If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
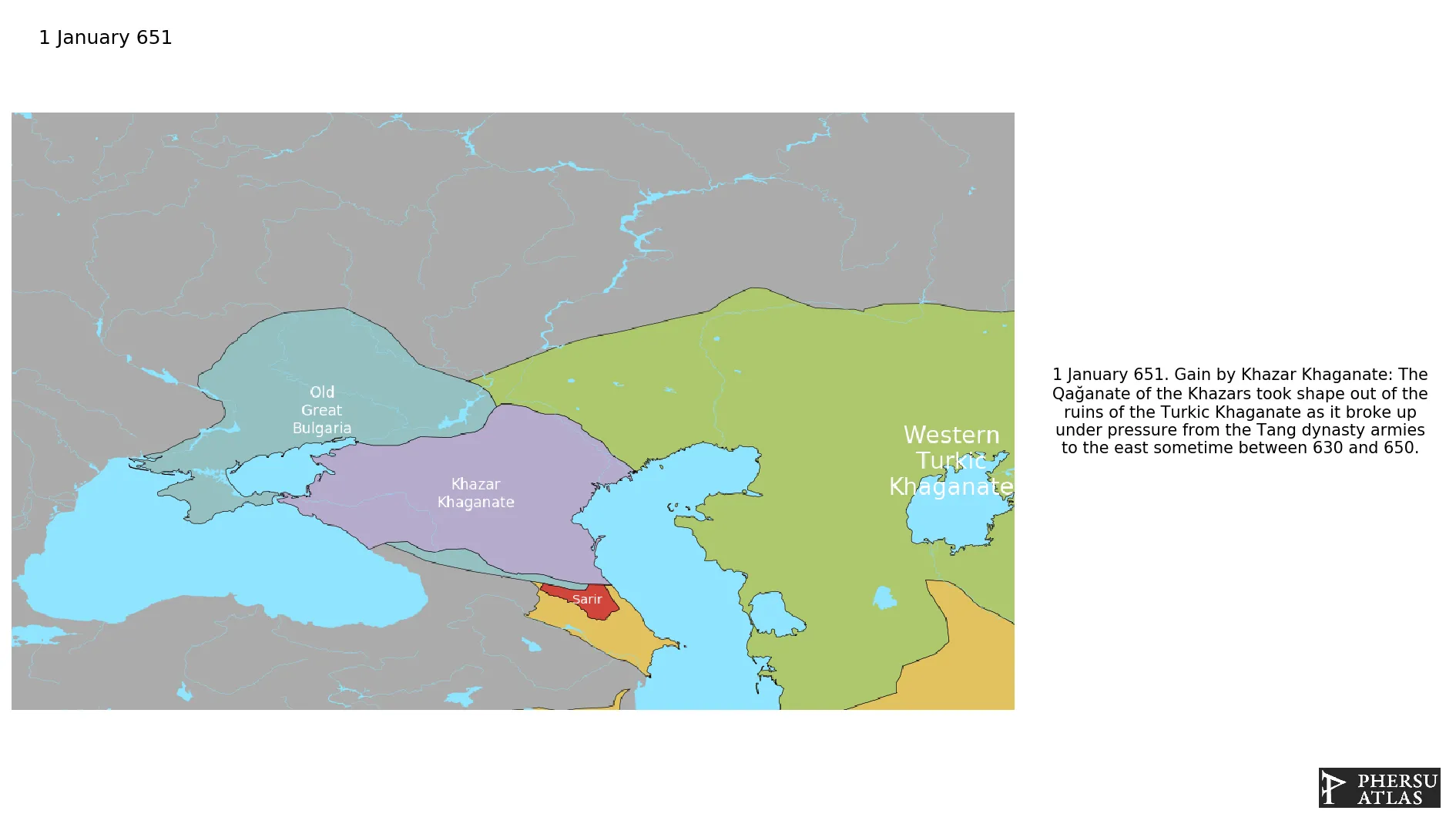
Was a polity that emerged from the Western Turkic Khaganate in the northern caucasus region.
Establishment
January 651: The Qağanate of the Khazars took shape out of the ruins of the Turkic Khaganate as it broke up under pressure from the Tang dynasty armies to the east sometime between 630 and 650.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were the military campaigns by the first three Islamic Caliphates (the Caliphate of Muhammad, the Rashidun Caliphate and the Umayyad Caliphate) that led to the Islamic conquest of most of the Middle East as well as the Iberian Peninsula.
1.1.Arab-Khazar Wars
Were a series of conflicts fought between the armies of the Khazar Khaganate and the Rashidun, Umayyad, and Abbasid caliphates and their respective vassals.
1.1.1.First Arab-Khazar War
Was a war between the Khazar Kahaganate and the Rashidun Caliphate.
