as Duke of Merania, thus Croatia and Dalmatia had disappeared from the Duchy.
January 1266: As a result of the War of the Thuringian Succession, Henry of Meissen gained the bulk of Thuringia in 1264, while the Hessian possessions of the landgraves was separated as the Landgraviate of Hesse.
January 1332: The share in Jena of the Lobdaburg Lordship fell to the Landgraves of Thuringia.
January 1336: Attempts by the Frankensteins to assert themselves against the strongest powers in the region - the Fulda monastery and the Thuringian landgraves - led to their downfall. In 1265, Frankenstein Castle was besieged and partially destroyed by Abbot Bertho II of Fulda. The castle was last important in 1335 in connection with a dispute between the last Frankenstein owners.
January 1343: In 1342, the counts of Tonna became vassals of the Wettin Margraves of Meissen. This was a significant event in the history of the Landgraviate of Thuringia, as it marked a shift in power dynamics within the region.
April 1346: The Thuringian War of the Counts followed from 1342 to 1346. As a result, the Wettins concluded the Peace of Dresden with the Counts of Weimar-Orlamünde on April 11, 1346. The Orlamünder had to give their ancestral land to the Wettins as a fief and thus lost their imperial immediacy and their political independence.
January 1347: The city of Salza was besieged and destroyed in 1346 because of a property dispute between the Landgrave of Thuringia, Friedrich II, and the Archbishop of Mainz, Heinrich von Virneburg (Thuringian Count War). The are fall into the possession of Thuringia.
January 1354: Hildburghausen came to the Landgraviate of Thuringia.
January 1373: In 1372, the fief of Ebeleben was divided between the Counts of Schwarzburg and the Landgrave of Thuringia.
January 1379: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XIV century.
May 1387: His land was sold by his mother, Countess Sophia von Schwarzburg, and his wife Mechthild on May 29, 1387 to Landgrave Balthasar of Thuringia.
January 1390: In 1389, Saalfeld was transferred from the Schwarzburg family to the Wettin family, specifically to the Landgraviate of Thuringia. The Wettins ruled over Saalfeld until the monarchy was abolished in 1918.
January 1401: Since 1400, Königsberg in Bayern belonged to the Wettin duchies.
January 1447: After the Landgraves of Thuringia died out in 1446, the areas of the Kevernburgers came to close relatives, the Counts of Schwarzburg.
January 1451: Presumably Gera was annexed by Thuringia after it was destroyed in 1450 in the Saxon Civil War.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
Disestablishment
January 1483: After the death of the Landgrave of Thuringia and Margrave of Meissen, in 1482 Saxon Elector Ernest inherited the landgraviate, uniting the Wettin lands under his rule.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 26-27
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 30-31
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Strakosh-Grassmann, G. (1893): Der Einfall der Mongolen in Mitteleuropa in den Jahren 1241 und 1242, Innsbruck (Austria), pp. 53-67

 Landgraviate of Thuringia
Landgraviate of Thuringia