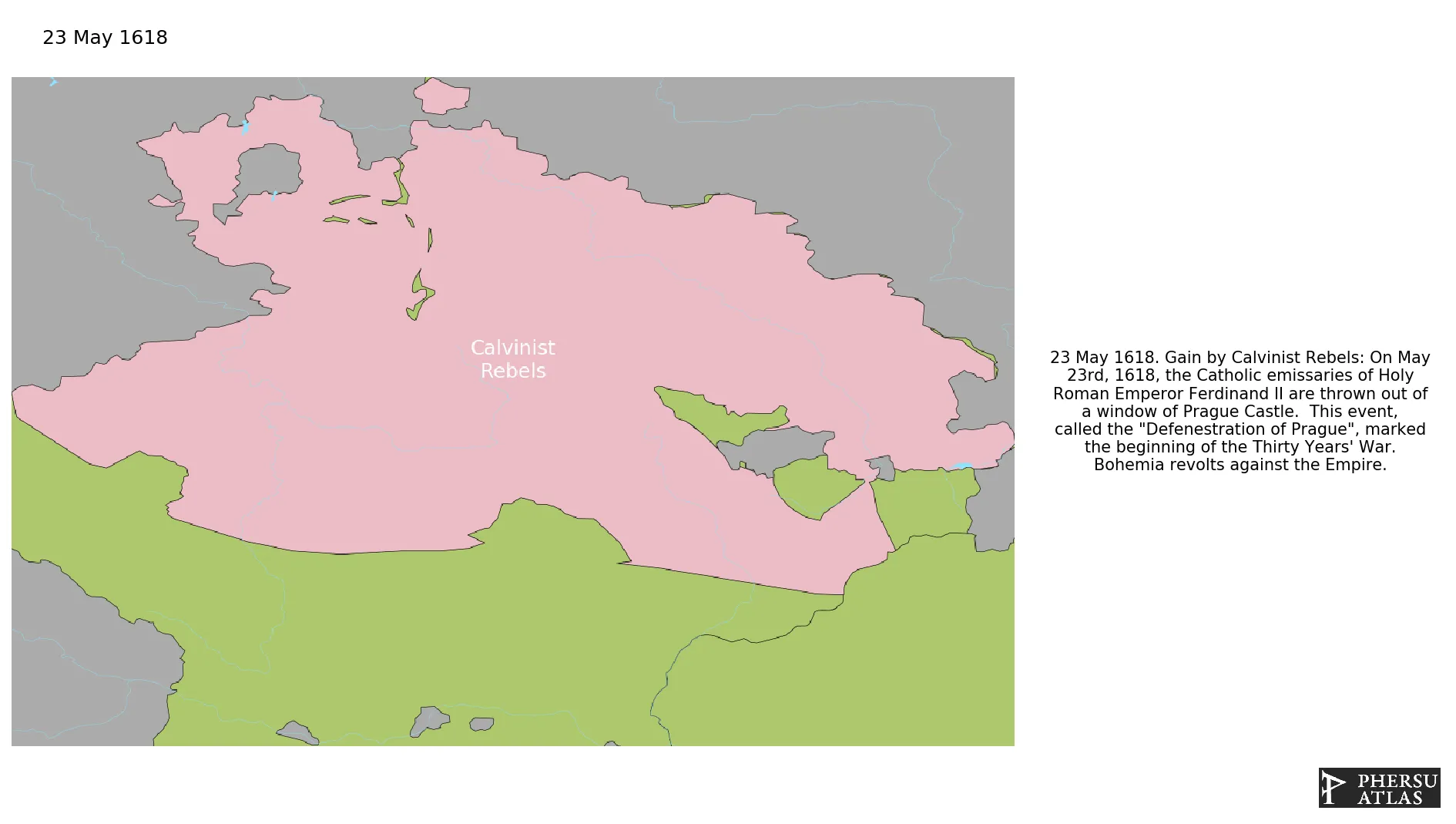
Calvinist Rebels
Calvinist Rebels
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Calvinist rebels during the Thirty Years' War.
Establishment
May 1618: On May 23rd, 1618, the Catholic emissaries of Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II are thrown out of a window of Prague Castle. This event, called the "Defenestration of Prague", marked the beginning of the Thirty Years' War. Bohemia revolts against the Empire.
November 1618: Battle of Lomnitz: The Bohemians defeat the Imperials commanded by the Count of Bucquoy.
