This article is about the specific polity German East Africa and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
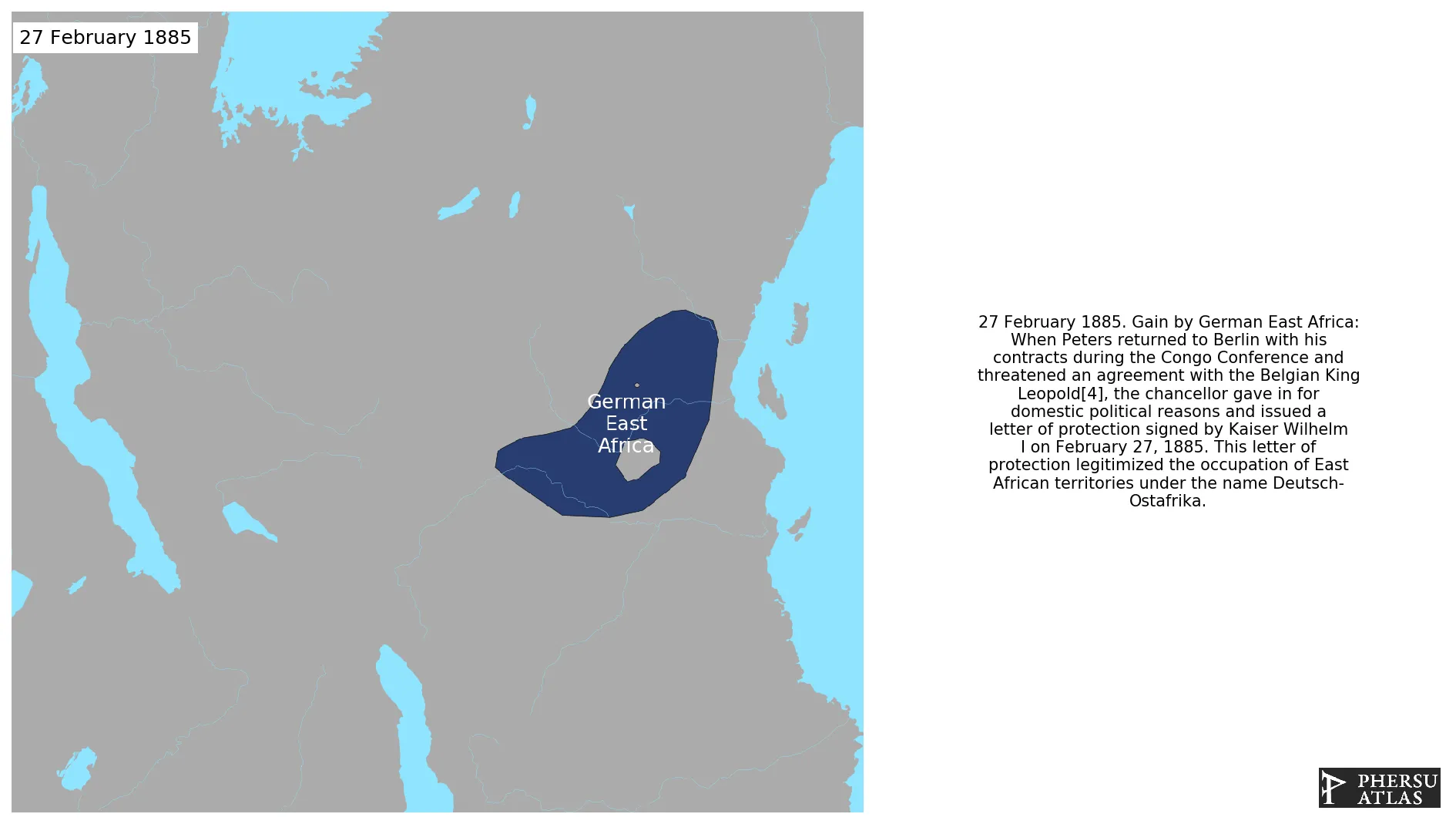
Was a German colony in the African Great Lakes region, which included present-day Burundi, Rwanda, the Tanzania mainland, and the Kionga Triangle, a small region later incorporated into Mozambique. The colony was conquered by the Entente during World War I and partitioned between Great Britain, Belgium and Portugal.
Establishment
February 1885: When Peters returned to Berlin with his contracts during the Congo Conference and threatened an agreement with the Belgian King Leopold[4], the chancellor gave in for domestic political reasons and issued a letter of protection signed by Kaiser Wilhelm I on February 27, 1885. This letter of protection legitimized the occupation of East African territories under the name Deutsch-Ostafrika.
June 1885: The Khutu Expedition was led by German explorer Dr. Karl Ludwig von Khutu in German East Africa. The contract signed with Golongo was likely for trade or land acquisition purposes in the Rufiji and Ulanga area.
November 1885: Usaramo-Expedition.
December 1885: Zweite Nyassa-Expedition - second expedition led by German explorer Hermann von Wissmann in 1885. The expedition aimed to establish German control over the regions of Ubena, Uhehe, Magindo, Mahenge, and Matschonde in German East Africa.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a global conflict between two coalitions, the Allies (primarily France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States) and the Central Powers (led by Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire). It was mainly caused by the competition of the western countries over domain in Europe and in the rest of the world with their colonial empires. The war ended with the defeat of the Central Powers. The war also caused the Russian Revolution and the ensuing Russian Civil War.
1.1.World War I African Theatre
Was the African Theatre of World War I.
January 1917: During World War I, Belgian troops from the neighbouring Belgian Congo invaded actual Rwanda and Burundi and occupied it.
