If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this nation you can find it here: All Statistics
The cluster includes all the forms of the country.
The cluster includes the following incarnations of the same nation:
Rubattino Shipping Company
Italian Eritrea
British Military Administration in Eritrea
State of Eritrea
Establishment
November 1869: The first Italian establishment in the area was the purchase of Assab by the Rubattino Shipping Company.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a war by Mahdist Sudan against Egyptian rule. The Mahdista were finally defeated by Egyptian and British forces, and Sudan became an Anglo-Egyptian condominium.
1.1.Mahdist Attacks to Eritrea
Was the invasion of Eritrea by Mahdist Sudan during the Mahdist War.
June 1892: Battle of Serobeti.
July 1892: Battle of Serobeti.
December 1893: The Second Battle of Agordat took place in 1893 between Italian forces led by General Baratieri and Mahdist Sudanese troops. The Italians were victorious, securing control of the territory for Italy in their colonial expansion in East Africa.
January 1894: The Second Battle of Agordat took place in 1894 in Agordat, Eritrea. It was a decisive victory for Italian forces led by General Oreste Baratieri over the Ethiopian army of Emperor Menelik II. This battle solidified Italian control over the territory, which became part of Italian Eritrea.
July 1894: In 1894, Governor Oreste Baratieri of Italian Eritrea attempted to capture Kassala to prevent Mahdist attacks on Eritrea. The Mahdists were followers of Muhammad Ahmad, who had established a state in Sudan and posed a threat to Italian interests in the region.
1.2.Anglo-Egyptian conquest of Sudan
Was the joint Anglo-Egyptian military invasion of Mahdist Sudan that ended the Mahdist War.
December 1897: In 1897, the Kingdom of Italy, led by Prime Minister Francesco Crispi, returned Kassala to the Kingdom of Egypt under British leadership. This was done in order to gain international recognition of Italy's colony of Eritrea, which was established in the late 19th century.
Were two invasion of Ethiopia by the Kingdom of Italy whose goal was to make Ethiopia a colony. The first invasion was not succesful, but after the second invasion Ethiopia became part of of Italian East Africa.
2.1.First Italo-Ethiopian War
Was an ultimately unsuccesful Italian invasion of Ethiopia.
January 1895: Battle of Coatit.
January 1895: In 1895, the Italians achieved a significant victory in Quatit, Italian Eritrea, by successfully repelling an invasion force led by Ethiopian Emperor Menelik II. This victory solidified Italian control over the territory and marked a turning point in the First Italo-Ethiopian War.
2.2.Second Italo-Ethiopian War
Was the second Italian military invasion of Ethiopia. At the end of the war the country became part of Italian East Africa.
2.2.1.Northern Front (Second Italo-Ethiopian War)
Was the northern front of the Second Italo-Ethiopian war.
2.2.1.1.Ethiopian Christmas Offensive
Was an Italian military offensive during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
January 1936: The Ethiopians reoccupied all of southern Tembien.
2.2.2.Southern Front (Second Italo-Ethiopian War)
Was the southern front of the Second Italo-Ethiopian war.
2.2.2.1.Graziani Offensive
Was an Italian military offensive commanded by General Rodolfo Graziani during the Second Italo-Ethiopian War.
May 1936: Italian general Graziani entered Dire Daua, a few hours before the arrival by train from Addis Ababa of the men of Badoglio. With this last formal act, the war on the southern front also ended.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
3.1.World War II (East African Theatre)
Was the East African theatre of World War II.
3.1.1.British invasion of Italian East Africa
Was the British invasion and occupation of Italian East Africa during World War II.
May 1941: British occupation of Eritrea.
June 1941: Italian forces held out at Assab, the last Italian harbour on the Red Sea. Operation Chronometer took place from 10 to 11 June, with a surprise landing at Assab by the 3/15th Punjab Regiment from Aden, carried by a flotilla comprising HMS Dido, Indus, Clive, Chakdina and SS Tuna.
