If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
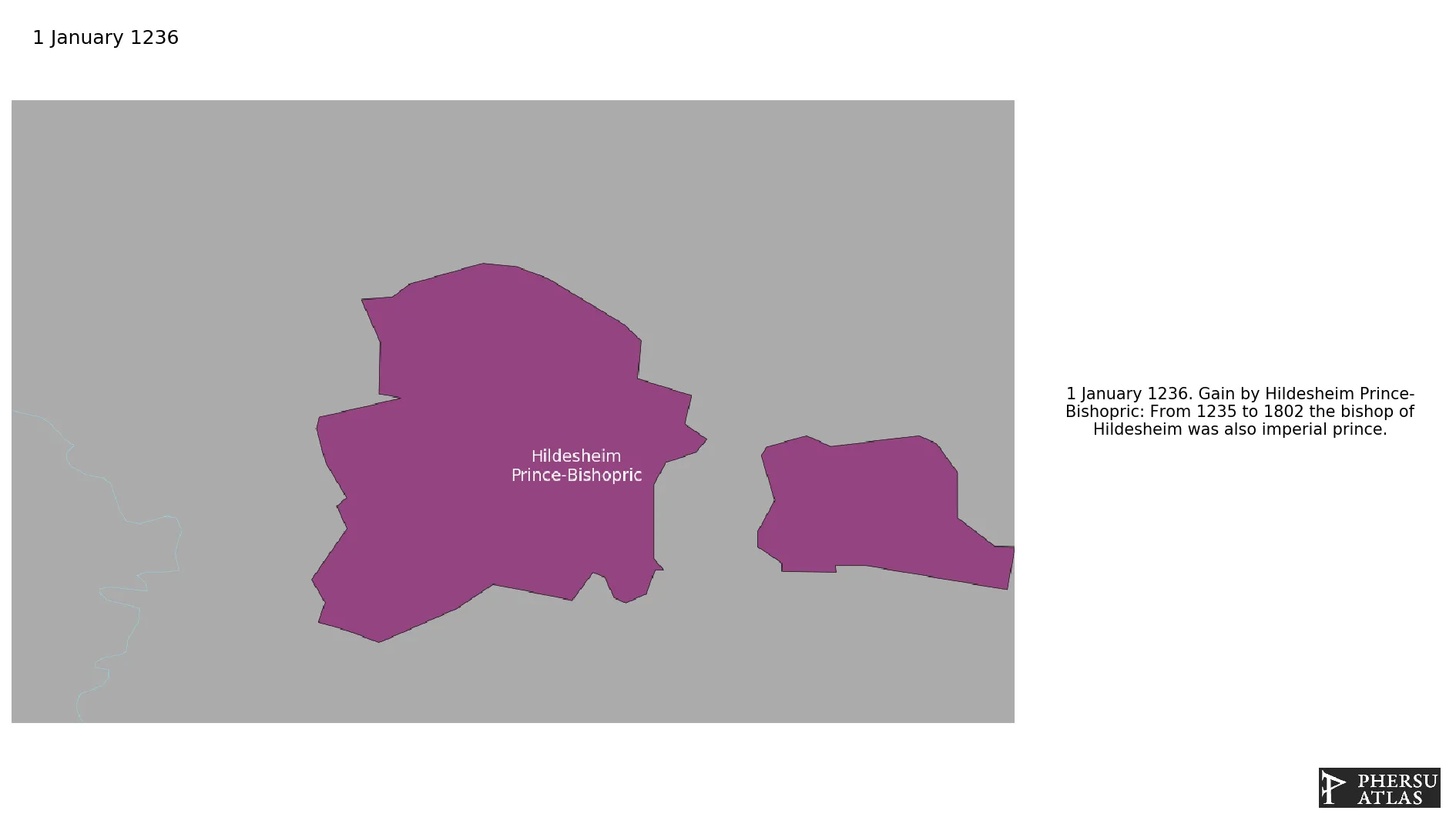
Was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire.
Establishment
January 1236: From 1235 to 1802 the bishop of Hildesheim was also imperial prince.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was a conflict that broke out in 1519 between the Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim and the principalities of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel and Calenberg.
1.1.Treaty of Quedlinburg
Was the treaty that ended the Hildesheim Diocesan Feud. The Prince-Nishopric of Hildesheim lost large territories to Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel.
May 1523: In the "Quedlinburger Rezess" of May 13, 1523, after lengthy negotiations, large territorial cessions to Braunschweig were decided. This meant a great gain for the princes of Braunschweig-Wolfenbüttel. The Bishopric of Hildesheim was left with only four of the original 22 provinces (Peine, Steuerwald, Marienburg and the cathedral provost) as well as the cities of Hildesheim and Peine.
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
2.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
2.1.1.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
2.1.1.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
December 1643: In 1643 Swedish general Torstensson invaded Moravia for the second time.
January 1644: In 1643, when the Torstensson War broke out, the Swedish military focused entirely on Denmark and thus enabled an imperial offensive to Jutland.
June 1648: In May 1648, there was the last major field battle of the Thirty Years' War between French-Swedish and Imperial-Bavarian armies near Augsburg.
2.1.2.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
October 1648: With the Peace of Westphalia Sweden received Western Pomerania (henceforth Swedish Pomerania), Wismar, and the Prince-Bishoprics of Bremen and Verden as hereditary fiefs. Sweden evacuated the remnant territories it had occupied in the Holy Roman Empire.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1804: The Hildesheim Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia.
February 1310: County of Dassel sold to Bishop Siegfried II of Hildesheim.
January 1384: When the Woldenberg rulers died out in 1383, their property fell to the Bishopric of Hildesheim.
January 1447: In 1446 the Counts of Wunstorf sold their county to the Bishop of Hildesheim.
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
January 1644: In 1643 the disputes between the Hildesheim monastery and the Dukes of Brunswick and Lüneburg were settled with the Hildesheim main recess. The Great Monastery fell back to the Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim.
January 1787: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
Disestablishment
January 1804: The Hildesheim Prince-Bishopric is acquired by the Kingdom of Prussia.
Selected Sources
Dreißigjähriger Krieg. Austria Forum. Retrieved on 30 march 2024 on https://austria-forum.org/af/AustriaWiki/Drei%C3%9Figj%C3%A4hriger_Krieg
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Matthias Blazek: An Himmelfahrt brannten elf Dörfer: Vor 500 Jahren wurde in Quedlinburg das Ende der Hildesheimer Stiftsfehde besiegelt. Sachsenspiegel, Cellesche Zeitung vom 20. und 27. Mai 2023
Spindler, M. (2017): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, Munich (Germany), p. 266
Westfälischer Friede - Vertrag von Osnabrück, https://de.wikisource.org/wiki/Westf%C3%A4lischer_Friede_%E2%80%93_Vertrag_von_Osnabr%C3%BCck

 Hildesheim Prince-Bishopric
Hildesheim Prince-Bishopric