November 1918: The German leader in the African Great Lakes, Paul Emil von Lettow-Vorbeck, did not surrender until notified about the Armistice of 11 November 1918 that ended the war.
1.1.1.East African campaign
Was a series of battles and guerrilla actions during World War I, which started in German East Africa (GEA) and spread to portions of Mozambique, Rhodesia, British East Africa, Uganda, and Belgian Congo.
1.1.1.1.British Offensive (East African campaign)
Was the British offensive against German forces in the East Africa Campaign of World War I.
March 1916: British conquest of Moshi.
April 1916: British conquest of Arusha.
April 1916: British conquest of Kondoa-Irangi.
June 1916: British conquest of Handeni.
July 1916: British conquest of Bukoba.
July 1916: British conquest of Mwanza.
August 1916: British conquest of Malangali.
August 1916: British conquest of Dodoma, Kilosa.
August 1916: British conquest of Morogoro.
August 1916: British conquest of Iringa.
September 1916: British conquest of Dar-Es-Salaam.
September 1916: British conquest of Kilwa and Lindi.
1.1.1.2.Belgian Offensive (East Africa Campaign)
Was the Belgian offensive against German forces in the East Africa Campaign of World War I.
May 1916: Belgian conquest of Kigali.
August 1916: Belgian conquest of Ujiji.
September 1916: Belgian conquest of Tabora.
October 1917: British conquest of Mahenge.
1.1.1.3.German Invasion of Portuguese East Africa
Was the German invasion of Portuguese Mozambique during World War I.
November 1917: German conquest of Ngomano.
1.1.1.4.Surrender of German East Africa
After the surrender of Germany in Europe, the troops of General Lettow-Vorbeck in German East Africa surrendered.
November 1918: When German general Lettow-Vorbeck received a telegram announcing the signing of the armistice by Germany, he agreed to a cease-fire. He marched his force to Abercorn and formally surrendered to the Entente on 25 November 1918. All the territories occupied by German forces in eastern Africa were freed, and the German colonies occupied.
January 1886: The Second Kilimanjaro Expedition in 1885 was led by German explorer Hans Meyer and Austrian mountaineer Ludwig Purtscheller. They successfully reached the summit of Mount Kilimanjaro, the highest peak in Africa, on October 6, 1889. This expedition marked the first recorded ascent of the mountain.
February 1886: Sabaki Expedition: First contacts made by the Germans with the Galla ethnic group on the Tana River. From the German's point of view, this was the "acquisition of Giriyama, the Wanika lands, the Galla areas and Ukamba".
June 1886: Second Usagara Expedition: Foundation of the stations Dunda, Madimola and Usungula on the Kingani River in the center of what later became German East Africa.
October 1886: The governments of Great Britain and Germany negotiated a delimitation of their spheres of interest and, on October 29, 1886, agreed on a division of East Africa into zones of interest, whereby Germany was assigned the southern part and Great Britain the northern part (today's Kenya).
January 1889: The Masai region was fe facto divided between the Germans and the British as the territory extended over both states.
July 1890: By 1st july 1890 Germany controlled all of Tanganyka (the continental part of modern-day Tanzania), Burundi and Rwanda as with the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty the treaty with the East Africa Protectorate controlled by Britain was fixed.
July 1890: Conquest of Kingdom of Soukouma. By 1st july 1890 Germany controlled all of Tanganyka (the continental part of modern-day Tanzania), Burundi and Rwanda as with the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty the treaty with the East Africa Protectorate controlled by Britain was fixed.
July 1890: In 1890, Burundi became part of the German colonial empire as part of German East Africa. By 1st july 1890 Germany controlled all of Tanganyka (the continental part of modern-day Tanzania), Burundi and Rwanda as with the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty the treaty with the East Africa Protectorate controlled by Britain was fixed.
July 1890: Conquest of Kingdom of Buzinza. By 1st july 1890 Germany controlled all of Tanganyka (the continental part of modern-day Tanzania), Burundi and Rwanda as with the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty the treaty with the East Africa Protectorate controlled by Britain was fixed.
July 1890: German colonial rule began for Buhaya in 1890. In July, Germany and Great Britain laid down their territorial claims.
January 1891: By 1st july 1890 Germany controlled all of Tanganyka (the continental part of modern-day Tanzania), Burundi and Rwanda as with the Heligoland-Zanzibar Treaty the treaty with the East Africa Protectorate controlled by Britain was fixed.
January 1892: The Heru Kingdom falls under German administration.
January 1896: Kanyangereko is annexed by the Germans.
January 1901: Kiziba became part of German East Africa.
Disestablishment
November 1918: The German leader in the African Great Lakes, Paul Emil von Lettow-Vorbeck, did not surrender until notified about the Armistice of 11 November 1918 that ended the war.
November 1918: When German general Lettow-Vorbeck received a telegram announcing the signing of the armistice by Germany, he agreed to a cease-fire. He marched his force to Abercorn and formally surrendered to the Entente on 25 November 1918. All the territories occupied by German forces in eastern Africa were freed, and the German colonies occupied.
Selected Sources
Langer, W. L. (1951): The Diplomacy of Imperialism, 1890-1902, (1951) , Cambridge (USA), pp. 6-10
Strachan, H. (2001): The First World War: To Arms. Vol. I, New York: Oxford University Press, p. 641
The Great War in East Africa. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 21 April 2021 on https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Datei:World_War_I_in_East_Africa.jpg

 German East Africa
German East Africa