If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
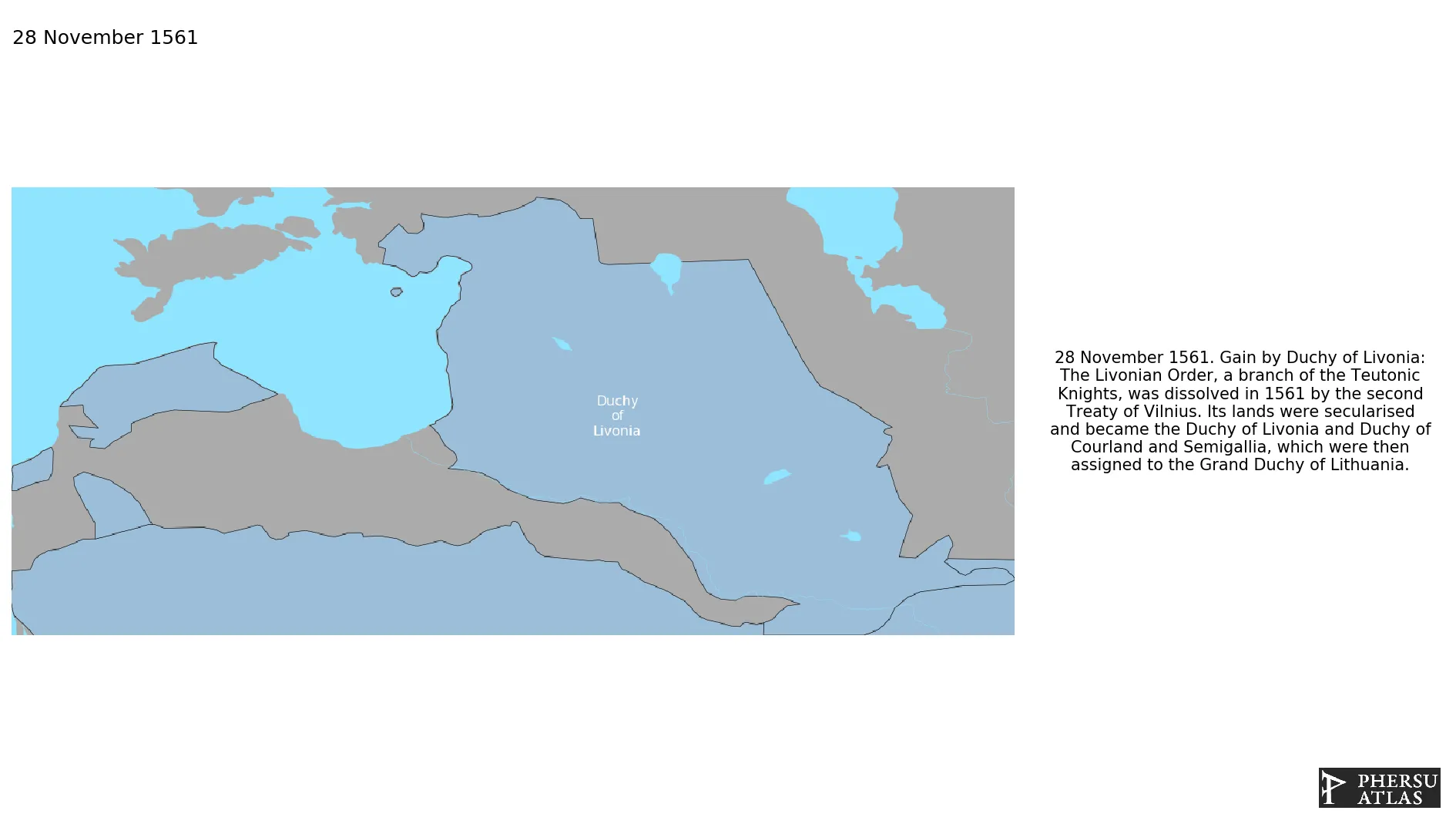
Was a territory of Poland-Lithuania that was created after the dissolution of the weakened Livonian with the second Treaty of Vilnius in 1561.
Establishment
November 1561: The Livonian Order, a branch of the Teutonic Knights, was dissolved in 1561 by the second Treaty of Vilnius. Its lands were secularised and became the Duchy of Livonia and Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, which were then assigned to the Grand Duchy of Lithuania.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
A series of wars fought in northern and northeastern Europe from the 16th to the 18th century.
1.1.Livonian War
Was a war fought over the control of Old Livonia. The Tsardom of Russia faced a varying coalition of the Dano-Norwegian Realm, the Kingdom of Sweden, and the Union (later Commonwealth) of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland. Old Livonia was finally partitioned between Sweden, Poland-Lithuania and Denmark-Norway.
January 1576: In 1575, Ivan the Terrible of Russia ordered an attack on Poland, leading to the capture of Salacgrīva and Pärnu in Livonia. This marked a significant expansion of the Tsardom of Russia's territory through military occupation.
1.1.1.Russian invasion of Livonia
Was a Russian invasion of Livonia by Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible).
September 1577: Magnus of Livonia besieged the the town of Wenden (Cesis) in August 1577.
December 1577: Polish forces re-captured the stronghold in Wenden (Cesis).
June 1578: Advancement of Russian forces by mid 1578.
1.1.2.Partition of Livonia
Was the partition of Old Livonia between Denmark, Sweden and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.
July 1562: Swdish king Erik XIV's forces seized Pernau (Pärnu) in June 1562.
1.1.3.Russian war with Lithuania
Was a Russian invasion of Lithuania by Ivan IV (Ivan the Terrible).