November 1618: On November 21, 1618 the city of Pilsen was taken by the Calvinist rebels. It was the first major battle of the Thirty Years' War, and the starting point of the Bohemian Revolt.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
1.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
1.1.1.Bohemian-Palatine period
Was the first period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with a protestant revolt in Bohemia, at the time a territory of the Habsburg Domains.
1.1.1.1.War in Bohemia
Was the theatre of war in Bohemia during the first phase of the Thirty Years' War.
June 1619: The Bohemian army under Heinrich Matthias von Thurn first forced the Moravian estates to join the uprising, then invaded the Austrian homelands of the Habsburgs and stood before Vienna on June 6, 1619.
June 1619: In 1619, during the Bohemian Revolt, Count von Bucquoy, a general in the Habsburg army, defeated Ernst von Mansfeld at the Battle of Sablat. This victory forced the Bohemian Governing Board in Prague to recall Thurn, a leader of the Protestant rebels, to defend Bohemia against the Habsburg forces.
June 1619: In 1619, during the Bohemian Revolt, Count von Bucquoy defeated Ernst von Mansfeld at the Battle of Sablat. This victory forced the Bohemian Governing Board in Prague to recall Thurn, a key leader of the revolt, to defend Bohemia against the Habsburg forces.
July 1619: The Bohemian Confederation was a treaty of alliance between the non-Catholic Estates of the Bohemian crown lands. It was formed in Prague on July 31, 1619. The Confederation regulated the state order of the Crown of Bohemia in a new way. The king, as the monarchical head of the group of countries, was largely deprived of power and governmental power was placed in the hands of the estates. Bohemia became an elective monarchy again. At the same time, the relationship between the communes was changed. The estates of the neighboring countries of Moravia, Silesia, Upper and Lower Lusatia were put on an equal footing with those of Bohemia. From then on they were allowed to take part in the election of the king. Protestantism was practically declared the state religion.
Disestablishment
June 1619: The Bohemian army under Heinrich Matthias von Thurn first forced the Moravian estates to join the uprising, then invaded the Austrian homelands of the Habsburgs and stood before Vienna on June 6, 1619.
June 1619: In 1619, during the Bohemian Revolt, Count von Bucquoy, a general in the Habsburg army, defeated Ernst von Mansfeld at the Battle of Sablat. This victory forced the Bohemian Governing Board in Prague to recall Thurn, a leader of the Protestant rebels, to defend Bohemia against the Habsburg forces.
June 1619: In 1619, during the Bohemian Revolt, Count von Bucquoy defeated Ernst von Mansfeld at the Battle of Sablat. This victory forced the Bohemian Governing Board in Prague to recall Thurn, a key leader of the revolt, to defend Bohemia against the Habsburg forces.
July 1619: The Bohemian Confederation was a treaty of alliance between the non-Catholic Estates of the Bohemian crown lands. It was formed in Prague on July 31, 1619. The Confederation regulated the state order of the Crown of Bohemia in a new way. The king, as the monarchical head of the group of countries, was largely deprived of power and governmental power was placed in the hands of the estates. Bohemia became an elective monarchy again. At the same time, the relationship between the communes was changed. The estates of the neighboring countries of Moravia, Silesia, Upper and Lower Lusatia were put on an equal footing with those of Bohemia. From then on they were allowed to take part in the election of the king. Protestantism was practically declared the state religion.
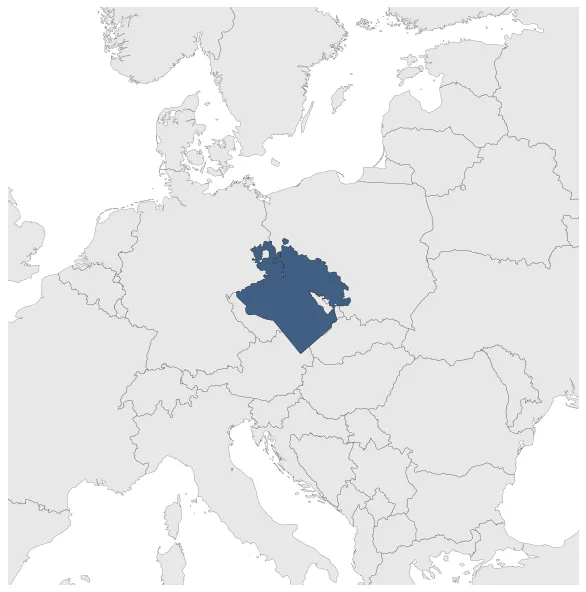
 Calvinist Rebels
Calvinist Rebels