If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Polity that includes all territories military occupied by Finland that are not part of a specific military territory.
Establishment
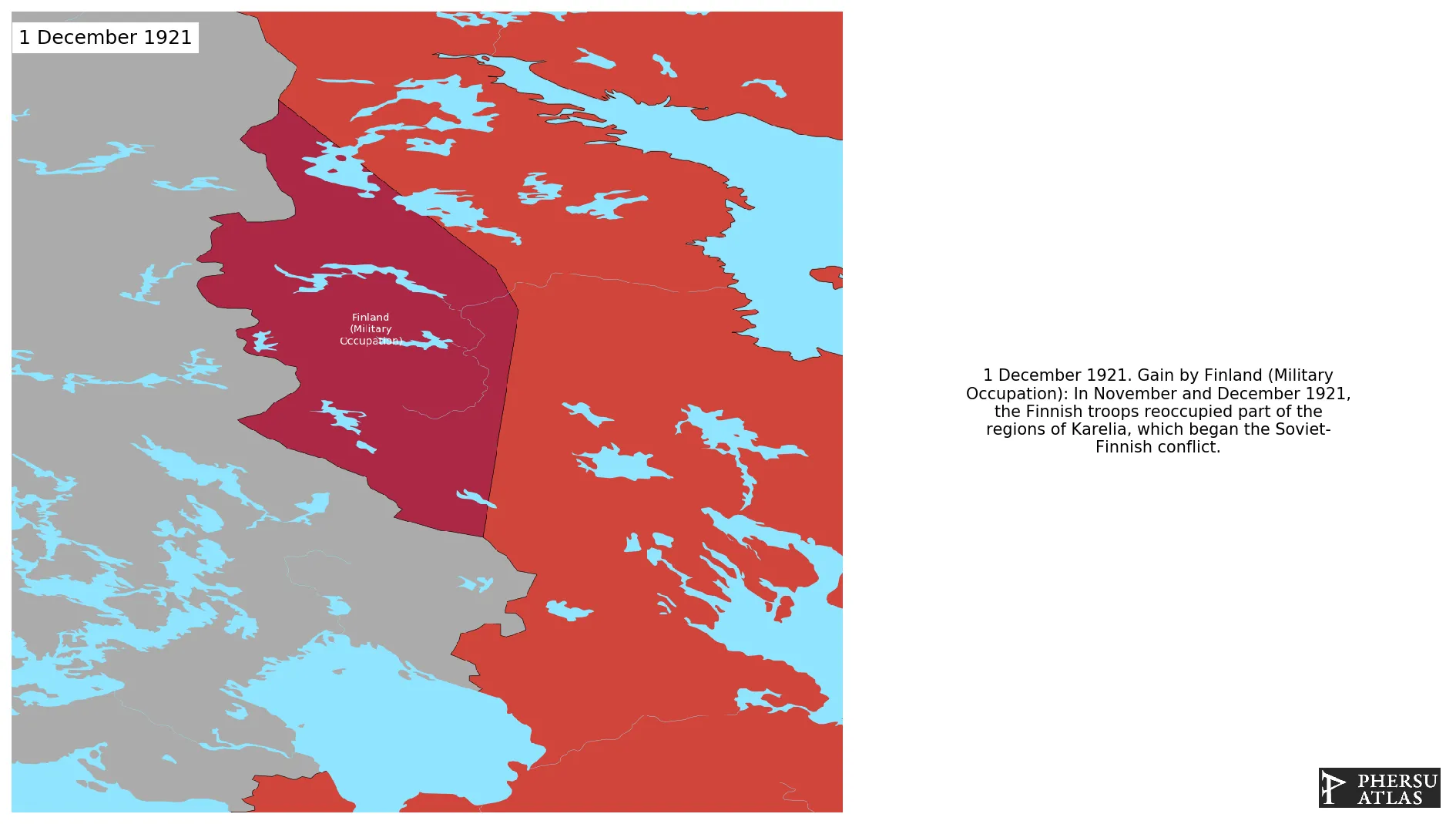
December 1921: In November and December 1921, the Finnish troops reoccupied part of the regions of Karelia, which began the Soviet-Finnish conflict.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a Civil War in Russia that involved varios factions but mainly the Bolsheviks and the conservative White Army in the core Russian territories, as well as a multitude of local secessionist states. At the end of war the Bolsheviks were victorious and established the Soviet Union.
1.1.Pro-independence movements in the Russian Civil War
Local independence movement caused several secessions and revolts during the Russian Civil War.
1.1.1.Soviet-Finnish conflict 1921-22
Was a conflict between Finland and the Russian SFSR during the Russian Civil War.
February 1922: In early February 1922 the Center Committee Karelian village of Uhtua was re-occupied by the Red Army.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
2.1.World War II (Eastern Theatre)
Was the Eastern European theatre of World War II.
2.1.1.Operation Barbarossa
Was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies.
2.1.1.1.Siege of Leningrad
Was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of Leningrad (present-day Saint Petersburg) on the Eastern Front of World War II.
September 1941: Finns captured the Beloostrov and Kirjasalo salients and conducted defensive preparations.
2.1.2.Continuation War
The Continuation War, also known as the Second Soviet-Finnish War, was a conflict fought by Finland and Nazi Germany against the Soviet Union from 1941 to 1944, as part of World War II.
