If you are looking for the page with the statistics about this polity you can find it here:All Statistics
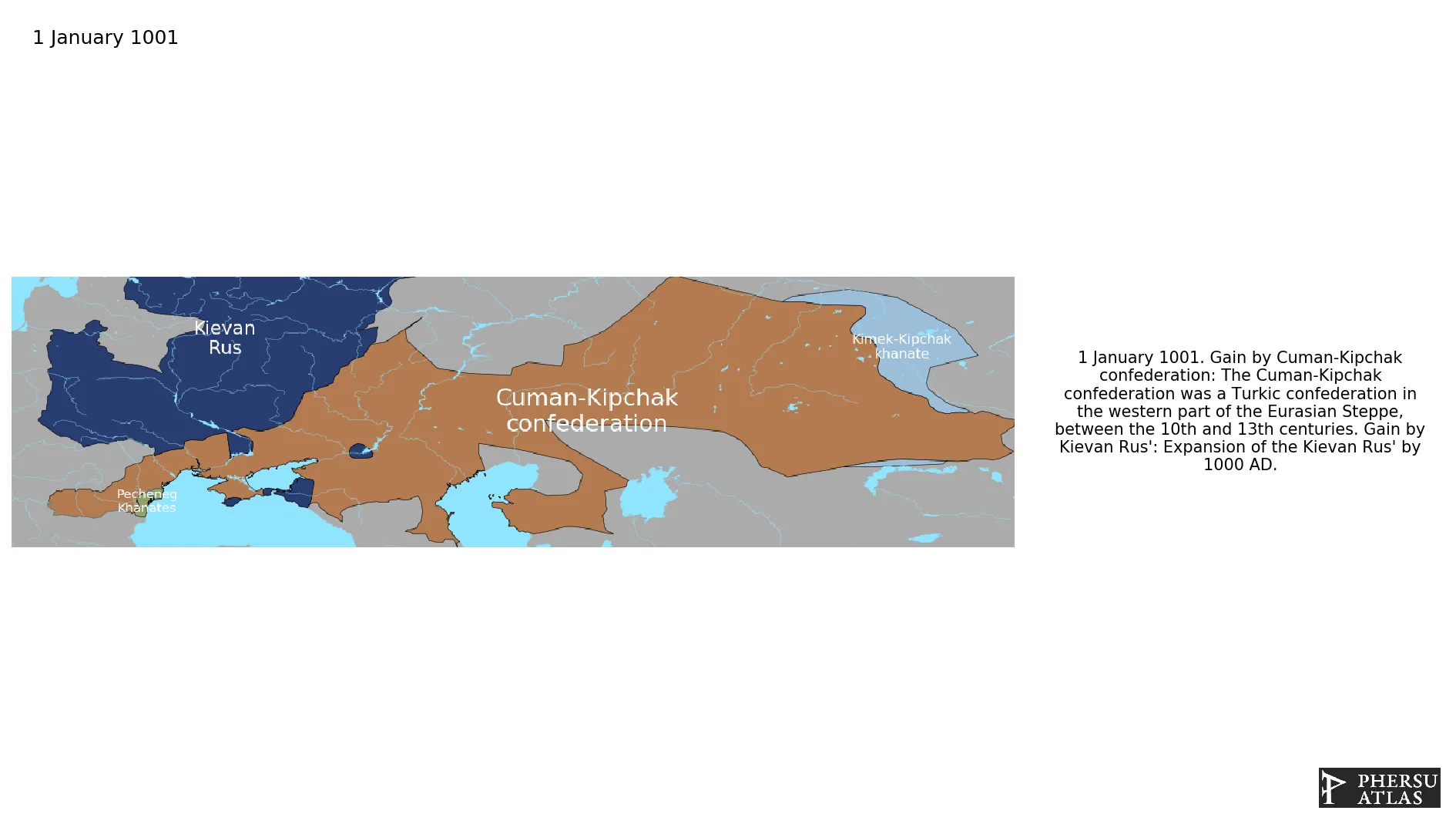
Was a Turkic confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries.
Establishment
January 1001: The Cuman-Kipchak confederation was a Turkic confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries.
January 1001: Expansion of the Kievan Rus' by 1000 AD.
Chronology
Interactive Chronologies with maps are available in the section Changes Navigation
Were a series of military conflicts between the Seljuk Empire and its vassals against the Kingdom of Georgia.
