If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
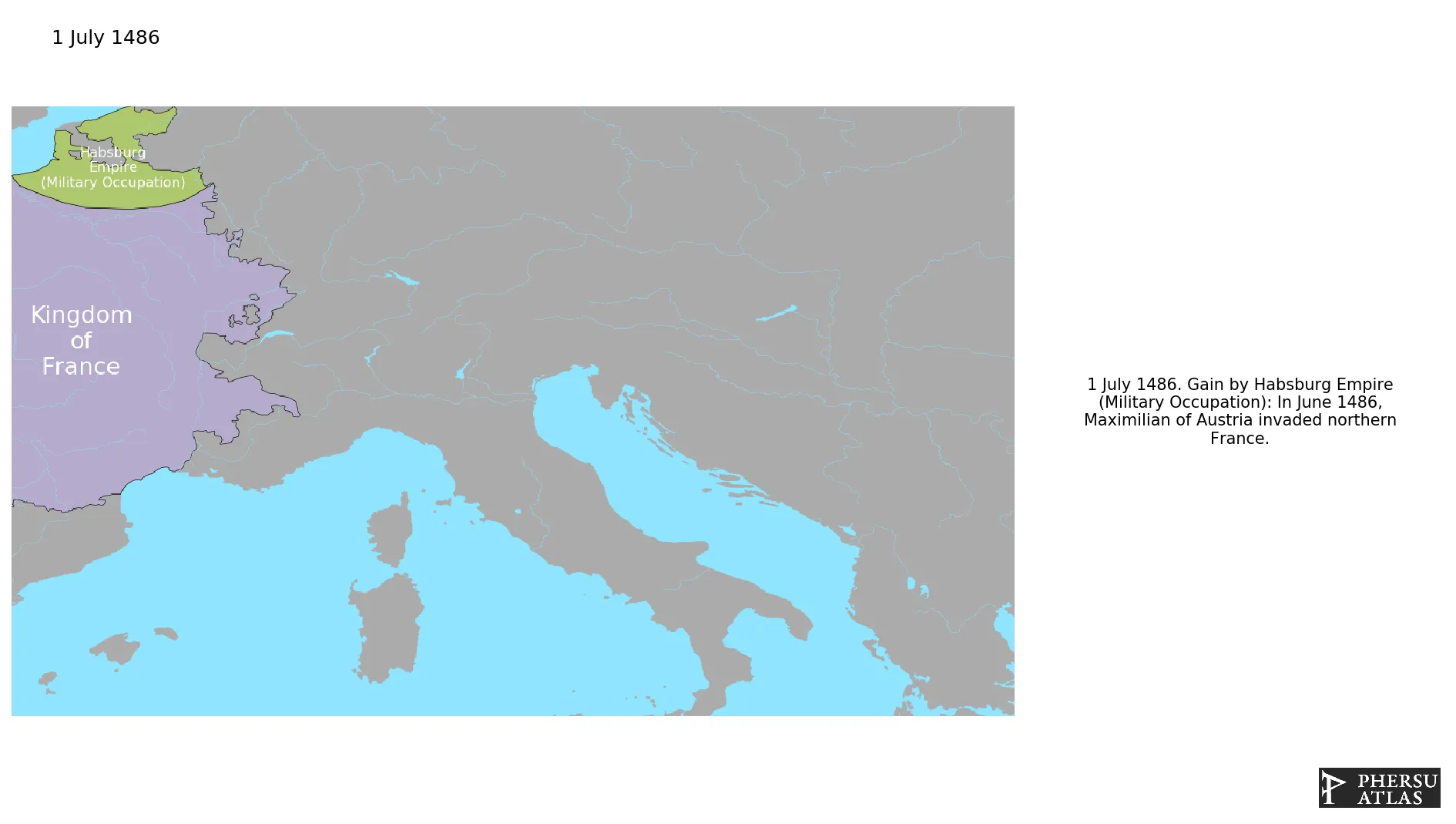
Territories militarly occupied by the Habsburg.
Establishment
July 1486: In June 1486, Maximilian of Austria invaded northern France.
August 1486: The Austrians leave northern France.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a late medieval conflict between a coalition of feudal lords and the French monarchy.
Was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of Habsburg.
February 1499: In January 1499, the Habsburg governor of Tyrol, Sigismund of Austria, militarily occupied Vinschgau and Münstertal to assert his claim against the episcopal rights and the church association led by Bishop Georg of Chur.
2.1.Treaty of Basel
Was the treaty that ended the Swabian War.
September 1499: On September 22, 1499, the Peace of Basel was sealed between Maximilian and the Confederates. Jurisdiction over Thurgau, previously an Imperial loan to the city of Constance, which was to pass to the Swiss Confederacy.
Was a war between the Habsburg Domains and the Ottoman Empire.
October 1716: Siege of Temeşvar.
August 1717: The Austrian defeat of the Ottomans in the Battle of Belgrade on August 16, 1717, led to the Ottoman cession of their portion of Hungary and much of Serbia.
3.1.Treaty of Passarowitz
Was the treaty that ended the Austro-Turkish War (1716-1718).