2.1.2.1.Operation Silver Fox
Was a joint German-Finnish military operation during the Continuation War on the Eastern Front of World War II against the Soviet Union. The objective of the offensive was to cut off and capture the key Soviet Port of Murmansk.
July 1941: The initial Finnish advance against its adversary, the 54th Rifle Division, was very successful. III Corps moved swiftly through the Arctic forest and defeated several Soviet regiments. It advanced 64 km to the canal between Lake Pyaozero and Lake Topozero in just 20 days.
2.1.2.2.Finnish invasion of Ladoga Karelia
Was the Finnish invasion of the region of Carelia in the area of lake Ladoga during the Continuation War.
July 1941: Loimola was captured by the Finnish forces.
July 1941: Finnish troops reached the shore of Lake Ladoga at Koirinoja.
July 1941: Soviet resistance on the eastern shore of the Jänisjärvi Lake, and clearing the resistance lasted until July 16.
July 1941: It took until July 17 for the Finnish VII Corps to finally reach the Jänisjoki River.
July 1941: Finnish forces encircled the defenders and captured Salmi.
July 1941: The Finnish VI Corps reached the 1939 border on July 23.
August 1941: By August 7 Finnish 2nd Division of the II Corps had already reached the shore of lake Ladoga at Lahdenpohja.
2.1.2.3.Finnish invasion of the Karelian Isthmus
Was a military campaign carried out by Finland in 1941 where Finnish forces liberated the Karelian Isthmus.
August 1941: The Finnish 15th Division's managed to capture the town of Hiitola.
August 1941: The Finnish 18th Division captured the town and crossing point of Antrea.
August 1941: The Finnish 18th Division started its crossing of Vuoksi river.
August 1941: Vyborg was captured by Finnish troops.
August 1941: Finnish forces reached the old border with Russia.
2.1.2.4.Finnish invasion of East Karelia
Finnish troops occupied East Karelia during the Continuation War.
September 1941: The Finnish forces captured Olonets on September 5.
September 1941: Finnish advance by Group L reached Svir river.
September 1941: The Finnish 11th Division captured Pryazha.
October 1941: The Finnish forces captured Petrozavodsk.
December 1941: The Finnish spearhead captured the town of Poventsa.
2.1.2.5.Vyborg-Petrozavodsk Offensive
Was a strategic operation by the Soviet on the Karelian Isthmus and East Karelia fronts of the Continuation War, on the Eastern Front of World War II.
June 1944: Soviet units captured frontline trenches and destroyed fortifications, shattering the first Finnish defense line in the Valkeasaari sector.
June 1944: The Soviet 21st Army's offensive reached the partially completed VT-line.
June 1944: Viipuri/Vyborg falls to Soviet forces of Leningrad Front, insuring safety of Leningrad and opening Gulf of Finland to Soviet fleet.
June 1944: The Soviet Union's Karelian Front attacked in the Olonets sector of White Karelia on June 20. Weakened Finnish forces proved unable to stop the offensive which reached Olonets.
June 1944: Petrozavodsk conquered by USSR.
July 1944: The first Karelian Front 7th Army's units reached the U-line.
2.1.2.6.Moscow Armistice
Was an armistice signed by Finland on one side and by the Soviet Union and United Kingdom on the other side on September 19, 1944, ending the Continuation War.
September 1944: Armistice signed between Finland on one side, and the Soviet Union and United Kingdom on the other side on September 19, 1944, ending the Continuation War. Karelia, Salla, Petsamo, and Porkkala fell to the Soviets.
Disestablishment
June 1944: Soviet units captured frontline trenches and destroyed fortifications, shattering the first Finnish defense line in the Valkeasaari sector.
June 1944: The Soviet 21st Army's offensive reached the partially completed VT-line.
June 1944: Viipuri/Vyborg falls to Soviet forces of Leningrad Front, insuring safety of Leningrad and opening Gulf of Finland to Soviet fleet.
June 1944: The Soviet Union's Karelian Front attacked in the Olonets sector of White Karelia on June 20. Weakened Finnish forces proved unable to stop the offensive which reached Olonets.
June 1944: Petrozavodsk conquered by USSR.
July 1944: The first Karelian Front 7th Army's units reached the U-line.
September 1944: Armistice signed between Finland on one side, and the Soviet Union and United Kingdom on the other side on September 19, 1944, ending the Continuation War. Karelia, Salla, Petsamo, and Porkkala fell to the Soviets.
Selected Sources
Nenye, Vesa; Munter, Peter; Wirtanen, Tony; Birks, Chris (2016). Finland at War: The Continuation and Lapland Wars 1941–45. Osprey Publishing. pp. 115-116.
Nenye, Vesa; Munter, Peter; Wirtanen, Tony; Birks, Chris (2016). Finland at War: The Continuation and Lapland Wars 1941–45. Osprey Publishing. pp. 119-120.
Nenye, Vesa; Munter, Peter; Wirtanen, Tony; Birks, Chris (2016). Finland at War: The Continuation and Lapland Wars 1941–45. Osprey Publishing. pp. 127-128.
Nenye, Vesa; Munter, Peter; Wirtanen, Tony; Birks, Chris (2016). Finland at War: The Continuation and Lapland Wars 1941–45. Osprey Publishing. pp. 131-132.
Williams, M.H. (1989): United States army in World War II - Special Studies - Chronology 1941-1945, p. 214
.webp)
.png.webp)
 Finland (Military Occupation)
Finland (Military Occupation)