This article is about the specific polity Kingdom of Norway and therefore only includes events related to its territory and not to its possessions or colonies. If you are interested in the possession, this is the link to the article about the nation which includes all possessions as well as all the different incarnations of the nation.
If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
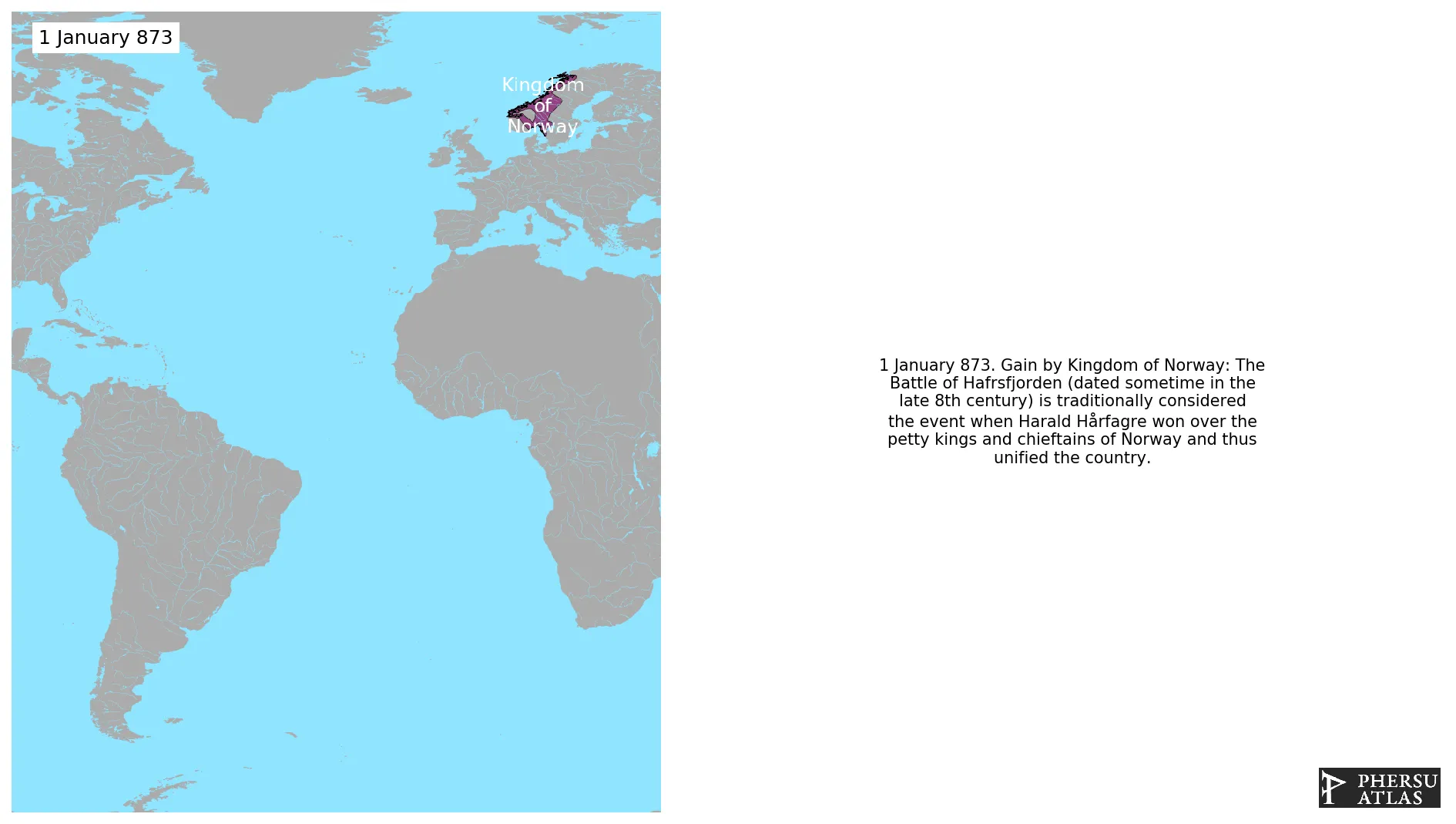
Is a country in Scandinavia. The Kingdom exists in since 873, although it did not exist the whole time as a separate Kingdom due to long periods of Personal Union with Denmark or Sweden.
Establishment
January 873: The Battle of Hafrsfjorden (dated sometime in the late 8th century) is traditionally considered the event when Harald Hårfagre won over the petty kings and chieftains of Norway and thus unified the country.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Was the establishment of the Kingdom of Norway through the unification of the petty kingdoms of the region.
1.1.Battle of Hafrsfjord
Was a great naval battle fought in Hafrsfjord sometime between 872 and 900 that resulted in the unification of Norway. After the battle, the victorious Viking chief Harald Fairhair proclaimed himself the first king of the Norwegians, merging several petty kingdoms under a single monarch.
January 901: The Battle of Hafrsfjorden (dated sometime in the late 8th century) is traditionally considered the event when Harald Hårfagre won over the petty kings and chieftains of Norway and thus unified the country.
