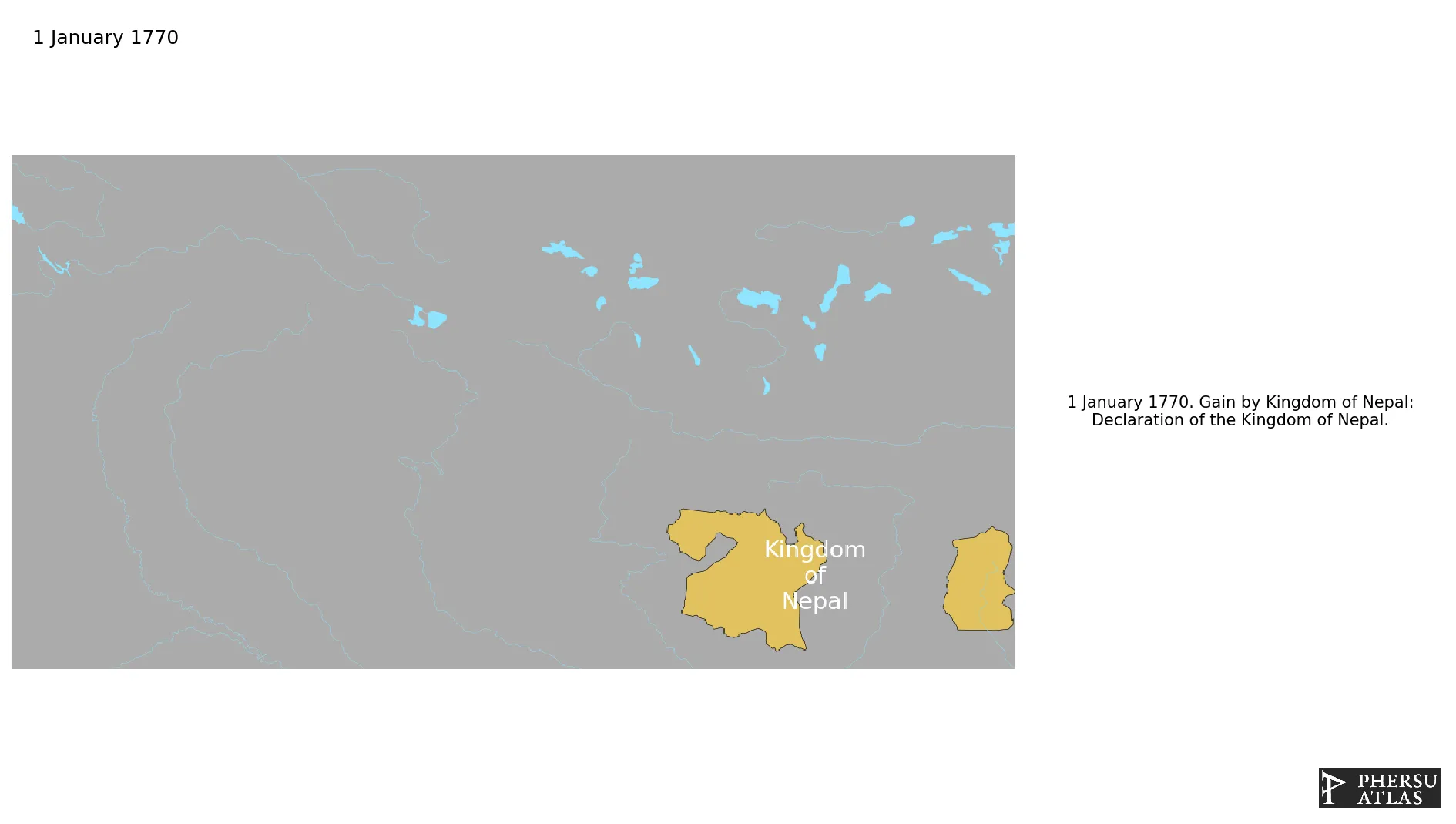
This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Nepal and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
The Gorkha Dynasty united the petty kingdoms that existed in Nepal and founded the Kingdom in 1769. The Kingdom lasted until 2008, when it was replaced by a Republic.