July 1718: The Ottoman Empire lost the Banat to Prince Eugene of Savoy and the Habsburg Monarchy in 1718. This marked a significant victory for the Habsburgs in their ongoing conflict with the Ottomans over control of territories in Eastern Europe.
July 1718: Southeastern Syrmia, central part of present-day Serbia (from Belgrade to south of Kruševac), was taken by the Austrians.
Was a war initiated by Spain to recover territories lost after the War of the Spanish Succession.
October 1718: The Austrians, led by Count Claude Florimond de Mercy, were defeated by the Spanish forces under the command of Duke Victor Amadeus of Savoy in the First Battle of Milazzo. The Habsburg Empire's military occupation of Milazzo was short-lived as they were unable to maintain control of the territory.
November 1719: In 1719, Prince Eugene of Savoy, leading the Habsburg Empire forces, achieved victory in the second Battle of Milazzo against the Spanish forces. Following this success, he captured the city of Messina in October, solidifying Habsburg control over the territory.
4.1.Treaty of The Hague
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Quadruple Alliance. Spain left all the territories occupied during the war.
February 1720: With the Treaty of The Hague the War of the Quadruple Alliance ended with the status quo ante bellum.
Were a series of wars between the Habsburg Domains and Prussia for the control of Silesia. The war started during the War of the Austrian Succession, when Frederick the Great of Prussia invaded Habsburg-held Silesia.
5.1.First Silesian War
Was the first of three wars between Austria and Prussia for the control of Silesia. It was part of the War of the Austrian Succession. The war started when Prussia invaded Silesia. The possession of the region by Prussia was aknowledged by Austria at the end of the war.
5.1.1.Silesian Theatre (First War)
Was the Silesian theatre of the First Silesian War.
June 1742: The Treaty of Breslau was a preliminary peace agreement signed in 1742 between Prussian King Frederick the Great and Austrian Empress Maria Theresa, ending the First Silesian War. The treaty ceded most of Silesia to Prussia, marking a significant territorial gain for the Kingdom of Prussia.
5.1.2.Austrian Theatre
Was the Austrian theatre of the First Silesian War.
January 1742: Surrender of 10,000 French soldiers at Linz Habsburg forces led by Prince Charles Alexander of Lorraine.
5.1.3.Bohemian Theatre (First Silesian WarWar)
Was the Bohemian theatre of the First Silesian War.
January 1743: Siege of Prague.
5.1.4.Moravian Theatre
Was the Moravian theatre of the First Silesian War.
May 1742: The Moravian campaign in 1742 was part of the War of the Austrian Succession. The Prussians, led by King Frederick the Great, retreated from Moravia after failing to make significant gains against the Habsburg Empire. The territory was then occupied by the Habsburg military.
5.1.5.Bavarian Theatre
Was the Bavarian theatre of the First Silesian War.
January 1742: Von Khevenhüller defeated a Bavarian army at Schärding.
February 1742: On January 24, 1742, during the War of the Austrian Succession, Bavarian Field Marshal Bärenklau captured the capital city of Munich, which was under the control of the Habsburg Empire at the time.
May 1743: The Battle of Simbach in 1743 saw the Bavarians defeated by Charles of Lorraine, who was a general in the Habsburg Empire. This military occupation resulted in the territory of Simbach falling under Habsburg control.
June 1743: In mid-June, the Pragmatic army arrived at Aschaffenburg, on the north bank of the River Main.
October 1744: Prince Charles's army was able to return to Bohemia quickly, in good order and at full strength, though it was forced to abandon control of Alsace and Bavaria. Austrian diplomats also persuaded Saxony to re-enter the conflict on Austria's side, though in a strictly defensive role. By early October the Austrians were advancing through southwestern Bohemia toward Prague.
April 1745: With Prussia's forces driven out of Bohemia, Austria renewed its offensive against Bavaria in March 1745, swiftly over-running the defences that had been reestablished there during the winter. On 15 April the Austrians under Count Batthyány decisively defeated the Franco-Bavarian army at the Battle of Pfaffenhofen and drove the allied forces entirely out of Bavaria.
April 1745: After this defeat, Maximilian III of Bavaria (the son of the late Emperor Charles Albert) made peace with Maria Theresa by the Treaty of Füssen on 22 April.
5.2.Second Silesian War
Was the second of three wars between Austria and Prussia for the control of Silesia. It was part of the War of the Austrian Succession.
5.2.1.Silesian Theatre (Second War)
Was the Silesian theatre of the Second Silesian War.
April 1745: Frederick abandoned the mountainous southern tip of Upper Silesia to the Austrian vanguard of pandurs, concentrating his defences around the town of Frankenstein in the valley of the Eastern Neisse.
May 1745: At the end of May, the Austrian-Saxon force crossed through the Giant Mountains and camped around the Silesian village of Hohenfriedberg.
June 1745: The ensuing Battle of Hohenfriedberg ended in a decisive Prussian victory, sending Prince Charles's army retreating in disarray back into the mountains.
Was a European conflict caused by the succession to the Habsburg Domains. Maria Theresa succeeded her father Charles VI, and the opposition to female inheritance of the throne was a pretext for starting a war. It was a global conflict that saw fight in Europe, Asia, America and Africa.
