If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Was the territory colonized by France in North America. It was lost in 1763 after the Seven Years' War and partitioned between Great Britain and Spain.
Establishment
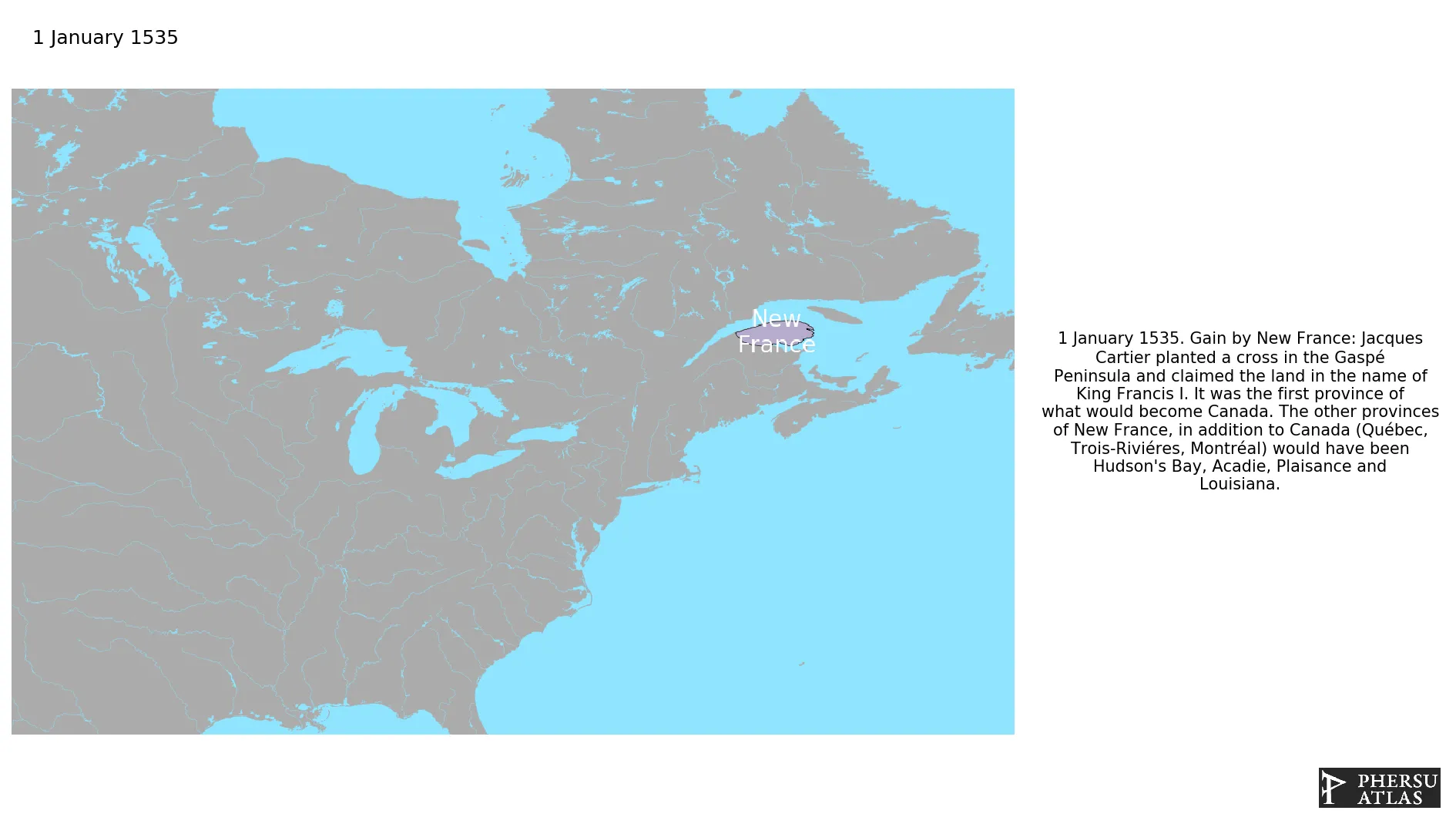
January 1535: Jacques Cartier planted a cross in the Gaspé Peninsula and claimed the land in the name of King Francis I. It was the first province of what would become Canada. The other provinces of New France, in addition to Canada (Québec, Trois-Riviéres, Montréal) would have been Hudson's Bay, Acadie, Plaisance and Louisiana.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout the Saint Lawrence River valley in Canada and the lower Great Lakes region which pitted the Iroquois League against the Hurons, northern Algonquians and their French allies.