January 653: The Khazars abandoned Balanjar and moved their capital further north, in an attempt to evade the reach of the Arab armies.
February 653: The Khazars abandoned Balanjar and moved their capital further north, in an attempt to evade the reach of the Arab armies.
1.1.2.Second Arab-Khazar War
Was a war between the Khazar Kahaganate and the Umayyad Caliphate.
August 722: Battle of Balanjar.
January 730: By 729, the Arabs had lost control of northeastern Transcaucasia.
December 730: The battle in 730 in Ardabil was between the Arab general al-Jarrah and the Khazars led by Barjik. The Khazars emerged victorious, defeating al-Jarrah's army of 25,000 soldiers. This victory solidified the Khazar Khaganate's control over the territory.
January 732: Sa'id ibn Yazid was a prominent Umayyad general who successfully recaptured the city of Akhlat on Lake Van in 731.
January 741: He restored the provinces of Albania to Muslim allegiance after meting out exemplary punishment to the inhabitants of Khaydhan, who resisted his advance, and reached Derbent, where he found a Khazar garrison of 1,000 men with their families installed. .
Expansion during the rule of Uthman in the Rashidun Caliphate.
January 654: An Arab emir was installed in Tbilisi about 653.
Was a military campaing by Bulgarian Khan Aspurah against the Byzantine Empire that resulted in the conquest of Moesia and Dobrugia.
January 681: Bulgar conquest of Moesia and Dobrugia.
Were a series of expansionistic military campaigns by Oleg, ruler of the Kievan Rus'.
January 882: In 880-82, Oleg of Novgorod led a military force south along the Dnieper river, capturing Smolensk and Lyubech before reaching Kiev. There, he deposed and killed Askold and Dir, proclaiming himself prince of Kievan Rus'.
January 884: In 883, Oleg of Novgorod, prince of the Kievan Rus', conquered the Drevlians, a Slavic tribe.
January 886: Territory of the Radimichs (an East Slavic tribe) conquered by Kievan Rus'.
January 886: In 885, Oleg of Novgorod, subjugated the Poliane people, a Slavic tribe.
January 886: The territories of the Vyatichi fall under control of the Kievian Rus'.
January 886: The Severians were a tribe or tribal confederation of early East Slavs occupying areas to the east of the middle Dnieper River and southeast of the Danube River. Oleg of Novgorod annexed their territory to the Kievan Rus'.
Were military raids undertaken by the Rus' between the late 9th century and c. 1041 on the Caspian Sea shores.
5.1.First Caspian expedition of the Rus'
The Rus' undertook the first large-scale expedition in the Caspian Sea in 913. Having arrived on 500 ships, they pillaged in the Georgan region, in the territory of present-day Iran, and more to the west, in Gilan and Mazandaran, taking slaves and goods.
January 914: The Rus' undertook the first large-scale Caspian expedition in 913. Having arrived on 500 ships, they pillaged in the Gorgan region, in the territory of present-day Iran, and more to the west, in Gilan and Mazandaran, taking slaves and goods.
February 914: The Rus' undertook the first large-scale Caspian expedition in 913. After having pillaged the Gorgan, Gilan and Mazandaran (Modern-day Iran), the Rus' forces left these regions.
The Magyars (or Hungarians) successfully conquered the Carpathian Basin (corresponding to the later Kingdom of Hungary) by the end of the ninth century, and launched a number of plundering raids thoughout Europe.
January 938: In 937, the Hungarians raided France as far west as Reims, Lotharingia, Swabia, Franconia, the Duchy of Burgundy and Italy as far as Otranto in the south.
January 938: The Hungarians attacked Bulgaria and the Byzantine Empire, reaching the walls of Constantinople.
February 938: The Hungarians attacked Bulgaria and the Byzantine Empire, reaching the walls of Constantinople.
February 938: In 937, the Hungarians raided France as far west as Reims, Lotharingia, Swabia, Franconia, the Duchy of Burgundy and Italy as far as Otranto in the south. After the ride they left these territories.
Were a series of conflicts fought between the Byzantines and Bulgarians which began when the Bulgars first settled in the Balkan peninsula in the 5th century, and intensified with the expansion of the Bulgarian Empire to the southwest after 680 AD.
7.1.Sviatoslav's invasion of Bulgaria
Was the invasion of the Bulgarian Empire by the Kievan Rus'.
September 971: Byzantine Emperor John I Tzimiskes and Sviatoslav I of Kiev agreed to a peace treaty: The Rus' army left the occupied territories, and their trading rights were re-affirmed in exchange for an oath to never again attack imperial territory.
7.1.1.Kievan Offensive
Was a military campaign by the invading Kievan Rus' in the Bulgarian Empire.