Was the Viking invasion of the British Isles that started with the arrival of the Great Heathen Army in 865 and resulted in the establishment of the Danelaw, the part of England dominated by the Danes.
January 876: Both Orkney and Shetland saw a significant influx of Norwegian settlers during the late 8th and early 9th centuries. Vikings made the islands the headquarters of their pirate expeditions carried out against Norway and the coasts of mainland Scotland. In response, Norwegian king Harald Fairhair annexed the Northern Isles, comprising Orkney and Shetland, in 875.
January 881: In the Middle Ages, Caithness came under the control of the Norwegian Jarle of Orkney. […] According to the Landnámabók, Thorstein Olafsson (fl c. 850-c. 880) and Sigurd Eysteinsson “conquered Caithness, Sutherland and Moray, and more than half of Argyll [and] Thorstein ruled over these territories as King”.
January 881: Sutherland was part of the Caithness mormaerdom for most of this title's history.
Eric the Victorious was a Swedish monarch as of around 970. Since he is the first Swedish king in a consecutive regnal succession, who is attested in sources independent of each other, Sweden's list of rulers usually begins with him.
January 971: The Kingdom of Sweden was probably established by Eric the Victorious, who was king from around 970. Since he is the first Swedish king in a consecutive regnal succession, who is attested in sources independent of each other, Sweden's list of rulers usually begins with him.
The Battle of Svolder was a naval battle fought in September 999 or 1000 in the western Baltic Sea between King Olaf Tryggvason of Norway and an alliance of his enemies. After the Battle of Svolder, the victorious leaders split Norway into areas of control.
September 1000: The Battle of Svolder was a naval battle fought in September 1000 in the western Baltic Sea between King Olaf Tryggvason of Norway and an alliance of his enemies. After the Battle of Svolder, the victorious leaders split Norway into areas of control.
Were a series of ephemeral Norse-ruled personal unions between England and Scandinavian countries.
February 1014: Sweyn Forkbeard died and his realm was divided.
January 1029: After a decade of conflict with opponents in Scandinavia, Cnut the Great of Denmark claimed the crown of Norway in Trondheim in 1028.
November 1035: After the death of Cnut the Great, the North Sea Empire was again divided into Denmark, England, and Norway.
The Norman invasion of Wales began shortly after the Norman conquest of England under William the Conqueror.
January 1099: Anglesey was a crown dependency of Gwynedd from 1098 to 1099.
Was a war between Denmark and Norway.
January 1297: North Halland ceded to Norway.
Were a series of conflicts between France and several European monarchies between 1792 and 1815. They encompass first the French Revolutionary Wars against the newly declared French Republic and from 1803 onwards the Napoleonic Wars against First Consul and later Emperor Napoleon Bonaparte. They include the Coalition Wars as a subset: seven wars waged by various military alliances of great European powers, known as Coalitions, against Revolutionary France - later the First French Empire - and its allies.
8.1.War of the Sixth Coalition
Was a war between France and a a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States. The coalition emerged after the decimation of the French army in the French invasion of Russia. The coalition ultimately invaded France and forced Napoleon to abdicate and go into exile.
May 1814: The Norwegians rejected declared independence and adopted their own constitution on 17 May.
8.2.Swedish-Norwegian War (1814)
Was a war initiated by Norway to gain independence from Sweden. The war resulted in a compromise, with Norway being forced into the United Kingdoms of Sweden and Norway, a union with Sweden under the Swedish king Charles XIII, but with Norway having its own constitution and parliament.
July 1814: The hostilities opened on 26 July with a swift Swedish naval attack against the Norwegian gunboats at Hvaler.
July 1814: The town of Fredrikstad in Norway surrendered to Swedish force.
August 1814: The Norwegian forces withdrew over the Glomma river at Langnes in Askim.
August 1814: Convention of Moss, was signed on 14 August 1814. Norway agreed to enter into a personal union with Sweden as a separate state with its own constitution and institutions, except for the common king and foreign service.
Was a global conflict that lasted from 1939 to 1945 (it started sooner in certain regions) between the Axis Powers (mainly Germany, Japan and Italy) and the Allies (mainly the Soviet Union, the U.S.A., the U.K., China and France). It was the war with more fatalities in history. The war in Asia began when Japan invaded China on July 7, 1937. The war in Europe began when Germany invaded Poland on September 1, 1939. The war ended with the complete defeat of the Axis powers, which were occupied by the Allies.
9.1.World War II (Western Front)
Was the Western European theatre of World War II.
9.1.1.Norwegian Campaign
Was the struggle for the control of Norway between Germany and the Allies that ended with the German military occupation of that country.
April 1940: German air-landed soldiers land at and capture the airport at Oslo.
April 1940: Bergen and Trondheim are captured by Germany.
April 1940: Egersund is captured without resistance by the Germans, as is Arendal.
April 1940: The Narvik landing force evades British naval forces and defeats the Norwegian vessels in the fjord.
April 1940: In Oslo, the Norwegian government has left, and Vidkun Quisling becomes the head of the new government.
April 1940: Kongsberg fell to German forces without a fight.