Establishment
January 1770: Declaration of the Kingdom of Nepal.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Expansion during the rule of Prithvi Narayan Shah in the Gorkha Kingdom.
July 1773: Chaudandi is annexed to Nepal.
January 1775: Limbuwan Kingdoms conquered by Kingdom of Nepal.
January 1775: Morang conquered by Kingdom of Nepal.
Expansion during the rule of Rana Bahadur Shah in the Kingdom of Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Nayakot was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Lamjung was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Rishing was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: Based on the border of Nepal in 1782.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Satahung was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Poin was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Gajarlot was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Tanahun was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Dhor was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Garabung was annexed by Nepal.
January 1783: The chaubisi raja (small principalities ruled by the Magar people of Nepal) of Ghiring was annexed by Nepal.
January 1786: Bhirkot is annexed to Nepal.
January 1786: Nuwakot is annexed to Nepal.
September 1786: Parbat is annexed to Nepal.
January 1787: Bangphi was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Cham was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Gulmi was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Chhidi was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Jehari was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Dailekh was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Doti is annexed to Nepal.
January 1787: Piuthan was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Galkot was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Jajarkot is annexed to Nepal.
January 1787: Khanchi is annexed to Nepal.
January 1787: Malneta was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Rukum was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Salianah was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Sattala was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Based on the border of Nepal in 1782.
January 1787: Isma was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Musikot is annexed to Nepal.
January 1787: Khungri was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
January 1787: Bhingri was annexed by Nepal ca. 1786.
November 1788: Jumla is annexed to Nepal.
May 1790: Lo under the Kingdom of Mustang.
January 1791: Dullu is annexed to Nepal.
September 1791: Bajura is annexed to Nepal.
January 1792: Kumaon Kingdom is incorporated into Nepal in 1791.
January 1796: Nepal tributary state of China.
January 1796: Tibet tributary state of China.
Were a series of military campaigns launched by the Qing dynasty of China in the mid-late 18th century during the reign of the Qianlong Emperor.
3.1.Sino-Burmese War
Was a war between Qing China and the Konbaung Dynasty of Burma. The war consisted of a series of unsuccesful Chinese invasions of Burma.
3.1.1.Second invasion (Sino-Burmese War)
Was the invasion of Burma by the Qing Dynasty, the third of four that form the Sino-Burmese War (1765-1769).
September 1792: In 1792, Nepalese troops under the command of King Rana Bahadur Shah launched a counterattack against the Qing forces led by General Chhewang Rinchhen, who were encamped at Jitpurfedi. This marked a significant event in the Nepal-Tibet conflict during the Qing Dynasty's military occupation of Tibet.
October 1792: The war ended in Nepal with the latter accepting to become a tributary state of Qing.
Expansion during the rule of Ranjit Singh in the Sikh Empire.
January 1810: Sikh invasion of the Kangra region.
Were a series of wars fought by the British East India Company in the Indian Subcontinent that resulted in the British conquest and colonial rule of the region.
5.1.Anglo-Nepalese War
Was a war between the Kingdom of Nepal and the British East India Company. .
5.1.1.First Campaign (Anglo-Nepalese War)
Was a British military campaign in Nepal during the Anglo-Nepalese War.
February 1814: The British advance to Jit Gadh in 1814 was led by General Amar Singh Thapa, a prominent military leader in the Gorkha Kingdom. The territory was eventually occupied by Great Britain as part of their expansion in the region.
November 1814: Battle of Nalapani.
December 1814: British Major General Martindale occupied the town of Nahan.
April 1815: Nepalese provincial governor Bam Shah surrendered Almora to the British on 27 April 1815.
May 1815: The Nepalese forces under the command of Amar Singh Thapa lost control of Malaon and Jaithak to the British forces led by General David Ochterlony in 1815.