June 968: In August 967 or 968, the Rus' crossed the Danube into Bulgarian territory, defeated a Bulgarian army of 30,000 men in the Battle of Silistra, and occupied most of the Dobruja.
January 669: Great Ancient Bulgaria is conquered by the Khazars.
January 671: After their conquest of the lower Volga region to the East, and an area westwards between the Danube and the Dniepr, and their subjugation of the Onoğur-Bulğar union, sometime around 670, a properly constituted Khazar Qağanate emerges, becoming the westernmost successor state of the formidable Göktürk Qağanate after its disintegration.
January 671: The Bulgars of Asparuh moved westwards to what is now Bessarabia, subdued the territories to the north of the Danube in modern Wallachia, and established themselves in the Danube Delta.
January 701: Political unification of the Volga valley under Khazar suzerainty.
January 744: The Kimek-Kipchak khanate was a Turkish khaganate (empire) from 743.
January 751: Oghuz Turks formed a tribal confederation conventionally named the Oghuz Yabgu State in Central Asia.
January 751: Expansion of the Khazar Khaganate by 750.
January 779: The Abkhazian Kingdom Declared independence from the Byzantine Empire.
January 806: Around 805, Bulgarian emperor Krum defeated the Avar Khaganate.
January 851: Expansion of the Khazar Khaganate by 850.
January 861: The Kaysite dynasty was a Muslim Arab dynasty that ruled an emirate centered in Manzikert from c. 860.
January 861: The Pechenegs settled towards the end of the ninth century between the Volga and the Ural River, north of the Caspian Sea.
January 886: Ashot restored the Armenian monarchy and became Armenia's first king.
January 891: The Sajid dynasty, an Iranian Muslim dynasty, ruled from 889-890 in Azerbaijan and Armenia.
January 894: The Kingdom of Hereti was a medieval monarchy which emerged in Caucasus on the Iberian-Albanian frontier.
January 901: The Kingdom of Alania was a medieval kingdom of the Iranian Alans (proto-Ossetians) that flourished in the Northern Caucasus, roughly in the location of latter-day Circassia and modern North Ossetia-Alania, from its independence from the Khazars in the late 9th century.
January 909: In about 908 Abkhazian king Constantine III (c.894 . 923) annexed a significant portion of Kartli.
January 966: De facto independence of Volga Bulgaria at the end of the Khazar Empire.
January 970: Between 965 and 969, the Kievan Rus' ruler, Sviatoslav I of Kiev, as well as his allies, conquered the capital, Atil, and ended Khazaria's independence.
Disestablishment
September 971: Byzantine Emperor John I Tzimiskes and Sviatoslav I of Kiev agreed to a peace treaty: The Rus' army left the occupied territories, and their trading rights were re-affirmed in exchange for an oath to never again attack imperial territory.
Selected Sources
Chasaren. Wikipedia. Retrieved on 7 April 2024 on https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Chasaren.jpg
Haldon, John F. (2001), The Byzantine Wars, Stroud: Tempus, p.104
Leyser, K. (1982): Medieval Germany and its neighbours, 900-1250, London (UK), p. 50
Lowe, S. (30 May 2011). The Magyars of Hungary. https://web.archive.org/web/20091027151814/http://www.geocities.com/egfrothos/magyars/magyars.html
Reuter, T. (1995): The New Cambridge Medieval History: c. 900-c. 1024, Cambridge (UK), p. 543
Stephenson, Paul (2000), Byzantium's Balkan Frontier: A Political Study of the Northern Balkans, 900–1204, Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press, p.53
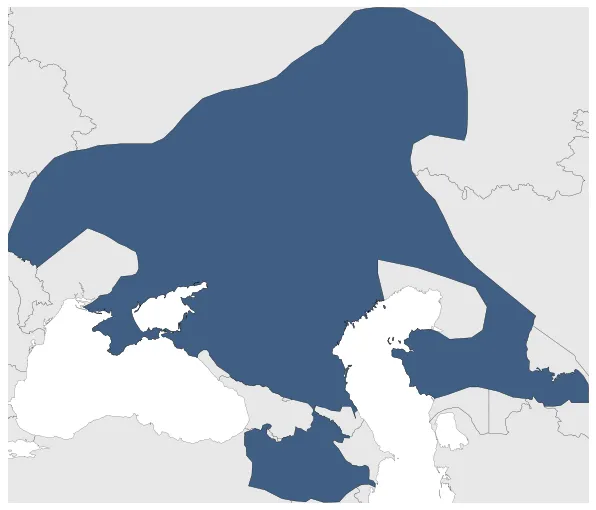
 Khazar Khaganate
Khazar Khaganate