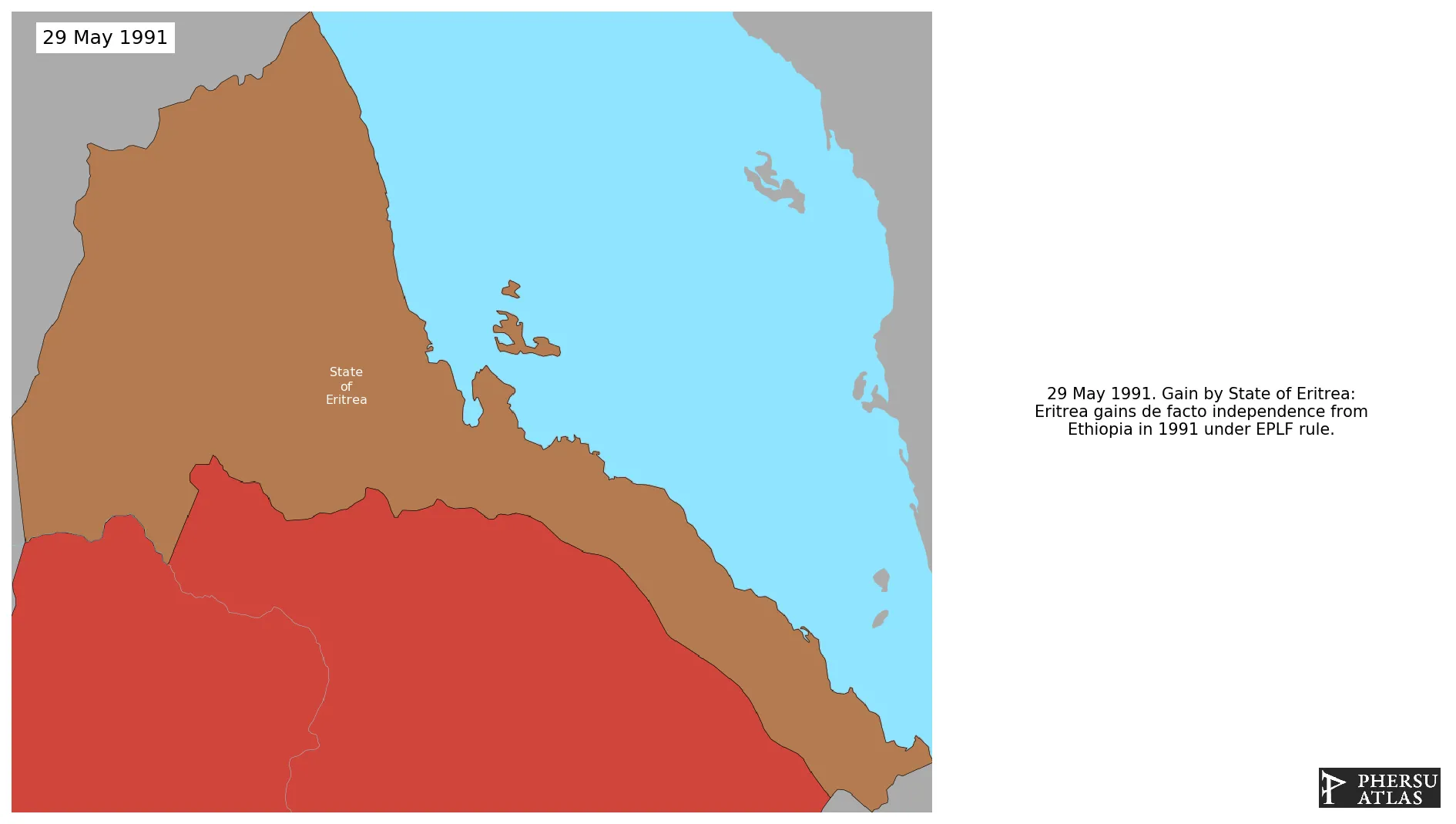
Were a series of related conflicts, part of the struggle for independence of Eritrea from Ethiopia.
May 1991: Eritrea gains de facto independence from Ethiopia in 1991 under EPLF rule.
Was a conflict between Yemen and Eritrea over the disputed island of Greater Hanish in the Red Sea.
December 1995: Eritrean forces attacked the Yemeni contingent and overran the entire island within three days of combat.
November 1998: The Permanent Court of Arbitration determined that most of the Hanish Isands belonged to Yemen, while Eritrea was to retain the right to fish the waters around all the islands and sovereignty over some small islands close to Eritrea. Yemeni Defence Minister Mohammad Diefallah Mohammad raised his country's flag over the island of Greater Hanish as Yemeni army and navy troops took up positions on it. At the same time, Eritrean troops departed on board a helicopter and a naval vessel.
