If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
Were the Domains of the Fugger Family in the Holy Roman Empire.
Establishment
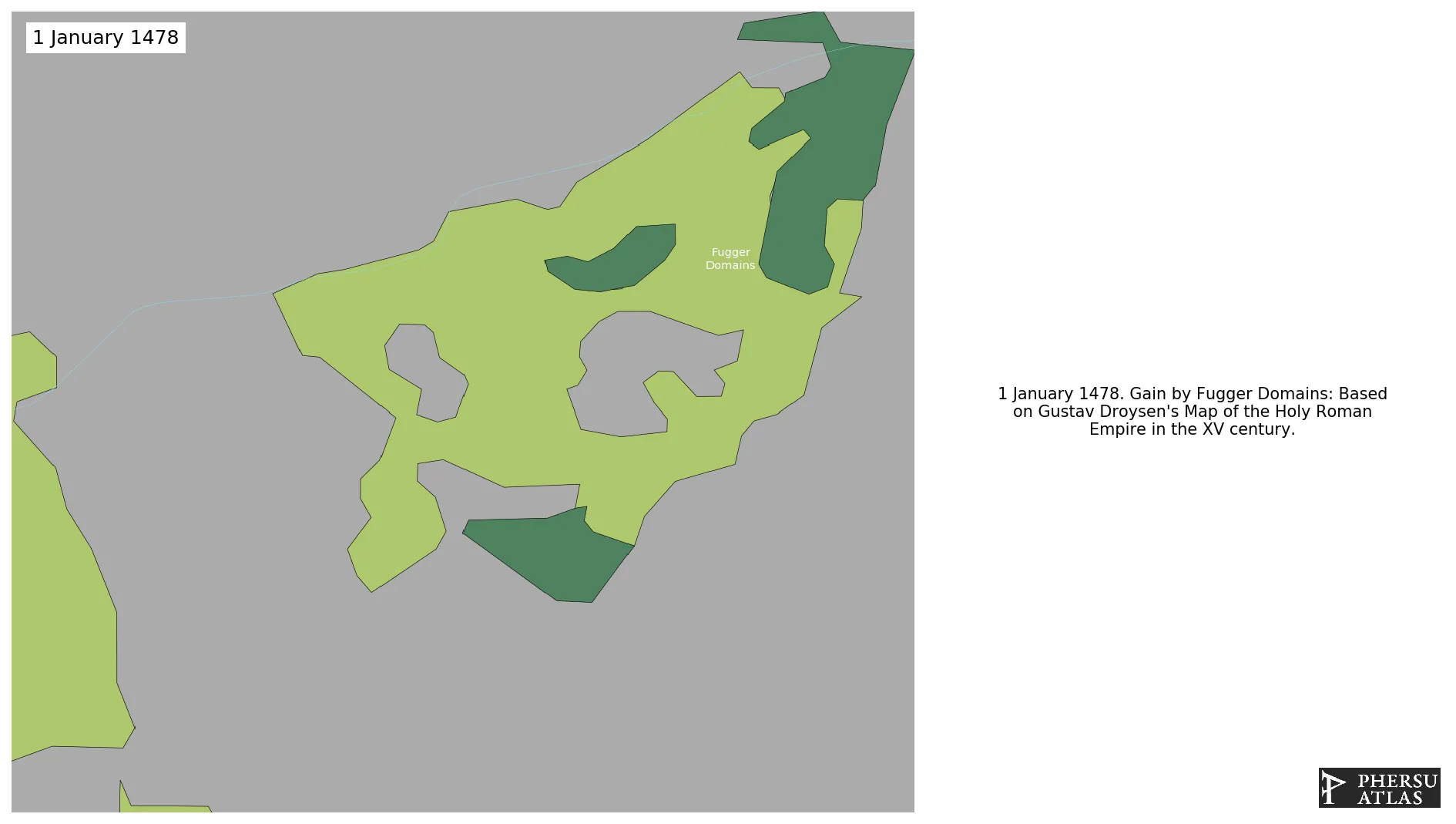
January 1478: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XV century.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of wars in Europe (and the overseas possessions of European countries) the 16th, 17th and early 18th that started after the Protestant Reformation. Although the immediate causes of the wars were religious, the motives were complex and also included territorial ambitions.
1.1.Thirty Years' War
Was a war that took place mainly in central Europe between 1618 and 1648. The war began as a religious conflict between Catholics and Protestant in the Holy Roman Empire but then escalated into a conflict for the hegemony in Europe between Habsburg Spain and Austria, Sweden and France.
1.1.1.Swedish Period
Was the third main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of Sweden.
April 1632: On April 15, during the Battle of Rain am Lech, east of Donauwörth, the Swedish troops under Gustavus Adolphus defeated the Imperial forces commanded by Tilly.
June 1634: In 1634, during the Thirty Years' War, Donauwörth was taken by the Imperial Army led by Johann von Aldringen.
1.1.2.Franco-Swedish Period
Was the fourth main period of the Thirty Years' War. It started with the intervention of the Kingdom of France.
1.1.2.1.North German Front (Sweden)
Was the north German front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
November 1637: After the death of Swedish King Ferdinand II, his son and successor Ferdinand III brought the Swedish troops back to Pomerania, leaving the territories occupied by Sweden in Germany.
June 1648: In May 1648, there was the last major field battle of the Thirty Years' War between French-Swedish and Imperial-Bavarian armies near Augsburg.
November 1648: When in November Gustaf of Sweden received a report about the signed peace, he ordered his troops to leave. Also the French troops started leaving the occupied territories in the Holy Roman Empire.