5.1.2.Second Campaign (Anglo-Nepalese War)
Was a British military campaign in Nepal during the Anglo-Nepalese War.
February 1816: The Nepalese troops, led by General Amar Singh Thapa, were driven back from Hariharpur Gadhi by the British forces, led by Major General David Ochterlony, during the Anglo-Nepalese War in 1816. This marked a significant victory for the British in their military occupation of the territory.
March 1816: During the Anglo-Nepalese War, British troops led by General Rollo Gillespie retreated from Sindhuli Gadhi and regrouped in Makawanpur in March 1816. The war ended with the signing of the Sugauli Treaty later that year.
5.1.3.Treaty of Sugauli
Was the treaty that ended the Anglo-Nepali War. Nepal lost one-third of its territory.
March 1816: The Anglo-Nepalese War ended with the Treaty of Sugauli, which has been considered as an unequal treaty vecause it led to Nepal losing one-third of its territory. The river Mechi became the new Eastern border and the Mahakali the Western boundary of Nepal.
March 1816: The Treaty of Sugauli, signed following the Anglo-Nepalese War of 1814-16, established the boundary line of Nepal.
January 1776: The Kingdom of Palpa supported Bahadur Shah of Nepal who annexed Dhurkot and in return, Palpa kings were given various item including 101 elephants, 1,001 horses, and money.
January 1776: Ilam conquered by Kingdom of Nepal.
January 1777: Yangwarok conquered by Kingdom of Nepal.
January 1785: In 1784, the British East India Company, represented by Warren Hastings, turned over the Bengal Duars territory to the Kingdom of Bhutan. The boundaries of the territory were poorly defined, leading to disputes between the two parties.
January 1804: The erstwhile Bushahr state was occupied by a Gorkha king from central Nepal from 1803 to 1815.
January 1804: Nepalese invasion of Garhwal.
January 1804: Kuthar State, located in present-day Himachal Pradesh, India, was occupied by Nepali forces led by King Prithvi Narayan Shah during his campaign to expand the Kingdom of Nepal from 1803 to 1815. This marked a significant period of conflict and territorial expansion in the region.
January 1804: Keonthal State, founded before the 19th century, was ruled by Rana Raghunath Sen. In 1803, it was occupied by Nepal under General Amar Singh Thapa until 1814.
January 1804: Bhajji State was occupied by Nepal from 1803 to 1815.
January 1805: Palpa is annexed to Nepal.
January 1806: Kutlehar State was occupied by the Kingdom of Nepal between 1805 and 1809. The Gorkha occupants, led by King Prithvi Narayan Shah, were eventually driven out by the British East India Company.
January 1807: Nepalese invasion of Bilaspur.
January 1807: Nepalese invasion of Sirmur.
January 1807: Nepalese invasion of Kangra.
January 1815: The state of Keonthal was occupied by Nepal until 1814.
February 1815: At the end of the Anglo-Nepalese War, the parties signed the Treaty of Sugauli, following which the Gurkhas were expelled from Kamru, the capital of Bushahr.
April 1815: The Treaty of Sugauli was signed between the British East India Company and the Kingdom of Nepal. The British annexed Pauri Garhwal and made Tehri Garhwal a princely state under their control in 1815.
March 1816: The Gorkhas were defeated by the East India Company in Anglo-Nepalese War and were forced to cede Kumaon to the British as part of the Treaty of Sugauli in 1816.
August 1856: Lambjang and Kaski granted to Jang Bahadur Kunwar Rana the Rana Prime minister of Nepal as a hereditary possession.
January 1860: Annexation of Tulsipur by British India.
January 1861: In 1860 some parts of western Terai, known as Naya Muluk ("new country") were restored to Nepal.
May 2008: Abolition of the Nepalese monarchy in 2008.
Disestablishment
May 2008: Abolition of the Nepalese monarchy in 2008.
Selected Sources
Rennell, J. (1782): Map of Hindustan, London (UK)
.svg.png.webp)
 Kingdom of Nepal
Kingdom of Nepal