February 1564: In January and February Russian forces attacked Dubrowna, Orsha, Druchevsk, Borisov, Kopos, Shklow, Teterin, Mogilev, Radoml, Mstislavl, and Chachersk, reaching as far as the border of Vilnius and the Berezina River.
1.1.4.Polish and Swedish counterattack (Livonian War)
Were the military operations of Sweden and Poland-Lithuania against the Russian invasion.
December 1577: By November, Lithuanian forces moving northward had captured Dünaburg.
1.1.4.1.Treaty of Yam-Zapolsky
The Truce or Treaty of Yam-Zapolsky (Ям-Запольский) or Jam Zapolski, signed on 15 January 1582 between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia, was one of the treaties that ended the Livonian War.
January 1582: The Truce or Treaty of Yam-Zapolsky, signed on 15 January 1582 between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia, was one of the treaties that ended the Livonian War. In the terms of the treaty, Russia renounced its claims to Livonia and Polotsk but conceded no core Russian territories as Batory and returned the territories his armies had been occupying.
Was a war between Sweden and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth mainly over the control of Livonia and Estonia.
2.1.Swedish invasion of Livonia and Estonia
Was the Swedish invasion of the Polish-Lithuanian territories in Estonia and Livonia during the Polish-Swedish War (1600-1611).
April 1600: By March 1600 the Swedes displaced Polish forces from Estonia and most of Livonia.
2.2.Polish Counterattack (Polish-Swedish War of 1600-1611)
Was the Polish counterattack against the Swedish invasion in the Polish-Swedish War (1600-1611).
October 1600: Pärnu was besieged on 17 September and after heavy bombardment it surrendered on 17 October.
October 1600: Battle of Karksi.
January 1601: Battle of Kies.
April 1601: The town of Kokenhausen was taken by the Swedish forces under the command of King Charles IX of Sweden.
June 1601: Battle of Kokenhausen.
October 1601: Siege of Wolmar.
December 1601: Siege of Wolmar.
March 1602: Siege of Fellin.
May 1602: Siege of Fellin.
April 1603: The city of Dorpat surrendered to the Swedish forces led by King Charles IX of Sweden.
February 1608: Pärnu is besieged by Duchy of Livonia.
March 1608: Pärnu is besieged by Duchy of Livonia.
August 1608: The Swedish army captured Daugavgrīva.
January 1609: Swedish forces led by Mansfeld captured Daugavgriva, Viljandi and Koknese.
October 1609: Battle of Daugavgrīva.
January 1612: After Charles IX of Sweden's death in 1611, a truce was signed in the Duchy of Livonia. The truce established the status quo ante bellum, returning the territory to its pre-war condition.
Was a War between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Kingdom of Sweden caused by disputes over the Duchies of Livonia and Estonia.
August 1617: The city of Parnu was attacked on August 11, and capitulated after a three-day siege.
August 1617: Salacgrīva was captured on August 18.
September 1617: In July 1617, Swedish forces led by King Gustavus Adolphus occupied the Livonian coast from Grobiņa to Pärnu.
October 1617: In 1617, the Swedish Empire, under the leadership of King Gustavus Adolphus, gained military control over Livonia, with the exception of the city of Riga.
October 1618: Military operations by Polish-Lithuanian forces led by Radziwill resulted in the recapture of almost all towns and strongholds occupied by Sweden, except for Pärnu.
Was a period of political crisis during the Tsardom of Russia which began in 1598 with the death of Fyodor I, the last of the Rurik dynasty, and ended in 1613 with the accession of Michael I of the House of Romanov.
4.1.Polish-Muscovite War (1605-1618)
Was a conflict fought between the Tsardom of Russia and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth together with Zaporozhian Cossacks.
4.1.1.Truce of Deulino
Was the treaty that ended the Polish-Muscovite War (1609-1618) with notable Polish territorial gains.
January 1619: With the Truce of Deulino at the end of the Polish-Muscovite War (1605-1618), Russia ceded various territories to Poland-Lithuania. The Commonwealth gained control over the Smolensk and Chernihiv Voivodeships.
Was a war in a long-running series of conflicts between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Swedish Empire. It began with a Swedish invasion of the Polish-Lithuanian fiefdom Livonia.
January 1622: In early January 1622, the Swedish forces led by King Gustavus Adolphus captured Valmiera, a town in present-day Latvia.
July 1625: On June 27, 1625, Gustav Adolf landed in Livonia with an army of 20,000. The main Swedish corps of almost 10,000 marched upwards the Daugava River, and besieged Koknese, capturing it after sixteen days.
August 1625: On August 27, 1625, Swedish forces led by King Gustavus Adolphus captured Tartu, a city in present-day Estonia.
Was a war between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and Sweden.
September 1626: Battle of Selburg.
6.1.Truce of Altmark
Was the treaty that ended the Polish-Swedish War (1626-1629).
September 1629: The truce of Altmark in 1629 allowed Sweden, under the rule of King Gustavus Adolphus, to retain control of Livonia, including Riga.
September 1629: The Commonwealth retained southeastern parts of the Wenden Voivodeship, renamed to Inflanty Voivodeship.
Disestablishment
September 1629: The truce of Altmark in 1629 allowed Sweden, under the rule of King Gustavus Adolphus, to retain control of Livonia, including Riga.
September 1629: The Commonwealth retained southeastern parts of the Wenden Voivodeship, renamed to Inflanty Voivodeship.

 Duchy of Livonia
Duchy of Livonia