January 1681: Iroquois attack in Illinois.
January 1701: Iroquois expansion until 1700.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
2.1.Nine Years' War
Was a conflict between France and the Grand Alliance, a coalition including the Holy Roman Empire, the Dutch Republic, England, Spain, and Savoy. It is considered the first war that saw fighting globally because battles occured in Europe, America, Africa and India.
2.1.1.King William's War
Was the North American theater of the Nine Years' War.
May 1690: The British captured Port Royal (in Nova Scotia), then the capital of Acadia.
July 1690: Joseph Robineau de Villebon, one of Meneval's assistants, returned to Port Royal from France in June, and reestablished French authority.
October 1690: The Battle of Québec in 1690 was led by French Governor Louis de Buade de Frontenac and English General Sir William Phips. It resulted in a victory for the French, defending the city against the English invasion during King William's War.
October 1690: The Battle of Québec in 1690 was a significant conflict during King William's War between New France, led by Governor Louis de Buade de Frontenac, and Massachusetts Bay, under the command of Sir William Phips. The outcome of the battle resulted in a victory for New France, solidifying their control over the territory of Quebec City.
The death of childless Charles II of Spain in November 1700 led to a struggle for control of the Spanish Empire between his heirs, Philip of Anjou and Charles of Austria, and their respective supporters. It was a global war, with fighting taking place in Europe, Asia, and America. At the end of the war, Philip II, who was the successor chosen by Charles II as a descendant of Charles' paternal half-sister Maria Theresa, became King of Spain and of its overseas empire. The Spanish possessions in Europe were partitioned between various European Monarchies.
3.1.Queen Anne's War
Was a war between the American territories of Great Britain against the the American territories of Spain and France. In Europe, it is generally viewed as the American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession; in the Americas, it is more commonly viewed as a standalone conflict.
3.1.1.Acadia and New England (Queen Anne’s War)
Was the theatre of War in Acadia and New England during Queen Anne’s War.
October 1710: In October 1710, 3,600 British and colonial forces led by Francis Nicholson finally captured Port Royal after a siege of one week. This ended official French control of the peninsular portion of Acadia.
Was a European conflict caused by the succession to the Habsburg Domains. Maria Theresa succeeded her father Charles VI, and the opposition to female inheritance of the throne was a pretext for starting a war. It was a global conflict that saw fight in Europe, Asia, America and Africa.
4.1.King George's War
Was a war between the British Empire and the French Empire that took place in the Americas. The conflict was part of the War of the Austrian Succession.
June 1745: In 1745, British colonial forces led by William Pepperrell and Peter Warren captured Fortress Louisbourg, a strategic French stronghold in Nova Scotia, after a six-week siege during the War of the Austrian Succession.
August 1745: The New Englanders also assumed control of Port-La-Joye on present-day Prince Edward Island.
January 1747: The New Englanders also assumed control of Port-La-Joye on present-day Prince Edward Island.
4.2.Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Austrian Succession, following a congress assembled on 24 April 1748 at the Free Imperial City of Aachen.
October 1748: In 1748, the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle restored Louisbourg to France. Louisbourg was a French fortress located on Cape Breton Island in present-day Nova Scotia, Canada. The treaty was signed by representatives of France, Great Britain, and other European powers to end the War of the Austrian Succession.