6.1.Italian Theatre (War of the Austrian Succession)
Was the Italian theatre of the War of the Austrian Succession.
October 1746: On 6 September 1746, Genoa was besieged by the Austrians who had crossed the territories of the King of Sardinia. The Austrians, led by General Brown and the Genoese exile Antoniotto Botta Adorno, had presented themselves in Sampierdarena imposing excruciating peace conditions on the Genoese. Among these conditions was the dismantling of the city fortifications and their transfer to the Austrians.
December 1746: The revolt in the city lasted three days, as on 9 December Botta Adorno agreed to the negotiations and left the city almost immediately.
6.2.Rhineland Theatre (Austrian Succession)
Was the theatre of war in the Rhineland during the War of the Austrian Succession.
July 1744: Prince Charles, who, assisted by the veteran Marshal Traun, skillfully manoeuvred his allied army over the Rhine near Philippsburg on 1 July 1744 and captured the lines of Weissenburg, and cut off Marshal Coigny and his army from Alsace.
6.3.Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.
October 1748: The State that obtained the greatest advantage was Prussia, which definitively annexed the rich region of Silesia, wrested from Austria.
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
7.1.Third Silesian War
Was the last of three wars between Austria and Prussia for the control of Silesia. It was also part of the Seven Years' War.
7.1.1.Silesian Theatre (Third War)
Was the Silesian theatre of the Third Silesian War.
November 1757: While Frederick's army manoeuvred in western Saxony and Thuringia, the Austrian army of Prince Charles and Daun pressed eastward into Lower Silesia. In November they reached Breslau, where they were opposed by the Silesian garrison under Bevern. The Austrians had overwhelming numbers, and in the Battle of Breslau on 22 November they drove the Prussians from the field. the commander of the garrison surrendered Breslau to the Austrians on 25 November in return for safe passage.
December 1757: Despite his troops' fatigue from the rapid march, Frederick engaged the superior Austrian force on 5 December and won another unexpected victory in the Battle of Leuthen.The Prussians pursued Prince Charles's defeated army all the way back to Bohemia.
December 1757: Breslau were besieged until their surrender on 19-20 December, bringing the bulk of Silesia back under Prussian control.
April 1758: Schweidnitz, the last Austrian-occupied stronghold in Silesia, surrendered.
March 1760: After an inconclusive engagement with the Prussian garrison near Neustat on 15 March, Laudon's Austrians gradually advanced through Lower Silesia.
June 1760: Battle of Landeshut.
July 1760: Liegnitz conquered by austria.
July 1760: Parchwitz conquered by austria.
July 1760: Glatz was taken by the Austrians on 29 July.
August 1760: Laudon's corps, moving ahead of Daun's main army, attacked Frederick's position near Liegnitz on 15 August. The resulting Battle of Liegnitz ended in a Prussian victory, with the Prussians defeating Laudon before Daun's larger force could arrive to support him. This reversal disrupted the Austrians' manoeuvres and restored Prussian control of Lower Silesia, as Daun moved his army back into Saxony.
October 1761: The allies, led by Russian Field Marshal Stepan Fyodorovich Apraksin, Austrian Field Marshal Leopold Joseph von Daun, and Swedish Field Marshal Carl Gustav Armfeldt, achieved a modest victory by capturing the fortress at Schweidnitz on 1 October 1761. This forced the Prussians, under the command of King Frederick the Great, to retreat to winter quarters in northern Silesia and Brandenburg.
October 1762: Daun's forces withdrew to Glatz, and the Prussians besieged Schweidnitz, recapturing it at length on 9 October.
7.1.2.Treaty of Hubertusburg
Was the treaty that ended the Third Silesian War, and, together with the Treaty of Paris (1763) it ended also the Seven Years' War.
February 1763: At the end of the Third Silesian War, the warring parties agreed restore the status quo ante bellum. Austria withdrew from Glatz, restoring full Prussian control of Silesia, in exchange for Prussia's evacuation of Saxony.
Was a war between the Habsbaug Domains and the Ottoman Empire.
October 1789: Belgrade was taken in a three-week campaign by the Austrian Field Marshal Laudon.
November 1789: Habsburg-occupied Serbia (1788-92) was established.
8.1.Treaty of Sistova
Was the treaty that ended the Austro-Turkish War (1788-1791). The Habsburgs gained some borderlands in Croatia.
August 1791: By 1791 the Austrians (the Habsburg) were forced into withdrawal across the Danube and Sava rivers, joined by thousands of Serbian families who feared Ottoman persecution.
January 1718: Formed from the territories to the south of the rivers Sava and Danube, corresponding to the Sanjak of Smederevo, it was conquered by the Habsburgs from the Ottoman Empire in 1717.
Disestablishment
August 1791: By 1791 the Austrians (the Habsburg) were forced into withdrawal across the Danube and Sava rivers, joined by thousands of Serbian families who feared Ottoman persecution.
Selected Sources
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, p.225
.png.webp)
 Habsburg Empire (Military Occupation)
Habsburg Empire (Military Occupation)