Was a war between Ethiopia and Eritrea that took place from May 1998 to June 2000. The cause of the war were territorial disputes.
6.1.Eritrean Invasion of Ethiopia
Was the Eritrean military invasion of Ethiopia at the beginning of the Eritrean-Ethiopian War.
May 1998: A large Eritrean mechanized force entered the Badme region.
6.2.First Ethiopian Offensive (Eritrean-Ethiopian War)
Was an Ethiopian military offensive to reconquer territories occupied by Eritrea at the beginning of the Eritrean-Ethiopian War. .
February 1999: Eritrea accepted the OAU peace plan on 27 February 1999.
February 1999: Ethiopian forces ha broken through Eritrea's fortified front and was 10 kilometers deep into Eritrean territory.
6.3.Second Ethiopian Offensive (Eritrean-Ethiopian War)
Was an Ethiopian military offensive in Eritrea during the Eritrean-Ethiopian War. .
May 1999: On 16 May 1999, Ethiopian forces launched an attack at Velessa on the Tsorona front-line, escalating tensions in the border conflict with Eritrea.
May 1999: After two days of heavy fighting the Eritreans had beaten back the Ethiopian attack on Tsorona.
6.4.Third Ethiopian Offensive (Eritrean-Ethiopian War)
Was an Ethiopian military offensive in Eritrea during the Eritrean-Ethiopian War. .
May 2000: The Ethiopians launched an offensive that broke through the Eritrean lines between Shambuko and Mendefera, and also crossed the Mareb River.
May 2000: Eritrean forces evacuated Barentu and fighting continued in Maidema.
May 2000: By 23 May Ethiopia claimed that its "troops had seized vital command posts in the heavily defended Zalambessa area.
6.5.Algiers agreement
Was a peace agreement between the governments of Eritrea and Ethiopia that was signed on 12 December 2000, at Algiers, Algeria, to formally end the Eritrean-Ethiopian War.
December 2000: On April 13, 2002, the EEBC border commission, acting as arbitrator, regulated the course of the border line “finally and bindingly” on the basis of the colonial treaties already mentioned.
An civil war in Ethiopia that started in 1974. It consists of several related phases that saw rebel and secessionist groups fight against the Ethiopian government.
7.1.Tigray War
A war between Ethiopia and the secessionist Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) of the Tigray region that started in 2020. Although the cessation of hostilities was agreed in November 2022, the TPLF still controls territories in Tigray acting as a factually independent state.
7.1.1.Eritrean occupation of the North-East
Eritrean troops occupied Ethiopian territories in the north of the country during the Tigray War.
March 2021: In February 2021, UN chief coordinator of humanitarian efforts Mark Lowcock said that up 40% of Tigray was not controlled by Ethiopian troops. He said that much of that area was under the control of Eritrean soldiers pursuing their own objectives independent of Ethiopian command.
7.1.2.Tigrayan counter-offensive
An offensive by the Tigray Defense Forces during the Tigray War.
June 2021: On 30 June 2021, the TDF had entered the town of Shire.
July 2021: Tigrayan forces captured southern Tigray, including the towns of Alamata and Korem.
March 1882: The Italian government bought the possession of Assab.
January 1886: With the help of the British, the city of Massawa came under Italian control and became part of Italy's colony of Eritrea in 1885.
May 1889: The Treaty of Wuchale was signed between Italy and Menelik II, the Emperor of Ethiopia. It established the borders between Italian Eritrea and the Ethiopian Empire in 1889.
June 1899: Abbas II of Egypt and the British decided to re-establish control over Sudan. Leading a joint Egyptian-British force, Lord Kitchener led military campaigns from 1896 to 1898. In 1899, Britain and Egypt formally agreed to establish a joint protectorate: Egypt on the basis of its previous claims and Britain by right of conquest. At this point the protectorate encompassed modern-day Sudan and South Sudan as well as the Sarra triangle.
June 1936: Italian Eritrea became part of Italian East Africa on 1 June 1936.
September 1952: The Eritrean-Ethiopian Federation was a coalition between the former Italian colony of Eritrea and the Ethiopian Empire. It was established as a result of the renunciation of Italy’s rights and titles to territorial possessions in Africa.

 eritrea
eritrea