Was a global conflict that involved most of the European great powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. At the end of the war the main winner was Great Britain, that obtained territories in North America, the Caribbean and India, becoming the most powerful maritime and colonial of the European powers.
5.1.French and Indian War
Was a theater of war of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes.
June 1755: Colonel Robert Monckton, a British military officer, captured Fort Beauséjour in June 1755 during the Seven Years' War. This victory cut off the French Fortress Louisbourg from land-based reinforcements, marking a significant strategic success for Great Britain in the conflict.
5.1.1.Conquest of New France (1758-1760)
Was a British military campaign in New France during the Seven Years' War.
July 1758: Louisbourg was a strategic French fortress located in present-day Nova Scotia, Canada. Major-General James Wolfe was a British Army officer known for his role in the capture of Quebec City during the Seven Years' War. The capture of Louisbourg was a significant victory for the British in their efforts to gain control of North America.
September 1759: Quebec city capitulated to Britain after the Battle of the Plains Abraham, securing British predominance in North America.
September 1760: In 1760, French military leaders Lévis and Vaudreuil surrendered the French colony of Canada to British forces. This marked the end of the French and Indian War in North America, with the British emerging victorious after the capitulation of Montreal.
5.2.Treaty of Paris (1763)
Was a treaty signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the Seven Years' War.
February 1763: Treaty of Paris (1763): France ceded the eastern half of French Louisiana to Britain, that is, the area from the Mississippi River to the Appalachian Mountains.
January 1537: Saint Pierre and Miquelon were made a French possession in 1536 by Jacques Cartier on behalf of the King of France. Though already frequented by Mi'kmaq people and Basque and Breton fishermen, the islands were not permanently settled until the end of the 17th century.
January 1563: Charlesfort was established when a French expedition, organized by Huguenot leader Admiral Gaspard de Coligny and led by the Norman navigator Jean Ribault, landed at the site on the May River in February 1562.
January 1564: The settlement of Charlesfort in Florida was abandoned by the French.
January 1605: Establishment of French Acadia in North America.
July 1608: Samuel de Champlain, a French explorer and cartographer, founded New France in 1608.
January 1610: The Territory of Sagadahock, also called the Sagadahoc Colony and New Castle, was an English colonial territory which included the eastern part of what was later colonial Maine and was more sparsely settled than the western region. The area included was east of the Kennebec River. On some accounts, the English first settled Sagadahoc in 1608-09.
January 1630: The first documented Scottish settlement in the Americas was Nova Scotia in 1629.
March 1632: The Scots were forced to abandon their Nova Scotia colony in its infancy. The French under Isaac de Razilly reoccupied Nova Scotia (Acadia), establishing their new capital at LaHave.
January 1635: Foundation of Trois-Riviéres.
January 1643: Foundation of Montréal.
January 1656: Foundation of Plaisance.
January 1656: France appointed a governor in Plaisance (Placentia), a former Basque fishing settlement, thus starting a formal French colonization period in Newfoundland.
January 1671: When granted the English Royal Charter in 1670 by King Charles II of England, the Hudson’s Bay Company, under the governorship of the king's cousin Prince Rupert of the Rhine, was granted "the sole Trade and Commerce of all those Seas, Streights, Bays, Rivers, Lakes, Creeks, and Sounds, in whatsoever Latitude they shall be, that lie within the entrance of the Streights commonly called Hudson's Streights, together with all the Lands, Countries and Territories, upon the Coasts and Confines of the Seas, Streights, Bays, Lakes, Rivers, Creeks and Sounds, aforesaid, which are not now actually possessed by any of our Subjects, or by the Subjects of any other Christian Prince or State", "and that the said Land be from henceforth reckoned and reputed as one of our Plantations or Colonies in America, called Rupert's Land".
January 1674: Louis Jolliet was a French-Canadian explorer and Jacques Marquette was a Jesuit missionary. They explored the Mississippi River in 1673, claiming the territory for New France. This expedition played a significant role in the French colonization of North America.