1.1.2.2.Rhineland Front (France)
Was the Rhineland front during the Franco-Swedish period of the Thirty Years' War.
May 1648: The French returned to Swabia and then to Bavaria. They defeated the Imperial forces at Zusmarshausen (May 17, 1648) and drove Maximilian of Bavaria out of Munich.
1.1.3.Peace of Westphalia
Were a series of treaties that ended the Thirty Years' War. Catholics and Protestants were redefined as equal in the territories of the Holy Roman Empire. There were major territorial adjustments. In particular, France, Sweden and Brandenburg had major territorial gains, and several religious territories of the Holy Roman Empire were secularized.
October 1648: With the Peace of Westphalia Sweden received Western Pomerania (henceforth Swedish Pomerania), Wismar, and the Prince-Bishoprics of Bremen and Verden as hereditary fiefs. Sweden evacuated the remnant territories it had occupied in the Holy Roman Empire.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
January 1807: The domains of all Fuggers (Prince of Fugger-Babenhausen, Count of Fugger-Glött, Count of Fugger-Kirchberg-Weissenhorn, Count of Fugger-Kirchheim, Count of Fugger-Nordendorf) fell to Bavaria.
2.1.War of the Second Coalition
Was the second war that saw revolutionary France against most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria, and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, Naples, and various German monarchies. Prussia did not join this coalition, and Spain supported France.
2.1.1.German Front (War of the Second Coalition)
Was the German theatre of the War of the Fifth Coalition.
May 1800: The French army forced the Austrians to retreat to Ulm.
June 1800: After being defeated by the French at the Battle of Höchstädt, Hungarian General Paul Kray retreated to Munich.
December 1800: Austria was defeated by France in the Battle of Hohenlinden (3 December 1800). By december, 25th the French forces were 80 km from Vienna. The Austrians requested an armistice, which French general Moreau granted on 25 December.
2.1.2.Treaty of Lunéville
Was a treaty between the French Republic and the Holy Roman Empire that formally ended the partecipation of Austria and the Holy Roman Empire in the War of the Second Coalition.
February 1801: The Treaty of Lunéville was signed in the Treaty House of Lunéville between the French Republic and Holy Roman Emperor Francis II. Certain Austrian holdings within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire were relinquished, and French control was extended to the left bank of the Rhine, "in complete sovereignty" but France renounced any claim to territories east of the Rhine. Contested boundaries in Italy were set. The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was awarded to the French.
2.2.War of the Third Coalition
Was a European conflict spanning the years 1805 to 1806. During the war, France and its client states under Napoleon I opposed an alliance, the Third Coalition, made up of the United Kingdom, the Holy Roman Empire, the Russian Empire, Naples, Sicily, and Sweden. Prussia remained neutral during the war.
2.2.1.Ulm Campaign
Was a series of French and Bavarian military maneuvers and battles to outflank and capture an Austrian army in 1805 during the War of the Third Coalition. It took place in the vicinity of and inside the city of Ulm.
October 1805: The French army crossed the Danube at Donauwörth.
October 1805: Battle at Wertingen between the Austrians led by Auffenburg troops and the French of Murat and Lannes.
2.2.2.Peace of Pressburg
Was the treaty that ended the War of the Third Coalition.
December 1805: French evacuation of occupied territories after the Peace of Pressburg.
January 1511: The Dynasty of Kirchberg-Wullenstetten get extinct and their territories went to the to Fugger.
January 1537: In 1536 Donauwörth came under the control of the Fuggers.
January 1548: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire at the time of the Reformation.
January 1715: In 1714 the city of Donauwörth was annexed by Bavaria.
January 1787: Based on Gustav Droysen's Map of the Holy Roman Empire in the XVIII century.
Disestablishment
January 1807: The domains of all Fuggers (Prince of Fugger-Babenhausen, Count of Fugger-Glött, Count of Fugger-Kirchberg-Weissenhorn, Count of Fugger-Kirchheim, Count of Fugger-Nordendorf) fell to Bavaria.
Selected Sources
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 34-35
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 38-39
Droysen, G. (1886): Historischer Handatlas, Bielefeld and Leipzig (Germany), pp. 46-47
Fournier. A (1913): Napoleon I. Eine Biographie, Vienna (Austria), p. 255
Gagliardo, J. (1980): Reich and Nation: The Holy Roman Empire as Idea and Reality, 1763–1806, Bloomington (USA), p. 192
Krumenacker, Y. (2008): La Guerre de Trente Ans, Paris, Ellipses, pp. 146-147
Phillipson, C. (2008): Termination of War and Treaties of Peace, Clark (USA), p. 273
Poole, R.L. (1902): Historical Atlas of Modern Europe, Oxford (United Kingdom), Plate XI
Schmidt, G. (2006): Der Dreißigjährige Krieg, Munich (Germany), p. 65
Schmiele, E. (1887): Zur Geschichte des schwedisch-polnischen Krieges von 1655 bis 1660, Berlin (Germany), p. 5
Smith, D. (1998): Napoleonic Wars Databook, London (UK), p. 178
Spindler, M. (2017): Geschichte Schwabens bis zum Ausgang des 18. Jahrhunderts, Munich (Germany), p. 266
Westfälischer Friede - Vertrag von Osnabrück, https://de.wikisource.org/wiki/Westf%C3%A4lischer_Friede_%E2%80%93_Vertrag_von_Osnabr%C3%BCck

 Fugger Domains
Fugger Domains