1.1.Georgian Reconquista
Were a series of military campaigns by the Kingdom of Georgia to reconquer lands controlled by the Seljukids and their vassals.
January 1121: Georgian expansion by 1120 AD.
April 1121: In the winter of 1120-1121 the Georgian troops successfully attacked the Seljuk settlements on the eastern and southwestern approaches to the Transcaucasus.
Following the death of Mstislav I of Kiev in 1132, the semi-autonomous states of the Kievan Rus' were de facto independent.
January 1133: After the weakening of the Rus' state, the Byzantine Empire, under the rule of Emperor John II Komnenos, took control of southern Crimea in 1132.
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the Medieval period. The best known of these military expeditions are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291.
3.1.Fourth Crusade
Was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem. However, the Western Crusaders sacked Constantinople in 1204 and partitioned the Byzantine Empire.
November 1204: The Latin Empire, established by the Crusaders in Constantinople, had poor control over former Byzantine territory, and Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire sprang up in Epirus, Trebizond, and Nicaea. Theodore appeared as his father-in-law's representative and secured the Bithynian towns' loyalty in Alexios III's name until the end of 1204. The local Greeks acknowledged him as the strategos (or military leader) of Bithynia.
Were a series of military campaigny by the Mongols that created the largest contiguous Empire in history, the Mongol Empire, which controlled most of Eurasia.
January 1231: The Mongols moved towards the west, gaining claim to parts of Russia, Ukraine, and whole countries in Central Asia, such as Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan and other countries.
4.1.Invasions of Georgia
Was the Mongol invasion of Georgia, in the Caucasus.
June 1223: The Mongols marched through the Caucasus into Alania and the South Russian steppes where they routed the Rus’-Kipchak armies at the Battle of the Kalka River.
July 1223: The Mongols marched through the Caucasus into Alania and the South Russian steppes where they routed the Rus’-Kipchak armies at the Battle of the Kalka River.
4.2.Mongol invasion of Kievan Rus'
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered the Kievan Rus' in the mid-13th century.
November 1236: The Mongols extinguish the resistance of the weak Volga Bulgars, the Cumans-Kipchaks and the Alans.
January 1035: In 1034 Harun, who was Ghaznavid Governor in Khwarazm, revolted against sultan Masʽud, establishing an independent domain.
January 1051: The Kimek-Kipchak khanate is conquered by the Cuman-Kipchak confederation.
January 1055: Expansion of the Kievan Rus' to the death of Prince Yaroslav I (1054).
January 1092: The Cumans of southern Ruthenia took control of the lands of Wallachia.
January 1125: Qara Khitai was a sinicized empire in Central Asia, ruled by the Khitan Yelü clan. The dynasty was founded by Yelü Dashi (Emperor Dezong of Liao), who led the remnants of the Liao dynasty to Central Asia after fleeing from the Jurchen conquest of their homeland in the north and northeast of modern-day China.
January 1126: The Mongolian plateau was occupied mainly by five powerful tribal confederations (khanlig): Keraites, Khamag Mongol, Naiman, Mergid, and Tatar.
January 1150: The Hungarians took back western Romania from the Cumans.
January 1150: The Cumans took over the Black Sea coast abandoned by the 'Rus.
January 1158: Territorial change based on available maps.
January 1186: Uprising of Asen and Peter: almost all of Bulgaria to the north of the Balkan Mountains (the region known as Moesia) immediately joined the rebels.
January 1195: In 1194, the last Sultan of the Great Seljuq Empire, Toghrul III, was defeated and killed by the Khwarezm ruler Ala ad-Din Tekish, who subsequently conquered parts of Khorasan and western Iran.
January 1201: In the 13th century, the Caucasian Avars formed a new Muslim state, traditionally known as Avaristan.
Disestablishment
November 1236: The Mongols extinguish the resistance of the weak Volga Bulgars, the Cumans-Kipchaks and the Alans.
Selected Sources
Barfield, T. J. (1992): The perilous frontier: nomadic empires and China, Hoboken (USA), p. 184
Chew, A.F. (1970): An Atlas of Russian History: Eleven Centuries of Changing Borders, Yale University Press, p.7
Shephard, W. R. (1923): Historical Atlas, New York, Henry Holt and Company, pp. 58-59
 Cuman-Kipchak confederation
Cuman-Kipchak confederation