April 1940: British forces land at Namsos and Harstad as Anglo-French forces prepare to launch operations against German forces at Trondheim and Narvik.
April 1940: British forces land at Åndalsnes.
April 1940: The British 146th Brigade is forced to withdraw from Steinkjer by German forces.
April 1940: German forces moved north from Oslo reach Lillehammer and captured the town.
May 1940: Anglo-French forces land at Mosjøen to block German advances to Narvik.
May 1940: French Foreign Legion and Polish forces land at Tromsø and Harstad.
May 1940: Territorial change based on available maps.
May 1940: Norwegian and Allied forces attack Narvik, entering the town after a short fight.
June 1940: The surrender of Norway to the German invading force is complete and resistance is ended.
9.1.2.Liberation of Finnmark
Was a military operation, lasting from 23 October 1944 until 26 April 1945, in which Soviet and Norwegian forces wrested away control of Finnmark, the northernmost county of Norway, from Germany.
October 1944: With the help of local fishermen, the Soviets were able to cross the Neiden River on 27 October and capture the ridge. Fighting was fierce, and the Germans managed to burn every building in the village, save for the local church, before withdrawing.
November 1944: Allied forces penetrated 116 km northwest of Neiden before halting in Tana.
April 1945: The Norwegians declared Finnmark to be free.
9.2.End of World War II in Europe
Refers to the surrender of Axis forces and the end of World War II and to the territorial changes that were a direct consequence of World War II but happened after the traditional end of the War.
9.2.1.The Surrender of German forces
Surrender of German forces at the end of World War II.
May 1945: General Franz Böhme announced the unconditional surrender of German troops in Norway.
January 951: Before 1000 AD Jämtland was an almost independent kingdom. The Jemtene had their own organization, an aristocratic "peasant republic", and their own thing, Jamtamót , on Frösön.
January 961: From c. 960 Harald Bluetooth appears to have established a kingdom in the lands of the Danes which stretched from Jutland to Skåne.
January 971: Arald's rule as king of Norway following the assassination of King Harald Greycloak of Norway was more tenuous, most likely lasting for no more than a few years in the 970s (c. 970 - c. 975/986).
January 977: Arald's rule as king of Norway following the assassination of King Harald Greycloak of Norway was more tenuous, most likely lasting for no more than a few years in the 970s (c. 970 - c. 975/986).
March 1016: In 1016, Óláfr Haraldsson, also known as Saint Olaf, arrived in Norway and claimed the throne. He defeated Sveinn, the Danish king, and his allies in the battle of Nesjar, solidifying his rule over the Kingdom of Norway.
January 1021: Conquest of the internal regions of Norway.
January 1036: Sigmundur Brestisson took possession of the Faroe islands for Olaf Tryggvason, King of Norway from 995 to 1000, annexing it in 1035.
January 1043: Magnus the Good was King of Norway from 1035 and King of Denmark from 1042, ruling over both countries until his death in 1047.
January 1048: Magnus the Good was King of Norway from 1035 and King of Denmark from 1042, ruling over both countries until his death in 1047.
January 1100: Anglesey, crown dependency from 1098 to 1099, reverted to Kingdom of Gwynedd as of lack of settlements.
January 1179: From the reign of King Sverre (1177-1202) Jämtland belonged politically to the Norwegian crown.
January 1201: The oldest testimony about Norwegian kings' interest in Finnmark dates from the Gulating Act, circa in the year 1200.
January 1240: Sutherland is acquired by Scotland.
January 1265: The old Covenant was an agreement which resulted in the union of Iceland and Norway.
January 1320: Magnus IV of Sweden was also King of Norway as Magnus VII from 1319.
January 1356: Magnus IV, who was already King of Sweden from 1319, became King of Norway as Magnus VII (including Iceland and Greenland).
January 1363: Haakon VI of Norway, also known as Håkan Magnusson, was also King of Sweden between 1362 and 1364.
January 1365: In 1364, Haakon VI of Norway lost the territory of Sweden to the Kingdom of Norway. Haakon VI was King of Norway from 1343 until his death and briefly King of Sweden from 1362 to 1364.
July 1380: When Haakon VI died in 1380, Olaf, who was already king of Denmark, also inherited the crown of Norway.
June 1905: On 7 June 1905, the Storting (Parlament) of Norway unilaterally declared its independence Sweden, ending the union of the two countries. Sweden officially accepted the union's dissolution on 26 October.
February 1920: The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty over the Svalbard Islands.
February 1930: On February 27, 1930, the Island of Jan Mayen became part of the Kingdom of Norway.
March 1931: Peter I Island, in the Antarctic, was a possession of Norway since 1929.
Selected Sources
Jämtland. Store norske leksikon. Retrieved on 31 March 2024 on https://snl.no/J%C3%A4mtland
Slaget i Hafrsfjorden. Store norske leksikon. Retrieved on 31 March 2024 on https://snl.no/Slaget_i_Hafrsfjorden
Slaget ved Svolder. Store norske leksikon. Retrieved on 31 March 2024 on https://snl.no/Slaget_ved_Svolder

 Kingdom of Norway
Kingdom of Norway