January 1683: Establishment of Louisiana.
January 1686: Fort Saint-Louis, Texas, was founded in 1685 by French explorer René-Robert Cavelier de La Salle on the banks of Garcitas Creek, a few kilometers inland from the mouth of the Lavaca River. La Salle had intended to establish the colony at the mouth of the Mississippi, but inaccurate charts and navigational errors led his ships more than six hundred kilometers to the west, to the coast of Texas.
January 1689: Most of the members of the French colony of Fort Saint Louis (Texas) were killed during a Karankawa raid in late 1688.
October 1702: Sieur Juchereau, Lieutenant General of Montréal, along with thirty-four Canadiens, founded Fort Vincennes on October 28, 1702, to trade for Buffalo hides with American Indians.
January 1711: Acadia was conquered by the British during Queen Anne's War.
April 1713: Île-Royale, consisting of Île Royale (now Cape Breton Island) and Île Saint-Jean (now Prince Edward Island), was a French colony in North America from 1713 to 1763. The territory was part of New France and was ceded to France in the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713.
April 1713: With the Treaty of Utrecht of 1713, which ended the War of the Spanish Succession, France ceded to the British its claims to Newfoundland (including its claims to the shores of Hudson Bay) and to the French possessions in Acadia.
April 1713: The Treaty of Utrecht in 1713 ended the War of the Spanish Succession. As part of the treaty, France ceded Saint Pierre and Miquelon to Great Britain. This transfer of territory marked a significant change in the control of the islands.
January 1733: The 1732 charter boundary provided that the new colony of Georgia would consist of all the land between the headwaters of the Savannah and the Altamaha rivers, with its eastern boundary formed by the Atlantic Ocean and its western boundary by the "south seas," a reference to the Pacific Ocean.
January 1741: French military officer and explorer La Vérendrye built the first forts in the Winnipeg Lake area.
January 1759: The British forces, led by General Jeffery Amherst, captured Île Royale and Île Saint-Jean from the French during the Seven Years' War, also known as the French and Indian War. This marked a significant victory for British North America in their efforts to gain control of the region.
November 1762: With the Treaty of Fointainebleau, France ceded the west split of Lousiana to Spain.
Disestablishment
February 1763: Treaty of Paris (1763): France ceded the eastern half of French Louisiana to Britain, that is, the area from the Mississippi River to the Appalachian Mountains.
Selected Sources
5 Nations Expansion. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 30 March 2024 on https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:5NationsExpansion.jpg
Rayback, R.J. (1957): Atlas of New York State, Frank E. Richards, p. 12
Treaty of Paris (1763), https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/Treaty_of_Paris_(1763)
Tucker, S.C. (2011) Battles that changed History - An Encyclopedia of World Conflict, ABC-CLIO, pp.237,240

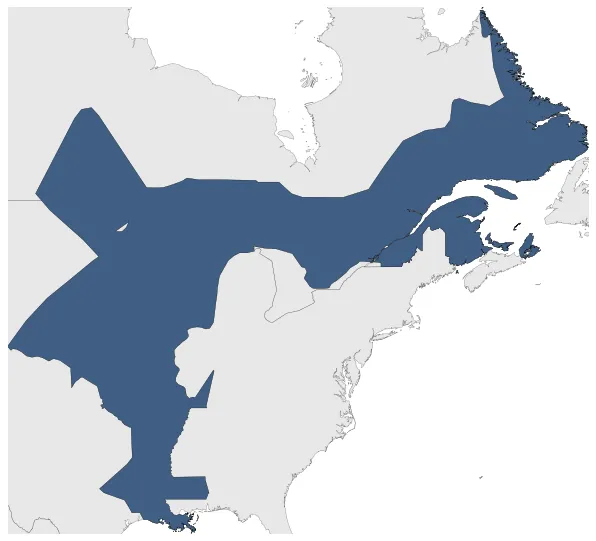
 New France
New France